Membrane Transporter/Ion Channel

Ion channels are pore-forming membrane proteins which allow the flow of ions across the membrane. The ion channels can be broadly grouped into six families including calcium channels, chloride channels, potassium channels, sodium channels, gap junction proteins and porins. Not all ion channels are gated, such as certain type of K+ and Cl– channels, transient receptor potential superfamily of cation channels, the ryanodine receptors and the IP3 receptors, but most Na+, K+, Ca2+ and some Cl– channels are all gated by voltage. Ligand-gated channels are regulated in response to ligand binding (e.g. neurotransmitters signaling). These ligand-gated neurotransmitter receptors are known as ionotropic receptors. Various neurotransmitters couple to ionotropic receptors such as glutamate, acetylcholine, glycine, GABA, and serotonin.
-
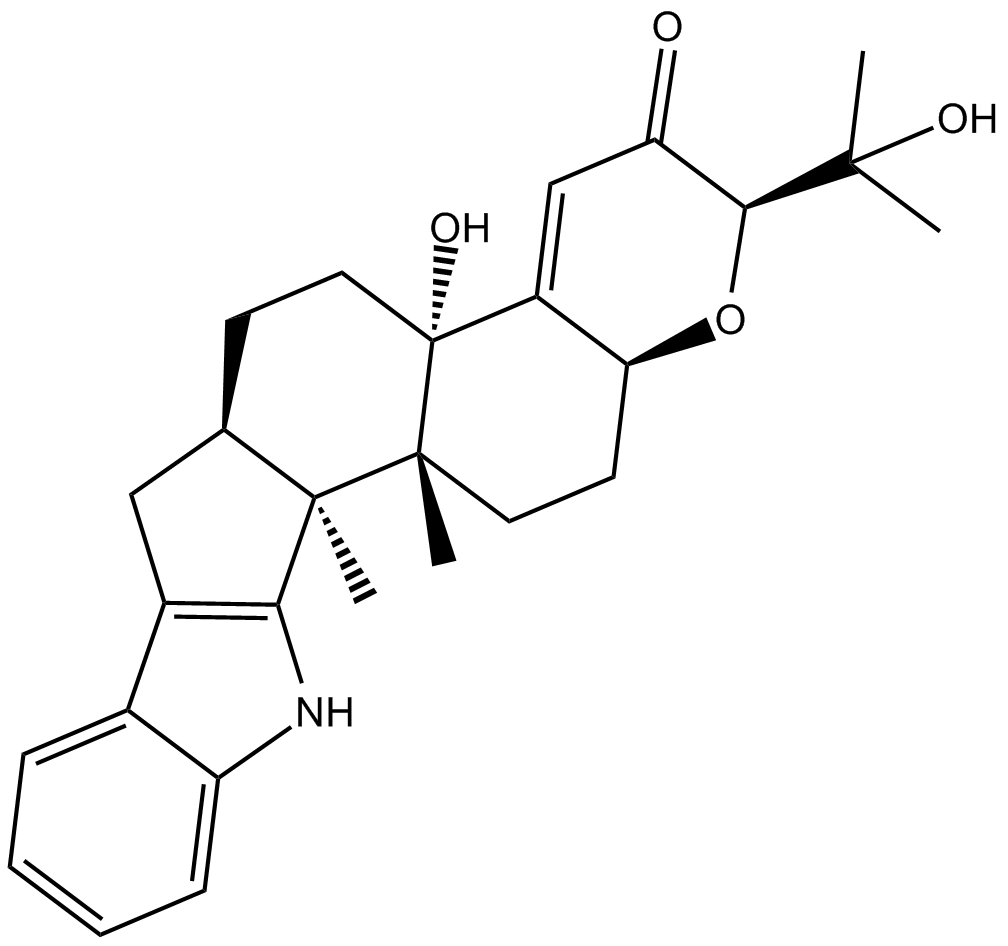 B6920 PaxillineSummary: high-conductance Ca2+-activated K+ (BKCa, KCa1.1) channels blocker
B6920 PaxillineSummary: high-conductance Ca2+-activated K+ (BKCa, KCa1.1) channels blocker -
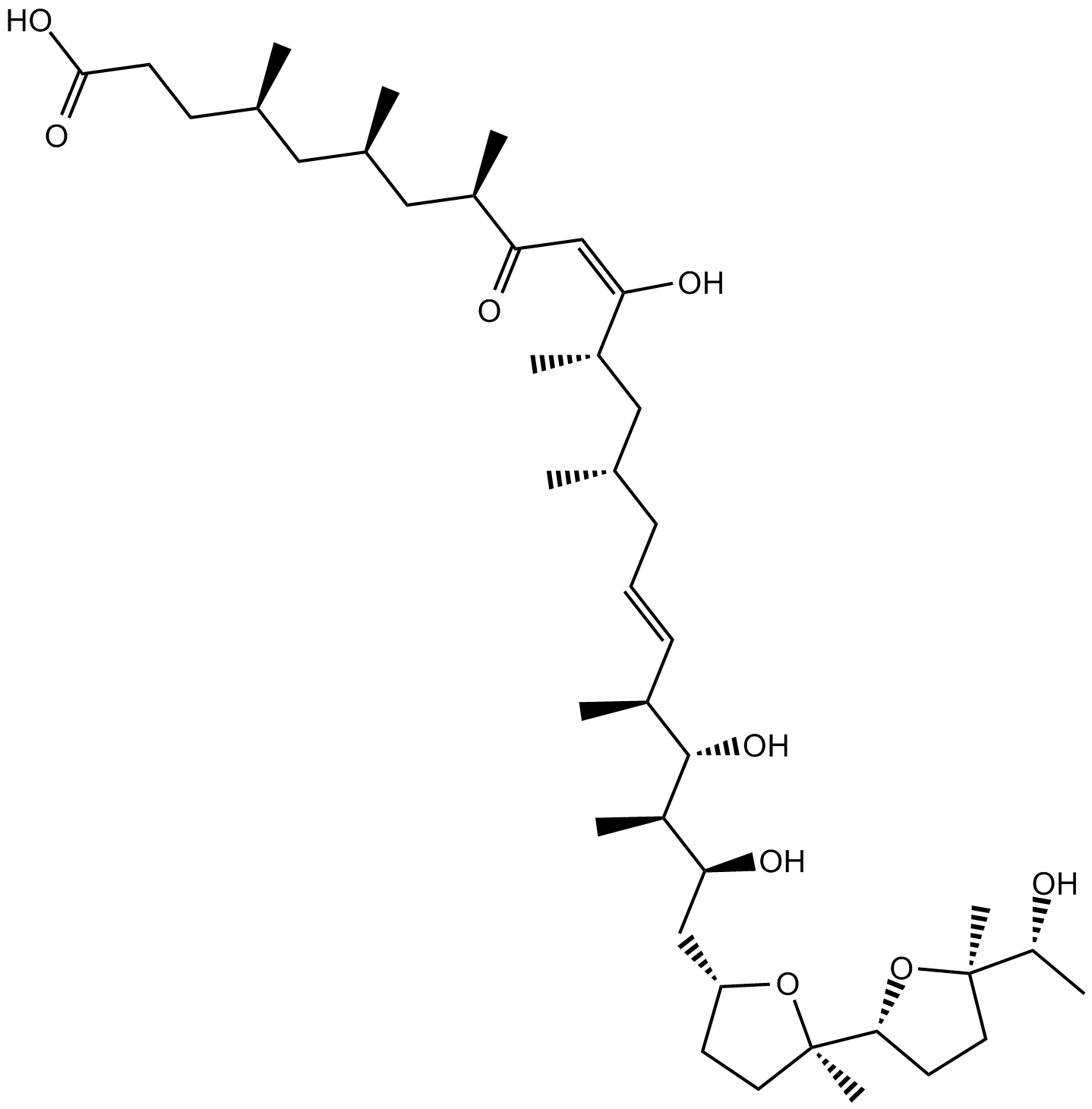 B6947 Ionomycin free acidTarget: Calcium ionophoresSummary: calcium ionophore
B6947 Ionomycin free acidTarget: Calcium ionophoresSummary: calcium ionophore -
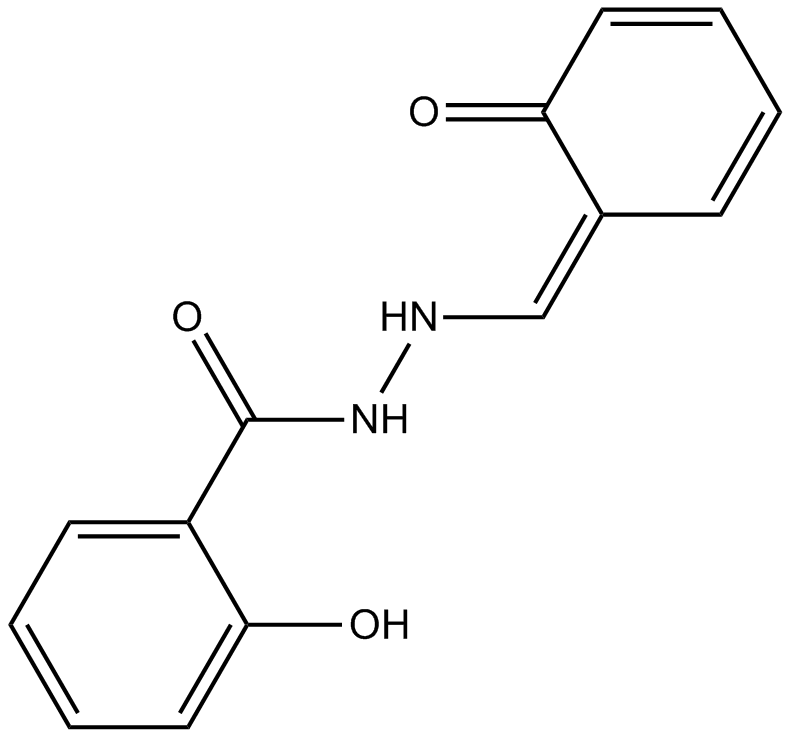 B6953 SCSSummary: GABAA receptor antagonist
B6953 SCSSummary: GABAA receptor antagonist -
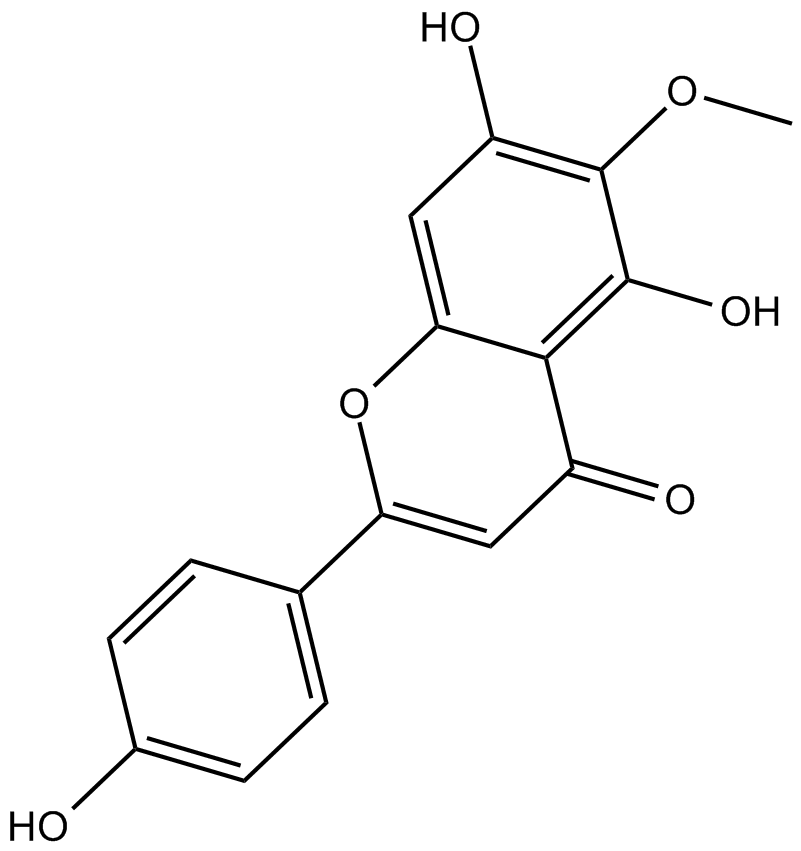 B6959 HispidulinSummary: Partial positive allosteric modulator at the benzodiazepine receptor
B6959 HispidulinSummary: Partial positive allosteric modulator at the benzodiazepine receptor -
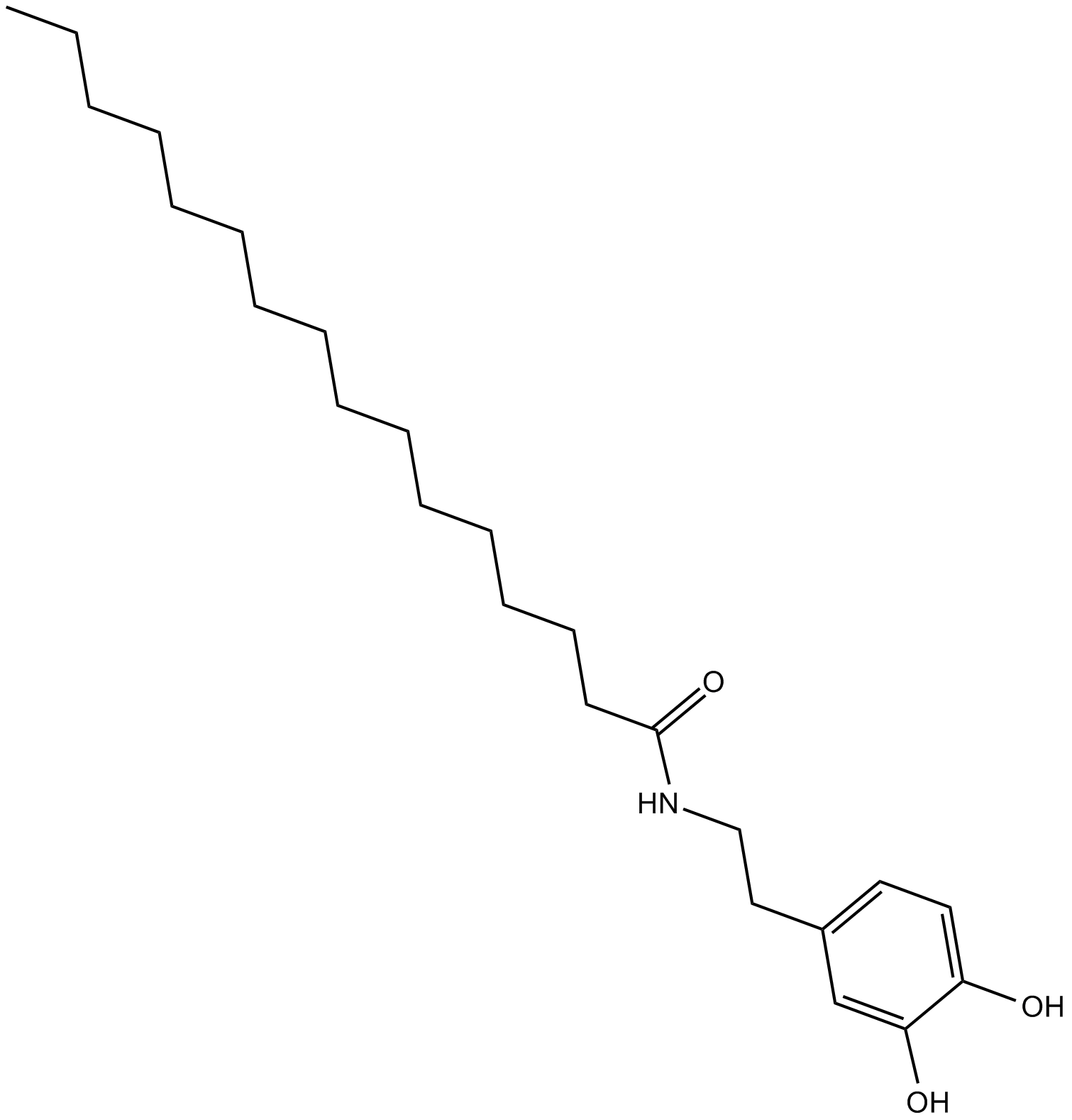 B6975 PALDASummary: potentiates TRPV1-mediated effects of NADA
B6975 PALDASummary: potentiates TRPV1-mediated effects of NADA -
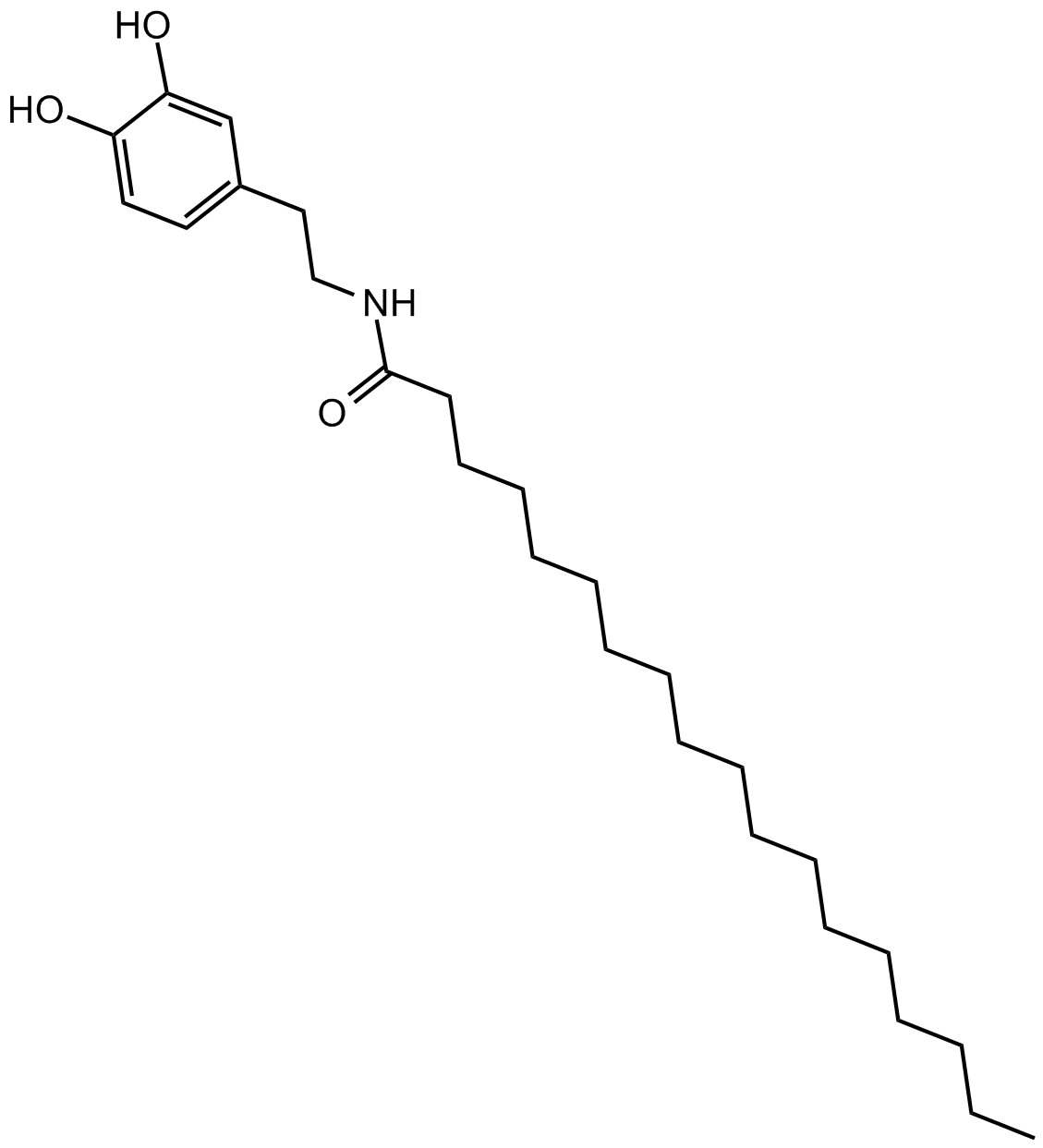 B6976 STEARDASummary: potentiates TRPV1-mediated effects of NADA
B6976 STEARDASummary: potentiates TRPV1-mediated effects of NADA -
 B6982 (±)-HIP-ASummary: excitatory amino acid transporter (EAAT) blocker
B6982 (±)-HIP-ASummary: excitatory amino acid transporter (EAAT) blocker -
 B6983 (±)-HIP-BSummary: excitatory amino acid transporter (EAAT) blocker
B6983 (±)-HIP-BSummary: excitatory amino acid transporter (EAAT) blocker -
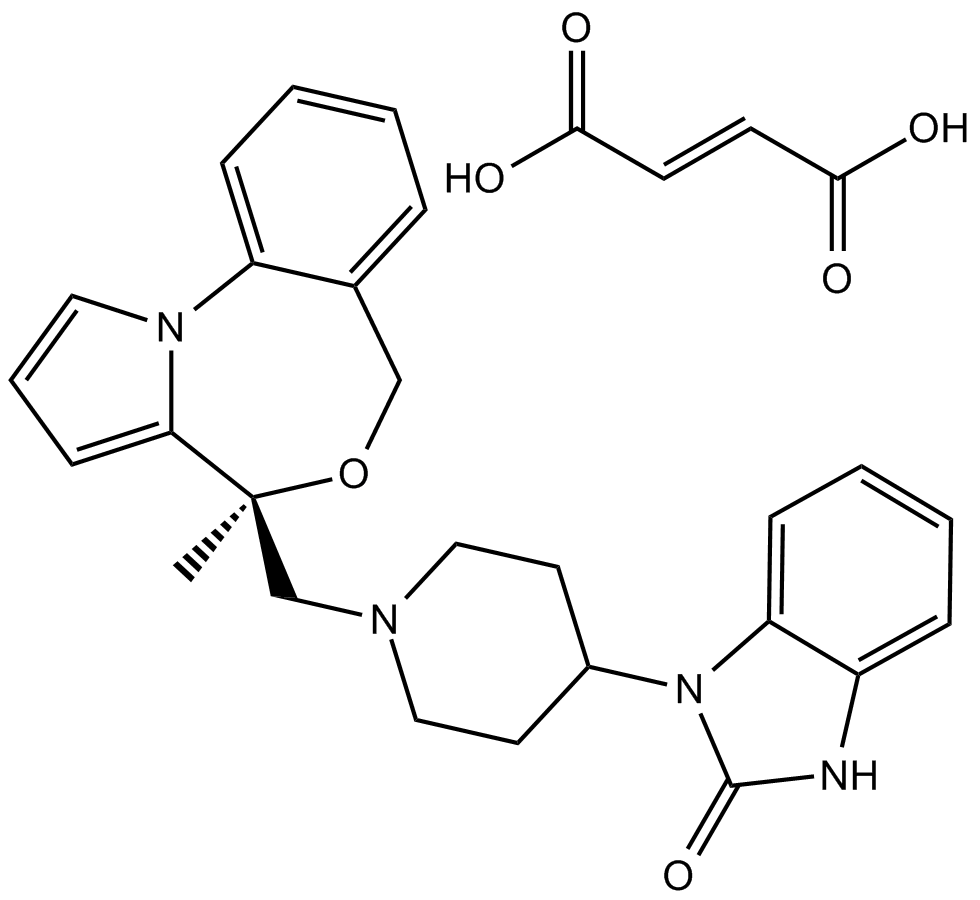 B6992 CGS 9343BSummary: Calmodulin antagonist
B6992 CGS 9343BSummary: Calmodulin antagonist -
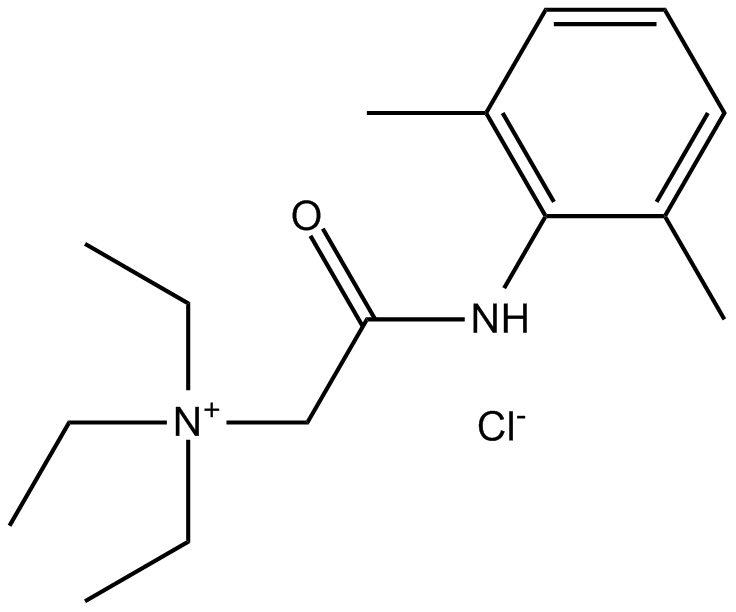 B7015 QX 314 chlorideSummary: A voltage-activated Na+ channel blocker
B7015 QX 314 chlorideSummary: A voltage-activated Na+ channel blocker

