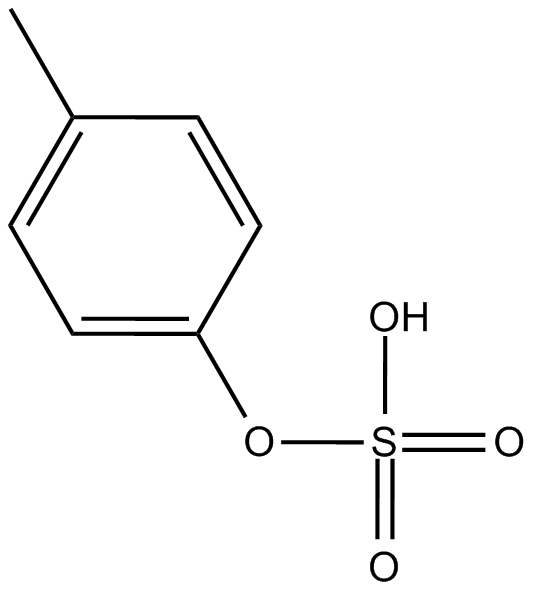
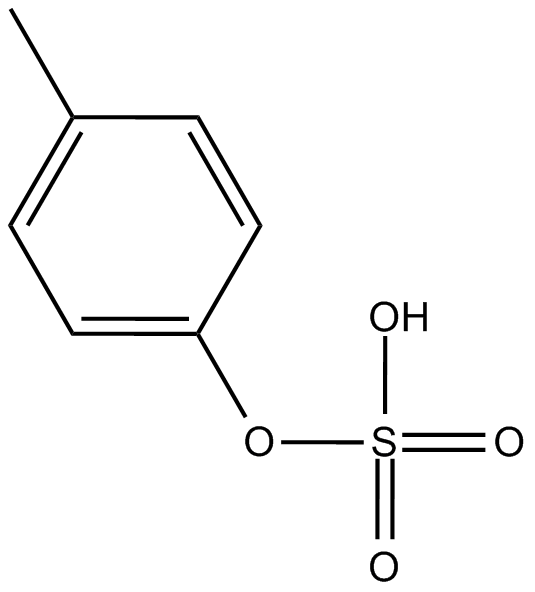
p-Cresyl sulfate
p-Cresyl sulfate (CAS 3233-58-7) is a protein-bound uremic retention solute derived from p-cresol, implicated in cardiovascular risk among chronic kidney disease patients undergoing dialysis. Elevated free p-cresyl sulfate levels in hemodialysis patients correlate strongly with increased cardiovascular morbidity. Mechanistically, p-cresyl sulfate inhibits endothelial cell proliferation and impairs wound healing without affecting cell viability, thereby potentially exacerbating vascular complications. Due to its role in endothelial dysfunction and cardiovascular events, p-cresyl sulfate is employed as a biomarker in uremia-related cardiovascular research.
References:
1. Meijers B K I, Bammens B, De Moor B, et al. Free p-cresol is associated with cardiovascular disease in hemodialysis patients. Kidney international, 2008, 73(10): 1174-1180.
2. Dou L, Bertrand E, Cerini C, et al. The uremic solutes p-cresol and indoxyl sulfate inhibit endothelial proliferation and wound repair. Kidney international, 2004, 65(2): 442-451.
- 1. Doureradjou Peroumal, Chetan V Jawale, et al. "The survival of B cells is compromised in kidney disease." Nat Commun. 2024 Dec 30;15(1):10842. PMID:39738044
- 2. Tao Ma, Wei Huang, et al. "AIBP protects drug-induced liver injury by inhibiting MAPK-mediated NR4A1 expression." Volume 27, Issue 10110873 October 18, 2024
- 3. Yuqi Shen, Yue Shen, et al. "Polyethyleneimine‐anchored liposomes as scavengers for improving the efficiency of protein‐bound uremic toxin clearance during dialysis." J Biomed Mater Res A. 2021 Dec 15. PMID: 34908219
- 4. Jui-Ning Yeh, Ya Yue, et al. "Entresto protected the cardiomyocytes and preserved heart function in cardiorenal syndrome rat fed with high-protein diet through regulating the oxidative stress and Mfn2-mediated mitochondrial functional integrity." Biomed Pharmacother. 2021 Dec;144:112244. PMID: 34601193
- 5. Yuanyuan Shi, Huajun Tian, et al. "Improved Dialysis Removal of Protein-Bound Uraemic Toxins with a Combined Displacement and Adsorption Technique." Blood Purif. 2022;51(6):548-558. PMID:34515053
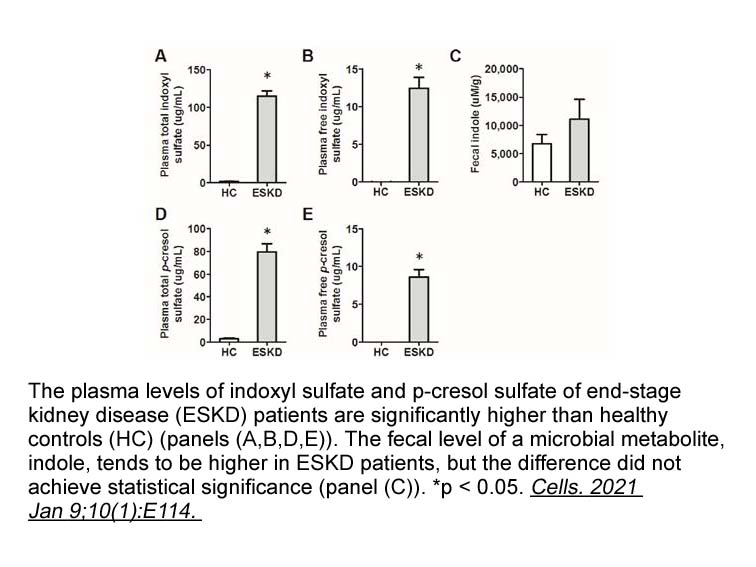
- 6. Chih-Yu Yang, Ting-Wen Chen, et al. "Synbiotics Alleviate the Gut Indole Load and Dysbiosis in Chronic Kidney Disease." Cells. 2021 Jan 9;10(1):114. PMID:33435396
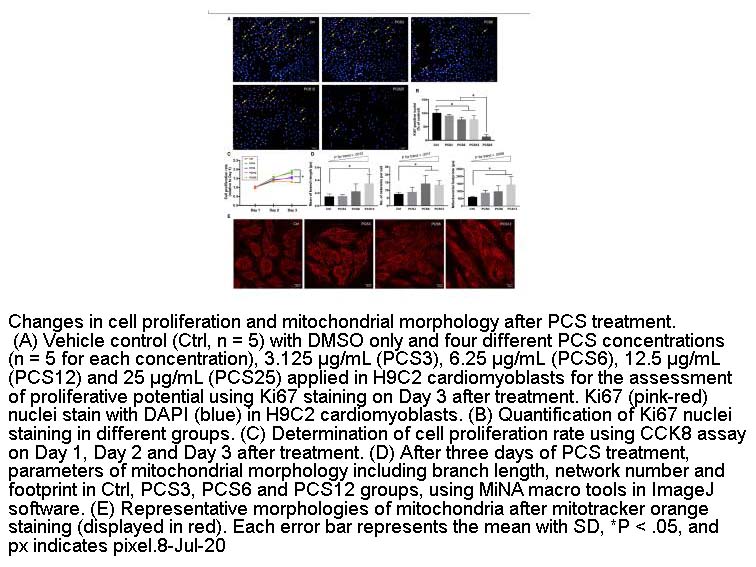
- 7. Tien-Hung Huang, Hon-Kan Yip, et al. "P-cresyl sulfate causes mitochondrial hyperfusion in H9C2 cardiomyoblasts." J Cell Mol Med. 2020 Aug;24(15):8379-8390. PMID:32639656
- 8. Van Buren J, Prasse C, et al. "Ring-Cleavage Products Produced during the Initial Phase of Oxidative Treatment of Alkyl-Substituted Aromatic Compounds." Environ Sci Technol. 2020;54(13):8352-8361. PMID:32519538
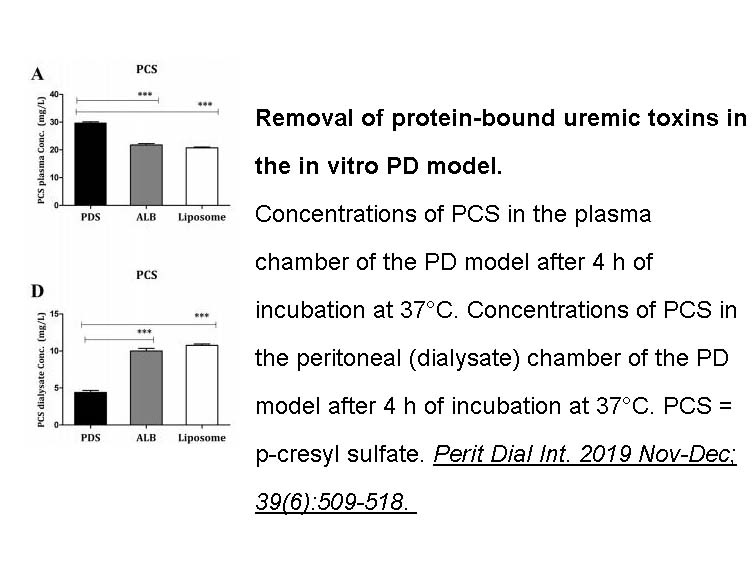
- 9. Shi Y, Tian H, et al. "Removal of Protein-Bound Uremic Toxins by Liposome-Supported Peritoneal Dialysis." Perit Dial Int. 2019 Nov-Dec;39(6):509-518. PMID:31690700
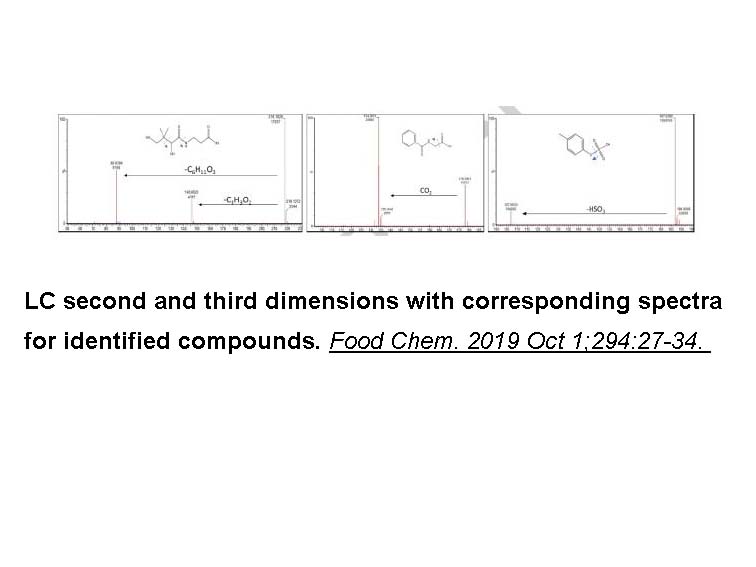
- 10. Potts DM, Peterson DG. "Identification of small molecule flavor compounds that contribute to the somatosensory attributes of bovine milk products." Food Chem. 2019 Oct 1;294:27-34. PMID:31126463
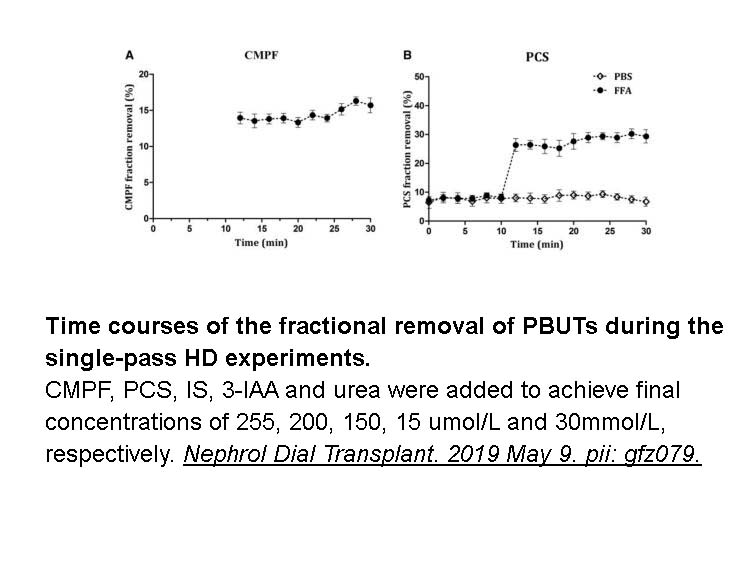
- 11. Shi Y, Zhang Y, et al. "Improved dialytic removal of protein-bound uremic toxins by intravenous lipid emulsion in chronic kidney disease rats." Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2019 May 9. pii: gfz079. PMID:31071223
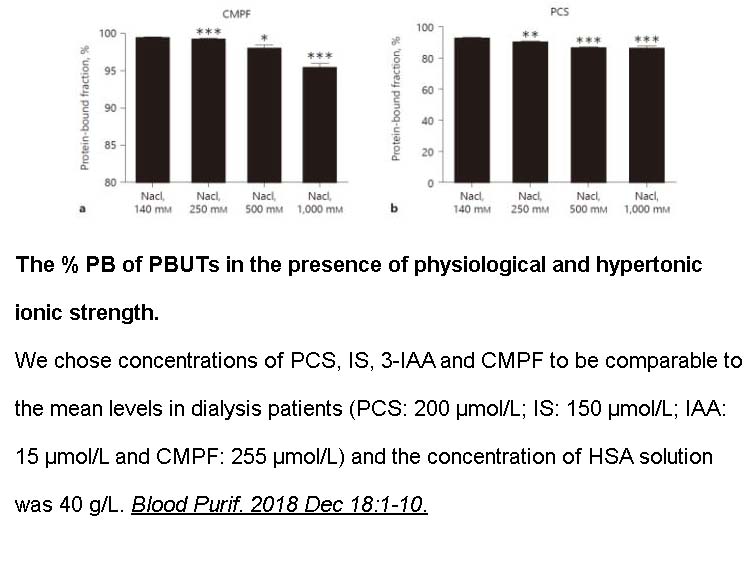
- 12. Shi Y, Tian H, et al. "Effect of Ionic Strength, pH and Chemical Displacers on the Percentage Protein Binding of Protein-Bound Uremic Toxins." Blood Purif. 2018 Dec 18:1-10. PMID:30562731
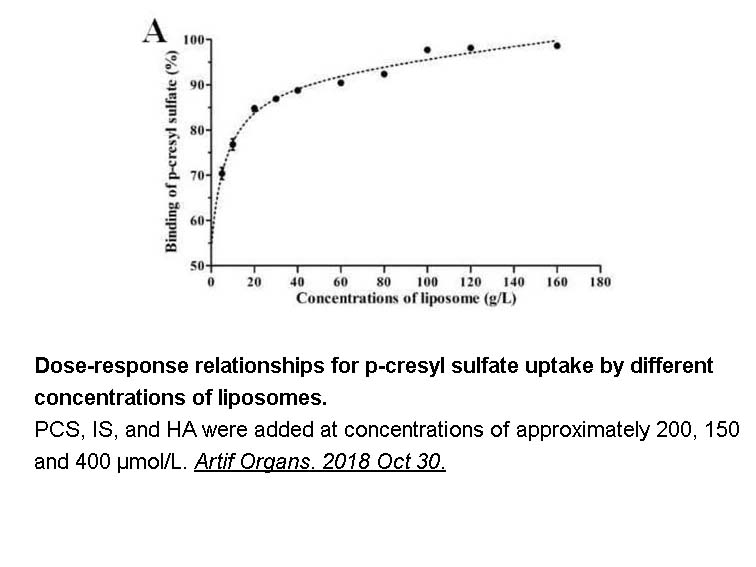
- 13. Shi Y, Wang Y, et al. "Increasing the removal of protein-bound uremic toxins by liposome-supported hemodialysis."Artif Organs. 2018 Oct 30. PMID:30375673
| Physical Appearance | A solid |
| Storage | Store at -20°CThe product is not stable in solution, please dissolve it immediately before use. |
| M.Wt | 188.20 |
| Cas No. | 3233-58-7 |
| Formula | C7H8O4S |
| Solubility | insoluble in EtOH; ≥30.1 mg/mL in DMSO; ≥50 mg/mL in H2O |
| Chemical Name | p-tolyl hydrogen sulfate |
| SDF | Download SDF |
| Canonical SMILES | Cc(cc1)ccc1OS(O)(=O)=O |
| Shipping Condition | Small Molecules with Blue Ice, Modified Nucleotides with Dry Ice. |
| General tips | We do not recommend long-term storage for the solution, please use it up soon. |
| Cell experiment [1]: | |
|
Cell lines |
Human umbilical vein endothelial cells |
|
Preparation method |
Limited solubility. General tips for obtaining a higher concentration: Please warm the tube at 37 ℃ for 10 minutes and/or shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while. Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. |
|
Reaction Conditions |
24 h |
|
Applications |
Without and with HSA, 10 mug/mL, 25 mug/mL and 50 mug/mL p-cresol induce a decrease in endothelial cell proliferation by 21%, 38% and 54%, respectively. Without HSA, endothelial wound repair in monolayers treated with p-cresol is prominently lower than in cells treated with control medium. 10 mug/mL, 25 mug/mL and 50 mug/mL p-cresol reduce endothelial wound repair by 19%, 28% and 40%, respectively. With HSA, only 50 mug/mL p-cresol prominently blocks endothelial wound repair. |
| Animal experiment [2]: | |
|
Animal models |
Rat |
|
Dosage form |
Intravenously injection of p-cresol (10 mg/kg) in rats with normal and decreased renal function |
|
Preparation method |
Dissolved in isotonic saline |
|
Applications |
P-cresol was injected in mice with normal and decreased renal function, and compared the results with those obtained for creatinine (60 mg/kg) under similar conditions. In rats with decreased renal function, p-cresol serum concentration displays a minimal decline, in contrast to rats with normal renal function. In rats with normal renal function, 21.0±10.0% of the injected p-cresol was excreted in urine. In rats with renal failure, the amount is 6.7±7.5%. |
|
Other notes |
Please test the solubility of all compounds indoor, and the actual solubility may slightly differ with the theoretical value. This is caused by an experimental system error and it is normal. |
|
References: 1. Dou L, Bertrand E, Cerini C, et al. The uremic solutes p-cresol and indoxyl sulfate inhibit endothelial proliferation and wound repair. Kidney international, 2004, 65(2): 442-451. 2. Lesaffer G, De Smet R, D'Heuvaert T et al. Comparative kinetics of the uremic toxin p-cresol versus creatinine in rats with and without renal failure. Kidney Int. 2003 Oct; 64(4):1365-73. |
|
Quality Control & MSDS
- View current batch:
Chemical structure
Related Biological Data
Related Biological Data
Related Biological Data
Related Biological Data
Related Biological Data
Related Biological Data
Related Biological Data