Losartan
Losartan (CAS 114798-26-4) is an angiotensin II type 1 (AT1) receptor antagonist widely studied in biomedical research. By selectively blocking the AT1 receptor, Losartan inhibits angiotensin II binding, thus disrupting downstream signaling pathways involved in vasoconstriction and blood pressure regulation. Losartan demonstrates potent antagonistic activity, exhibiting an IC50 of approximately 20 nM for AT1 receptor binding inhibition. Due to its clear mechanism and receptor specificity, it serves as an essential tool in studies of cardiovascular physiology, hypertension pathogenesis, and related therapeutic interventions.
| Physical Appearance | A solid |
| Storage | Store at -20°C |
| M.Wt | 422.91 |
| Cas No. | 114798-26-4 |
| Formula | C22H23ClN6O |
| Solubility | ≥2.48 mg/mL in H2O with gentle warming and ultrasonic; ≥2.9 mg/mL in EtOH with gentle warming; ≥84.6 mg/mL in DMSO |
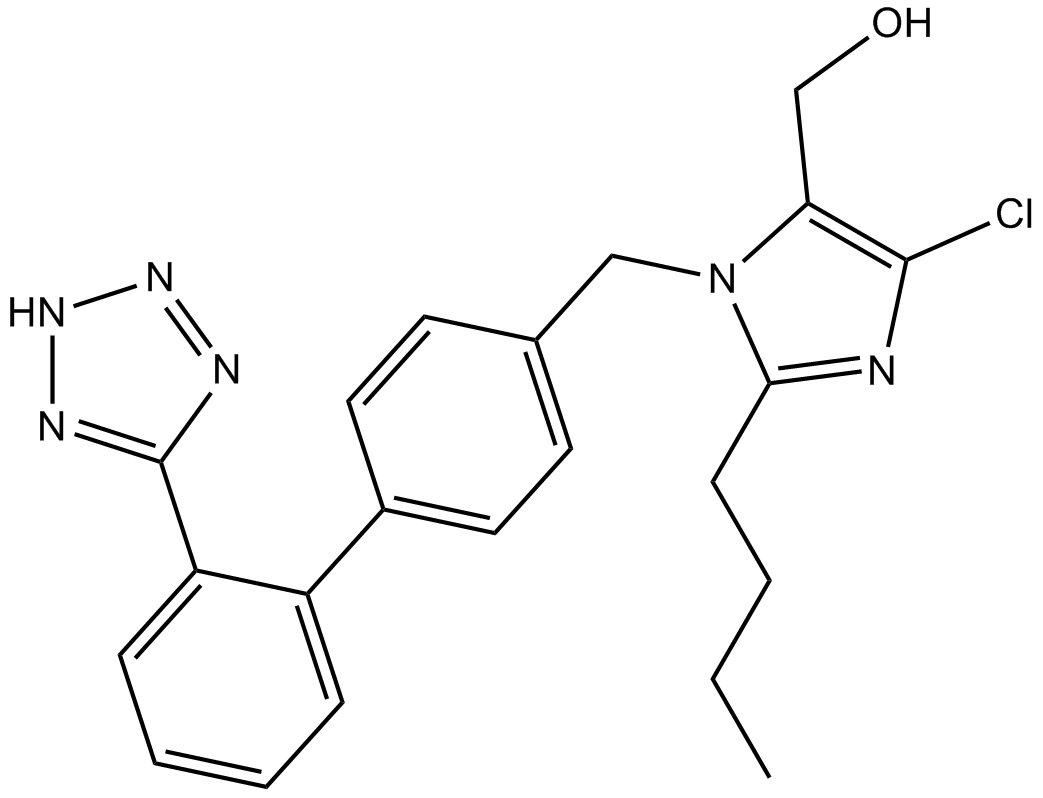
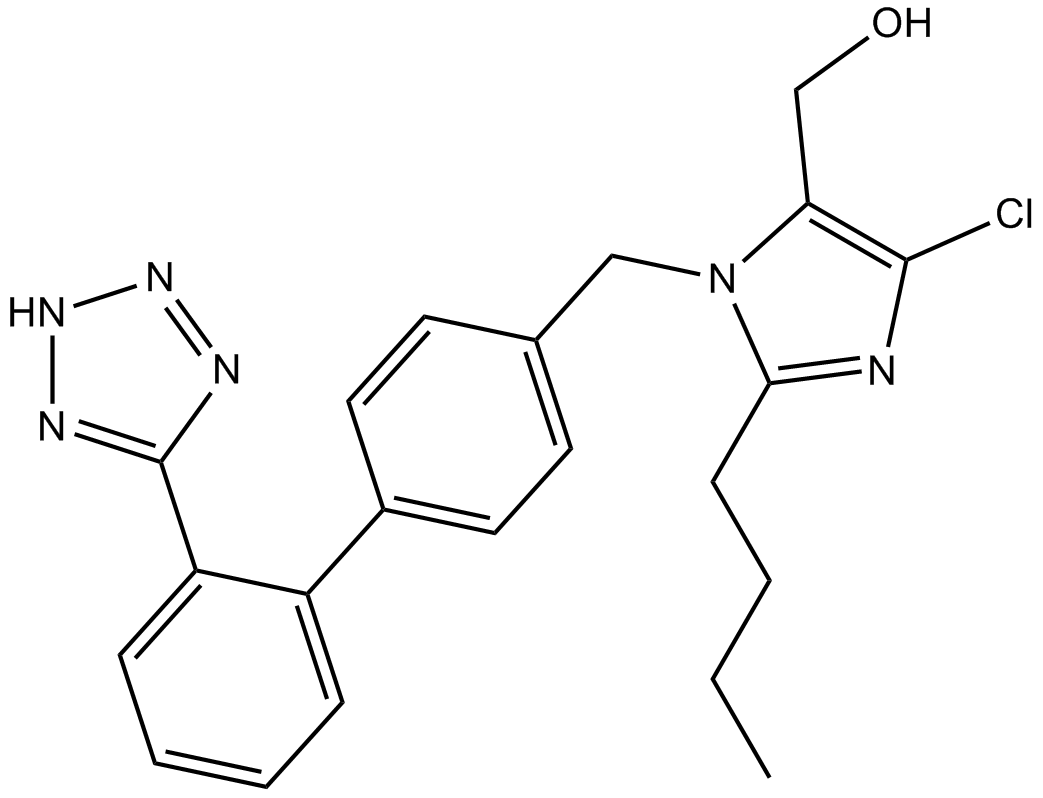
| Chemical Name | [2-butyl-5-chloro-3-[[4-[2-(2H-tetrazol-5-yl)phenyl]phenyl]methyl]imidazol-4-yl]methanol |
| SDF | Download SDF |
| Canonical SMILES | CCCCc1nc(Cl)c(CO)[n]1Cc(cc1)ccc1-c(cccc1)c1-c1n[nH]nn1 |
| Shipping Condition | Small Molecules with Blue Ice, Modified Nucleotides with Dry Ice. |
| General tips | We do not recommend long-term storage for the solution, please use it up soon. |
| Cell experiment:[1] | |
|
Cell lines |
Vascular smooth muscle cells (VSMCs) |
|
Reaction Conditions |
0, 1, 5, 10 μM losartan for 48 h incubation |
|
Applications |
Losartan dose-dependently decreased the angiotensin Ⅱ (Ang Ⅱ)- or 15% fetal bovine serum (FBS)-induced VSMC proliferation by inhibiting the expression of cell cycle associated proteins, such as p-Rb, cyclin D, and cyclin E. |
| Animal experiment:[2] | |
|
Animal models |
Wistar-Kyoto (WKY) rats and stroke-prone, spontaneously hypertensive rats (SHR-SP) |
|
Dosage form |
10 mg/kg/day Administered by oral route for 2 weeks |
|
Applications |
In SHR-SP, losartan decreased systolic blood pressure, increased the number of circulating endothelial progenitor cells (EPCs) and colony formation, and inhibited oxidation. In addition, losartan was able to stimulated EPC migration. These data suggest that losartan can improve the proliferation and function of EPCs in hypertension, with the potential to repair hypertensive vascular injuries. |
|
Note |
The technical data provided above is for reference only. |
|
References: 1. Kim JE, Choi HC. Losartan inhibits vascular smooth muscle cell proliferation through activation of AMP-activated protein kinase. The Korean Journal of Physiology & Pharmacology, 2010, 14(5): 299-304. 2. Yao EH, Fukuda N, Matsumoto T, et al. Losartan improves the impaired function of endothelial progenitor cells in hypertension via an antioxidant effect. Hypertension Research, 2007, 30(11): 1119-1128. |
|
Quality Control & MSDS
- View current batch:
Chemical structure