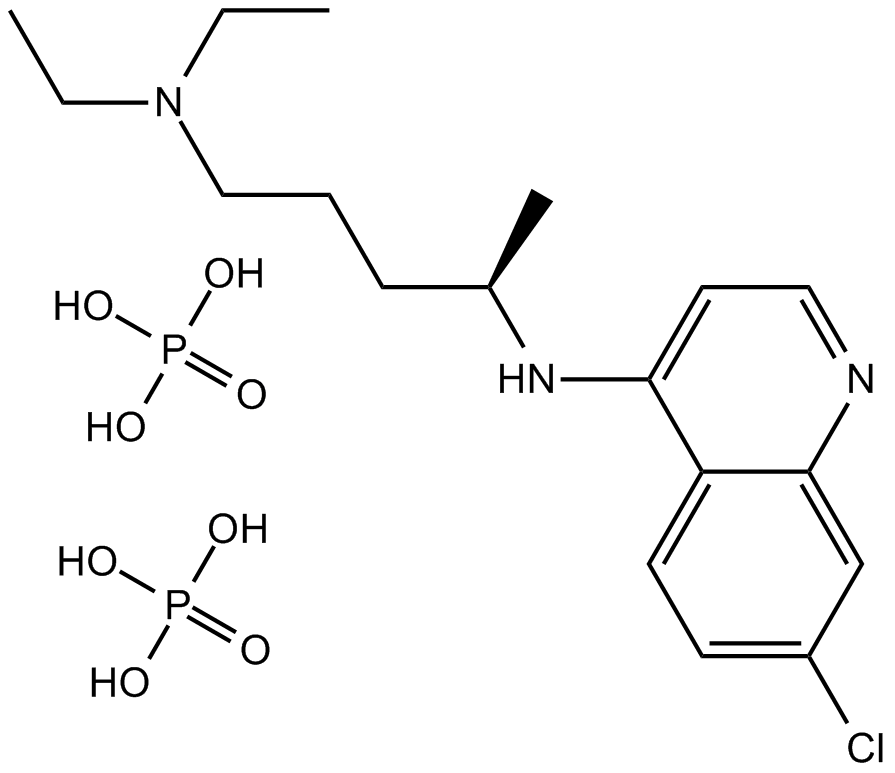
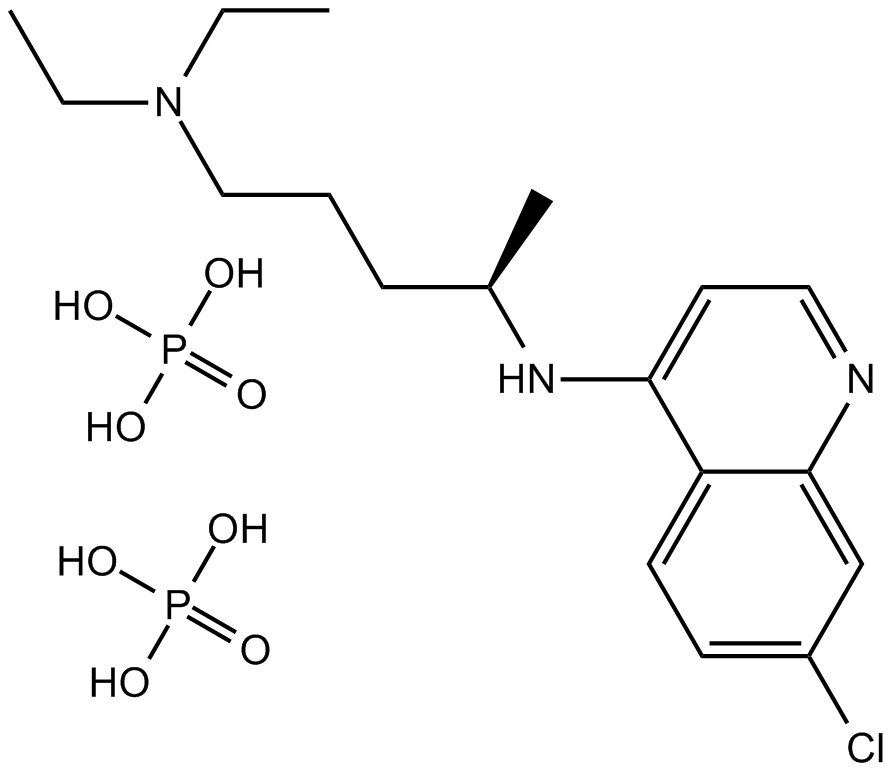
Chloroquine diphosphate
Chloroquine diphosphate (CAS 50-63-5) is an antimalarial agent and inhibitor of TLR7 and TLR9, commonly used in biomedical research to modulate autophagic processes. On the cellular level, chloroquine diphosphate promotes autophagy through cell cycle arrest at the G1 phase, involving increased expression of p27 and p53 and decreased levels of CDK2 and cyclin D1. Additionally, chloroquine diphosphate enhances sensitivity of cancer cells toward chemotherapy and radiotherapy treatments by elevating autophagy and apoptotic responses. In vitro studies demonstrated dose-dependent activity, with reported IC50 values typically ranging from approximately 15 to 40 µM depending on cell types. This compound is widely utilized as an autophagy modulator and therapeutic adjuvant in tumor cell models.
References:
[1]. Gewirtz, D.A., An autophagic switch in the response of tumor cells to radiation and chemotherapy. Biochem Pharmacol, 2014. 90(3): p. 208-11.
[2]. Jiang, P.D., et al., Antitumor and antimetastatic activities of chloroquine diphosphate in a murine model of breast cancer. Biomed Pharmacother, 2010. 64(9): p. 609-14.
[3]. Choi, J.H., et al., Chloroquine enhances the chemotherapeutic activity of 5-fluorouracil in a colon cancer cell line via cell cycle alteration. APMIS, 2012. 120(7): p. 597-604.
[4]. Zhou, Z.R., et al., Poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase-1 regulates the mechanism of irradiation-induced CNE-2 human nasopharyngeal carcinoma cell autophagy and inhibition of autophagy contributes to the radiation sensitization of CNE-2 cells. Oncol Rep, 2013. 29(6): p. 2498-506.
[5]. Sasaki, K., et al., Resistance of colon cancer to 5-fluorouracil may be overcome by combination with chloroquine, an in vivo study. Anticancer Drugs, 2012. 23(7): p. 675-82.
- 1. Chuanjin Luo, Caijiao Ma, et al. "Hepatitis B surface antigen hijacks TANK-binding kinase1 to suppress type I interferon and induce early autophag." Cell Death Dis. 2025 Apr 15;16(1):304. PMID: 40234418
- 2. Xiandong Jiang, Yingying Huang, et al. "Exogenous dihomo-γ-linolenic acid triggers ferroptosis via ACSL4-mediated lipid metabolic reprogramming in acute myeloid leukemia cells." Translational Oncology Volume 52, February 2025, 102227. PMID: 39644823
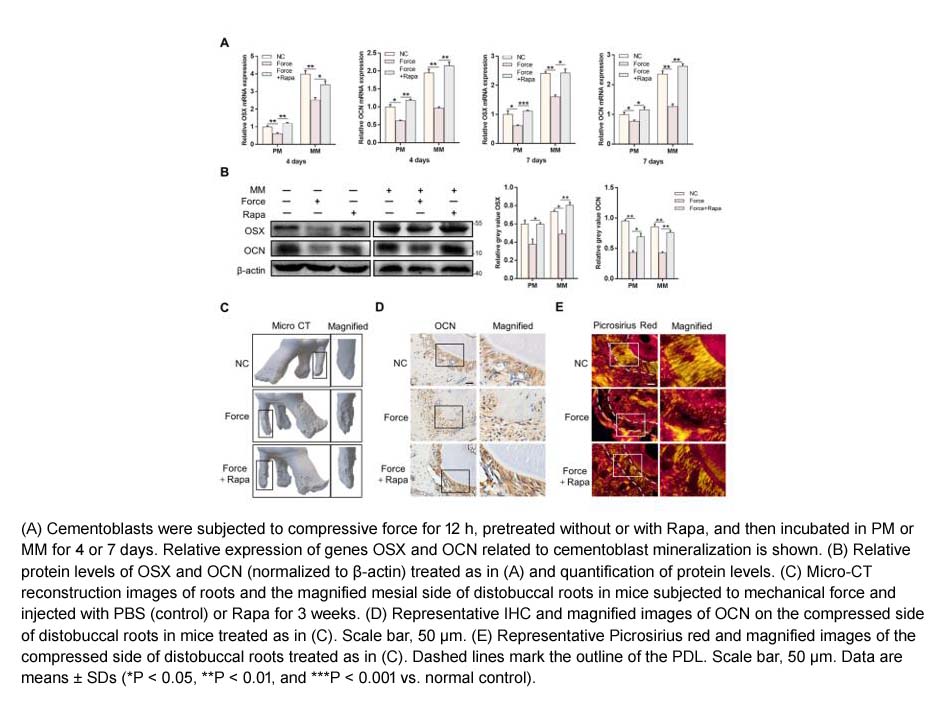
- 3. Yi Zhao, Yuhui Yang, et al. "Orthodontic tension promotes cementoblast mineralization by regulating autophagy." Journal of Dental Sciences Volume 19, Issue 4, October 2024, Pages 2186-2195
- 4. Ting Yao, Yu Huang, et al. "Response mechanisms to acid stress promote LF82 replication in macrophages." Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2023 Oct 10:13:1255083. PMID: 37881369
- 5. Yang Du, Yaqiong Shang, et al. "Plk1 promotes renal tubulointerstitial fibrosis by targeting autophagy/lysosome axis." Cell Death Dis. 2023 Aug 29;14(8):571. PMID: 37640723
- 6. Mingchao Mu, Qin Zhang, et al. "3-Bromopyruvate overcomes cetuximab resistance in human colorectal cancer cells by inducing autophagy-dependent ferroptosis." Cancer Gene Ther. 2023 Aug 9. PMID: 37558749
- 7. Yuhui Yang, Hao Liu, et al. "Autophagy mediates cementoblast mineralization under compression through periostin/β‐catenin axis." J Cell Physiol. 2023 Jul 21. PMID: 37475648
- 8. Zhenhua Feng, Siyue Tao, et al. "The deubiquitinase UCHL1 negatively controls osteoclastogenesis by regulating TAZ/NFATC1 signalling." Int J Biol Sci. 2023 Apr 24;19(8):2319-2332. PMID: 37215988
- 9. Weiran Li, Yuhui Yang, et al. "Autophagy mediates cementoblast mineralization through periostin/β-catenin signaling axis under compression." Research Square October 13th, 2022
- 10. Zhaodi Wang, Yukang Wen, et al. "Incomplete autophagy promotes the replication of Mycoplasma hyopneumoniae." J Microbiol. 2021 Aug;59(8):782-791. PMID: 34219210
- 11. Yuhui Yang, Yiping Huang, et al. "Compressive force regulates cementoblast migration via downregulation of autophagy." J Periodontol. 2021 Nov;92(11):128-138 PMID: 34231875
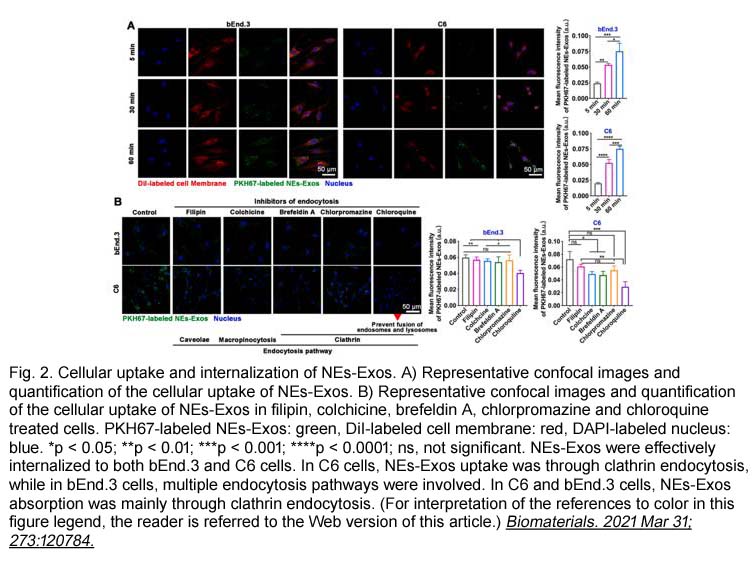
- 12. Jun Wang, Wei Tang, et al. "Inflammatory tumor microenvironment responsive neutrophil exosomes-based drug delivery system for targeted glioma therapy." Biomaterials. 2021 Jun;273:120784 PMID: 33848731
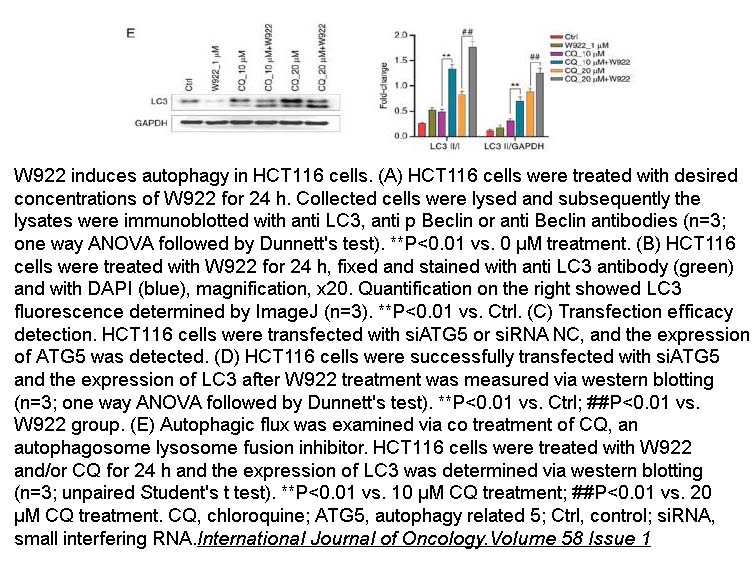
- 13. JIN WANG, DONG LIANG, et al. "Novel PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling inhibitor, W922, prevents colorectal cancer growth via the regulation of autophagy." Int J Oncol. 2020 Nov 23;58(1):70-82. PMID: 33367926
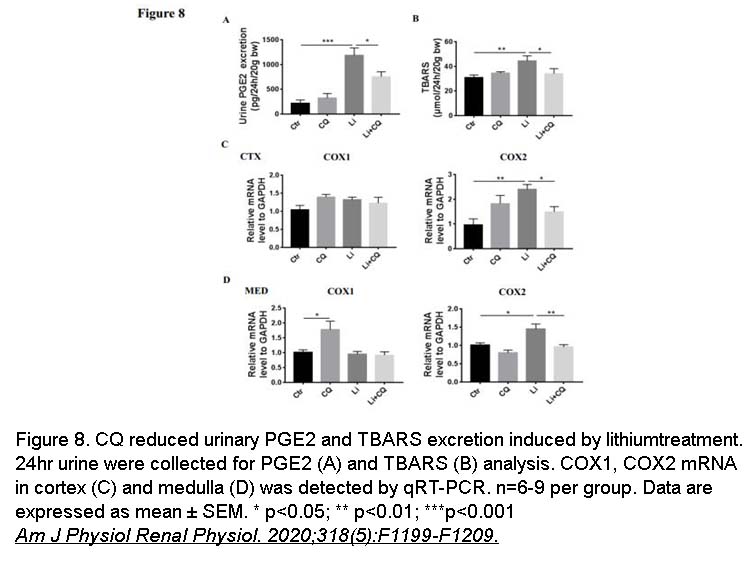
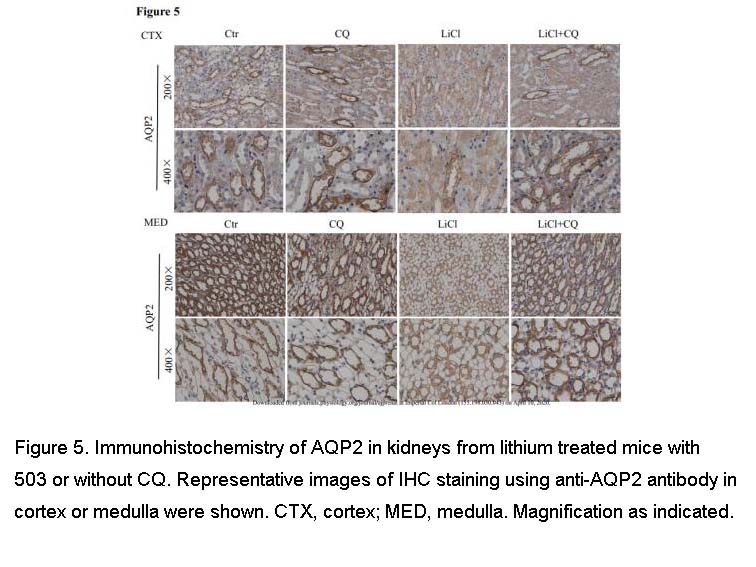
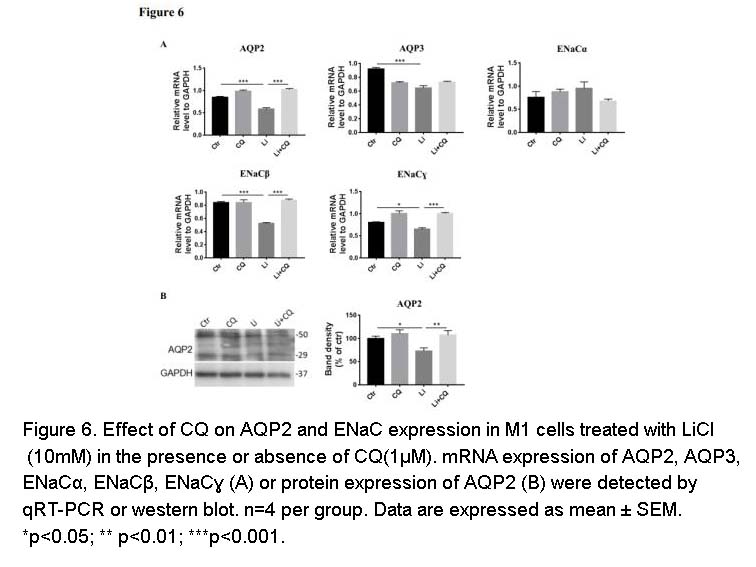
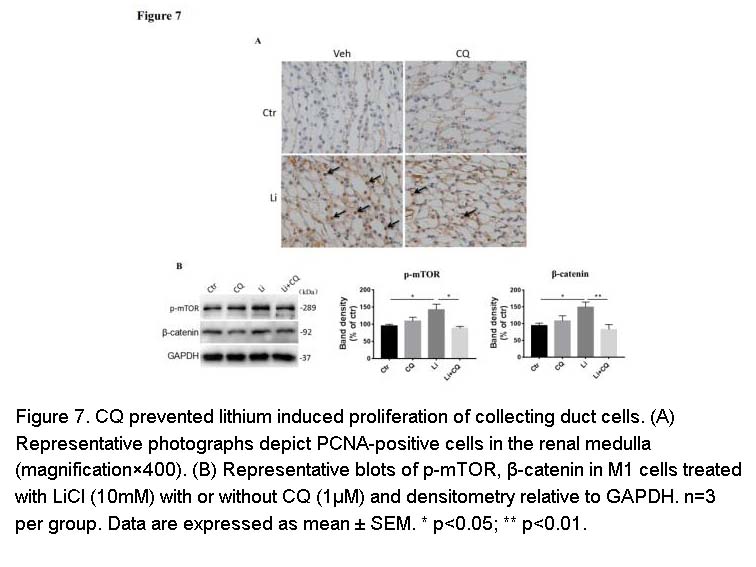
- 14. Du Y, Qian Y, et al. "Chloroquine attenuates lithium-induced NDI and proliferation of renal collecting duct cells." Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2020;318(5):F1199-F1209 PMID: 32249612
- 15. White SM, Avantaggiati ML, et al. "YAP/TAZ Inhibition Induces Metabolic and Signaling Rewiring Resulting in Targetable Vulnerabilities in NF2-Deficient Tumor Cells." Dev Cell. 2019 May 6;49(3):425-443.e9 PMID: 31063758
- 16. Shan M, Qin J, et al. "Autophagy suppresses isoprenaline-induced M2 macrophage polarization via the ROS/ERK and mTOR signaling pathway." Free Radic Biol Med. 2017 Jun 21. pii: S0891-5849(17)30594-4 PMID: 28647611
| Physical Appearance | A solid |
| Storage | Desiccate at RT |
| M.Wt | 515.86 |
| Cas No. | 50-63-5 |
| Formula | C18H26ClN3·2H3PO4 |
| Solubility | insoluble in DMSO; insoluble in EtOH; ≥106.06 mg/mL in H2O |
| Chemical Name | 4-N-(7-chloroquinolin-4-yl)-1-N,1-N-diethylpentane-1,4-diamine;phosphoric acid |
| SDF | Download SDF |
| Canonical SMILES | CCN(CC)CCCC(C)NC1=C2C=CC(=CC2=NC=C1)Cl.OP(=O)(O)O.OP(=O)(O)O |
| Shipping Condition | Small Molecules with Blue Ice, Modified Nucleotides with Dry Ice. |
| General tips | We do not recommend long-term storage for the solution, please use it up soon. |
| Cell experiment [1]: | |
|
Cell lines |
Mouse breast cancer 4T1 cells |
|
Preparation method |
The solubility of this compound in DMSO is limited. General tips for obtaining a higher concentration: Please warm the tube at 37°C for 10 minutes and/or shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while. Stock solution can be stored below - 20°C for several months. |
|
Reacting condition |
3.125, 6.25, 12.5, 25, 50 and 100 μM; 24, 48 and 72 hrs |
|
Applications |
According to the results of the MTT assay, Chloroquine Diphosphate dose- and time-dependently inhibited proliferation of 4T1 cells. |
| Animal experiment [1]: | |
|
Animal models |
4T1 tumor-bearing BALB/c mice |
|
Dosage form |
25 and 50 mg/kg; i.p.; q.d., for 28 days |
|
Applications |
Chloroquine Diphosphate treatment at the doses of 25 and 50 mg/kg significantly reduced the rates of primary tumor growth. In addition, 30% and 60% of mice in the 25 and 50 mg/kg Chloroquine Diphosphate-treated groups still survived on 61st day. |
|
Other notes |
Please test the solubility of all compounds indoor, and the actual solubility may slightly differ with the theoretical value. This is caused by an experimental system error and it is normal. |
|
References: [1]. Jiang, P.D., et al., Antitumor and antimetastatic activities of chloroquine diphosphate in a murine model of breast cancer. Biomed Pharmacother, 2010. 64(9): p. 609-14. |
|
Quality Control & MSDS
- View current batch:
Chemical structure
Related Biological Data
Related Biological Data
Related Biological Data
Related Biological Data
Related Biological Data
Related Biological Data
Related Biological Data