Ubiquitination/ Proteasome
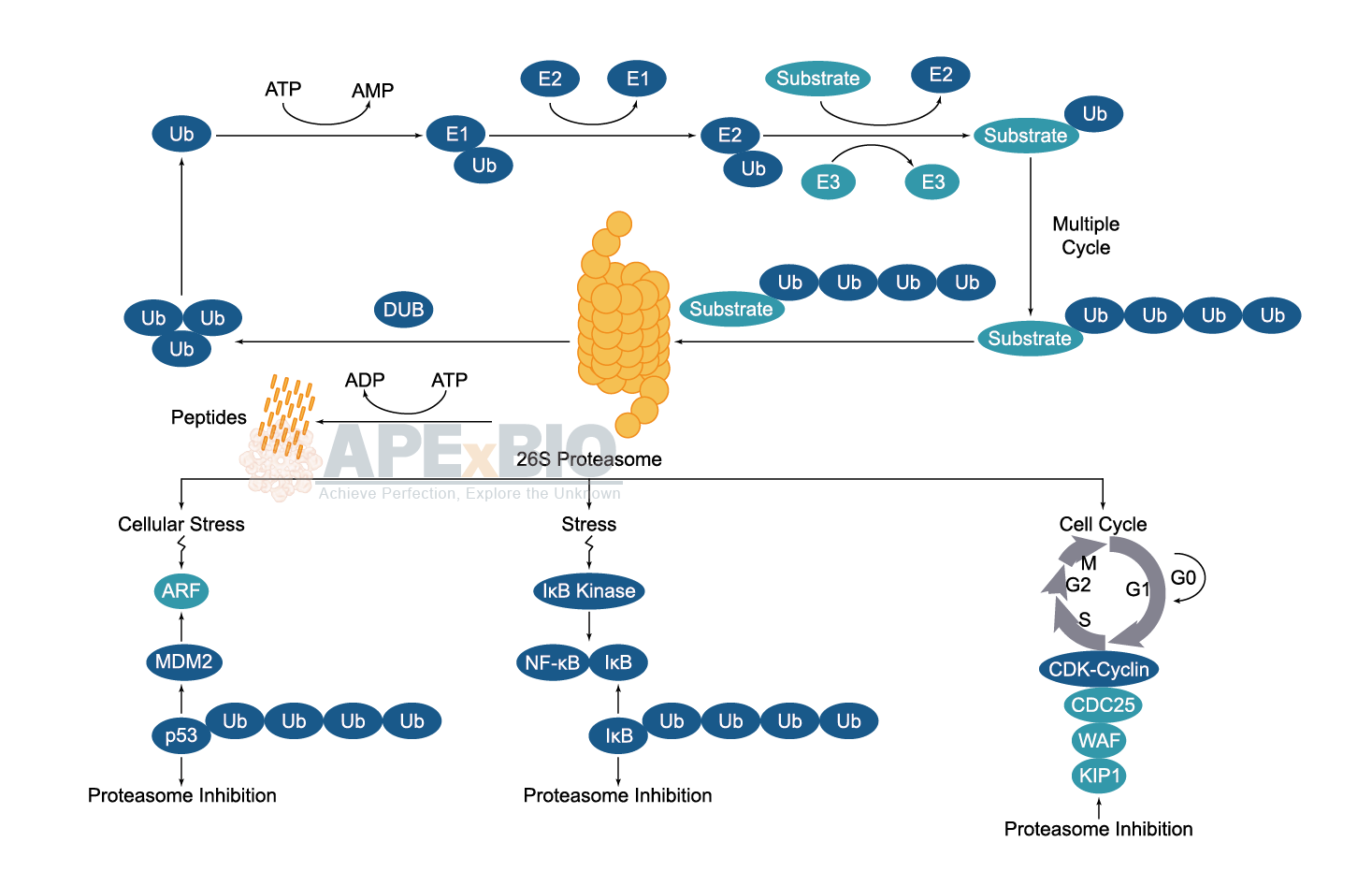
Once the substrate protein is labeled, proteasome will bind to a polyubiquitin chain, allowing the degradation of the labeled protein. The polyubiquitinated target protein is then recognized and degraded by the 26S proteasome. Deubiquitinating enzymes (DUBs) reverse the process of ubiquitination by removing ubiquitin from its substrate protein. Dysregulation of the ubiquitin-proteasome system has been linked to cancer, diabetes, cardiovascular and neurodegenerative diseases etc.
-
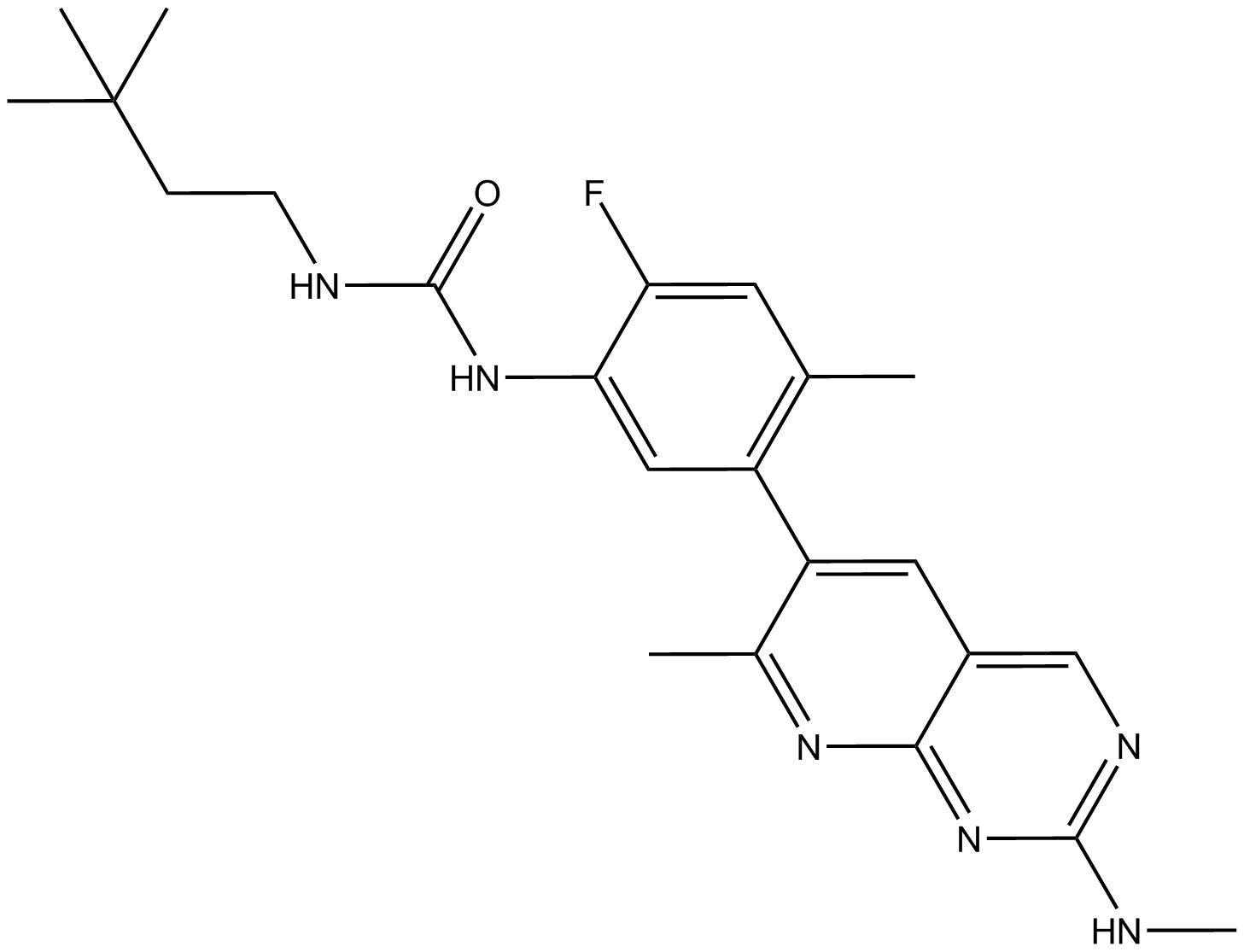 A8716 LY3009120Target: RafSummary: pan-RAF and RAF dimer inhibitor
A8716 LY3009120Target: RafSummary: pan-RAF and RAF dimer inhibitor -
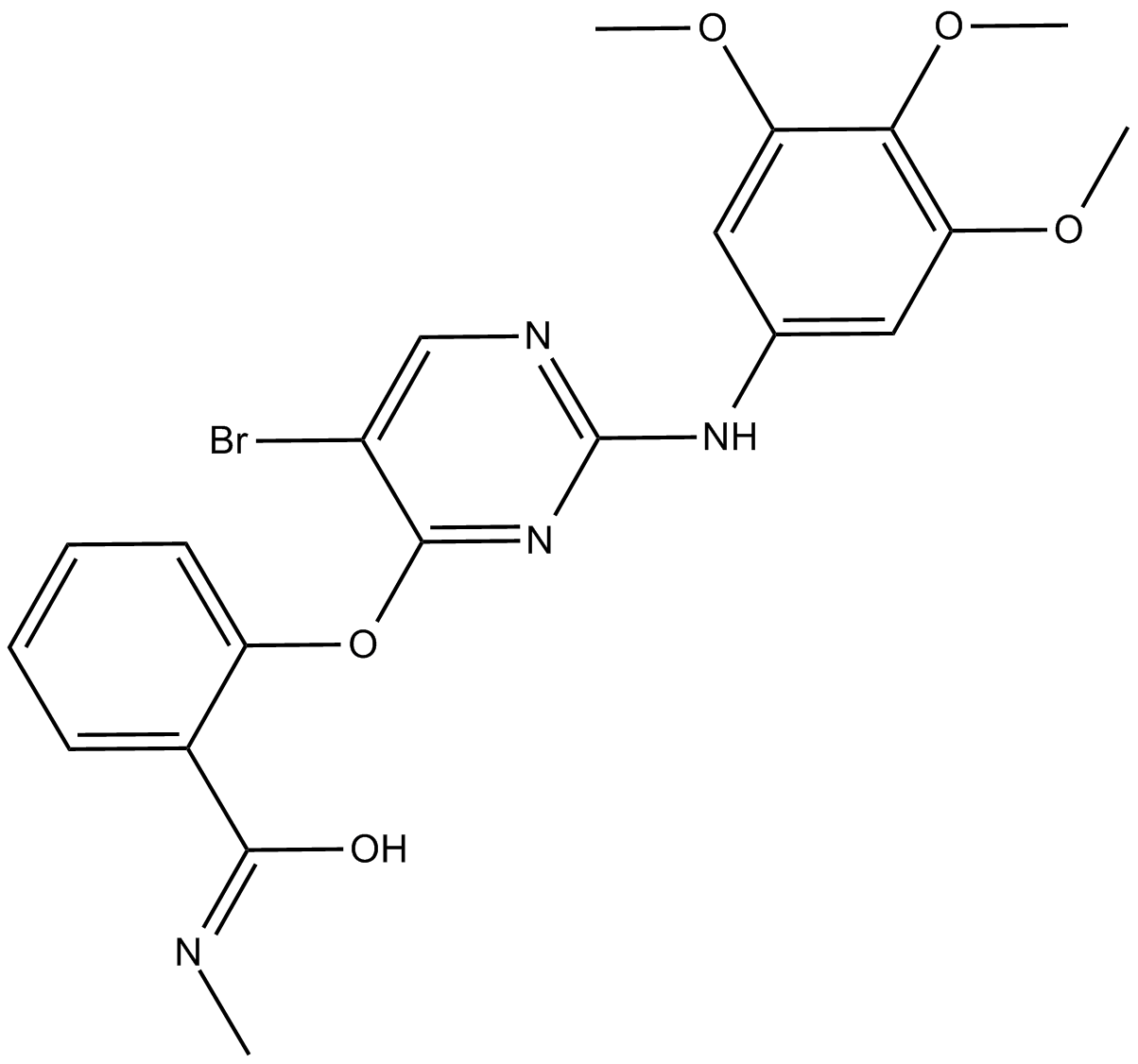 A8715 SBI-02069652 CitationTarget: ULK1Summary: ULK1 inhibitor
A8715 SBI-02069652 CitationTarget: ULK1Summary: ULK1 inhibitor -
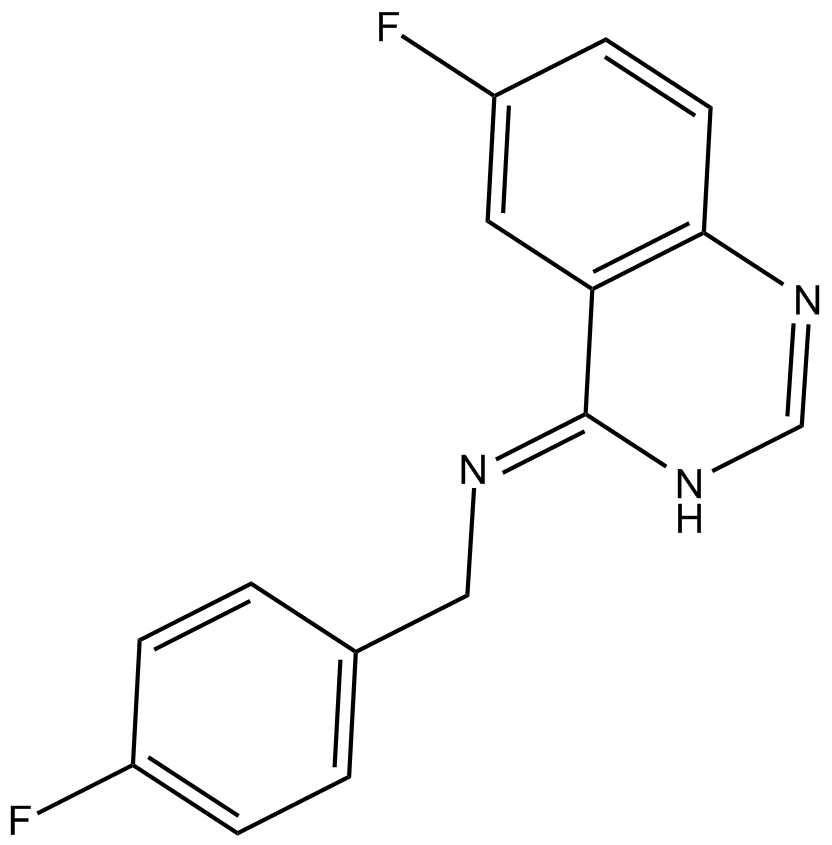 B5873 Spautin-11 CitationTarget: Deubiquitinating enzymes (DUBs)|AutophagySummary: Novel autophagy inhibitor
B5873 Spautin-11 CitationTarget: Deubiquitinating enzymes (DUBs)|AutophagySummary: Novel autophagy inhibitor -
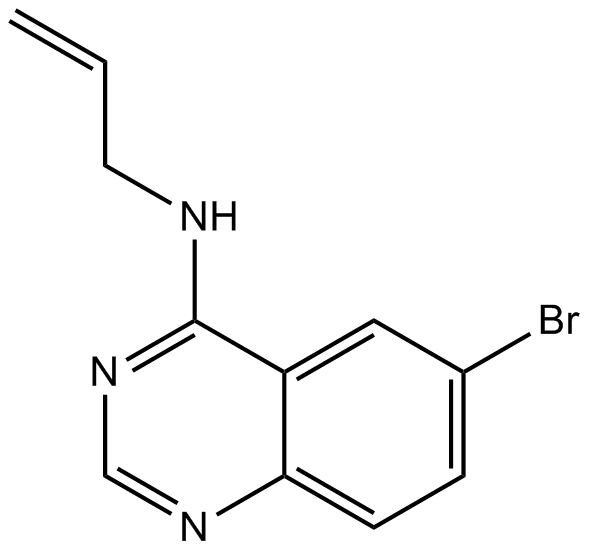 B7637 SMER 28Summary: Positive regulator of autophagy
B7637 SMER 28Summary: Positive regulator of autophagy -
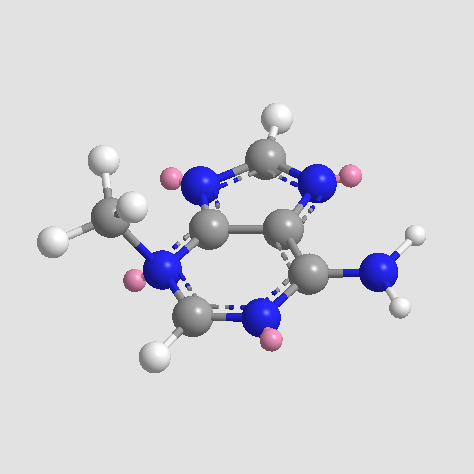 A8353 3-Methyladenine3 CitationTarget: PI3KSummary: Class III PI3K inhibitor
A8353 3-Methyladenine3 CitationTarget: PI3KSummary: Class III PI3K inhibitor -
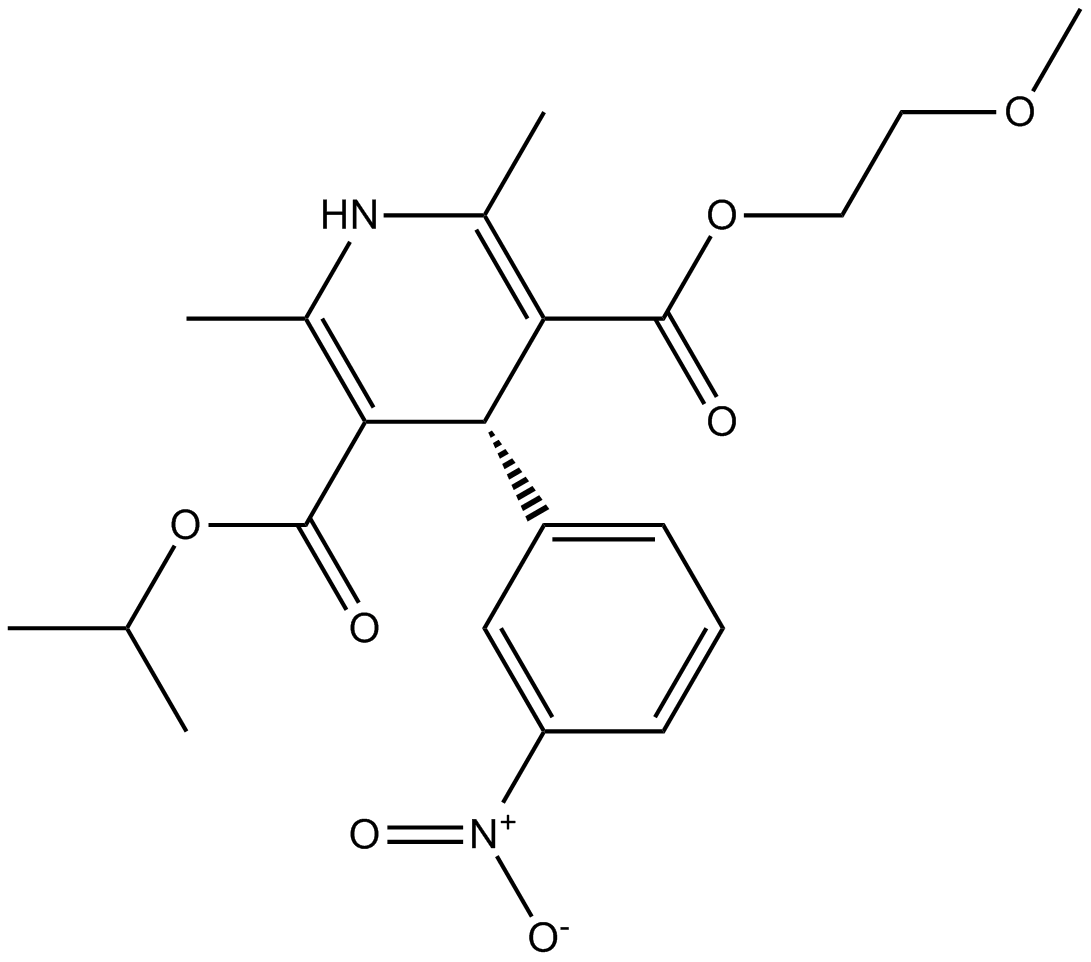 A8484 NimodipineSummary: Calcium Channel inhibitor & Autophagy activator
A8484 NimodipineSummary: Calcium Channel inhibitor & Autophagy activator -
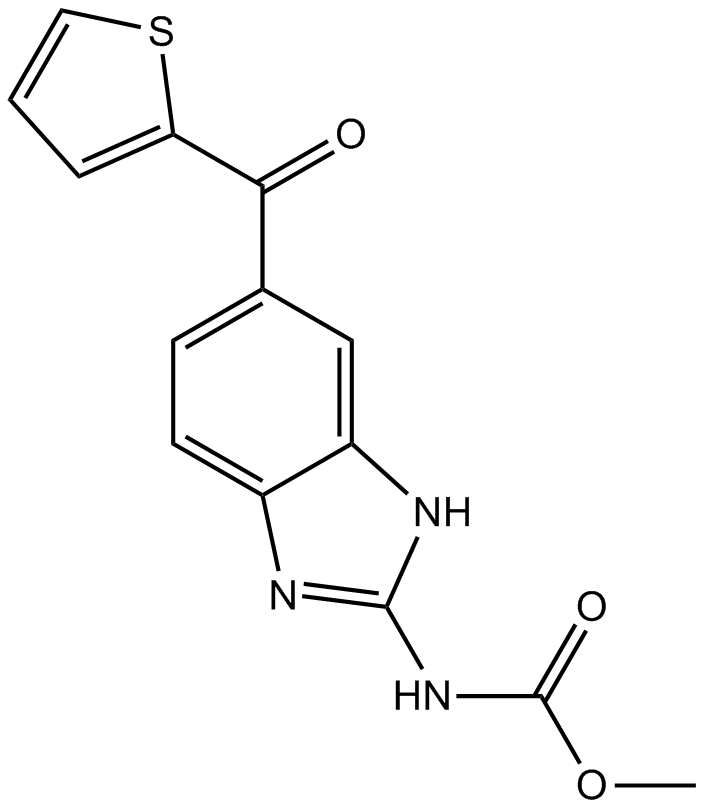 A8487 Nocodazole1 CitationTarget: Microtubules/TubulinsSummary: Tubulin production inhibitor,anti-neoplastic agent
A8487 Nocodazole1 CitationTarget: Microtubules/TubulinsSummary: Tubulin production inhibitor,anti-neoplastic agent -
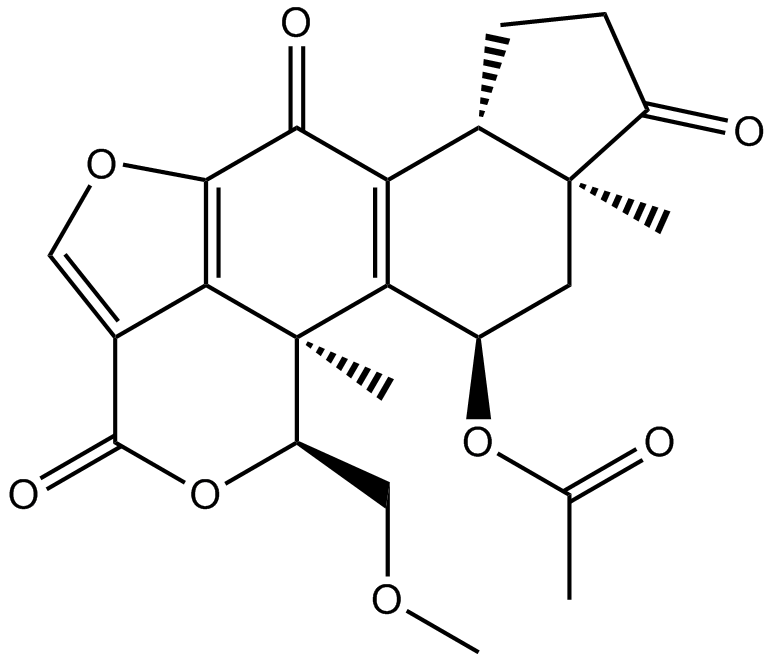 A8544 Wortmannin5 CitationSummary: PI3K inhibitor,selective and irreversible
A8544 Wortmannin5 CitationSummary: PI3K inhibitor,selective and irreversible -
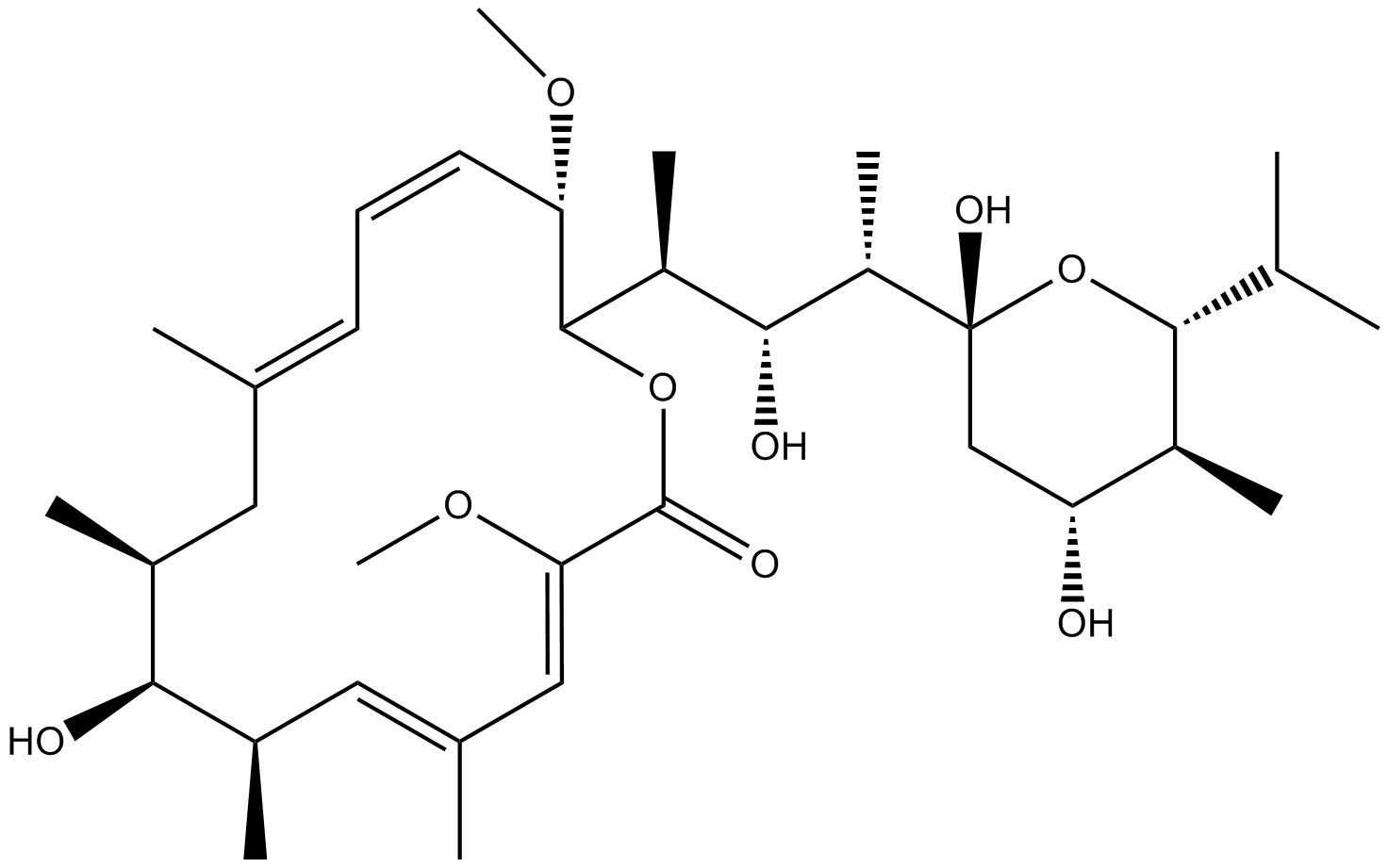 A8627 Bafilomycin A15 CitationSummary: V-ATPase inhibitor,selective and reversible
A8627 Bafilomycin A15 CitationSummary: V-ATPase inhibitor,selective and reversible -
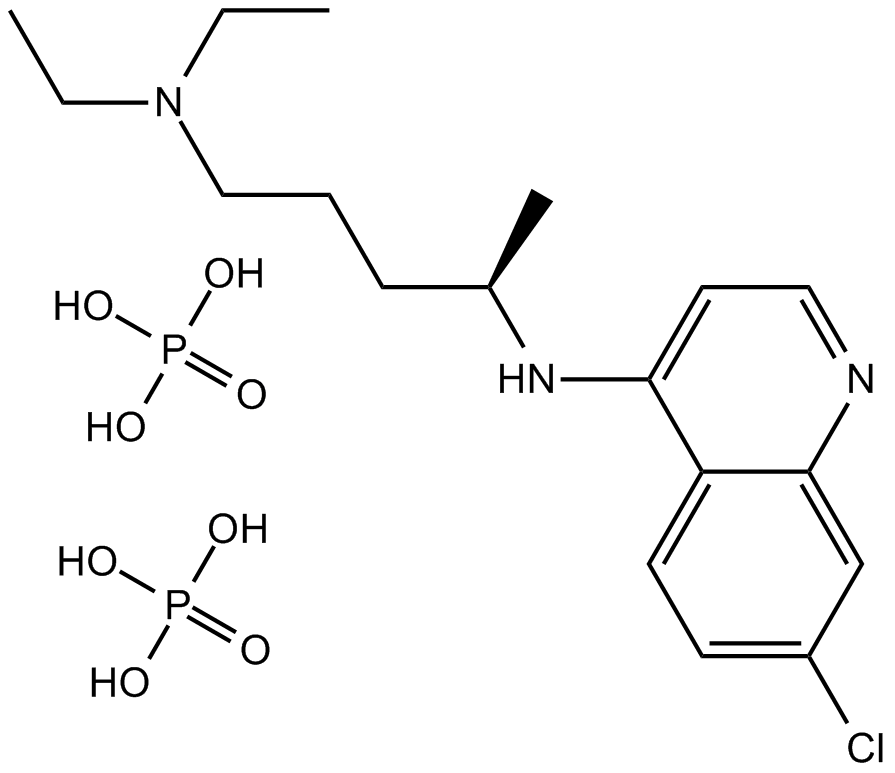 A8628 Chloroquine diphosphate1 CitationTarget: AutophagySummary: Antimalarial drug,TLR7 TLR9 inhibitor
A8628 Chloroquine diphosphate1 CitationTarget: AutophagySummary: Antimalarial drug,TLR7 TLR9 inhibitor

