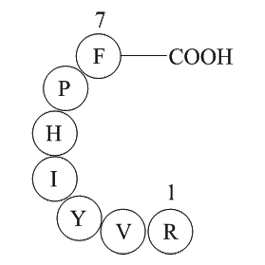
Angiotensin I (human, mouse, rat)
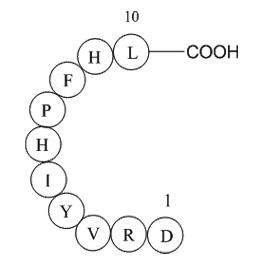
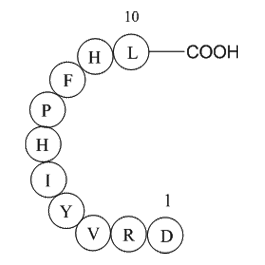
Angiotensin I (human, mouse, rat; CAS 484-42-4) is a decapeptide (sequence: H-Asp-Arg-Val-Tyr-Ile-His-Pro-Phe-His-Leu-OH) resulting from the renin-catalyzed cleavage of angiotensinogen. Angiotensin I itself lacks direct biological activity and functions primarily as the immediate precursor of angiotensin II (Ang II). Conversion occurs via angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE), which removes two amino acids, yielding Ang II. Ang II mediates biological effects by activating Gq protein-coupled receptors in vascular smooth muscle cells, triggering IP3-dependent intracellular pathways that result in vasoconstriction and elevated blood pressure. Angiotensin I serves as an essential research tool to investigate renin-angiotensin system regulation, cardiovascular disease mechanisms, and antihypertensive drug screening.
- 1. Katelin X. Oliveira, Fariha E. Bablu, et al. "Naturally Occurring Angiotensin Peptides Enhance the SARS-CoV-2 Spike Protein Binding to Its Receptors." Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Jun 24;26(13):6067 PMID: 40649848
- 2. Pengjie Zhang, Bin Du, et al. "Identification and Removal of Pollen Spectral Interference in the Classification of Hazardous Substances Based on Excitation Emission Matrix Fluorescence Spectroscopy" Molecules. 2024 Jul 1;29(13):3132 PMID: 38999084
- 3. Jiwei Xu, Jianjie Xu, et al. "Impact of different classification schemes on discrimination of proteins with noise-contaminated spectra using laboratory-measured fluorescence data." Spectrochim Acta A Mol Biomol Spectrosc. 2023 Aug 5:296:122646. PMID: 37003145
| Physical Appearance | A solid |
| Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| M.Wt | 1296.5 |
| Cas No. | 484-42-4 |
| Formula | C62H89N17O14 |
| Synonyms | Asp-Arg-Val-Tyr-Ile-His-Pro-Phe-His-Leu |
| Solubility | ≥129.6 mg/mL in DMSO; ≥124.2 mg/mL in H2O; ≥9.16 mg/mL in EtOH |
| Chemical Name | Angiotensin I (human, mouse, rat) |
| SDF | Download SDF |
| Canonical SMILES | CCC(C)C(C(=O)NC(CC1=CN=CN1)C(=O)N2CCCC2C(=O)NC(CC3=CC=CC=C3)C(=O)NC(CC4=CN=CN4)C(=O)NC(CC(C)C)C(=O)O)NC(=O)C(CC5=CC=C(C=C5)O)NC(=O)C(C(C)C)NC(=O)C(CCCN=C(N)N)NC(=O)C(CC(=O)O)N |
| Shipping Condition | Small Molecules with Blue Ice, Modified Nucleotides with Dry Ice. |
| General tips | We do not recommend long-term storage for the solution, please use it up soon. |
| Animal experiment:[1] | |
|
Animal models |
Time-dated pregnant ewes (gestational day 125 ± 5, term ~ 145 days) |
|
Dosage form |
5 μg/kg Intracerebroventricular injection |
|
Applications |
Intracerebroventricular injection of Ang I significantly increased fetal blood pressure and c-fos expression in the supraoptic nuclei (SON) and the paraventricular nuclei (PVN) in the hypothalamus, accompanied by an increase of fetal plasma arginine vasopressin (AVP). Double labeling experiments showed colocalization of AT1 receptor and c-fos expression in both SON and PVN following Ang I treatment. The results indicate that central angiotensin I increases fetal AVP neuron activity and pressor responses. |
|
Note |
The technical data provided above is for reference only. |
|
References: 1. Shi L, Mao C, Zeng F, et al. Central angiotensin I increases fetal AVP neuron activity and pressor responses. American Journal of Physiology - Endocrinology and Metabolism, 2010, 298(6): E1274-1282. |
|
Quality Control & MSDS
- View current batch:
Chemical structure