Proteases
Proteases, also known as peptidases or proteolytic enzymes, consists of a large number of enzymes catalyzing the hydrolysis of peptide bonds and subsequently resulting in the degradation of protein substrates into amino acids. Proteases are involved in a wide range of human diseases, including cancer, neurodegenerative disorders, inflammatory diseases and cardiovascular diseases. Thus numerous proteases inhibitors (small molecules and proteins) have been identified to block activity of proteases. Proteases inhibitors can be classified into different types based on the class of proteases they inhibit through two general mechanisms, irreversible “trapping” reactions and reversible tight-binding reactions. Proteases inhibitors have been used as diagnostic or therapeutic agents for the treatment of proteases-related diseases.
-
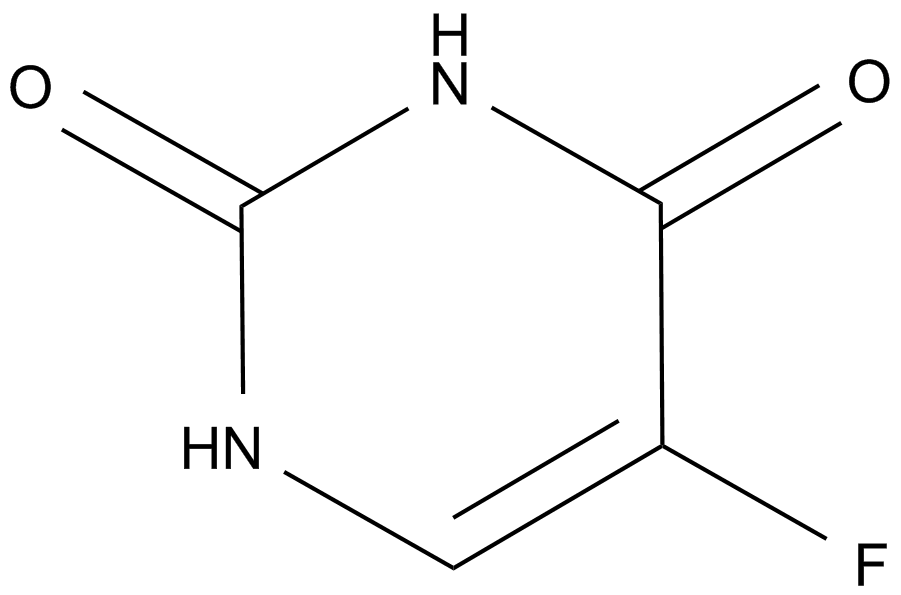 A4071 Fluorouracil (Adrucil)3 CitationTarget: Thymidylate SynthaseSummary: Antitumor agent;inhibitor of thymidylate synthase
A4071 Fluorouracil (Adrucil)3 CitationTarget: Thymidylate SynthaseSummary: Antitumor agent;inhibitor of thymidylate synthase -
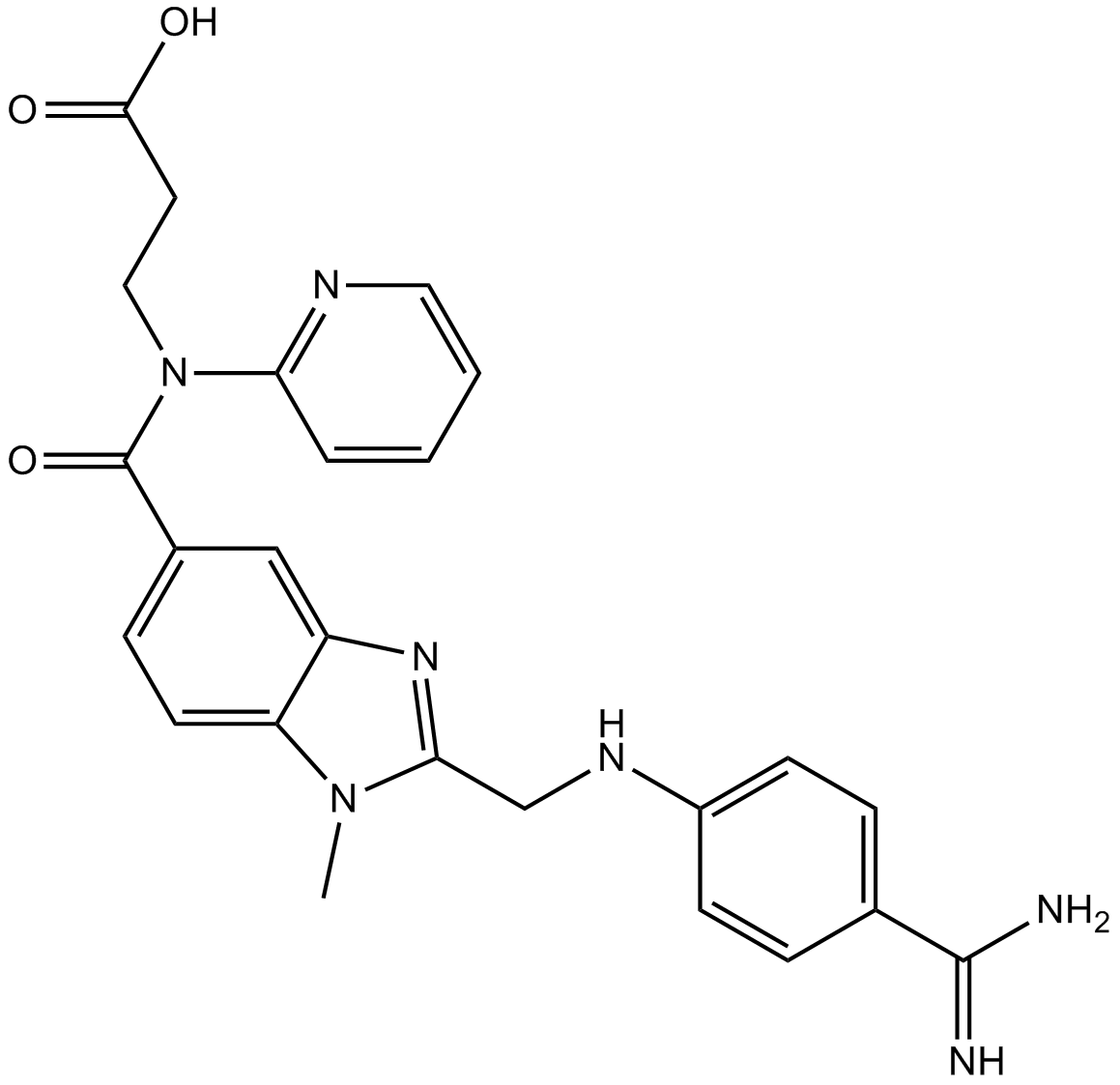 A4077 BIBR 953 (Dabigatran, Pradaxa)Summary: Thrombin inhibitor,potent,reversible and direct
A4077 BIBR 953 (Dabigatran, Pradaxa)Summary: Thrombin inhibitor,potent,reversible and direct -
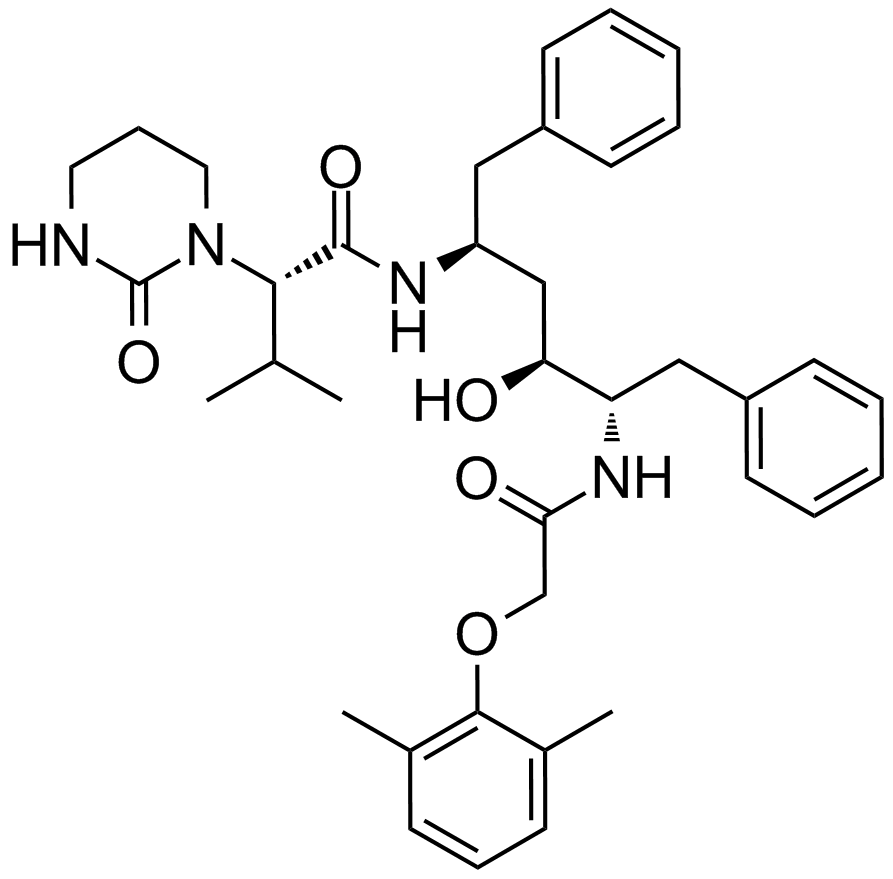 A8204 LopinavirSummary: HIV protease inhibitor,highly potent
A8204 LopinavirSummary: HIV protease inhibitor,highly potent -
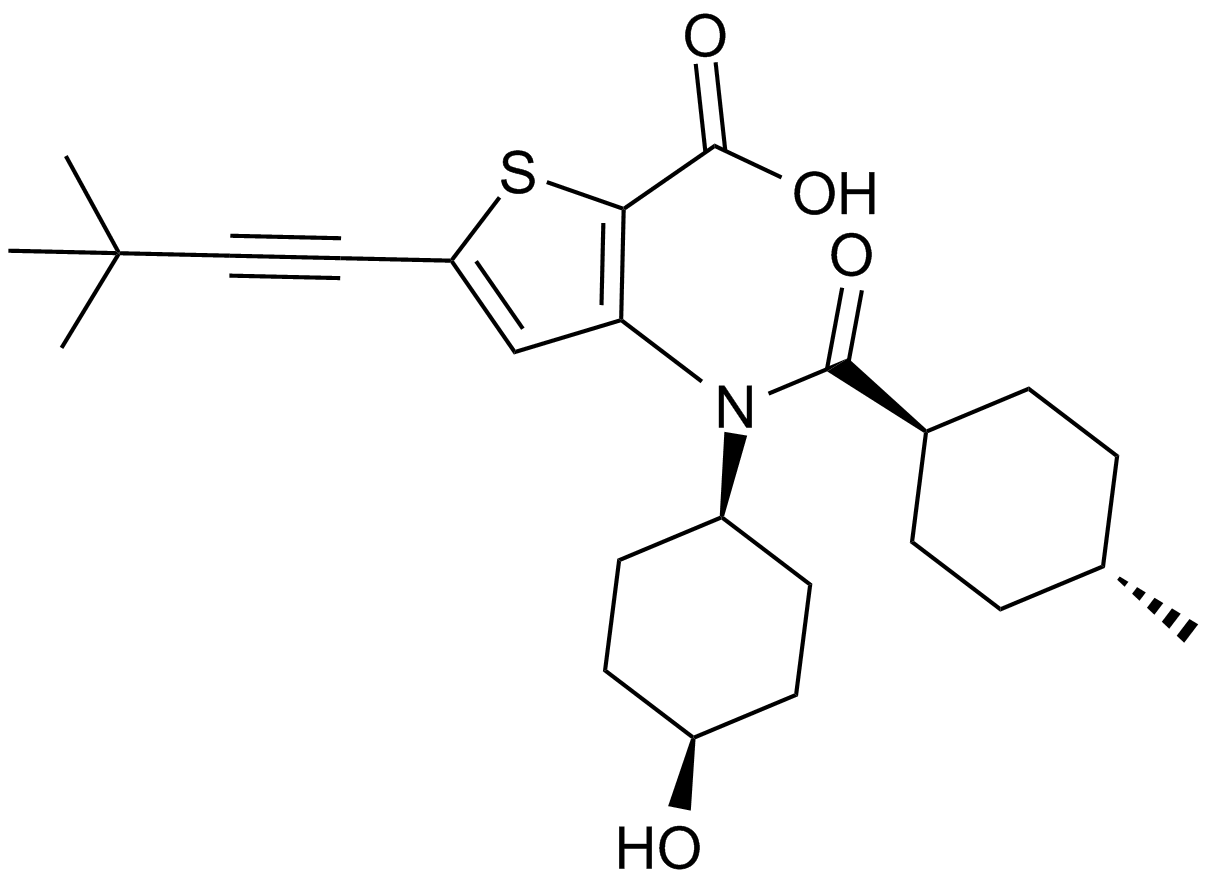 A4032 VX-222 (VCH-222, Lomibuvir)Target: HCV polymeraseSummary: NNI of HCV RNA polymerase
A4032 VX-222 (VCH-222, Lomibuvir)Target: HCV polymeraseSummary: NNI of HCV RNA polymerase -
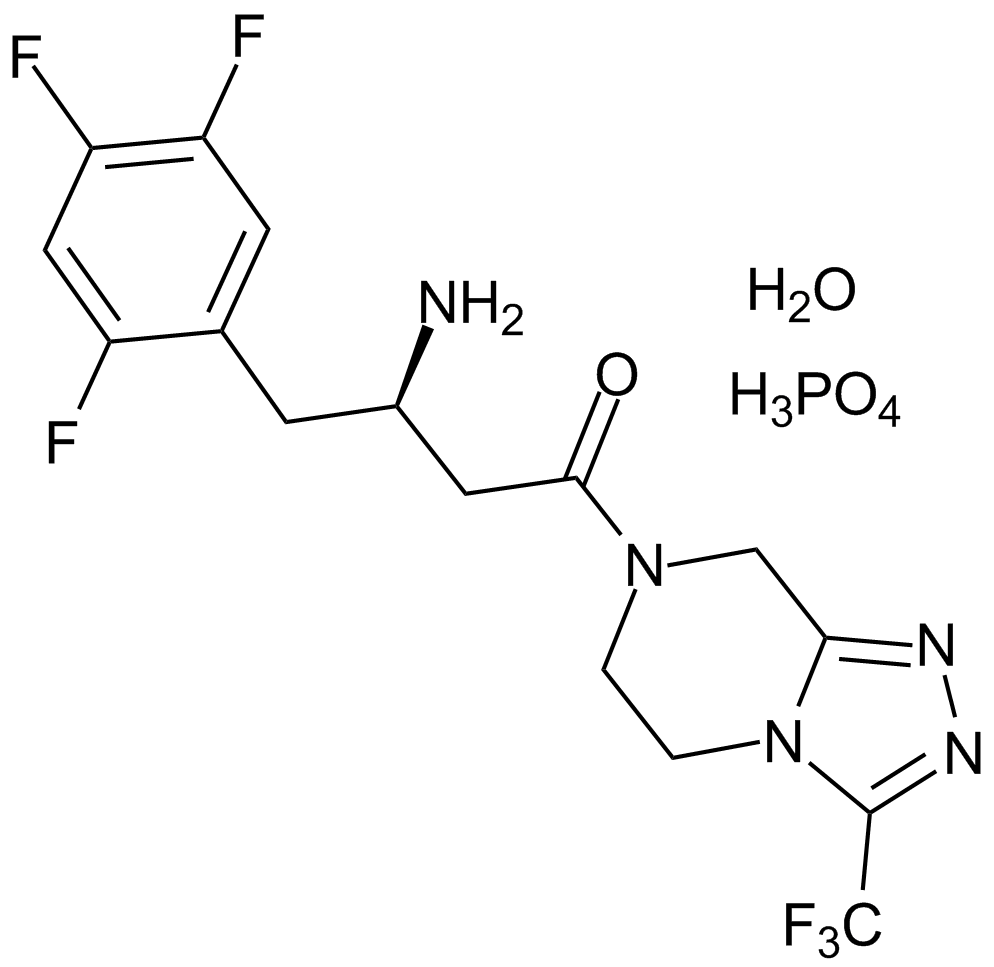 A4036 Sitagliptin phosphate monohydrate5 CitationTarget: DPP-4Summary: Potent DPP-4 inhibitor
A4036 Sitagliptin phosphate monohydrate5 CitationTarget: DPP-4Summary: Potent DPP-4 inhibitor -
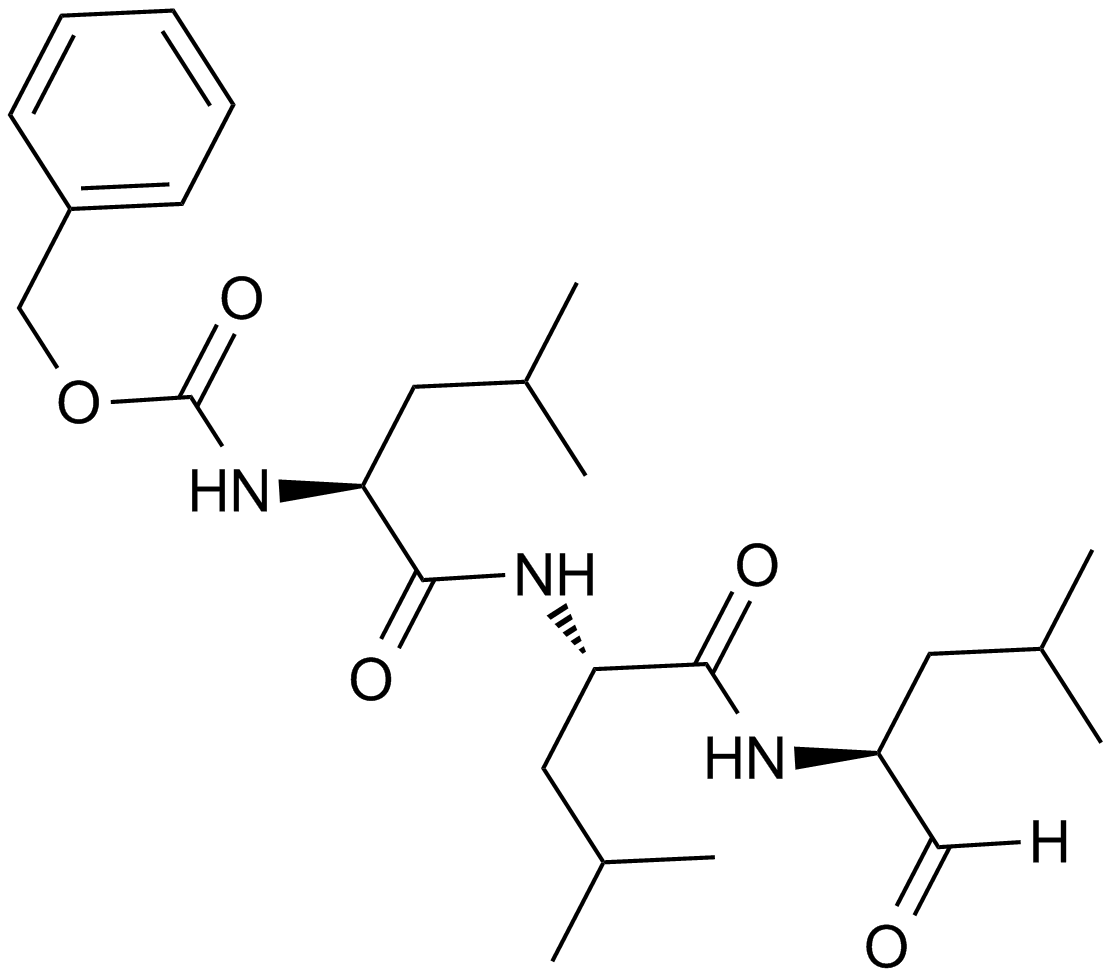 A2585 MG-13226 CitationTarget: ProteasomeSummary: Proteasome inhibitor, Cell permeable, reversible
A2585 MG-13226 CitationTarget: ProteasomeSummary: Proteasome inhibitor, Cell permeable, reversible -
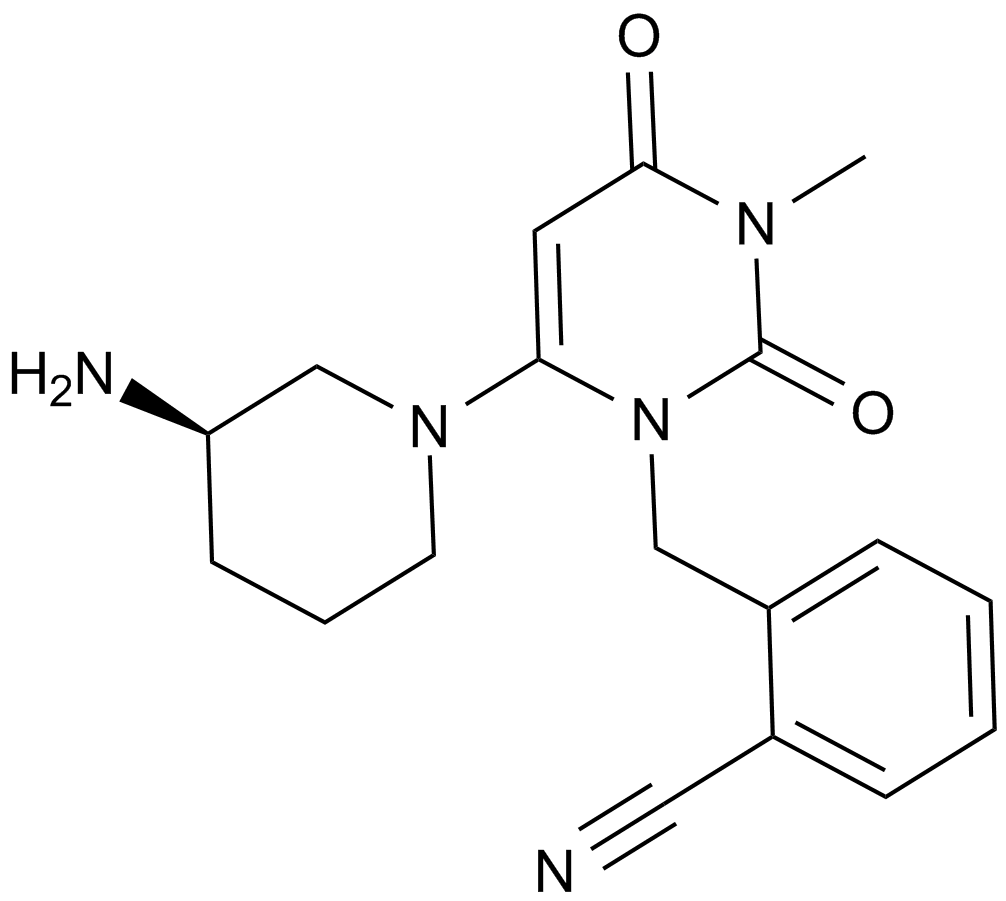 A4038 Alogliptin (SYR-322)1 CitationTarget: DPP-4Summary: DPP-4 inhibitor,potent and highly selective
A4038 Alogliptin (SYR-322)1 CitationTarget: DPP-4Summary: DPP-4 inhibitor,potent and highly selective -
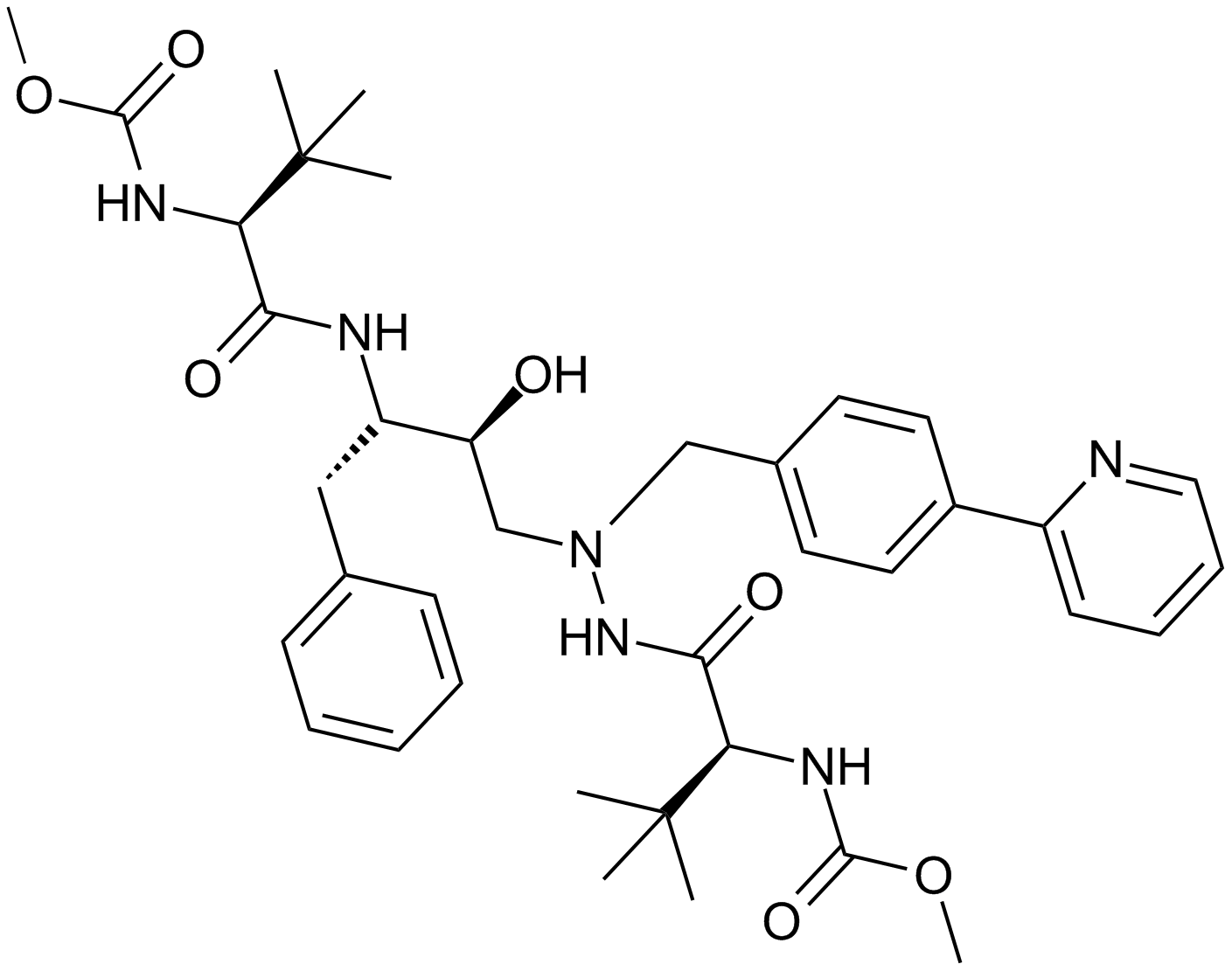 A8205 Atazanavir1 CitationSummary: HIV protease inhibitor,highly potent
A8205 Atazanavir1 CitationSummary: HIV protease inhibitor,highly potent -
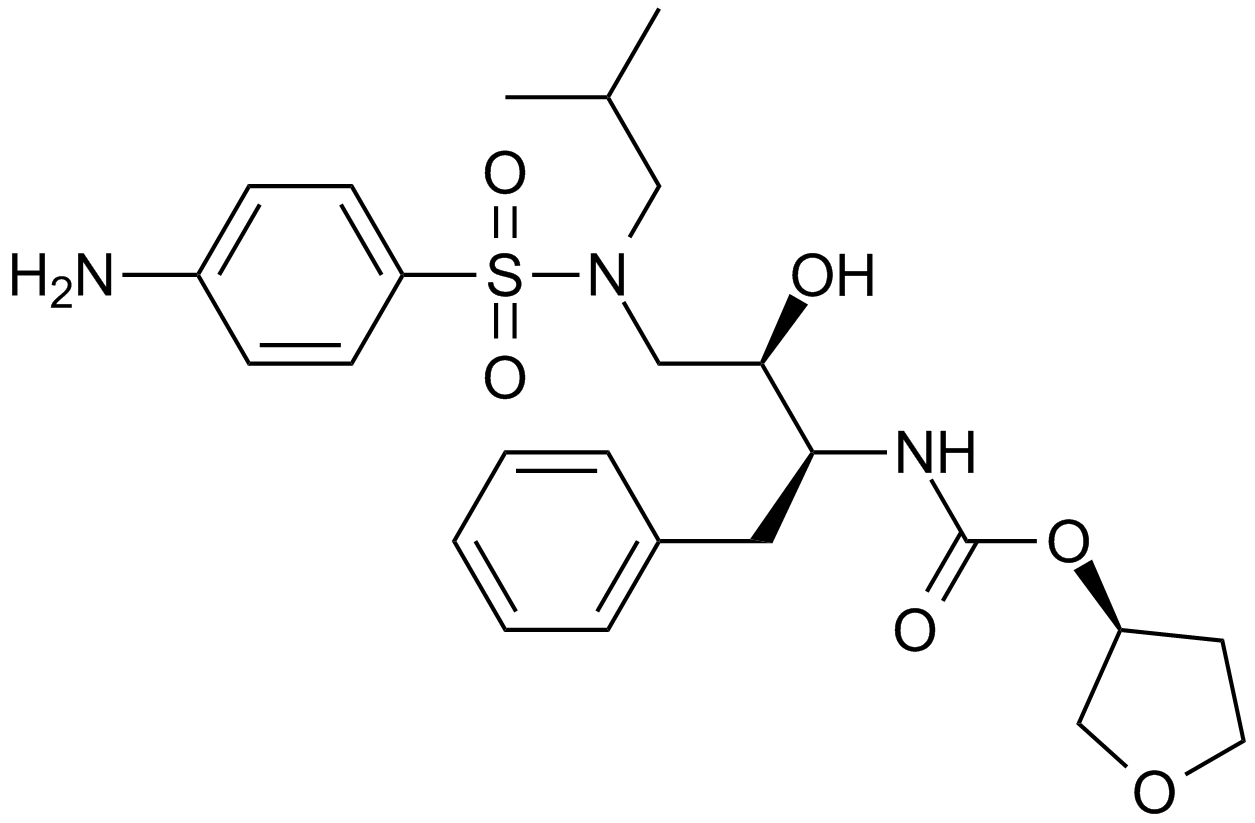 A8201 Amprenavir (agenerase)Summary: HIV-1 protease inhibitor
A8201 Amprenavir (agenerase)Summary: HIV-1 protease inhibitor -
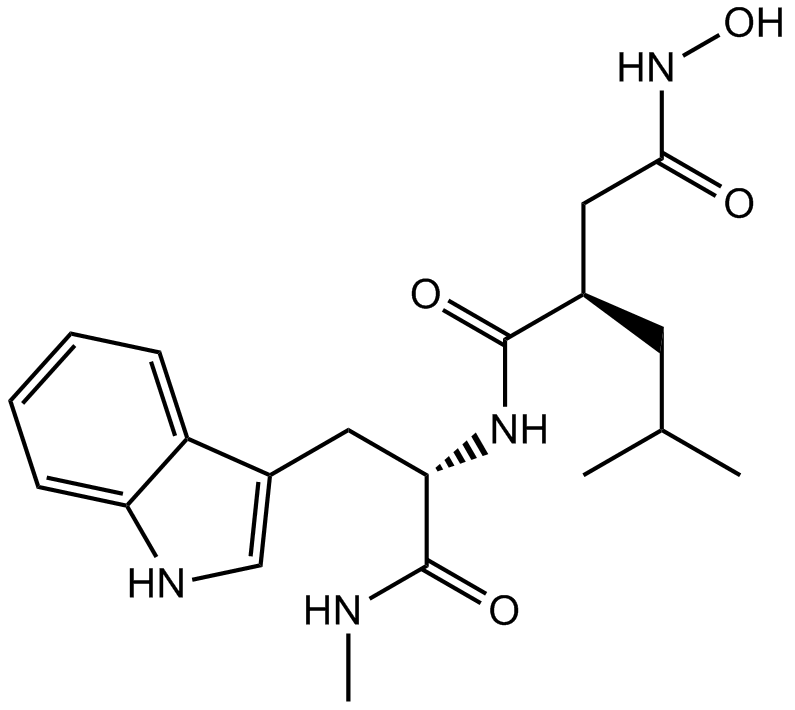 A4050 GM 60012 CitationTarget: MMPSummary: Broad spectrum MMP inhibitor
A4050 GM 60012 CitationTarget: MMPSummary: Broad spectrum MMP inhibitor

