Other Signal Transduction

Signal Transduction
Cellular responses are triggered by proteins, drugs, or pathogens binding to specific receptors. Receptor mediated signaling is a cascade of enzymatic reactions that amplifies the signal. The agonists and antagonists modulating receptor functionality are essential tools for research and medical practice. read more
-
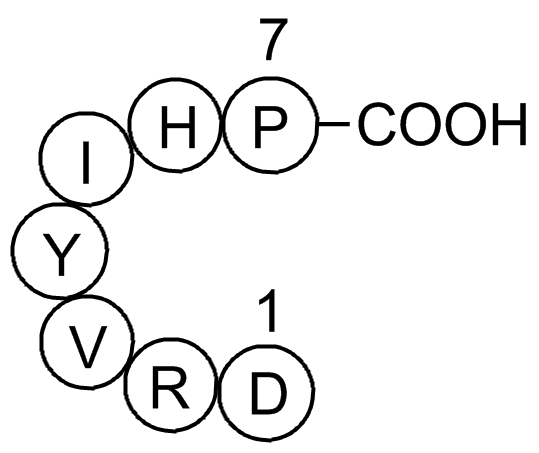 A1041 Angiotensin (1-7)6 CitationSummary: Vasoconstriction peptide hormone
A1041 Angiotensin (1-7)6 CitationSummary: Vasoconstriction peptide hormone -
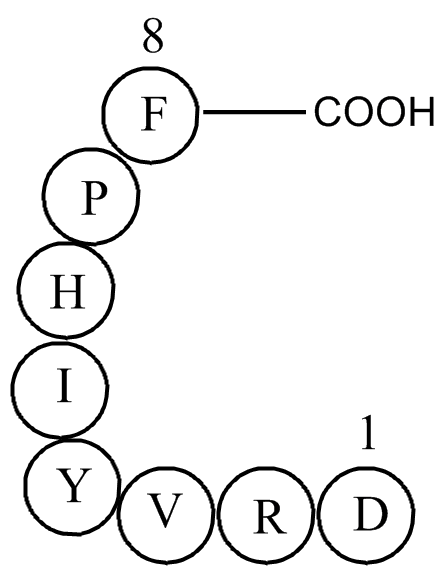 A1042 Angiotensin II21 CitationSummary: Potent vasopressor and GPCR agonist
A1042 Angiotensin II21 CitationSummary: Potent vasopressor and GPCR agonist -
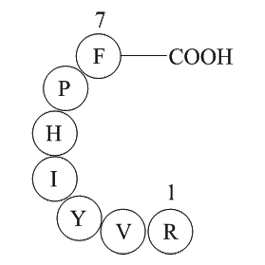 A1043 Angiotensin III (human, mouse)Summary: Aldosterone stimulator
A1043 Angiotensin III (human, mouse)Summary: Aldosterone stimulator -
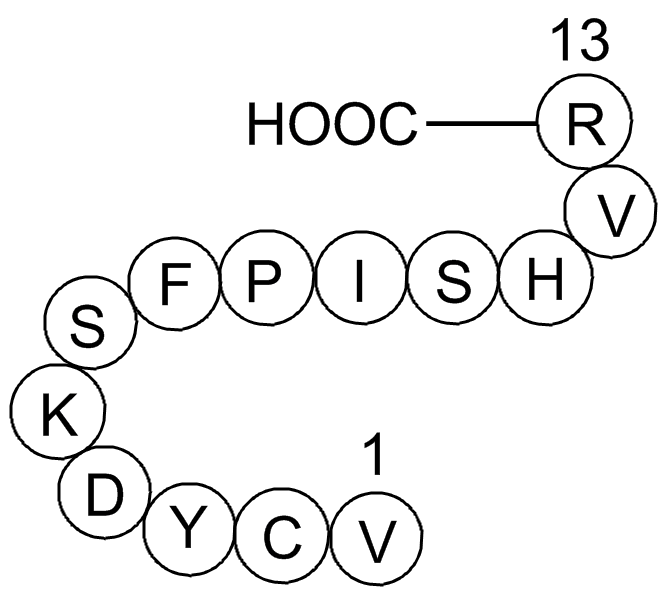 A1044 Gap 268 CitationTarget: Gap JunctionsSummary: Gap junction blocker peptide, mapping to connexin 43 residue 63-75
A1044 Gap 268 CitationTarget: Gap JunctionsSummary: Gap junction blocker peptide, mapping to connexin 43 residue 63-75 -
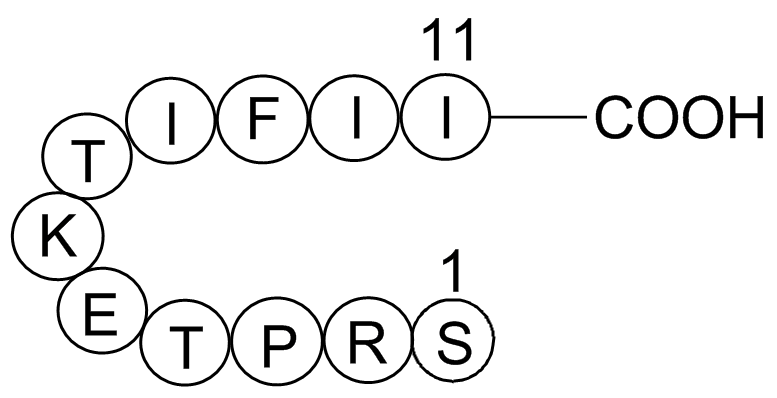 A1045 Gap 274 CitationTarget: Gap JunctionsSummary: Selective gap junction blocker
A1045 Gap 274 CitationTarget: Gap JunctionsSummary: Selective gap junction blocker -
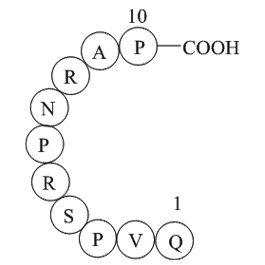 A1046 Dynamin inhibitory peptideSummary: Peptide inhibitor of GTPase dynamin
A1046 Dynamin inhibitory peptideSummary: Peptide inhibitor of GTPase dynamin -
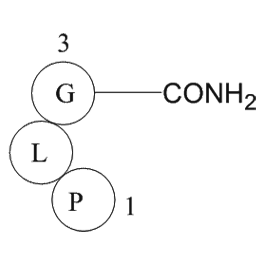 A1121 Melanocyte stimulating hormone release inhibiting factorSummary: MSH release-inhibiting factor
A1121 Melanocyte stimulating hormone release inhibiting factorSummary: MSH release-inhibiting factor -
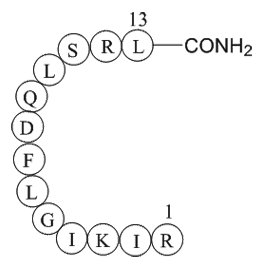 A1132 β-PompilidotoxinTarget: sodium channelsSummary: Slows Na+ channel inactivation
A1132 β-PompilidotoxinTarget: sodium channelsSummary: Slows Na+ channel inactivation -
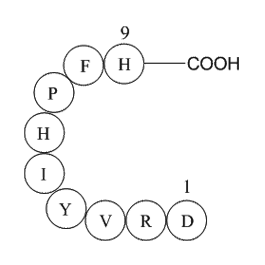 A1007 Angiotensin 1/2 (1-9)Summary: Vasoconstrictor
A1007 Angiotensin 1/2 (1-9)Summary: Vasoconstrictor -
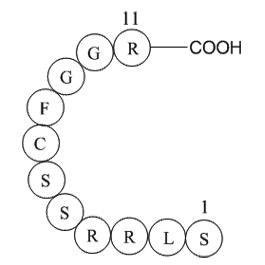 A1009 ANP (1-11), ratSummary: Vasodilator
A1009 ANP (1-11), ratSummary: Vasodilator

