Membrane Transporter/Ion Channel

Ion channels are pore-forming membrane proteins which allow the flow of ions across the membrane. The ion channels can be broadly grouped into six families including calcium channels, chloride channels, potassium channels, sodium channels, gap junction proteins and porins. Not all ion channels are gated, such as certain type of K+ and Cl– channels, transient receptor potential superfamily of cation channels, the ryanodine receptors and the IP3 receptors, but most Na+, K+, Ca2+ and some Cl– channels are all gated by voltage. Ligand-gated channels are regulated in response to ligand binding (e.g. neurotransmitters signaling). These ligand-gated neurotransmitter receptors are known as ionotropic receptors. Various neurotransmitters couple to ionotropic receptors such as glutamate, acetylcholine, glycine, GABA, and serotonin.
-
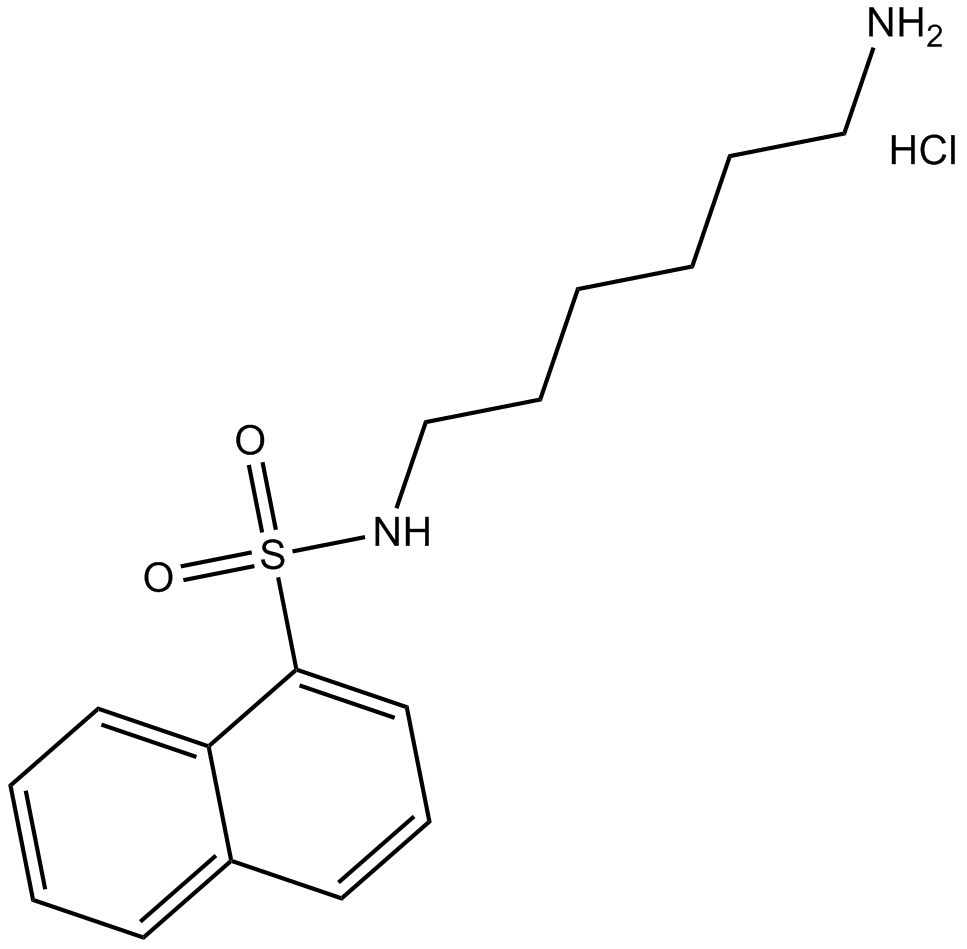 B6277 W-5 hydrochlorideSummary: calmodulin antagonist
B6277 W-5 hydrochlorideSummary: calmodulin antagonist -
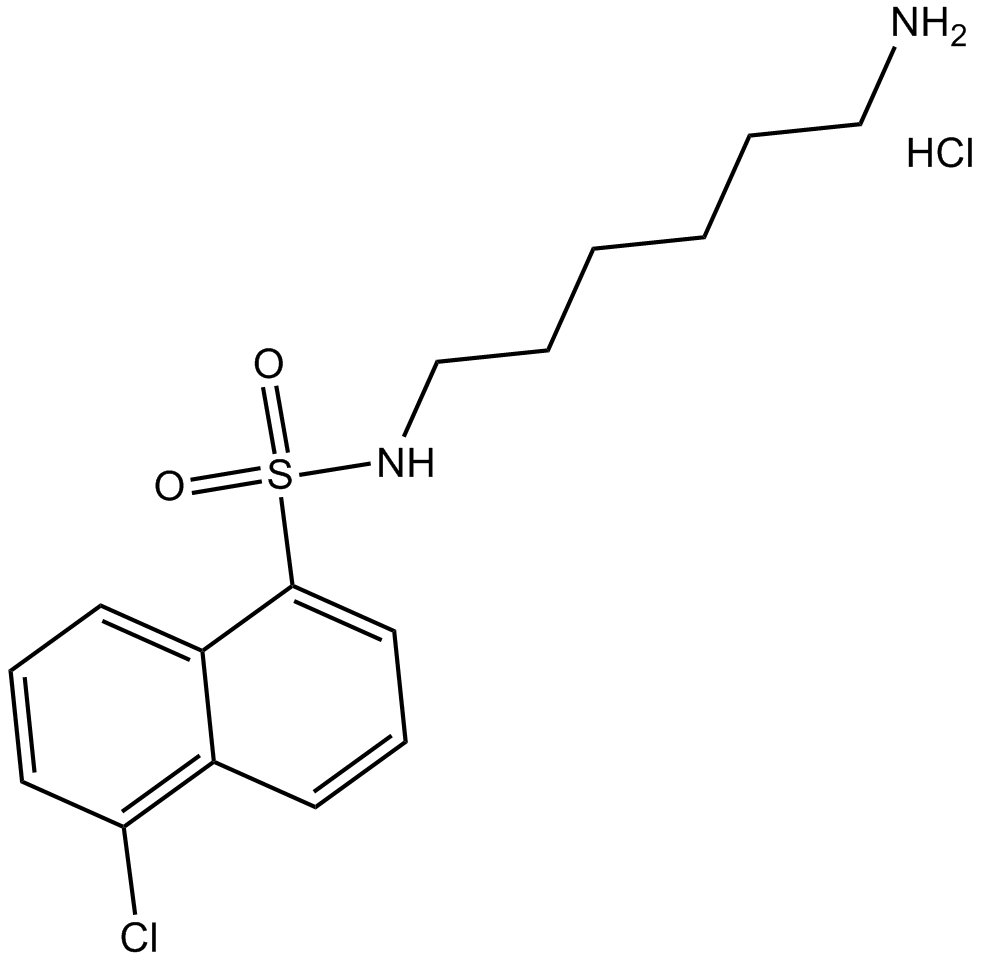 B6278 W-7 hydrochlorideTarget: CalmodulinsSummary: calmodulin antagonist
B6278 W-7 hydrochlorideTarget: CalmodulinsSummary: calmodulin antagonist -
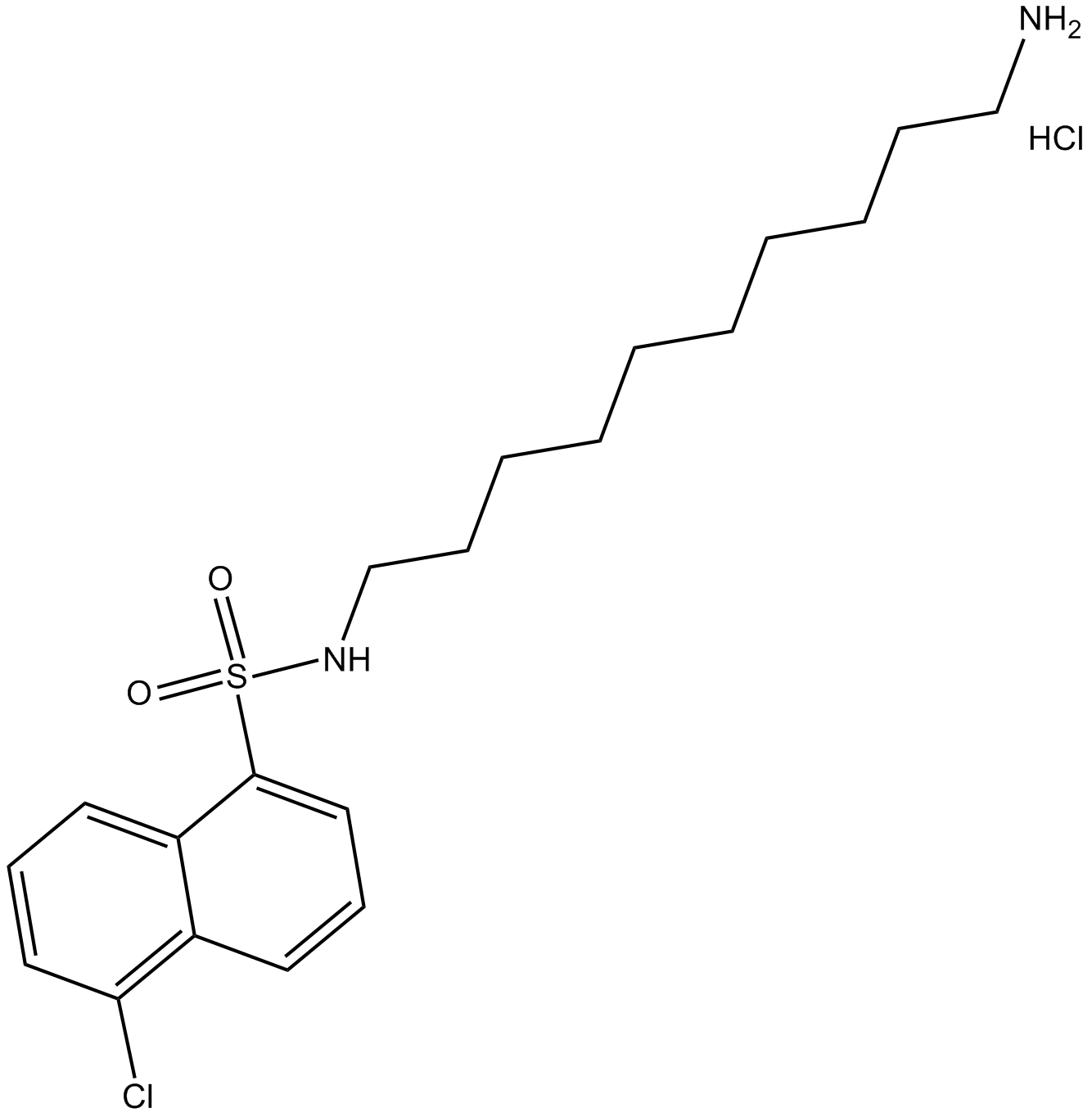 B6281 A-7 hydrochlorideSummary: calmodulin antagonist
B6281 A-7 hydrochlorideSummary: calmodulin antagonist -
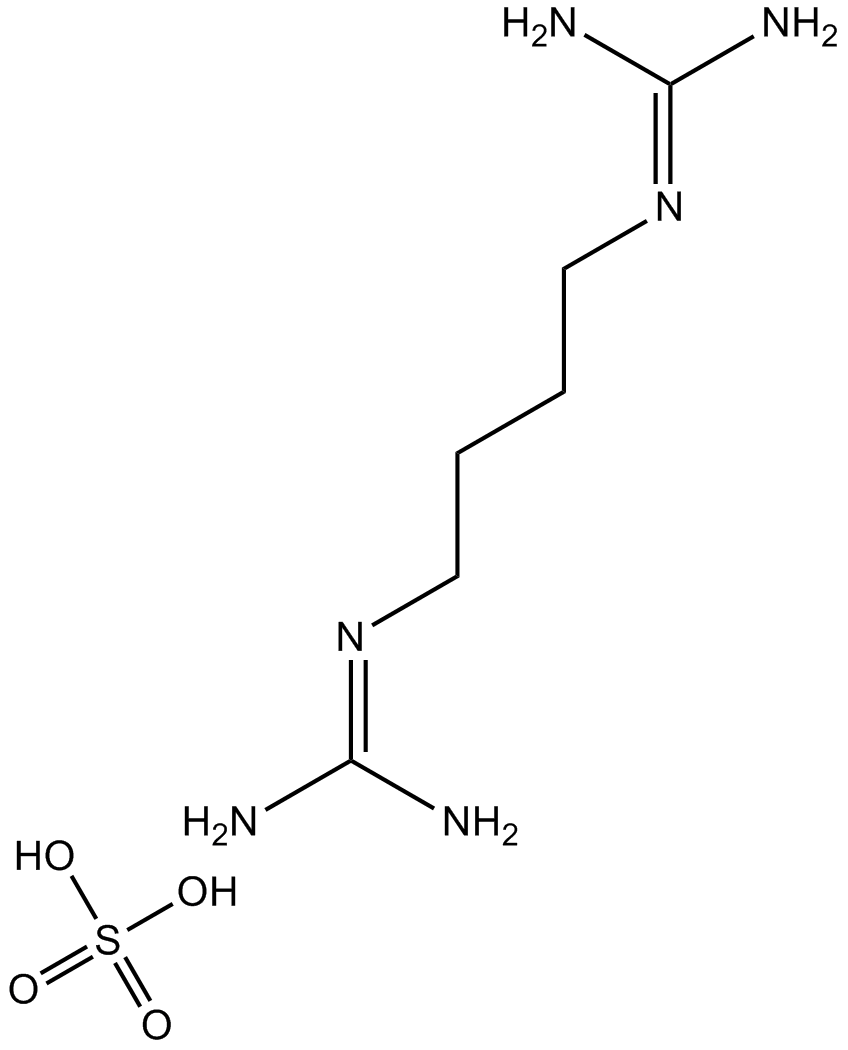 B6287 Arcaine sulfateSummary: NMDA antagonist
B6287 Arcaine sulfateSummary: NMDA antagonist -
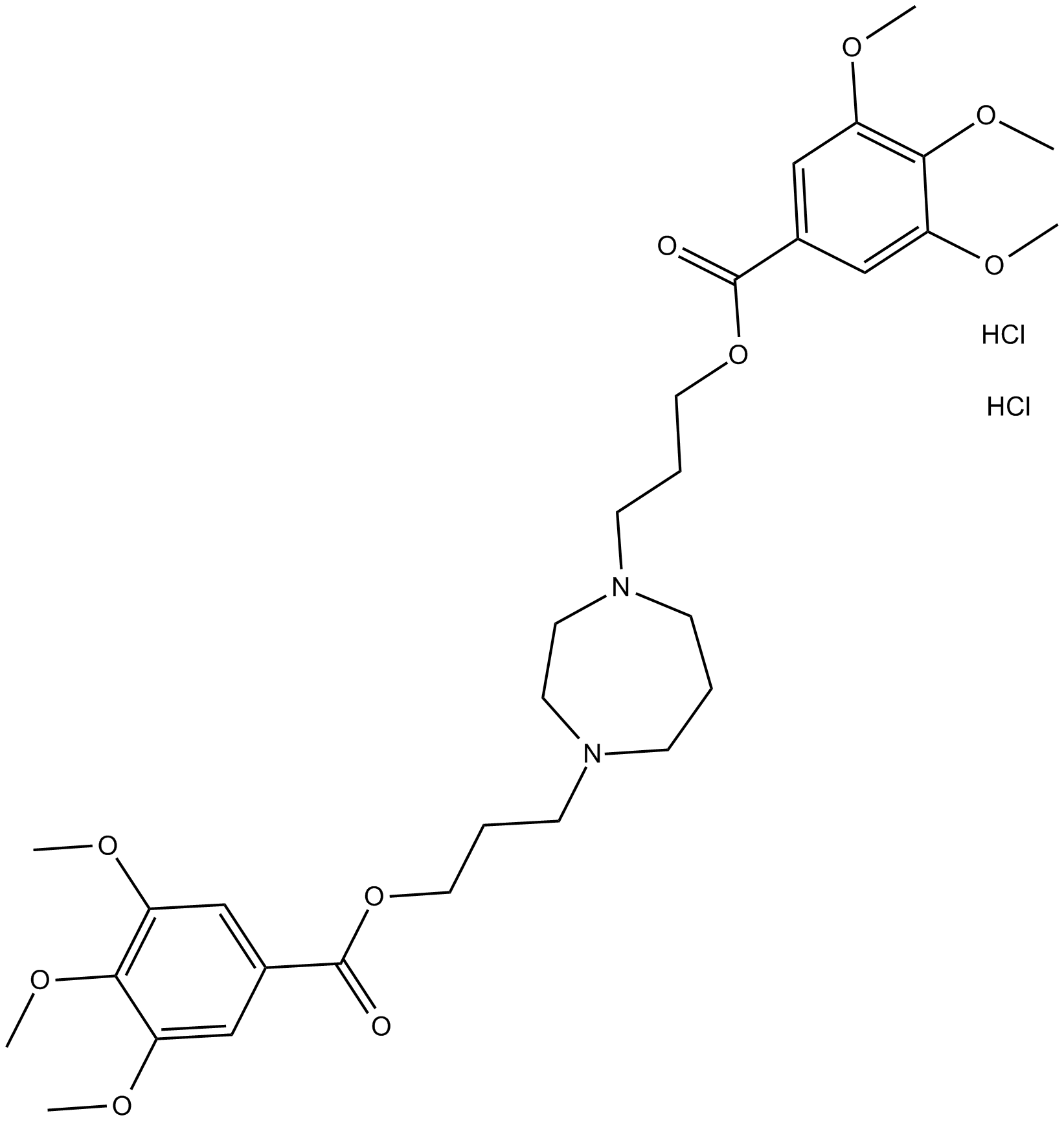 B6316 Dilazep dihydrochlorideSummary: vasodilator that acts as an adenosine reuptake inhibitor
B6316 Dilazep dihydrochlorideSummary: vasodilator that acts as an adenosine reuptake inhibitor -
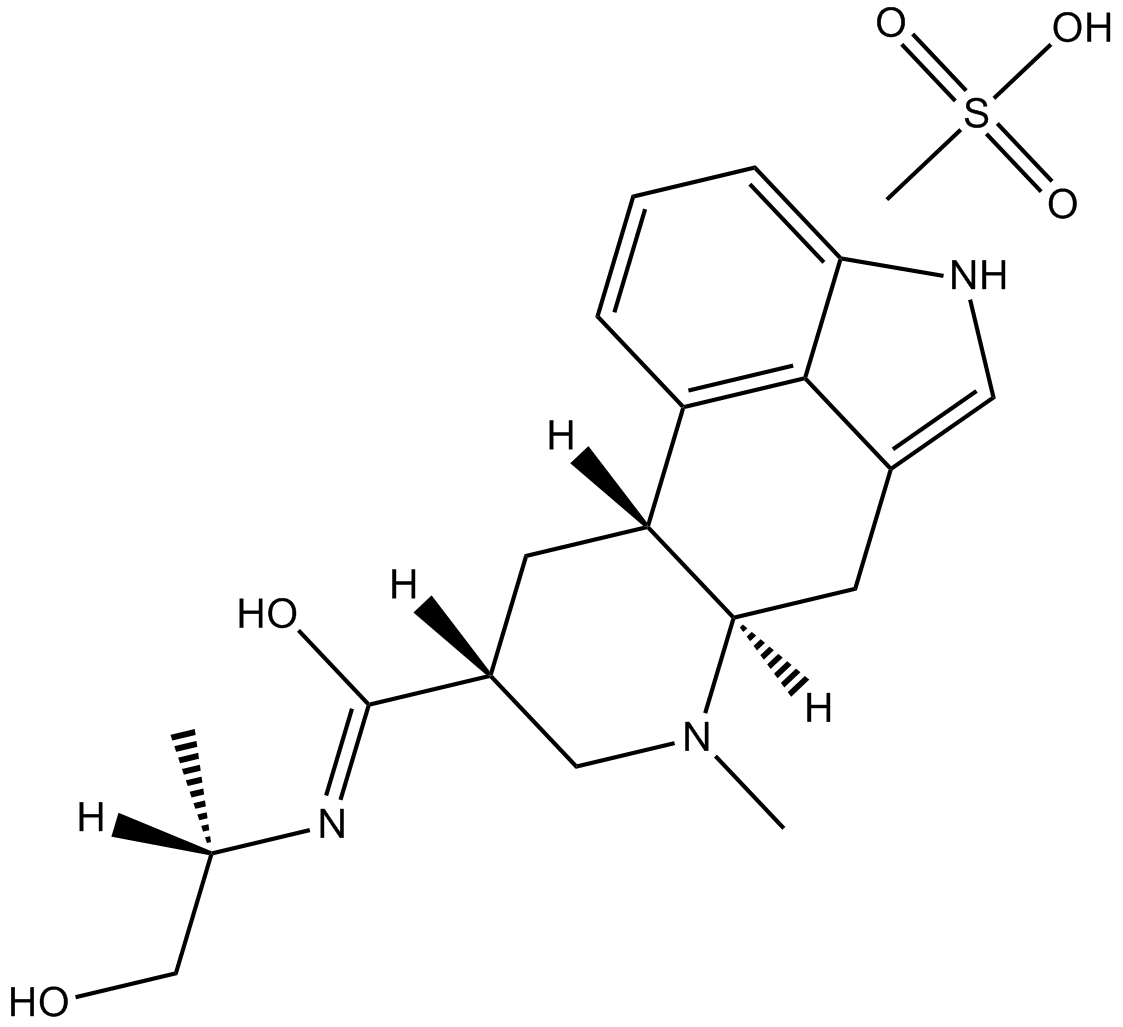 B6327 Dihydroergotoxine mesylateSummary: GABAA receptor modulator
B6327 Dihydroergotoxine mesylateSummary: GABAA receptor modulator -
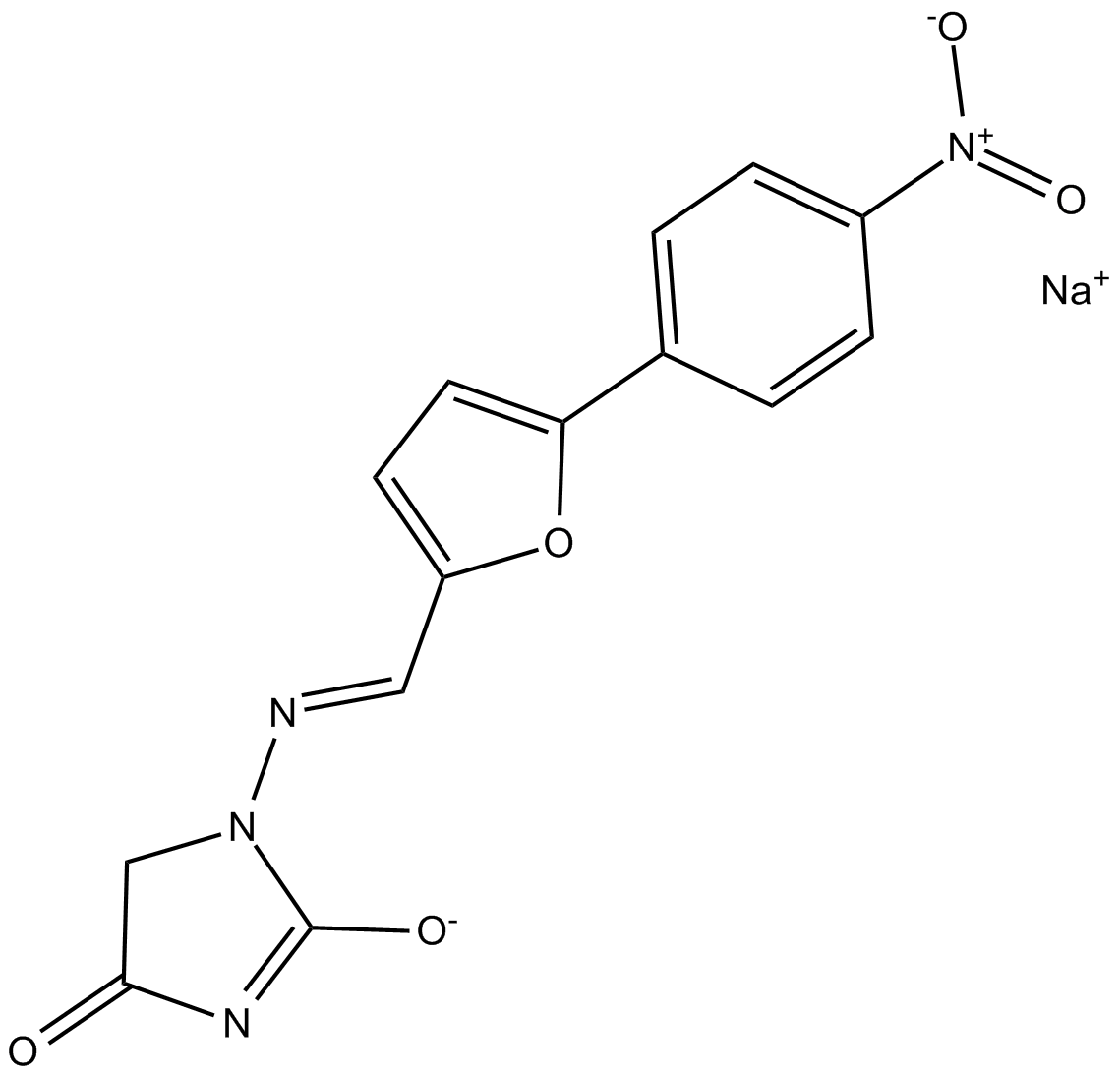 B6329 Dantrolene, sodium saltSummary: ryanodine receptor (RYR) channels inhibitor
B6329 Dantrolene, sodium saltSummary: ryanodine receptor (RYR) channels inhibitor -
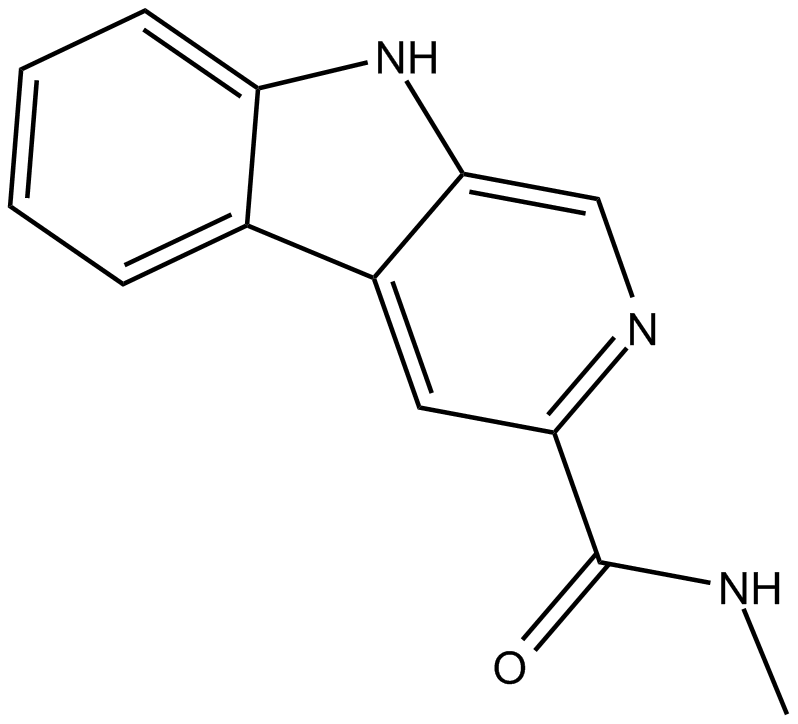 B6350 FG 7142Summary: benzodiazepine inverse agonist and anxiogenic agent
B6350 FG 7142Summary: benzodiazepine inverse agonist and anxiogenic agent -
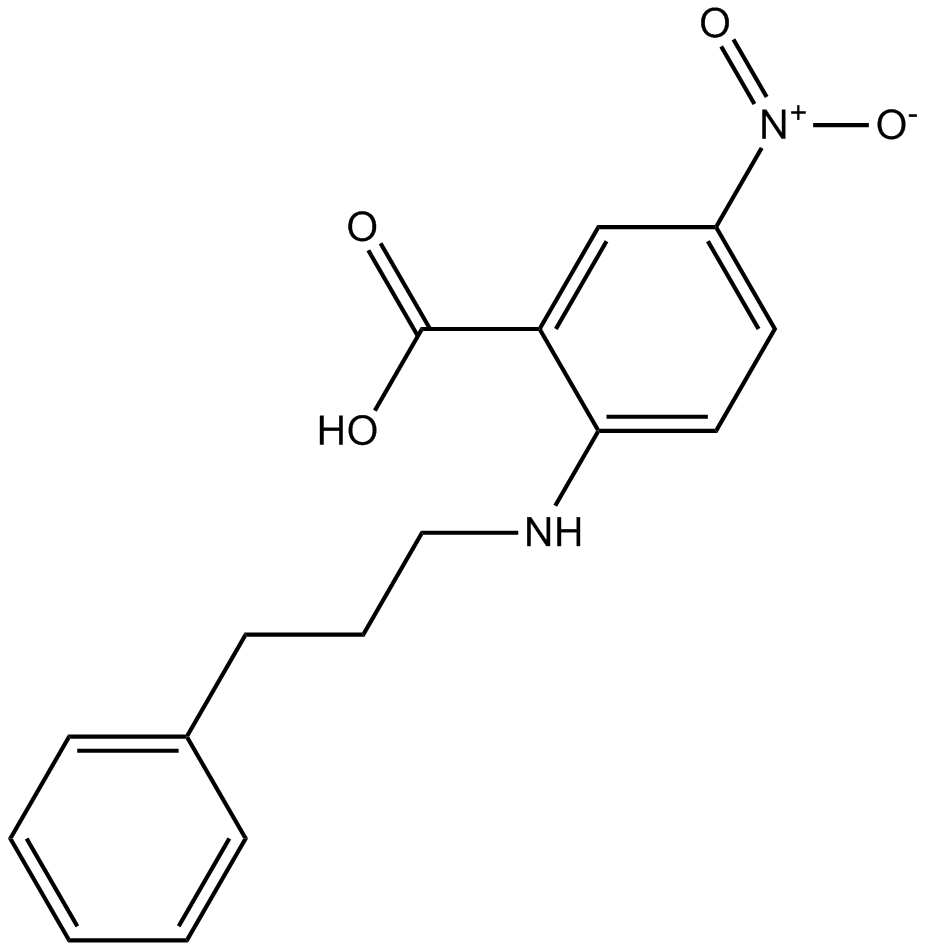 B6367 NPPBTarget: Calcium-activated chloride channels (CaCC)|GPR35Summary: inhibitor of chloride channel
B6367 NPPBTarget: Calcium-activated chloride channels (CaCC)|GPR35Summary: inhibitor of chloride channel -
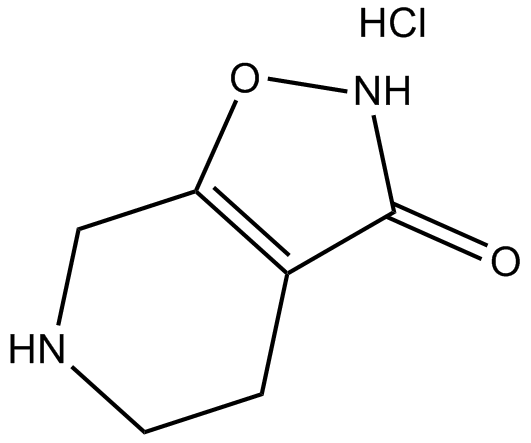 B6460 THIP hydrochlorideSummary: GABAA receptor agonist and GABAA-ρ receptor antagonist
B6460 THIP hydrochlorideSummary: GABAA receptor agonist and GABAA-ρ receptor antagonist

