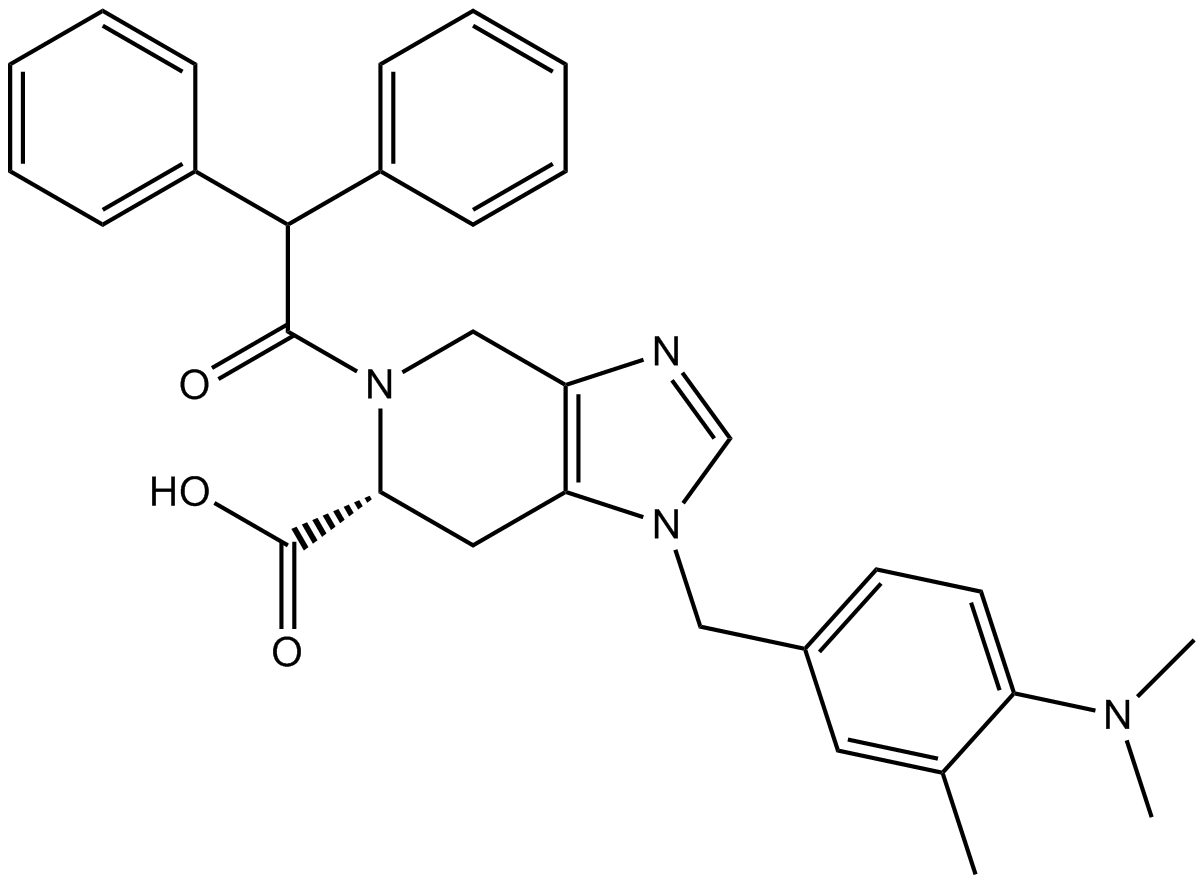
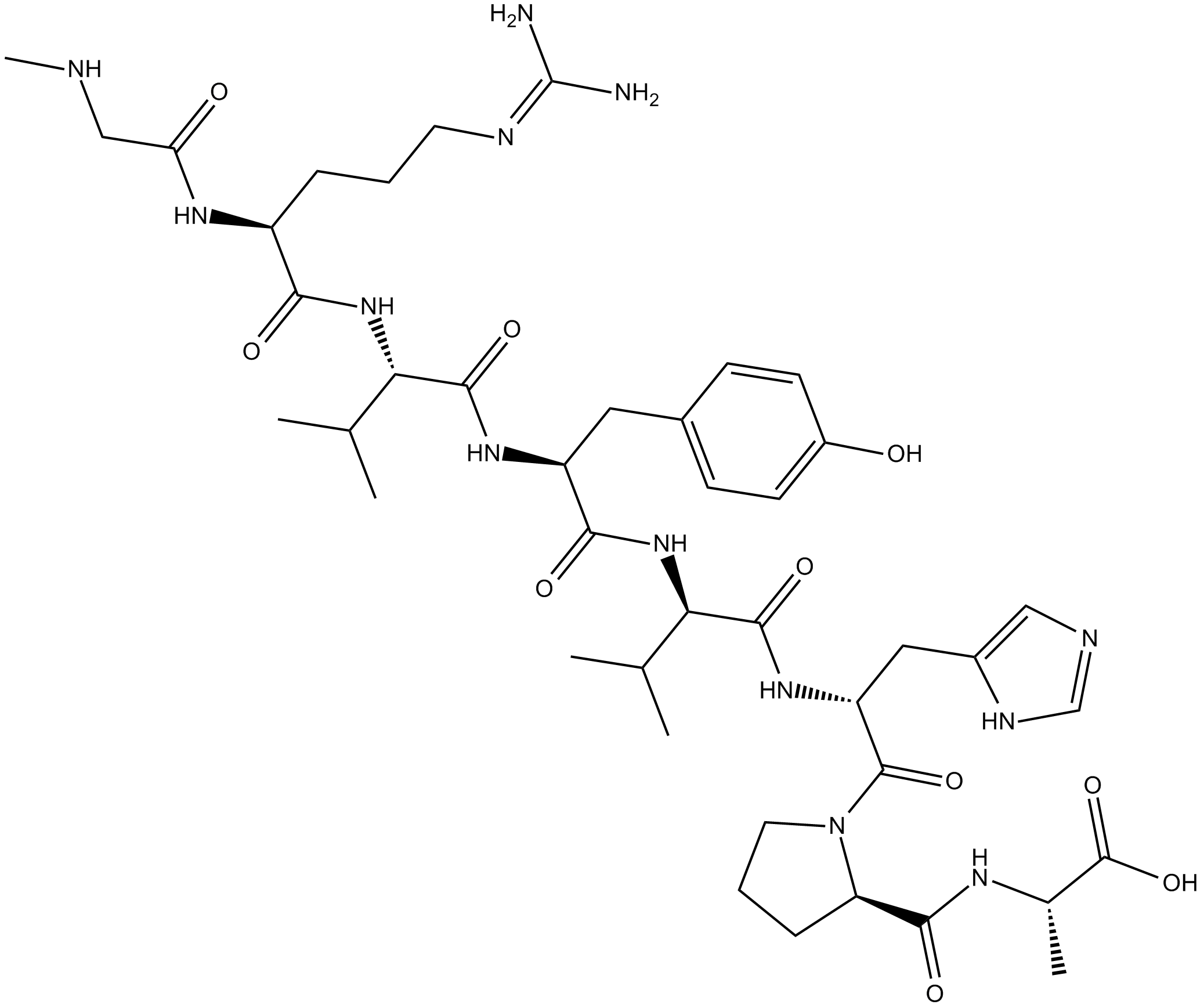
Angiotensin II
Angiotensin II (CAS 4474-91-3), an endogenous octapeptide, exerts potent vasoconstrictive effects through activation of angiotensin receptors on vascular smooth muscle cells. This peptide stimulates contraction via binding G protein-coupled receptors, triggering intracellular signaling cascades involving phospholipase C activation, subsequent IP3-dependent calcium release and protein kinase C-mediated pathways. Angiotensin II additionally promotes aldosterone secretion from adrenal cortical cells, enhancing renal sodium and water reabsorption. Experimentally, angiotensin II is utilized extensively for investigating mechanisms of hypertension, cardiovascular remodeling, vascular smooth muscle cell hypertrophy, and inflammatory responses in vascular injury models. Reported IC50 values for receptor binding typically range between 1-10 nM depending on assay conditions.
Ref:
1. Ruiz-Ortega M, Lorenzo O, Ruperez M, Esteban V, Suzuki Y, Mezzano S, Plaza JJ, Egido J. Role of the renin-angiotensin system in vascular diseases: expanding the field. Hypertension. 2001; 38: 1382–1387.
2. Geisterfer AA, Peach MJ, Owens GK. Angiotensin II induces hypertrophy, not hyperplasia, of cultured rat aortic smooth muscle cells. Circ Res. 1988; 62: 749–756.
3. Berk BC, Vekshtein V, Gordon HM, Tsuda T. Angiotensin II-stimulated protein synthesis in cultured vascular smooth muscle cells. Hypertension. 1989; 13: 305–314.
- 1. Hongyi Huang, Quan Zuo, Siqi Zhang. "Synthesis and Evaluation of Cyclic Peptide-Based PET Tracers Targeting ADAMTS4 for Early Detection and Monitoring of Aortic Aneurysms." J Med Chem. 2025 Dec 1. PMID: 41324323
- 2. Yikai Cui, Liwei Liu, Jinyan Zhang. "Macrophage Mertk mediates pressure overload-induced heart failure via type I interferon response." Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2025 Oct 7:787:152767. PMID: 41076977
- 3. Joshua Harrison, Kelvin M. Risby, et al. "The Role of Aerosol Liquid Water in Droplet-Assisted Ionization Mass Spectrometry." Anal Chem. 2025 Sep 16;97(36):19918-19925. PMID: 40886134
- 4. Sophia Gagliardi, Tristan Hotchkin, et al. "The Renin–Angiotensin System Modulates SARS-CoV-2 Entry via ACE2 Receptor." Viruses. 2025 Jul 19;17(7):1014. PMID: 40733630
- 5. Pingao Zhang, Chenghuan Song, et al. "Endothelium-specific endoglin triggers astrocyte reactivity via extracellular vesicles in a mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease." Mol Neurodegener. 2025 Jul 23;20(1):84. PMID: 40702549
- 6. Katelin X. Oliveira, Fariha E. Bablu, et al. "Naturally Occurring Angiotensin Peptides Enhance the SARS-CoV-2 Spike Protein Binding to Its Receptors." Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Jun 24;26(13):6067. PMID: 40649848
- 7. Yiyan Xu, Ying Wang, et al. "Precision Drug Delivery for Multifunctional Treatment of Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm Using Bioactive Tea Polyphenol Nanoparticles." ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2025 Jun 18;17(24):35080-35098. PMID: 40479730
- 8. Zhenyu GU, Qi HUA et al. "Benzyl alcohol improves Ang II-induced vascular and renal injury." Turk J Med Sci. 2025 Feb 19;55(2):509-517. PMID: 40342326
- 9. Songwen Li, Gang Liu, et al. "Pharmacological and genetic inhibition of BTK ameliorates vascular degeneration, dissection, and rupture." Life Sci. 2025 May15:369:123533. PMID: 40049365
- 10. Jingjing Zhang, Yuyi Tang, Shan Zhang. "Mitochondrial NAD+ deficiency in vascular smooth muscle impairs collagen III turnover to trigger thoracic and abdominal aortic aneurysm." Nat Cardiovasc Res. 2025 Mar;4(3):275-292. PMID: 39843801
- 11. Shuli Zhang, Jiayin Li, et al. "Cellular Senescence Genes as Cutting‐Edge Signatures for Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm Diagnosis: Potential for Innovative Therapeutic Interventions." J Cell Mol Med. 2025 Jan;29(2):e70323. PMID: 39823264
- 12. Jim S. Walker, Bryan R. Bzdek, et al. "Rapid and Sensitive Chemical Analysis of Individual Picolitre Droplets by Mass Spectrometry." Analytical Chemistry Cite this: Anal. Chem. 2025, 97, 1, 854–861
- 13. Liang Song, Weiwei Zheng, et al. "ROS-responsive core–shell microgels for phase-specific treatment of myocardial infarction via programmed drug delivery." Volume 507,1 March 2025,160295
- 14. Jiayin Li , Zheming Yang, et al. "The role of mitofusin 2 in regulating endothelial cell senescence: Implications for vascular aging." iScience. 2024 Aug 24;27(9):110809. PMID: 39290834
- 15. Pengjie Zhang, Bin Du, et al. "Identification and Removal of Pollen Spectral Interference in the Classification of Hazardous Substances Based on Excitation Emission Matrix Fluorescence Spectroscopy." Molecules. 2024 Jul 1;29(13):3132. PMID: 38999084
- 16. Sheng Yin, et al. "A Natural Small Molecule Mitigates Kidney Fibrosis by Targeting Cdc42‐mediated GSK‐3β/β‐catenin Signaling." Adv Sci (Weinh). 2024 Apr;11(13):e2307850. PMID: 38240457
- 17. Manfen Shao, Wei Zhao, et al. "Peptides fromHarpadon nehereusBone Ameliorate Angiotensin II-Induced HUVEC Injury and Dysfunction through Activation of the AKT/eNOS and Nrf2 Pathway." ACS Omega. 2023 Oct 25;8(44):41655-41663. PMID: 37969981
- 18. Hanlin Lu, Xiuxin Jiang, et al. "Endothelial Sp1/Sp3 are essential to the effect of captopril on blood pressure in male mice." Nat Commun. 2023 Sep 21;14(1):5891. PMID: 37735515
- 19. Yao Lin, Jingchen Xu, et al. "Axl promotes intracranial aneurysm rupture by regulating macrophage polarization toward M1 via STAT1/HIF-1α." Carbohydr Polym. 2023 Aug 15:314:120962. PMID: 37173016
- 20. Jiwei Xu, Jianjie Xu, et al. "Impact of different classification schemes on discrimination of proteins with noise-contaminated spectra using laboratory-measured fluorescence data." Spectrochim Acta A Mol Biomol Spectrosc. 2023 Aug 5:296:122646. PMID: 37003145
- 21. Yu, Yi-Gui, Han, Jun-Hui, et al. "The variations of Endophilin A2-FoxO3a-autophagy signal in AngⅡ-induced dopaminergic neuron injury mouse model and By Biochanin A." Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 2021 Dec;99(12):1298-1307 PMID: 34310897
- 22. Zhou Z, Ni J, et al. "Angiotensin II induces RAW264. 7 macrophage polarization to the M1-type through the connexin 43/NF-κB pathway." Mol Med Rep. 2020;21(5):2103-2112 PMID: 32186758
- 23. Zhang SF, Mao XJ, et al. "Qian Yang Yu Yin Granule protects against hypertension-induced renal injury by epigenetic mechanism linked to Nicotinamide N-Methyltransferase (NNMT) expression." J Ethnopharmacol. 2020;255:112738 PMID: 32147479
- 24. Zhou Z, Ni J, et al. "RIG -I aggravates interstitial fibrosis via c-Myc-mediated fibroblast activation in UUO mice." J Mol Med (Berl). 2020;10.1007/s00109-020-01879-x PMID: 32036390
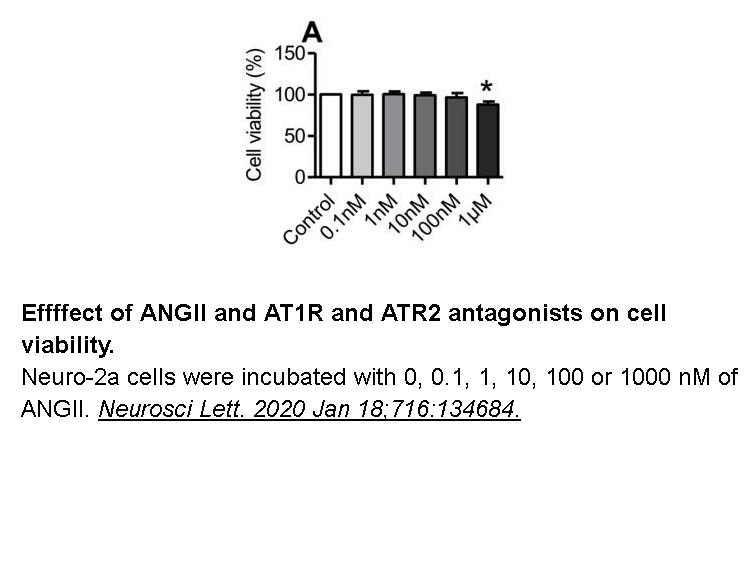
- 25. Chen YJ, Qian ZM, et al. "Angiotensin II down-regulates transferrin receptor 1 and ferroportin 1 expression in Neuro-2a cells via activation of type-1 receptor." Neurosci Lett. 2020 Jan 18;716:134684 PMID: 31830506
| Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| M.Wt | 1046.2 |
| Cas No. | 4474-91-3 |
| Formula | C50H71N13O12 |
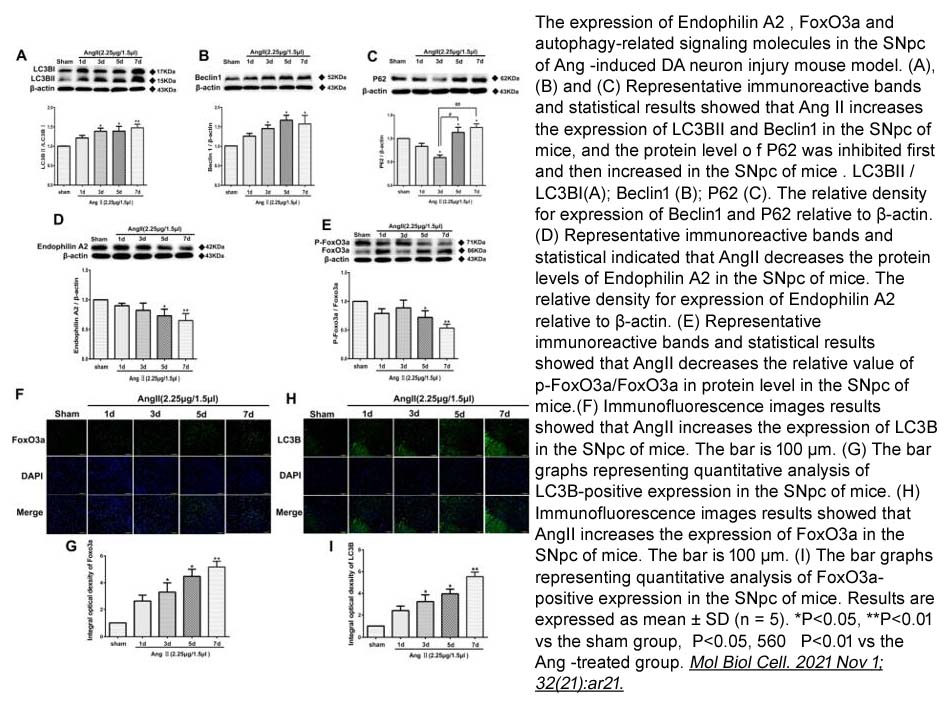
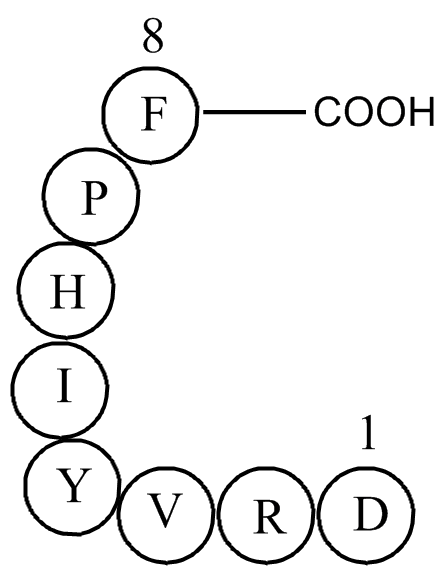
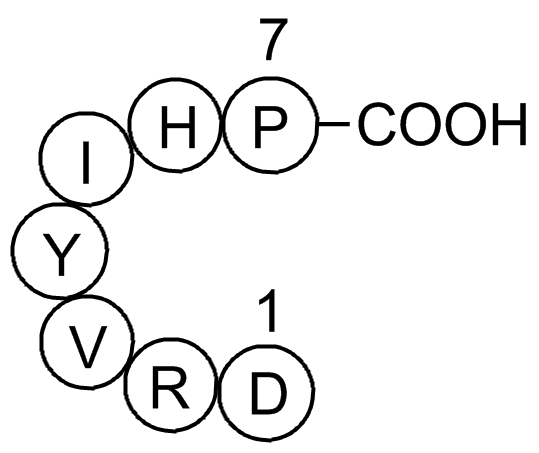
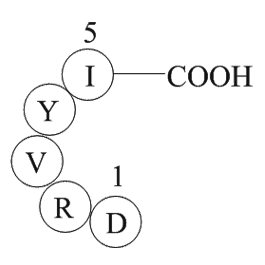
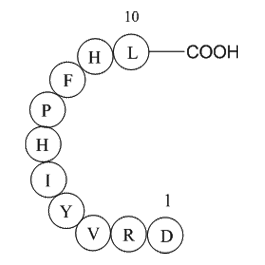
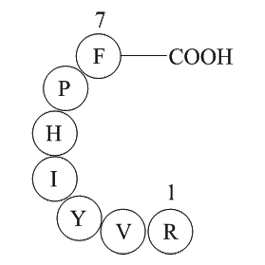
| Synonyms | Asp-Arg-Val-Tyr-Ile-His-Pro-Phe |
| Solubility | ≥234.6 mg/mL in DMSO; insoluble in EtOH; ≥76.6 mg/mL in H2O |
| Chemical Name | Angiotensin II |
| SDF | Download SDF |
| Canonical SMILES | CCC(C)C(C(=O)NC(CC1=CN=CN1)C(=O)N2CCCC2C(=O)NC(CC3=CC=CC=C3)C(=O)O)NC(=O)C(CC4=CC=C(C=C4)O)NC(=O)C(C(C)C)NC(=O)C(CCCN=C(N)N)NC(=O)C(CC(=O)O)N.CC(=O)O |
| Shipping Condition | Small Molecules with Blue Ice, Modified Nucleotides with Dry Ice. |
| General tips | We do not recommend long-term storage for the solution, please use it up soon. |
| Cell experiment: [1] | |
|
Cell lines |
Vascular smooth muscle cells |
|
Preparation method |
The solubility of this peptide in sterile water is >10 mM. Stock solution should be splited and stored at -80°C for several months. |
|
Reaction Conditions |
100 nM, 4 hours |
|
Applications |
Treatment of Angiotensin II caused a large increase in both NADH and NADPH oxidase activity, both in terms of initial rate and peak response. The increase in oxidase activity was not apparent until ~ 1 hour and continued to increase for at least 6 hours. |
| Animal experiment: [2] | |
|
Animal models |
C57BL/6J (apoE–/– ) mice |
|
Dosage form |
Drugs were delivered through the minipumps placed into the subcutaneous space in the back of the neck. 500 or 1000 ng/min/kg for 28 days. |
|
Applications |
Ang II infusion promotes the development of abdominal aortic aneurysms. The region in the abdominal aorta from an Ang II–infused mouse was markedly increased in size. The tissue encompassing this region was resistant to the dissection process typically used to remove adventitial tissue. The bulbous aortic abdominal shape occurred in 20% and 33% of mice in the groups infused with 500 and 1,000 ng/min/kg of Ang II, respectively. |
|
Other notes |
Please test the solubility of all compounds indoor, and the actual solubility may slightly differ with the theoretical value. This is caused by an experimental system error and it is normal. |
|
References: [1] Griendling K K, Minieri C A, Ollerenshaw J D, et al. Angiotensin II stimulates NADH and NADPH oxidase activity in cultured vascular smooth muscle cells. Circulation research, 1994, 74(6): 1141-1148. [2] Daugherty A, Manning M W, Cassis L A. Angiotensin II promotes atherosclerotic lesions and aneurysms in apolipoprotein E–deficient mice. Journal of Clinical Investigation, 2000, 105(11): 1605-1612. |
|
Quality Control & MSDS
- View current batch:
Chemical structure
Related Biological Data
Related Biological Data
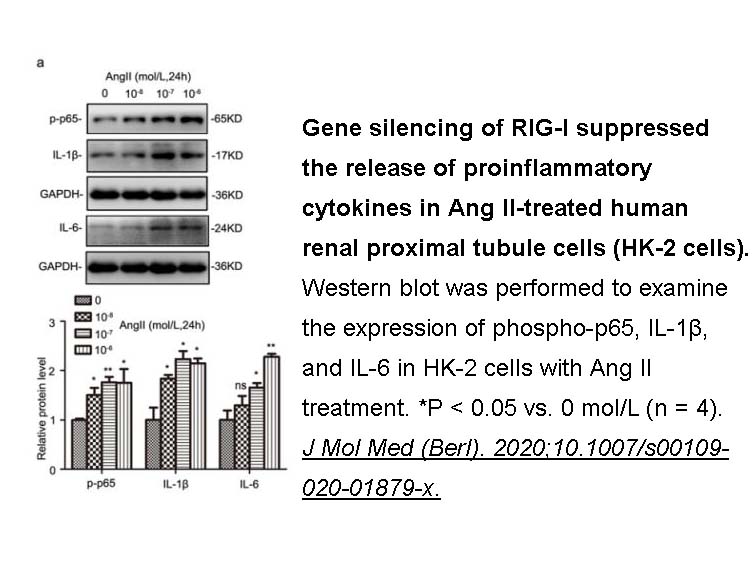
Related Biological Data
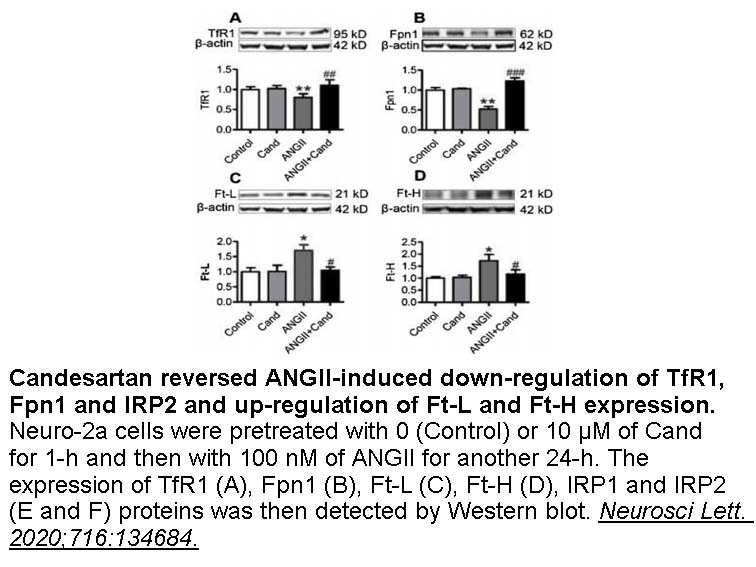
Related Biological Data
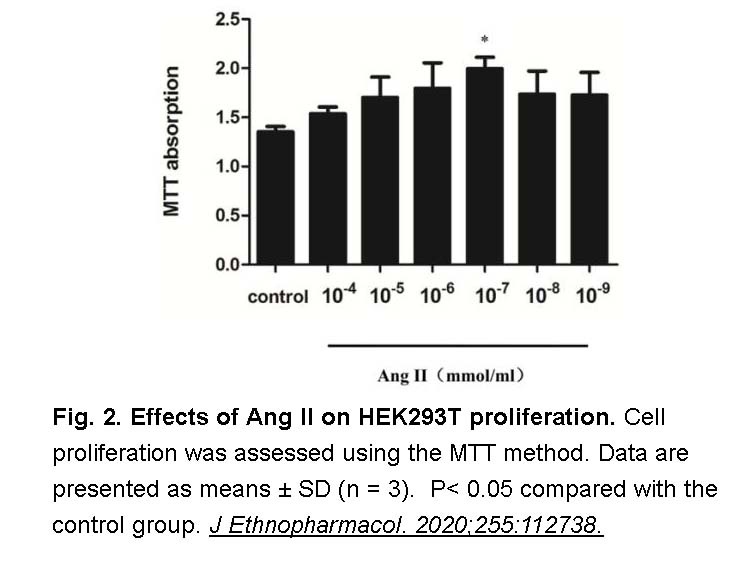
Related Biological Data
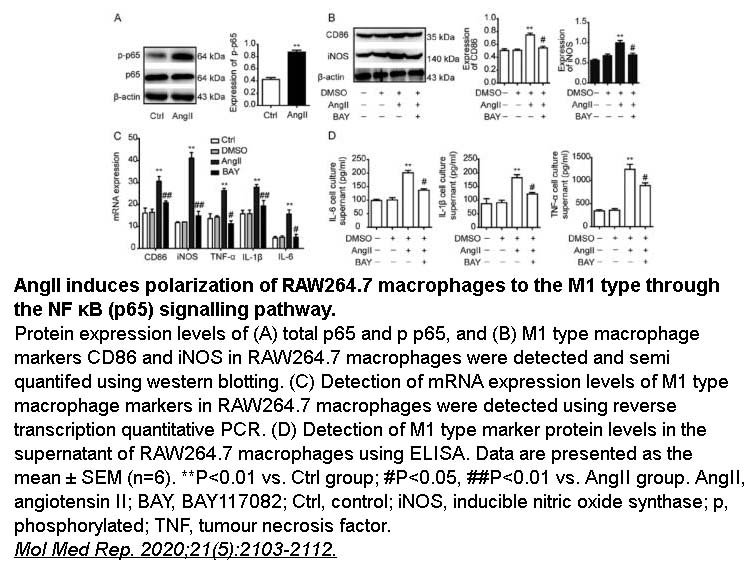
Related Biological Data