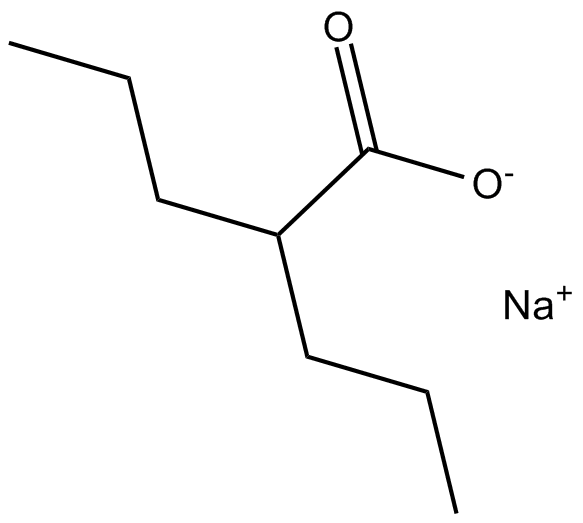
Valproic acid sodium salt (Sodium valproate)
IC50: 0.4 mM
Valproic acid (VPA) is a histone deacetylase inhibitor.
Histone deacetylases (HDACs), which have been recognized for their roles in controlling chromatin remodeling through histone acetylation/deacetylation, are currently known to modify a large number of non-histone proteins to regulate diverse cell processes.
In vitro: VPA showed to have cellular neuroprotective properties. In cultured neurons, VPA protected from thapsigargin-induced endoplasmic reticulum stress, glutamate-induced excitotoxicity, as well as lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced dopaminergic neuronal death. In midbrain neuron-glia cultures, VPA was also shown to inhibit LPS-induced, microglia-mediated inflammation [1].
In vivo: Post-pMCAO injections with VPA could decrease the brain infarct volume. Postinsult treatment with VPA also reduced the number of microglia, suppressed microglial activation, and inhibited other inflammatory markers in the ischemic brain. The reduction in acetylated histone H3 was prevented by treatment with VPA. Moreover, VPA superinduced heat-shock protein 70 and blocked pMCAO-induced down-regulation of cyclooxygenase-2. The sensory, motor, and reflex performance of pMCAO rats was improved by VPA treatment [1].
Clinical trial: In CRPC patients, VPA levels and VPA exposure duration were independent predictors for declining prostate-specific antigen (PSA). Oral VPA was not well tolerated in this patient population due to grade 1 and 2 neurologic symptoms and fatigue. Total and free VPA levels were useful for preventing severe toxicities from oral VPA. It was unlikely that PSA responses from oral VPA were related to HDAC inhibition [2].
References:
[1] Kim HJ,Rowe M,Ren M,Hong JS,Chen PS,Chuang DM. Histone deacetylase inhibitors exhibit anti-inflammatory and neuroprotective effects in a rat permanent ischemic model of stroke: multiple mechanisms of action. J Pharmacol Exp Ther.2007 Jun;321(3):892-901. Epub 2007 Mar 19.
[2] Sharma S,Symanowski J,Wong B,Dino P,Manno P,Vogelzang N. A Phase II Clinical Trial of Oral Valproic Acid in Patients with Castration-Resistant Prostate Cancers Using an Intensive Biomarker Sampling Strategy. Transl Oncol.2008 Sep;1(3):141-7.
| Storage | Store at -20°C |
| M.Wt | 166.19 |
| Cas No. | 1069-66-5 |
| Formula | C8H15NaO2 |
| Solubility | ≥8.35 mg/mL in DMSO; ≥88.2 mg/mL in H2O; ≥90.2 mg/mL in EtOH |
| Chemical Name | sodium;2-propylpentanoate |
| SDF | Download SDF |
| Canonical SMILES | CCCC(CCC)C(=O)[O-].[Na+] |
| Shipping Condition | Small Molecules with Blue Ice, Modified Nucleotides with Dry Ice. |
| General tips | We do not recommend long-term storage for the solution, please use it up soon. |
Quality Control & MSDS
- View current batch:
Chemical structure