Membrane Transporter/Ion Channel

Ion channels are pore-forming membrane proteins which allow the flow of ions across the membrane. The ion channels can be broadly grouped into six families including calcium channels, chloride channels, potassium channels, sodium channels, gap junction proteins and porins. Not all ion channels are gated, such as certain type of K+ and Cl– channels, transient receptor potential superfamily of cation channels, the ryanodine receptors and the IP3 receptors, but most Na+, K+, Ca2+ and some Cl– channels are all gated by voltage. Ligand-gated channels are regulated in response to ligand binding (e.g. neurotransmitters signaling). These ligand-gated neurotransmitter receptors are known as ionotropic receptors. Various neurotransmitters couple to ionotropic receptors such as glutamate, acetylcholine, glycine, GABA, and serotonin.
-
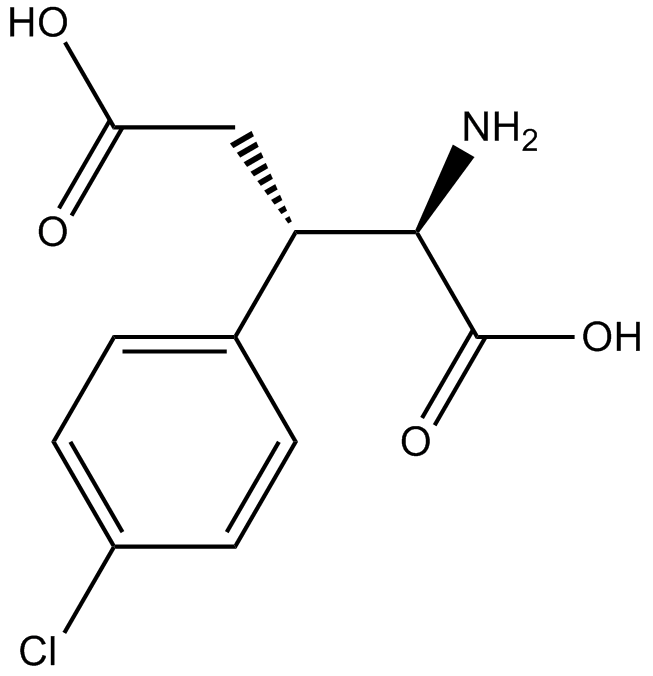 B6462 (2R,3S)-ChlorphegSummary: NMDA receptor antagonist
B6462 (2R,3S)-ChlorphegSummary: NMDA receptor antagonist -
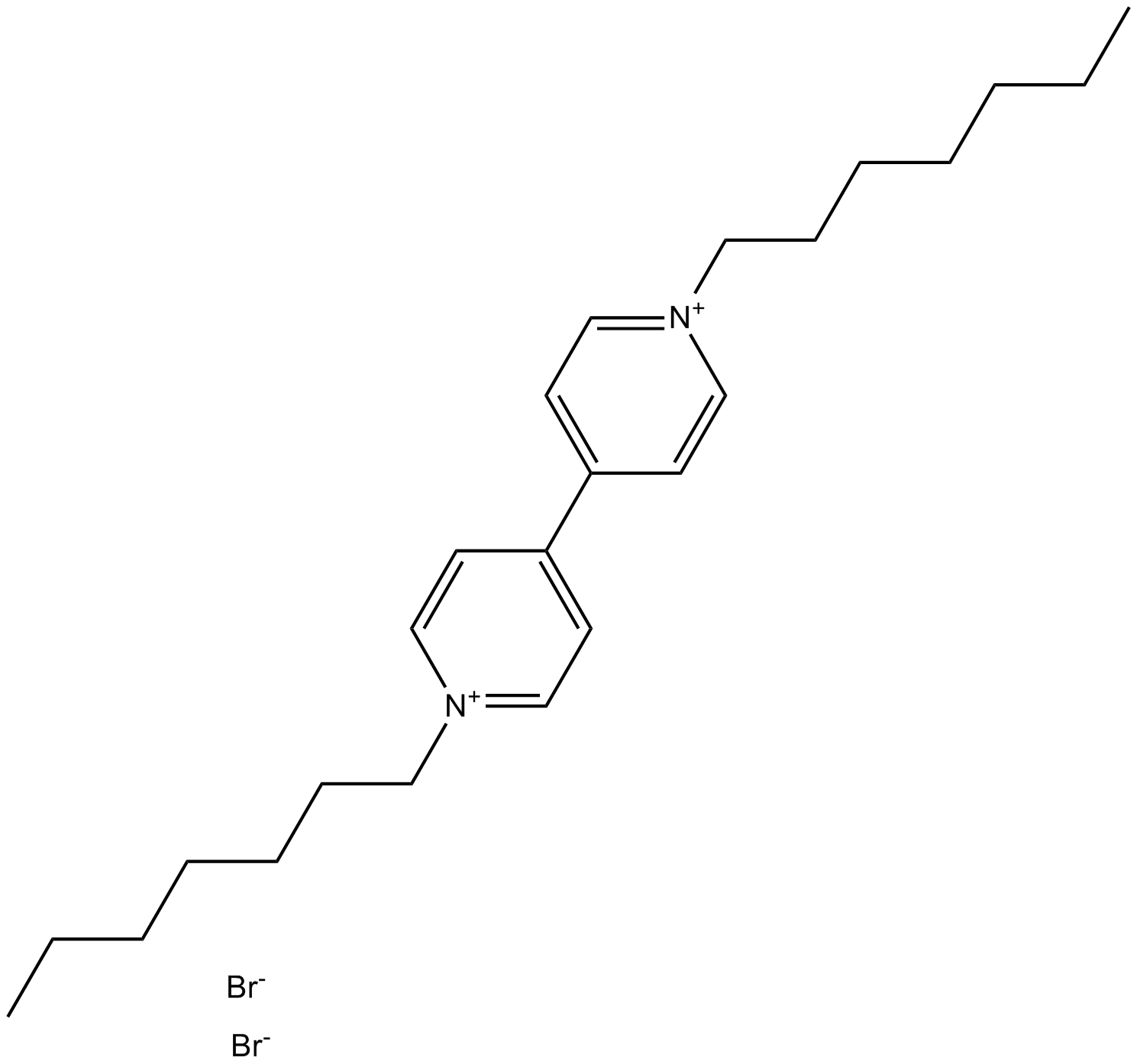 B6468 DHBP dibromideSummary: ryanodine receptor blocker
B6468 DHBP dibromideSummary: ryanodine receptor blocker -
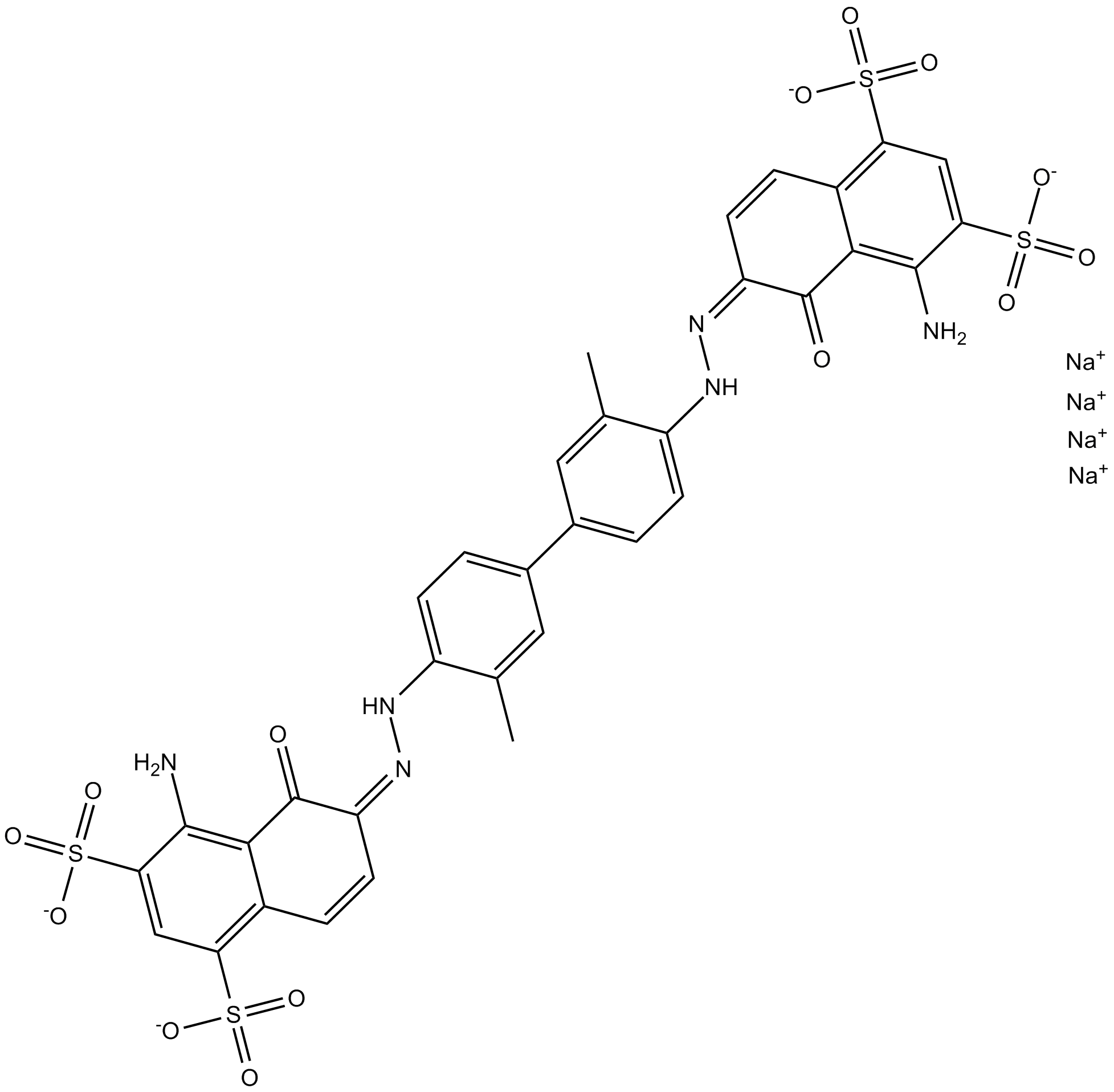 B6472 Evans Blue tetrasodium saltSummary: L-glutamate uptake inhibitor,dye used to detect cell viability and plasma membrane integrity
B6472 Evans Blue tetrasodium saltSummary: L-glutamate uptake inhibitor,dye used to detect cell viability and plasma membrane integrity -
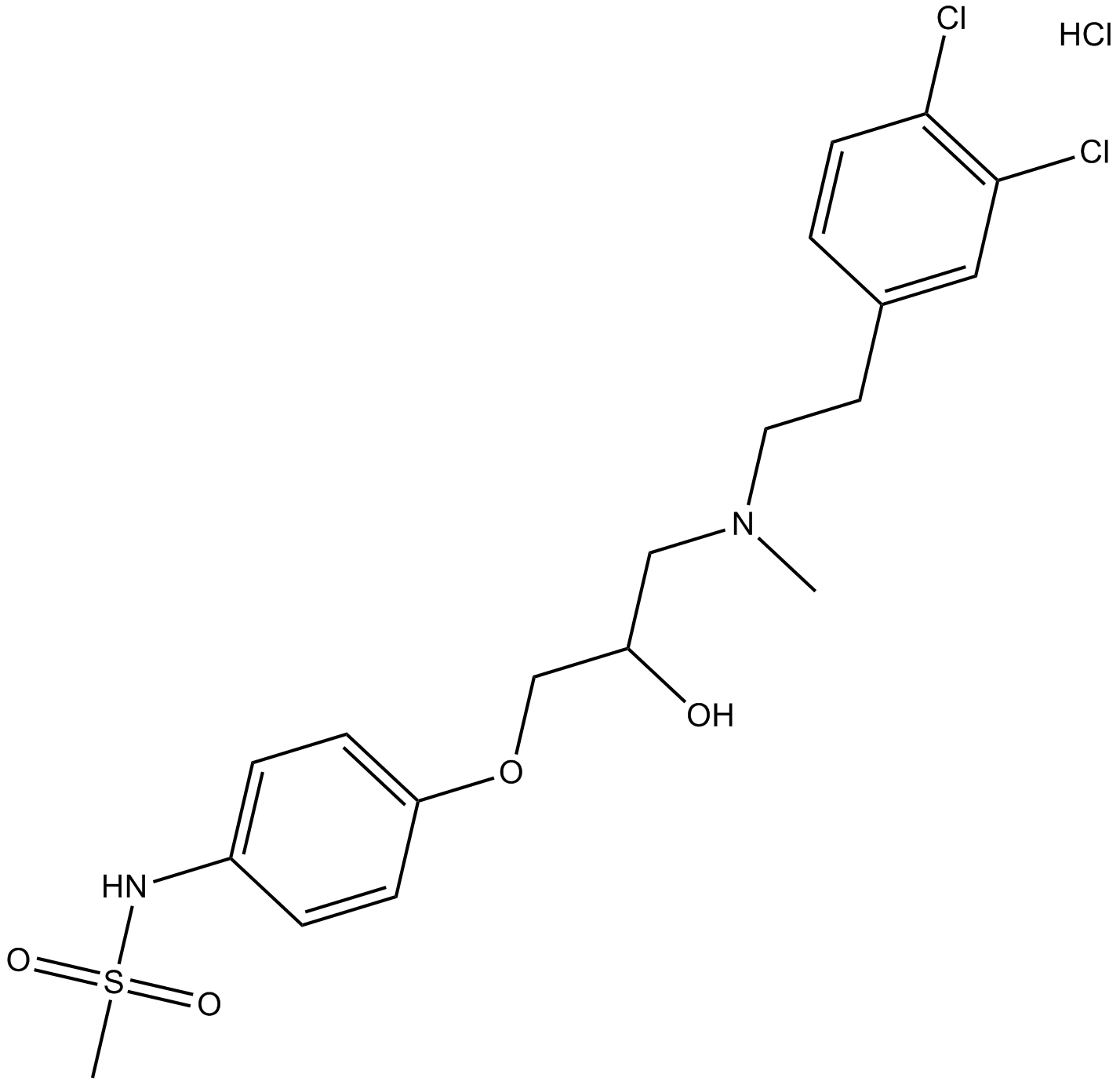 B6482 AM 92016 hydrochlorideSummary: Potassium channel blocker
B6482 AM 92016 hydrochlorideSummary: Potassium channel blocker -
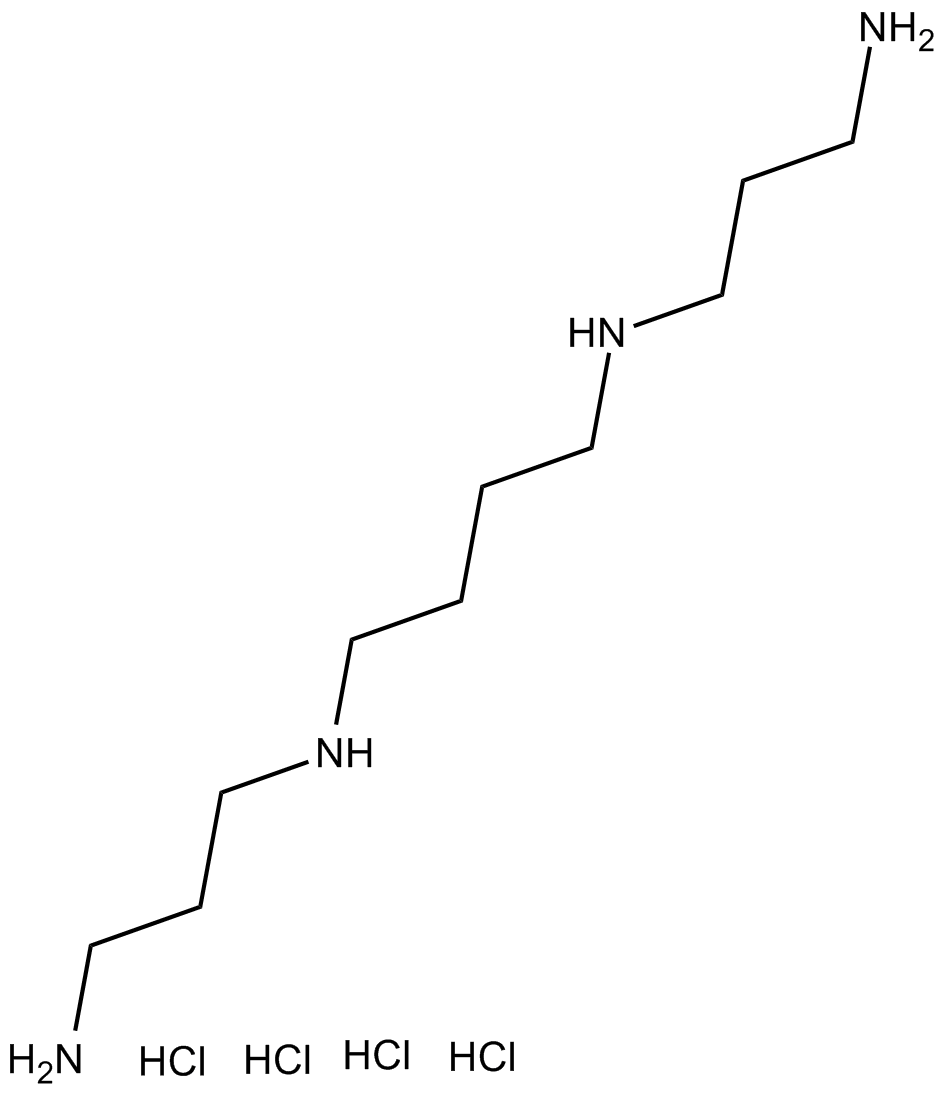 B6522 Spermine tetrahydrochlorideSummary: NMDA receptor modulator
B6522 Spermine tetrahydrochlorideSummary: NMDA receptor modulator -
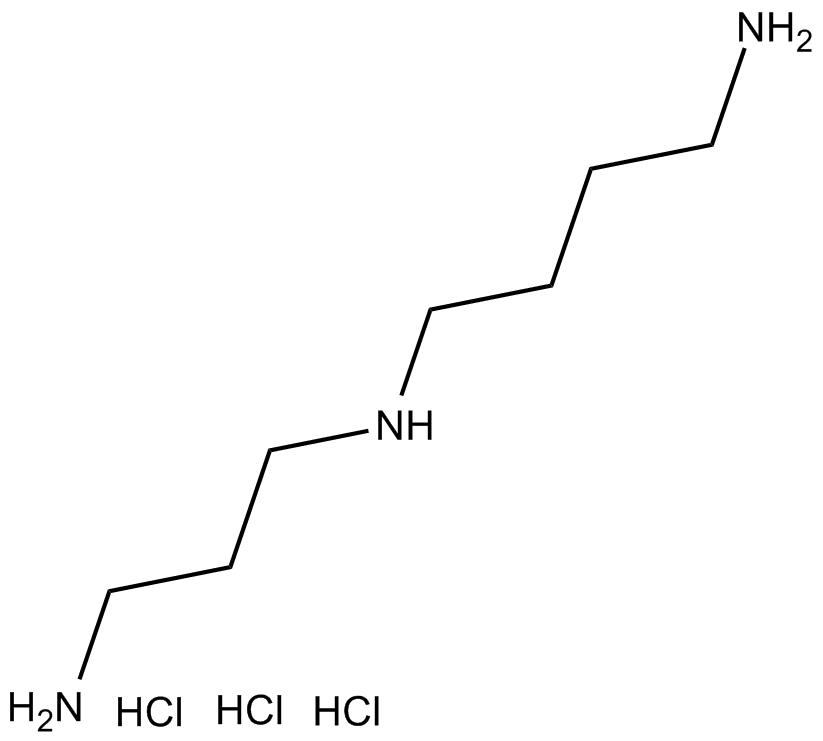 B6523 Spermidine trihydrochlorideTarget: NMDA ReceptorsSummary: A NMDA receptor agonist
B6523 Spermidine trihydrochlorideTarget: NMDA ReceptorsSummary: A NMDA receptor agonist -
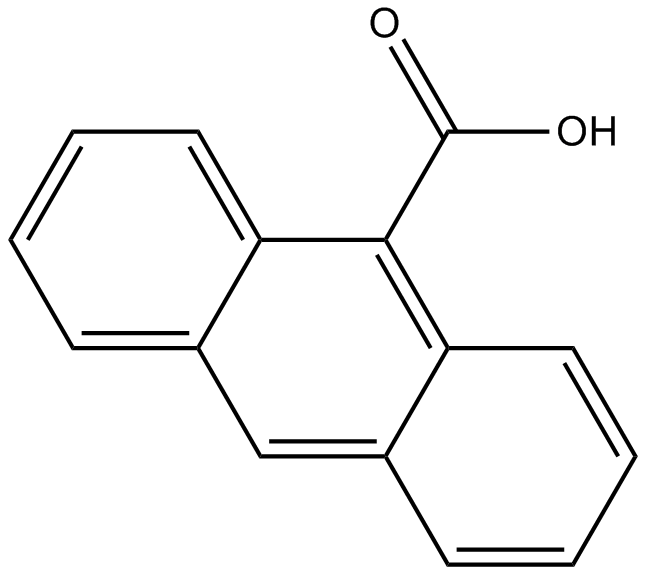 B6525 9-ACSummary: Cl- transport inhibitor
B6525 9-ACSummary: Cl- transport inhibitor -
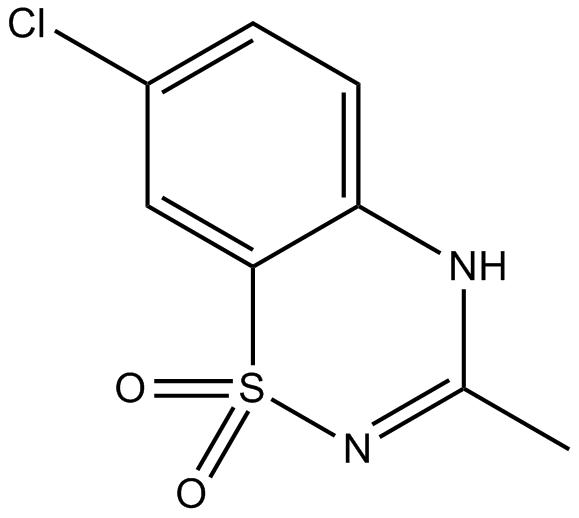 B6526 DiazoxideSummary: positive allosteric modulator of the AMPA and kainate receptors
B6526 DiazoxideSummary: positive allosteric modulator of the AMPA and kainate receptors -
 B6531 MPDCSummary: inhibitor of the Na+-dependent high-affinity synaptosomal glutamate transporter
B6531 MPDCSummary: inhibitor of the Na+-dependent high-affinity synaptosomal glutamate transporter -
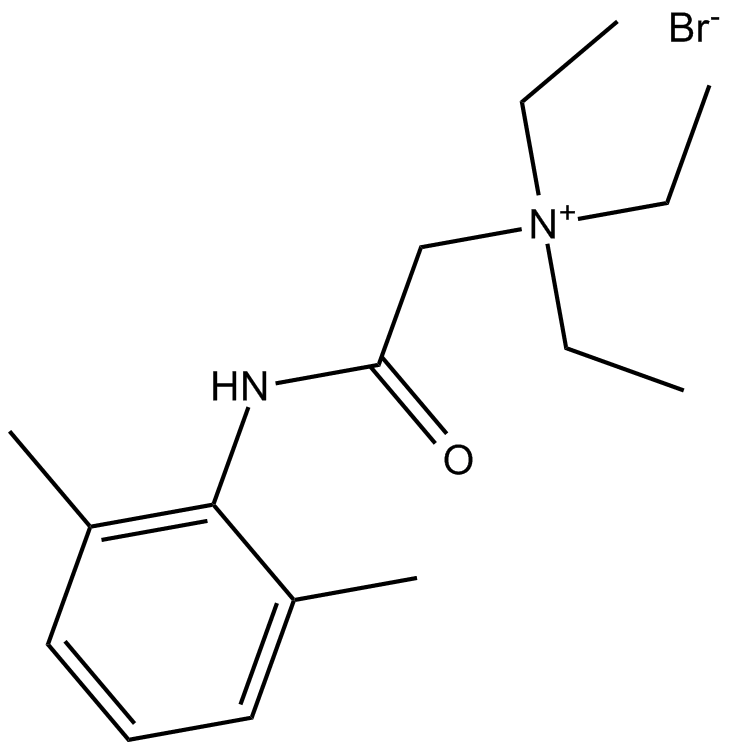 B6547 QX 314 bromideSummary: voltage-activated Na+ channels blocker
B6547 QX 314 bromideSummary: voltage-activated Na+ channels blocker

