Nocodazole
Nocodazole (CAS 31430-18-9) is an anti-mitotic small molecule commonly utilized in biomedical research as a potent and reversible inhibitor of microtubule polymerization. Its mechanism involves direct binding to β-tubulin, disrupting microtubule assembly and stability. It exhibits inhibitory effects on various kinases associated with oncogenesis, including Abl, c-Kit, BRAF, and MEK, and induces apoptosis in cancer cells. In vitro exposure at high concentrations rapidly depolymerizes microtubules, while lower concentrations primarily affect their dynamic instability. Nocodazole serves as a valuable tool in studies probing microtubule dynamics, intracellular trafficking, cell cycle regulation, and antitumor therapeutic evaluations.
References:
[1]. Park H, Hong S, Hong S. Nocodazole is a High‐Affinity Ligand for the Cancer‐Related Kinases ABL, c‐KIT, BRAF, and MEK[J]. ChemMedChem, 2012, 7(1): 53-56.
[2]. Xu K, Schwarz P M, Ludue a R F. Interaction of nocodazole with tubulin isotypes[J]. Drug development research, 2002, 55(2): 91-96.
[3]. Nara A, Aki T, Funakoshi T, et al. Hyperstimulation of macropinocytosis leads to lysosomal dysfunction during exposure to methamphetamine in SH-SY5Y cells[J]. Brain research, 2012, 1466: 1-14.
[4]. Liao G, Nagasaki T, Gundersen G G. Low concentrations of nocodazole interfere with fibroblast locomotion without significantly affecting microtubule level: implications for the role of dynamic microtubules in cell locomotion[J]. Journal of Cell Science, 1995, 108(11): 3473-3483.
[5]. Wang Y J, Jeng J H, Chen R J, et al. Ketoconazole potentiates the antitumor effects of nocodazole: In vivo therapy for human tumor xenografts in nude mice[J]. Molecular carcinogenesis, 2002, 34(4): 199-210.
- 1. Fabrizio Vacca, Renuka Prasad, et al. "Lysosome-Dependent Sphingolipid Regulation as a potential therapeutic Target for Cohen Syndrome." bioRxiv [Preprint]. September 04, 2025
- 2. Ronald P Wong, Mariia Likhodeeva, et al. "The INO80 chromatin remodeller facilitates DNA damage bypass via postreplicative gap repair." EMBO J. 2025 Oct 13. PMID: 41083907
- 3. Mengjun Zhang, Zhuang Gu, et al. "Phosphorylation-dependent charge blocks regulate the relaxation of nuclear speckle networks." Mol Cell. 2025 May 1;85(9):1760-1774.e7
- 4. Lei Li, Shuangshuang Sun, et al. "Metabolic regulation of cytoskeleton functions by HDAC6-catalyzed α-tubulin lactylation." Research Square. 26 Sep, 2024
- 5. Yongman Liu, Jianye Wang, et al. "Quantifying 3D cell–matrix interactions during mitosis and the effect of anticancer drugs on the interactions." Nano Res. 14, 4163–4172 (2021) s12274-021-3357-4
- 6. Mitchell DC, Menon A, et al. "Cyclin-dependent kinase 4 inhibits the translational repressor 4E-BP1 to promote cap-dependent translation during mitosis-G1 transition." FEBS Lett. 2020 Apr;594(8):1307-1318. PMID: 31853978
- 7. Wei P, Ning M, et al. "Spiroplasma eriocheiris entered Drosophila Schneider 2 cells and relied on clathrin-mediated endocytosis and macropinocytosis." Infect Immun. 2019 Aug 26. pii: IAI.00233-19. PMID: 31451616
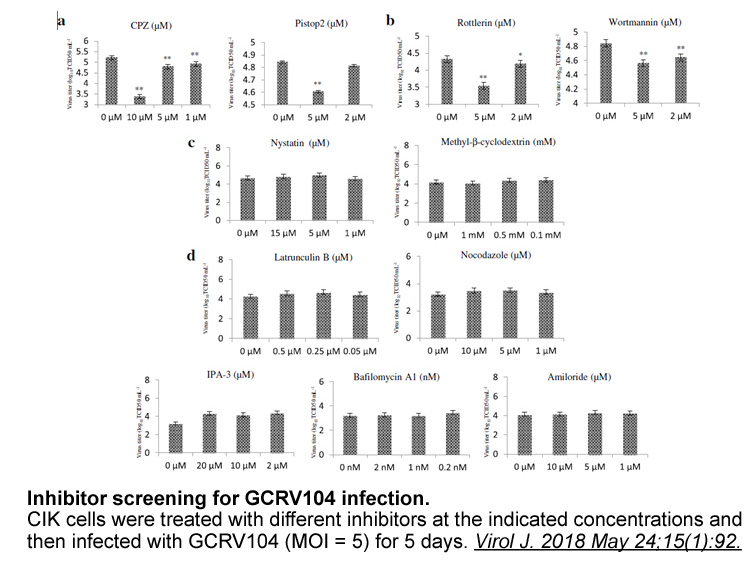
- 8. Wang H, Liu W, et al. "Inhibitor analysis revealed that clathrin-mediated endocytosis is involed in cellular entry of type III grass carp reovirus." Virol J. 2018 May 24;15(1):92 PMID: 29793525
| Physical Appearance | A solid |
| Storage | Store at -20°C |
| M.Wt | 301.32 |
| Cas No. | 31430-18-9 |
| Formula | C14H11N3O3S |
| Solubility | insoluble in H2O; insoluble in EtOH; ≥15.066 mg/mL in DMSO |
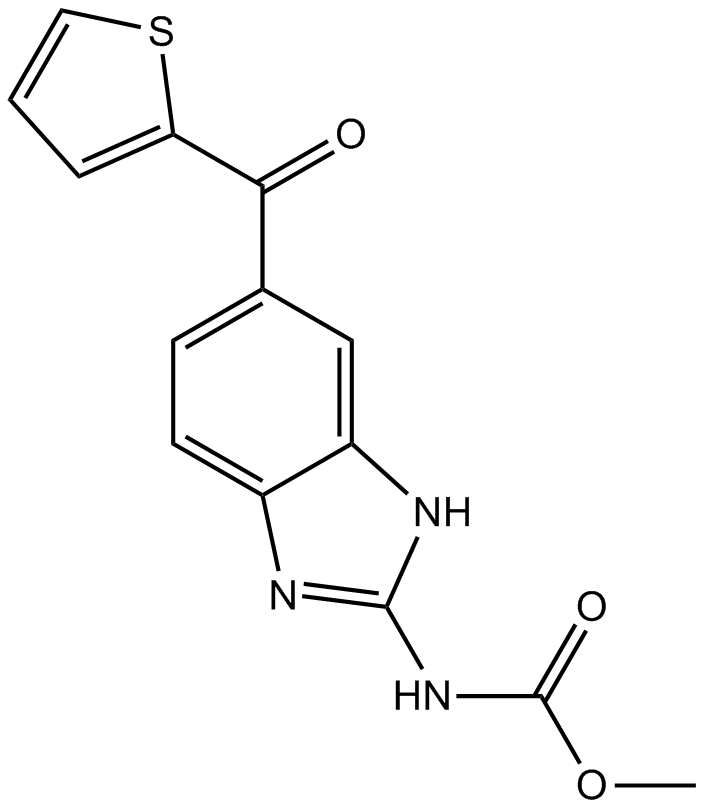
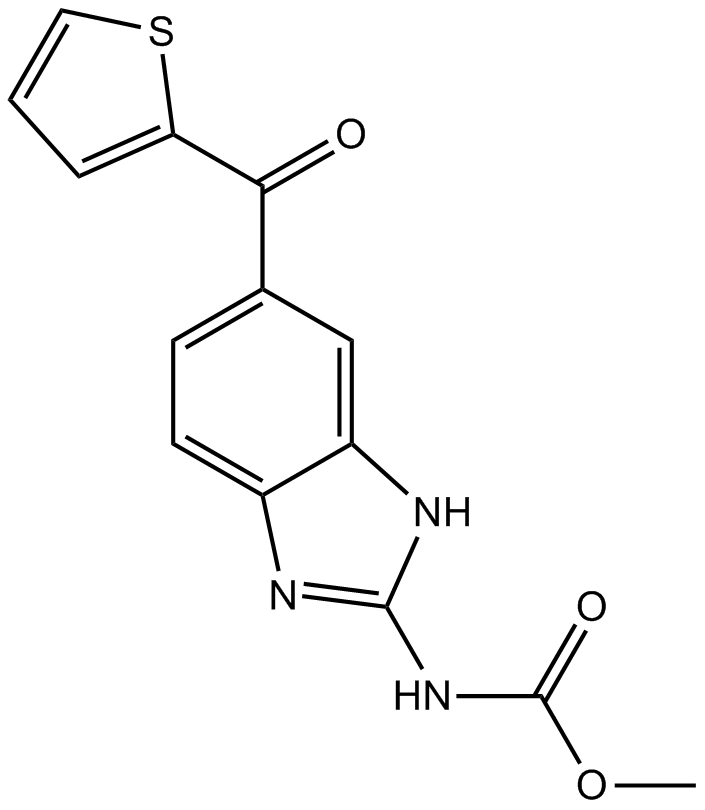
| Chemical Name | methyl N-[6-(thiophene-2-carbonyl)-1H-benzimidazol-2-yl]carbamate |
| SDF | Download SDF |
| Canonical SMILES | COC(Nc1nc(ccc(C(c2ccc[s]2)=O)c2)c2[nH]1)=O |
| Shipping Condition | Small Molecules with Blue Ice, Modified Nucleotides with Dry Ice. |
| General tips | We do not recommend long-term storage for the solution, please use it up soon. |
| Cell experiment [1]: | |
|
Cell lines |
SH-SY5Y cells, NRK fibroblasts |
|
Preparation method |
The solubility of this compound in DMSO is >15.1 mg/mL. General tips for obtaining a higher concentration: Please warm the tube at 37℃ for 10 minutes and/or shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while. Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. |
|
Reacting condition |
25 nM to 400 nM, 1 μM; 30 min |
|
Applications |
In SH-SY5Y cells, Nocodazole (1 μM) disrupted microtubules by binding to β-tubulin, prevented the formation of one of the two interchain disulfide linkages and impaired the transport of vesicles. Nocodazole significantly attenuated METH-induced cell death and lysosomal dysfunction. Nocodazole (400 nM) completely inhibited cell locomotion that was maintained throughout the nocodazole treatment (>2 hours). Nocodazole treatment resulted in a dose-dependent decrease in the rate of locomotion. Nocodazole (25 nM, 100 nM) significantly inhibited cell locomotion. |
| Animal experiment [2]: | |
|
Animal models |
Athymic mice bearing COLO 205 tumor xenografts |
|
Dosage form |
5 mg/kg/three times per week |
|
Application |
The antitumor effects of nocodazole were significantly potentiated by ketoconazole in mice after 6 wk of treatment. No gross signs of toxicity were observed in mice receiving these treatments. |
|
Other notes |
Please test the solubility of all compounds indoor, and the actual solubility may slightly differ with the theoretical value. This is caused by an experimental system error and it is normal. |
|
References: [1]. Liao G, Nagasaki T, Gundersen G G. Low concentrations of nocodazole interfere with fibroblast locomotion without significantly affecting microtubule level: implications for the role of dynamic microtubules in cell locomotion[J]. Journal of Cell Science, 1995, 108(11): 3473-3483. [2]. Liao G, Nagasaki T, Gundersen G G. Low concentrations of nocodazole interfere with fibroblast locomotion without significantly affecting microtubule level: implications for the role of dynamic microtubules in cell locomotion[J]. Journal of Cell Science, 1995, 108(11): 3473-3483. |
|
| Description | Nocodazole is a potent and reversible inhibitor of tubulin production. | |||||
| Targets | tubulin | |||||
| IC50 | ||||||
Quality Control & MSDS
- View current batch:
Chemical structure
Related Biological Data