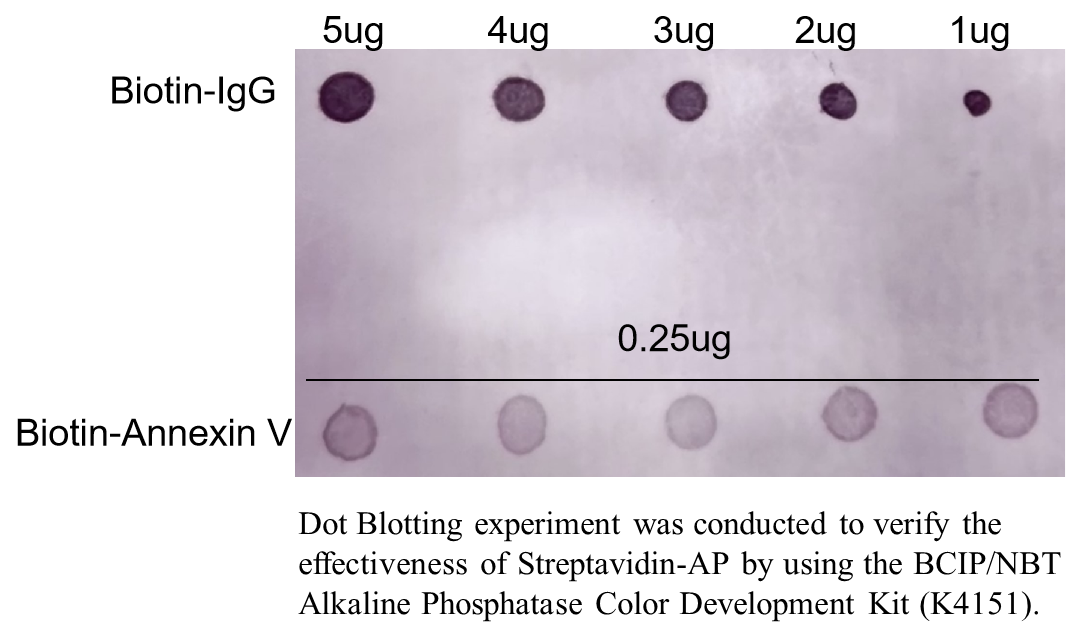
Streptavidin-AP
Streptavidin is a 52,800 dalton tetrameric protein that binds to Biotin with high specificity, and one molecule Streptavidin can bind to 4 Biotin molecules, and this binding is irreversible. Compared with avidin, the affinity of Streptavidin and Avidin, which is derived from egg white, is highly similar to that of Biotin, but Streptividin is almost uncharged under neutral conditions, so the non-specific binding of Streptavidin is much lower than that of Avidin, and the non-specific background of the detection is much less. Streptavidin can be used for the detection of Biotin-labeled antibodies, nucleic acids, proteins, or other biotin-labeled molecules.
Alkaline phosphatase (AP/ALP/AKP/ALKP/ALPase/Alk Phos), often referred to as alkaline phosphatase (EC 3.1.3.1), is a class of hydrolase enzymes that remove the phosphate groups on the substrate molecule by hydrolyzing phosphate monoesters, generate phosphate ions and free hydroxyl groups, and its dephosphorylation substrates include proteins, nucleotides and alkaloids, etc., and are most effective under alkaline conditions. The enzyme is a collective term for a group of isoenzymes. The common calf intestinal alkaline phosphatase (CIAP/CIP) is widely used for the labeling of secondary antibodies, and finally for the detection of proteins and nucleic acids, such as catalyzing the chromogenic reagents such as BCIP/NBT to develop color or catalyze the production of chemiluminescence by appropriate chemiluminescence reagents. This product is labeled with calf intestinal alkaline phosphatase.
Streptavidin - AP is a product that combines Streptavidin protein with AP and can be used in experiments such as Western, ELISA, IHC, IC, ISH, EMSA, Northern, Southern etc.