NU7441 (KU-57788)
NU7441 (KU-57788; CAS 503468-95-9) is a selective inhibitor targeting DNA-dependent protein kinase (DNA-PK) via competition with ATP, exhibiting an IC50 of approximately 13 nM and a Ki of 0.65 nM. It demonstrates high specificity, showing minimal inhibition of related kinases ATM and ATR at concentrations up to 100 μM, and substantially weaker activity towards mTOR and PI3K (IC50 values of 1.7 and 5 μM, respectively). NU7441 sensitizes HeLa cells to etoposide, enhancing cytotoxicity, and augments tumor growth delay when co-administered in SW620 xenograft mouse models. The molecule serves as a tool compound in DNA repair and oncology research.
References:
[1] Hardcastle I R, Cockcroft X, Curtin N J, et al. Discovery of potent chromen-4-one inhibitors of the DNA-dependent protein kinase (DNA-PK) using a small-molecule library approach. Journal of medicinal chemistry, 2005, 48 (24): 7829-7846.
[2] Zhao Y, Thomas H D, Batey M A, et al. Preclinical evaluation of a potent novel DNA-dependent protein kinase inhibitor NU7441. Cancer research, 2006, 66 (10): 5354-5362.
- 1. Zhenyan Miao, Jifei Li, et al. "Hsa_circ_0136666 stimulates gastric cancer progression and tumor immune escape by regulating the miR-375/PRKDC Axis and PD-L1 phosphorylation." Mol Cancer. 2023 Dec 13;22(1):205. PMID: 38093288
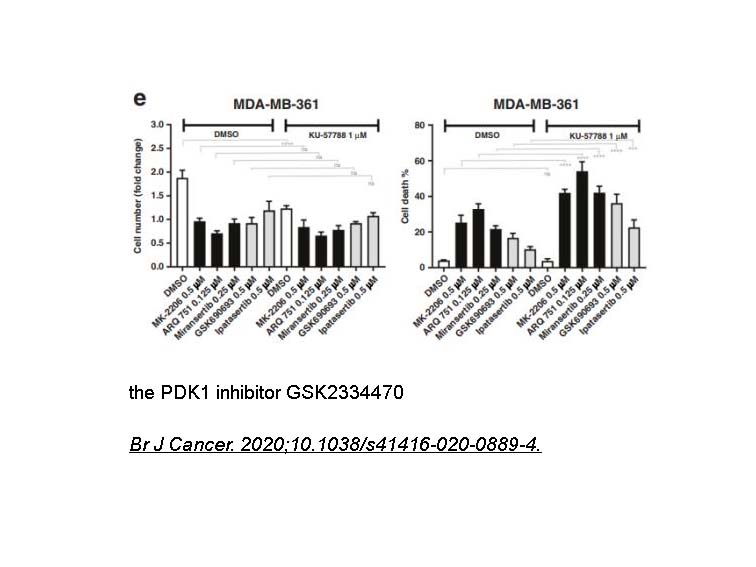
- 2. Kostaras E, Kaserer T, et al. "A systematic molecular and pharmacologic evaluation of AKT inhibitors reveals new insight into their biological activity." Br J Cancer. 2020;10.1038/s41416-020-0889-4. PMID:32439931
- 3. Jennifer Risso-Ballester, Rafael Sanjuán. "High Fidelity Deep Sequencing Reveals No Effect of ATM, ATR, and DNA-PK Cellular DNA Damage Response Pathways on Adenovirus Mutation Rate." Viruses 2019, 11(10), 938.
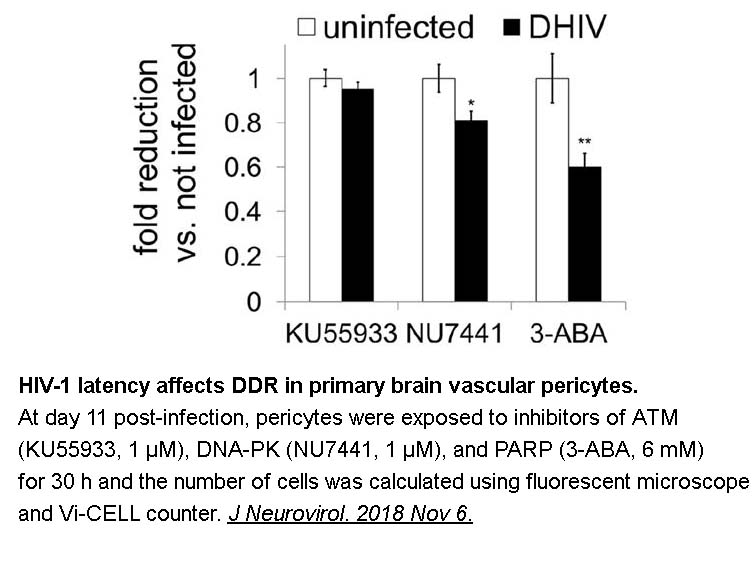
- 4. Piekna-Przybylska D, Nagumotu K, et al. "HIV-1 infection renders brain vascular pericytes susceptible to the extracellular glutamate." J Neurovirol. 2018 Nov 6. PMID:30402824
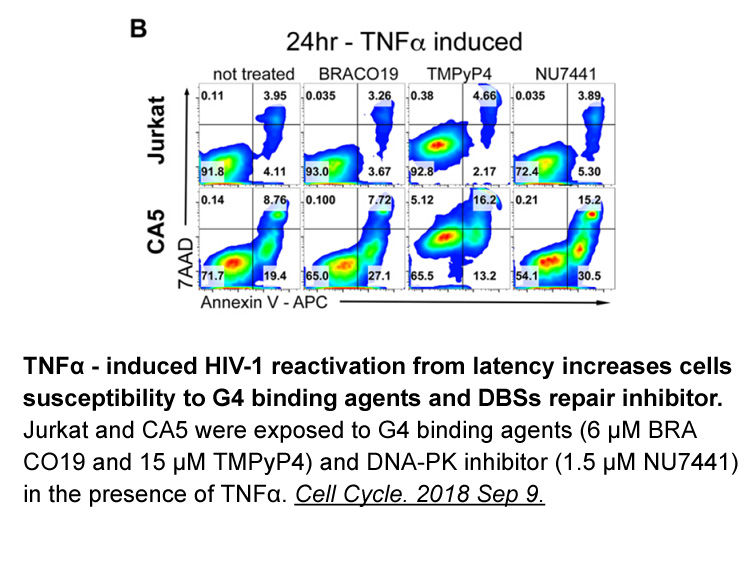
- 5. Piekna-Przybylska D, Maggirwar SB. "CD4+ memory T cells infected with latent HIV-1 are susceptible to drugs targeting telomeres." Cell Cycle.2018;17(17):2187-2203. PMID:30198385
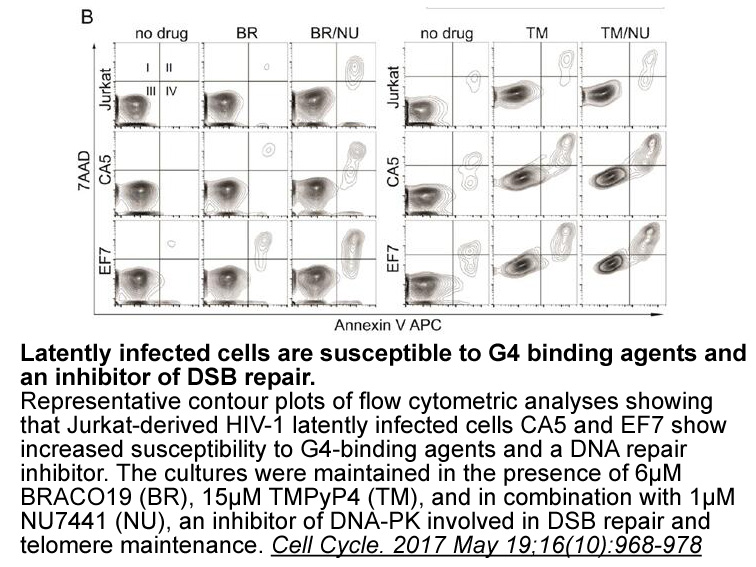
- 6. Piekna-Przybylska D, Sharma G, et al. "Deficiency in DNA damage response, a new characteristic of cells infected with latent HIV-1." Cell Cycle. 2017 May 19;16(10):968-978. PMID:28388353
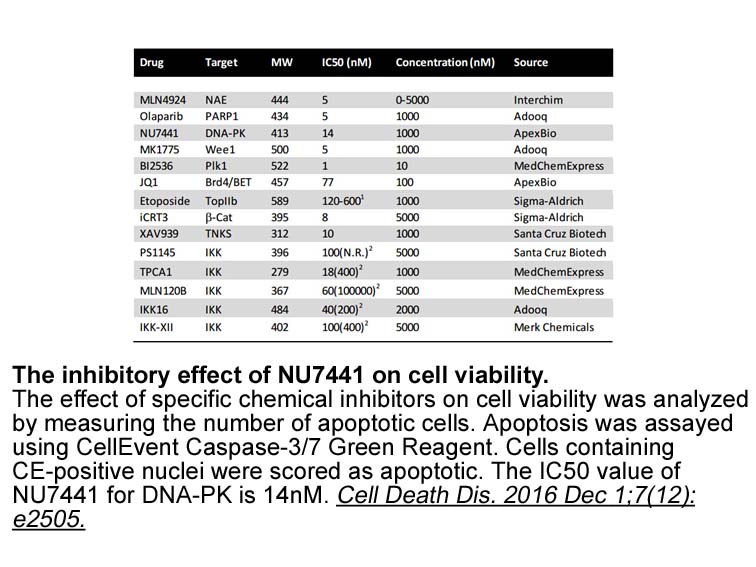
- 7. Rulina AV, Mittler F, et al. "Distinct outcomes of CRL-Nedd8 pathway inhibition reveal cancer cell plasticity." Cell Death Dis. 2016 Dec 1;7(12):e2505. PMID:27906189
| Storage | Store at -20°C |
| M.Wt | 413.49 |
| Cas No. | 503468-95-9 |
| Formula | C25H19NO3S |
| Synonyms | KU 57788; NU-7441; KU57788; NU7441; NU 7441 |
| Solubility | insoluble in EtOH; insoluble in H2O; ≥4.13 mg/mL in DMSO |
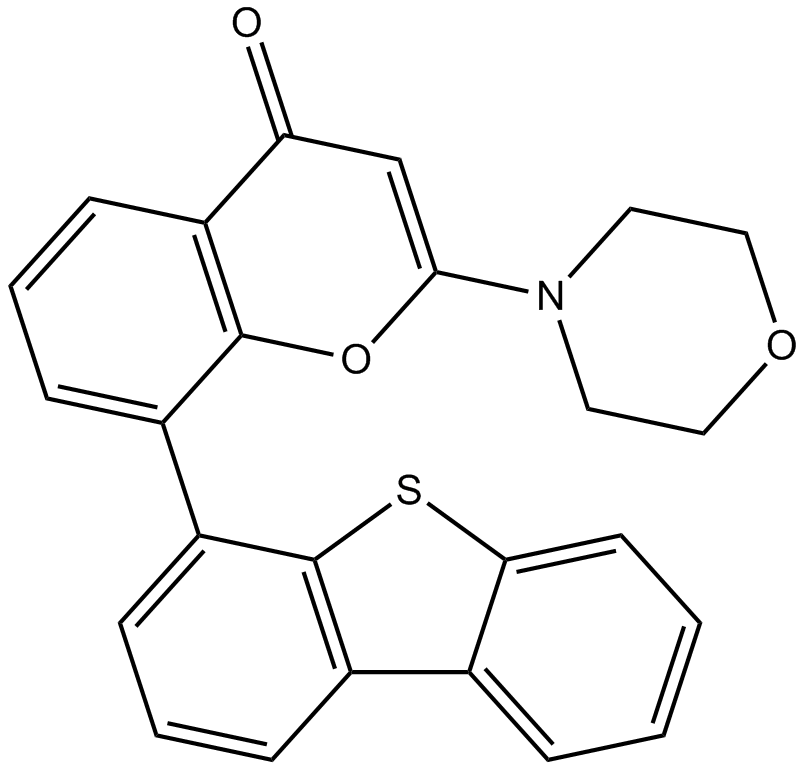
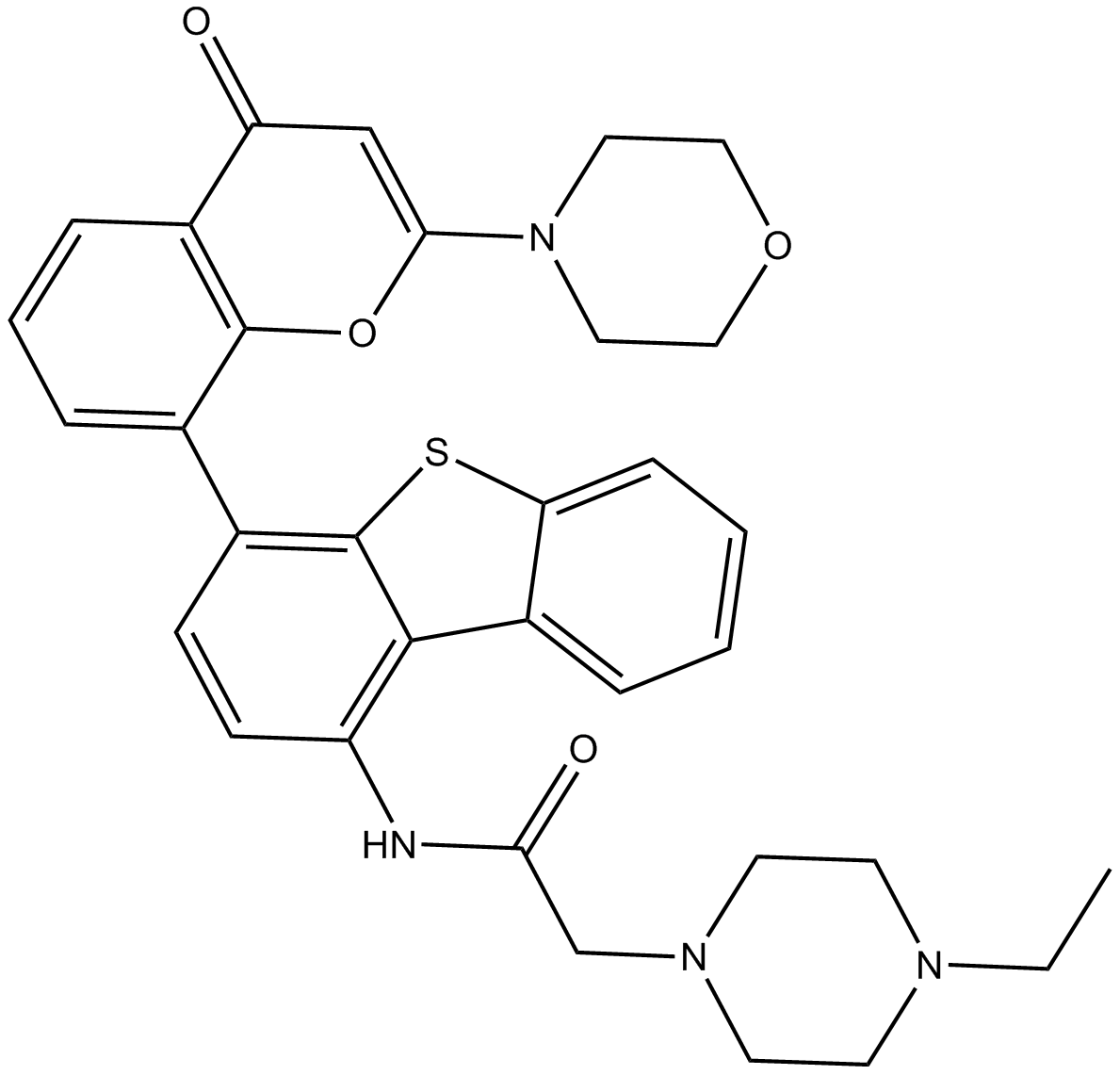
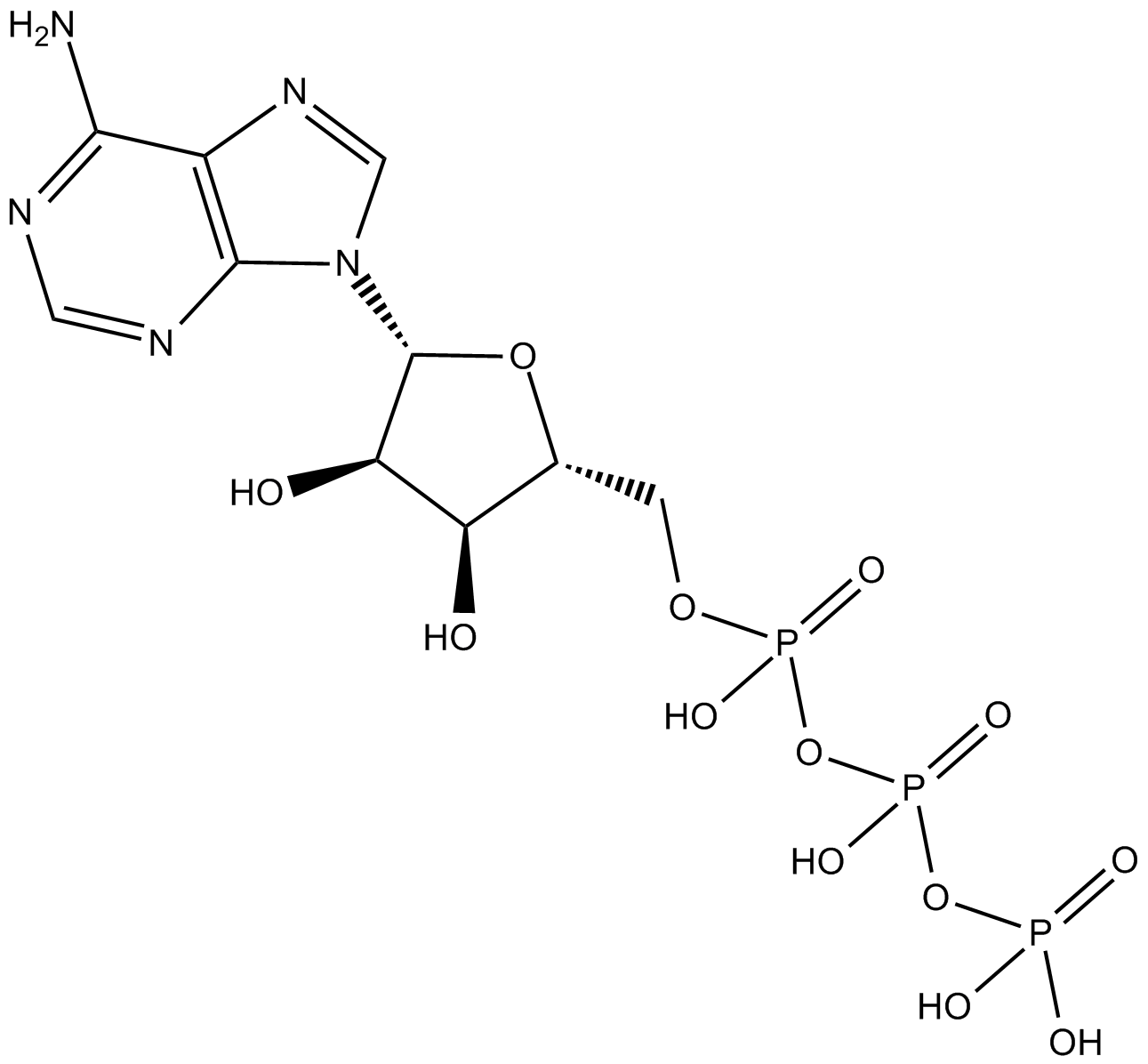
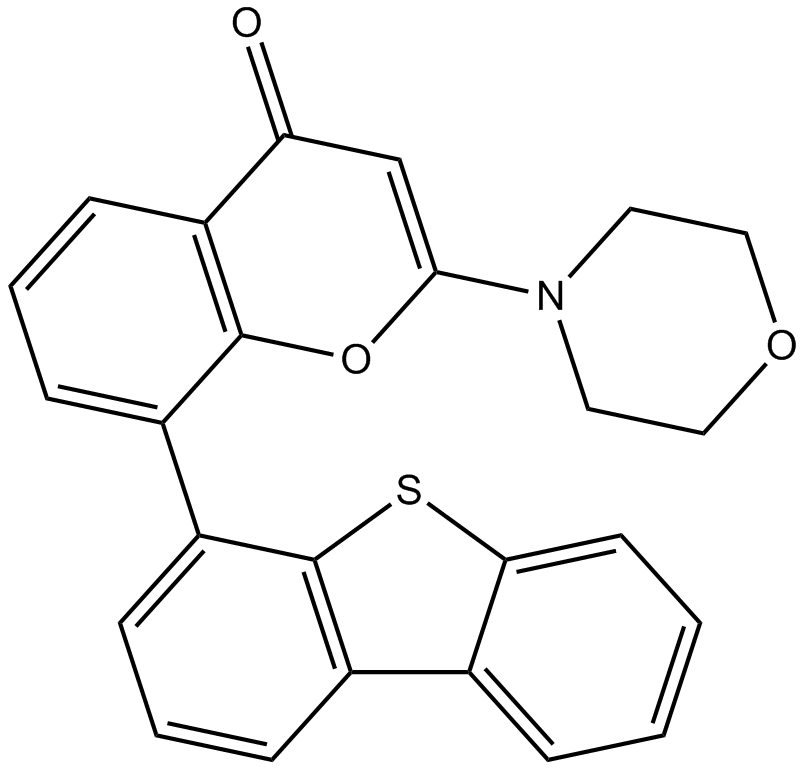
| Chemical Name | 8-dibenzothiophen-4-yl-2-morpholin-4-ylchromen-4-one |
| SDF | Download SDF |
| Canonical SMILES | O=C1c2cccc(-c3c4[s]c(cccc5)c5c4ccc3)c2OC(N2CCOCC2)=C1 |
| Shipping Condition | Small Molecules with Blue Ice, Modified Nucleotides with Dry Ice. |
| General tips | We do not recommend long-term storage for the solution, please use it up soon. |
| Cell experiment: [1] | |
|
Cell lines |
LoVo and SW620 cells |
|
Preparation method |
The solubility of this compound in DMSO is |
|
Reaction Conditions |
1 μM, 16 hours |
|
Applications |
To investigate the effects of NU7441 on the cell cycle phase distribution, LoVo and SW620 cells were treated with NU7441 for 16 hours, with and without 2Gy ionizing radiation or coincident 16 hours of exposure to etoposide or doxorubicin, by flow cytometry. NU7441 alone caused a modest 15% increase in G1, with consequent 24% reduction in the S phase in p53 mutant SW620 cells. In the p53 wt LoVo cells, NU7441 caused a more substantial 54% increase in G1 and 72% decrease in S phase in accordance with its pronounced growth inhibitory effect in this cell line. |
| Animal experiment: [1] | |
|
Animal models |
CD-1 nude mice bearing SW620 cancer xenografts |
|
Dosage form |
Intraperitoneal injection, 10 mg/kg |
|
Applications |
Mice were treated with normal saline (contro animals), single agent NU7441 (dissolved in 40% PEG 400 in saline), or etoposide phosphate (11.35 mg/kg in saline) i.p. daily for 5 days. For combinations, NU7441 was given immediately before etoposide phosphate. Tumors in control mice reached four times their starting volume (RTV4) at a median time of 5.6 days (i.e., time to RTV4 = 5.6 days). Treatment with etoposide phosphate alone caused a tumor growth delay of 2.7 days (time to RTV4 = 8.3 days), which was extended to 5.4 days (time to RTV4 = 11 days, P = 0.0159 compared with etoposide alone) by coadministration of NU7441. Thus, NU7441 enhanced etoposide phosphate efficacy by 100%. |
|
Other notes |
Please test the solubility of all compounds indoor, and the actual solubility may slightly differ with the theoretical value. This is caused by an experimental system error and it is normal. |
|
References: [1] Zhao Y, Thomas H D, Batey M A, et al. Preclinical evaluation of a potent novel DNA-dependent protein kinase inhibitor NU7441. Cancer research, 2006, 66 (10): 5354-5362. |
|
| Description | NU7441 (KU-57788) is a highly potent and selective inhibitor of DNA-PK with IC50 of 14 nM and also inhibits PI3K with IC50 of 5 μM. | |||||
| Targets | DNA-PK | |||||
| IC50 | 14 nM | |||||
Quality Control & MSDS
- View current batch:
Chemical structure
Related Biological Data
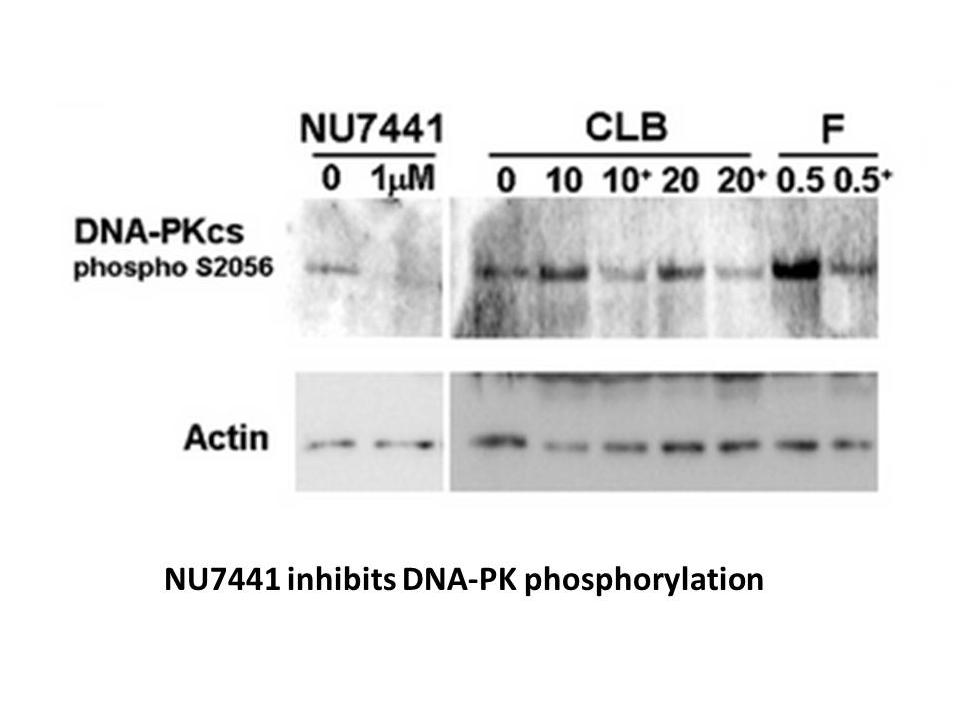
Related Biological Data
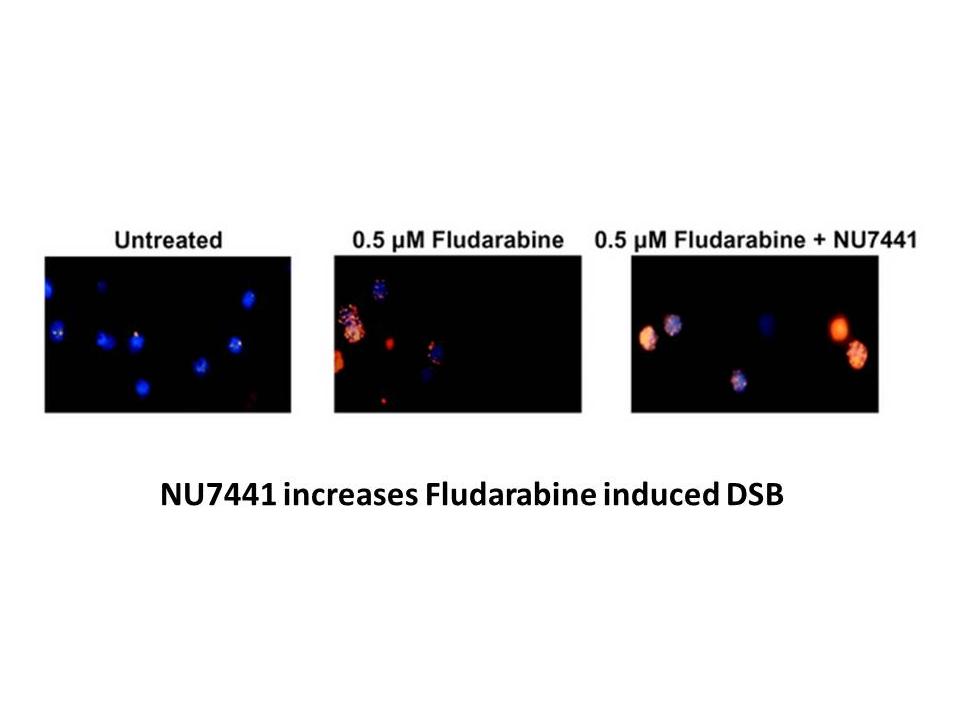
Related Biological Data
Related Biological Data
Related Biological Data
Related Biological Data
Related Biological Data