Cardiovascular

Cardiovascular
The cardiovascular system consists of the heart, blood and blood vessels. These organs form the 3 major closed circulation systems in the body, i.e., the pulmonary, coronary and systemic circulations. Cardiovascular disease includes heart disease, vascular diseases of the brain and kidney, and peripheral arterial diseases. Cardiovascular disease is the leading cause of death globally. Studies on cardiovascular regulation are important to provide a better understanding of this group of diseases and to help improve the corresponding treatment. read more
-
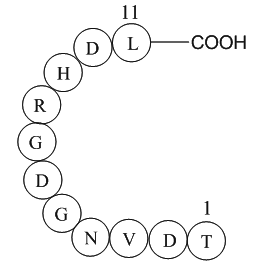 A1018 Platelet Membrane Glycoprotein IIB Peptide (296-306)Summary: Inhibits platelet aggregation
A1018 Platelet Membrane Glycoprotein IIB Peptide (296-306)Summary: Inhibits platelet aggregation -
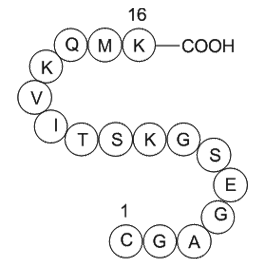 A1022 GTP-Binding Protein Fragment, G alphaSummary: Hydrolyzes GTP to GDP
A1022 GTP-Binding Protein Fragment, G alphaSummary: Hydrolyzes GTP to GDP -
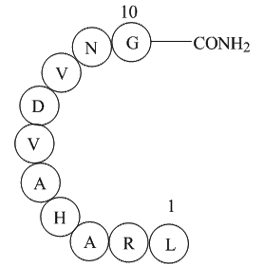 A1028 Cadherin Peptide, avianSummary: Role in cell adhesion
A1028 Cadherin Peptide, avianSummary: Role in cell adhesion -
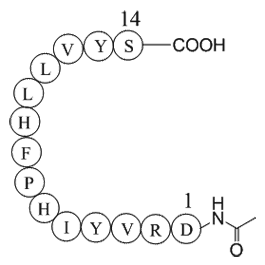 A1034 Acetyl Angiotensinogen (1-14), porcineSummary: Angiotensinogen precursor
A1034 Acetyl Angiotensinogen (1-14), porcineSummary: Angiotensinogen precursor -
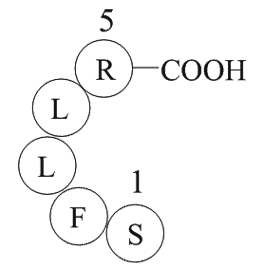 A1036 Thrombin Receptor Activator for Peptide 5 (TRAP-5)Target: Thrombin ReceptorSummary: Thrombin Receptor Activator for Peptide 5
A1036 Thrombin Receptor Activator for Peptide 5 (TRAP-5)Target: Thrombin ReceptorSummary: Thrombin Receptor Activator for Peptide 5 -
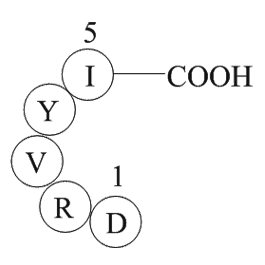 A1047 Angiotensin 1/2 (1-5)Summary: Vasoconstrictor
A1047 Angiotensin 1/2 (1-5)Summary: Vasoconstrictor -
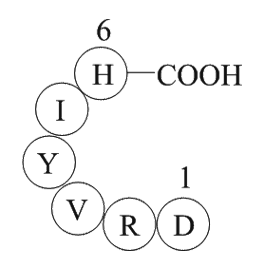 A1048 Angiotensin 1/2 (1-6)Summary: Vasoconstrictor
A1048 Angiotensin 1/2 (1-6)Summary: Vasoconstrictor -
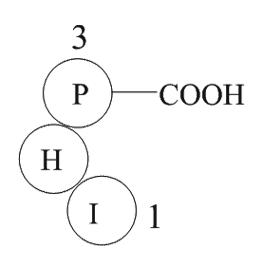 A1049 Angiotensin 1/2 (5-7)Summary: Vasoconstrictor
A1049 Angiotensin 1/2 (5-7)Summary: Vasoconstrictor -
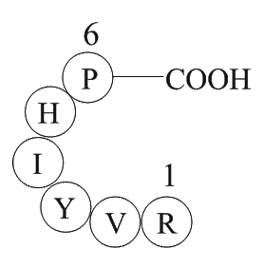 A1050 Angiotensin 1/2 (2-7)Summary: Vasoconstrictor
A1050 Angiotensin 1/2 (2-7)Summary: Vasoconstrictor -
![amyloid A protein fragment [Homo sapiens]](/pub/media/prod_images/a/1/a1053.png) A1053 amyloid A protein fragment [Homo sapiens]Summary: Apolipoproteins related to HDL in plasma
A1053 amyloid A protein fragment [Homo sapiens]Summary: Apolipoproteins related to HDL in plasma

