Metabolism
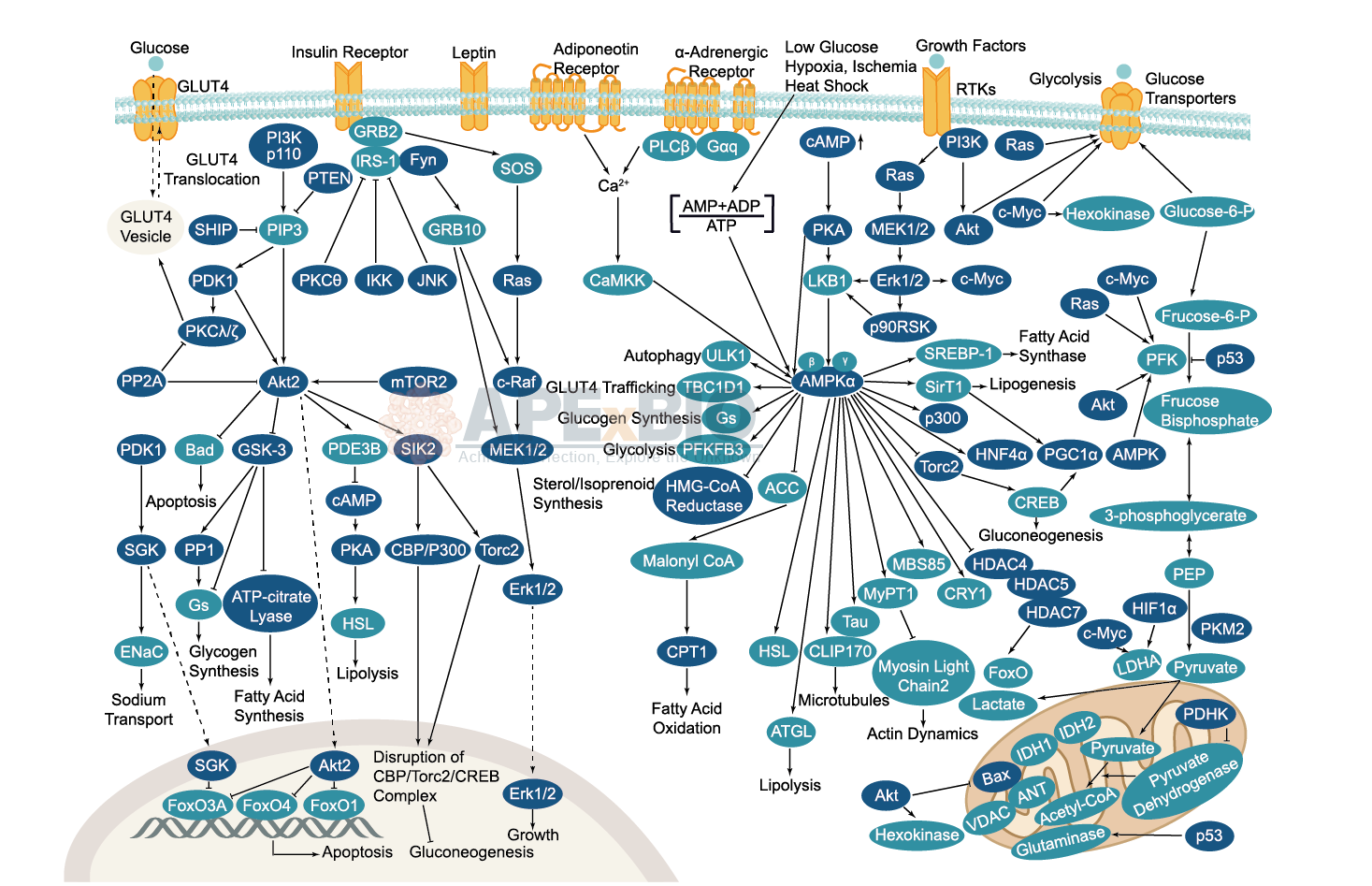
Serine/threonine kinase AMPK upregulates glucose uptake by promoting the expression and function of glucose transporters. AMPK is activated by increased AMP/ATP ratio, resulting from cellular and environmental stress, e.g. low glucose, heat shock, hypoxia and ischemia. AMPK activation positively modulates signaling transductions that refill ATP levels. Moreover, it also stimulates catabolic processes such as fatty acid oxidation and glycolysis through inhibition of ACC and activation of PFK2. AMPK negatively regulates various proteins which are important to ATP-consuming mechanisms, e.g. mTORC2, glycogen synthase, SREBP-1, and TSC2, causing the downregulation/inhibition of gluconeogenesis and glycogen, lipid and protein synthesis.
-
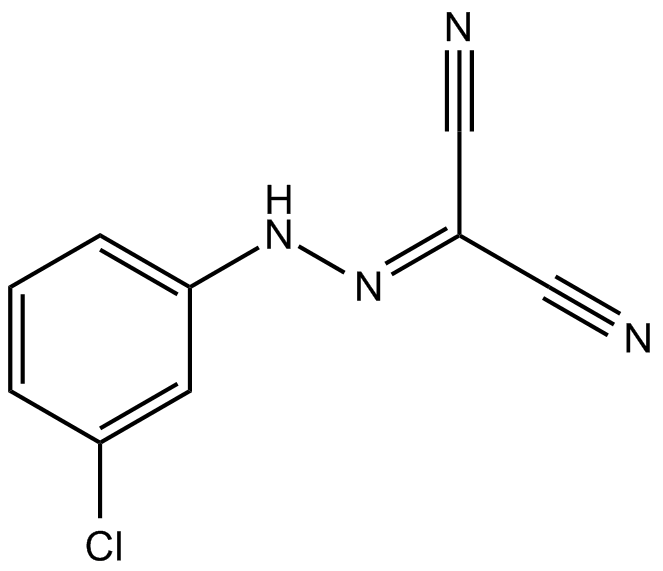 B5003 CCCP2 CitationSummary: uncoupler of oxidative phosphorylation
B5003 CCCP2 CitationSummary: uncoupler of oxidative phosphorylation -
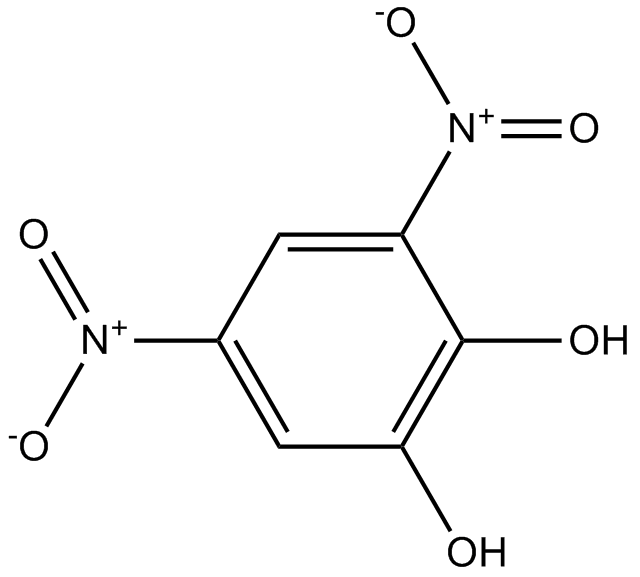 B5006 OR-486Summary: inhibitor of catechol-O-methyl-transferase
B5006 OR-486Summary: inhibitor of catechol-O-methyl-transferase -
 B5247 Nogo-66 (1-40)Summary: competitive antagonist at the Nogo-66 receptor (NgR)
B5247 Nogo-66 (1-40)Summary: competitive antagonist at the Nogo-66 receptor (NgR) -
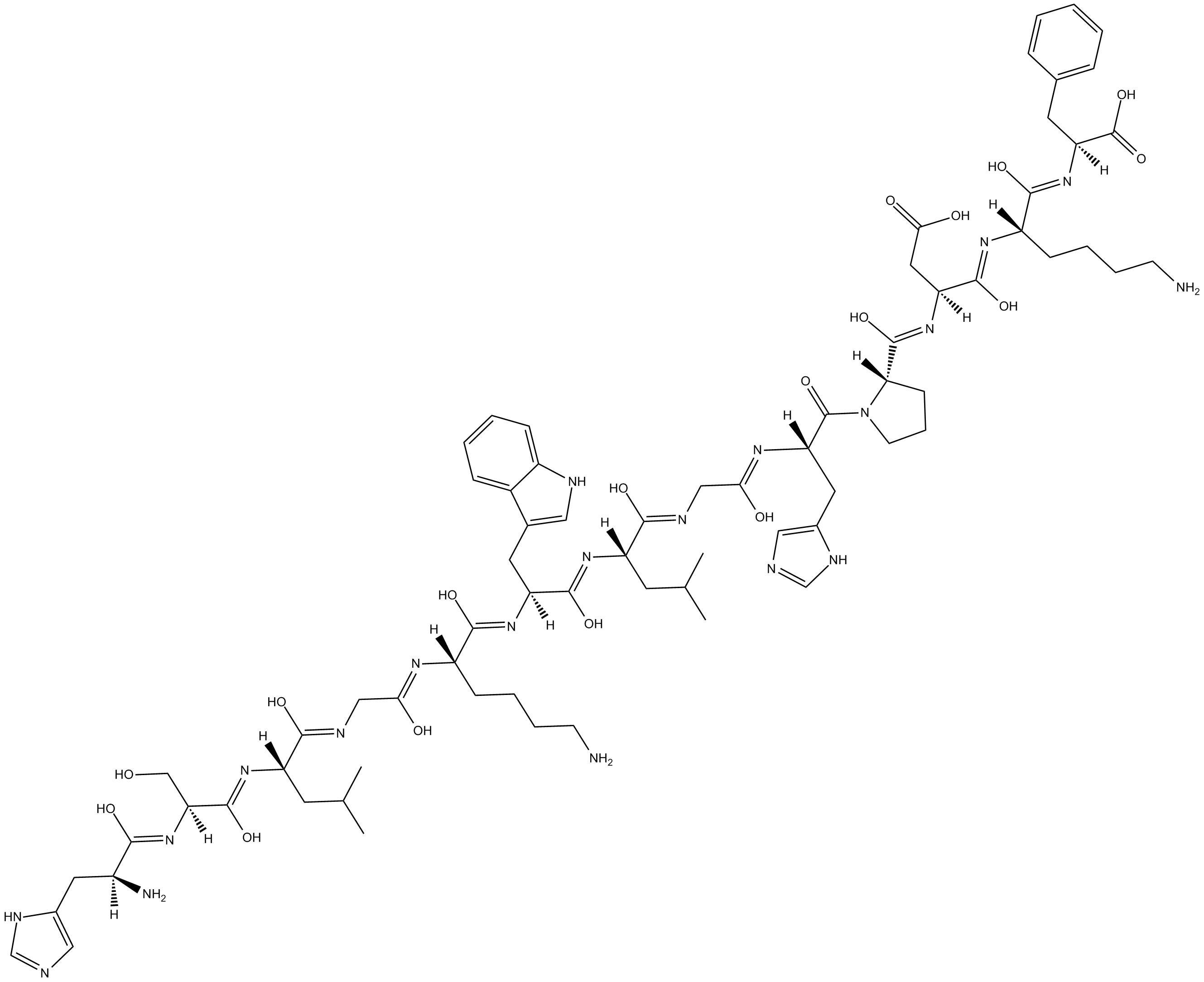 B5315 PLP (139-151)Summary: Synthetic myelin proteolipid protein (PLP) fragment
B5315 PLP (139-151)Summary: Synthetic myelin proteolipid protein (PLP) fragment -
 B5433 Prion Protein 106-126 (human)Summary: Prion peptide fragment that exhibits neurotoxicity
B5433 Prion Protein 106-126 (human)Summary: Prion peptide fragment that exhibits neurotoxicity -
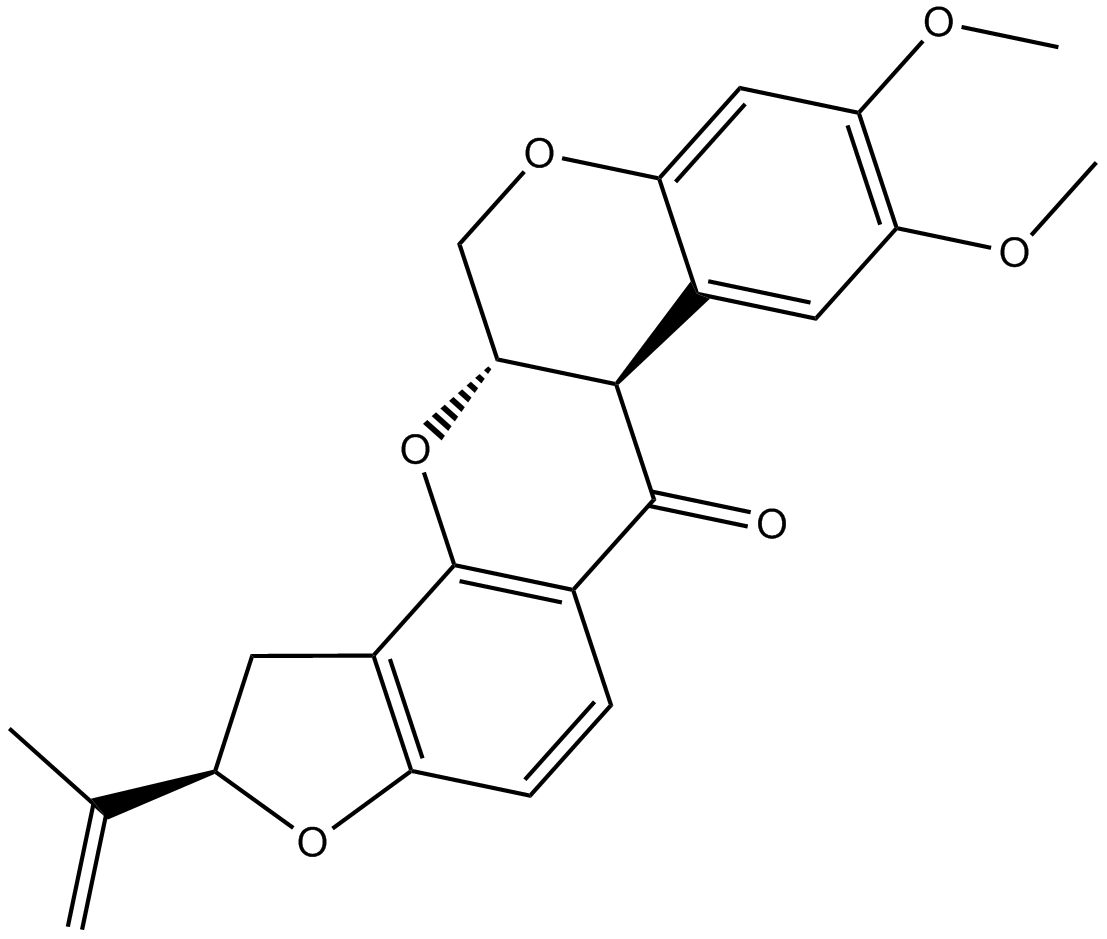 B5462 RotenoneTarget: complex I of the mitochondrial electron transport chainSummary: mitochondrial Complex I inhibitor
B5462 RotenoneTarget: complex I of the mitochondrial electron transport chainSummary: mitochondrial Complex I inhibitor -
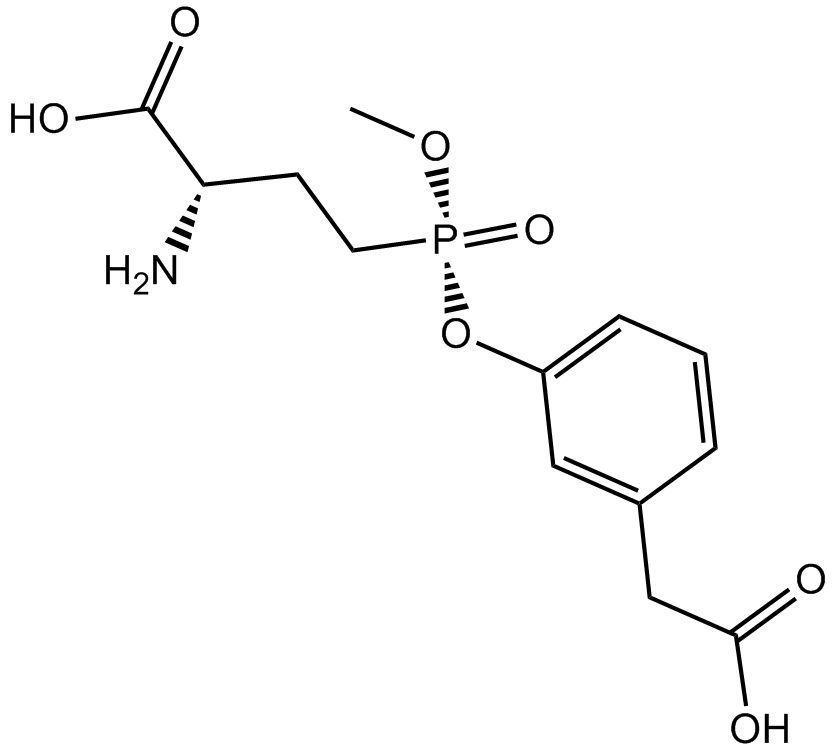 B5602 GGsTopSummary: γ-glutamyl transpeptidase (GGT) inhibitor, novel and irreversible
B5602 GGsTopSummary: γ-glutamyl transpeptidase (GGT) inhibitor, novel and irreversible -
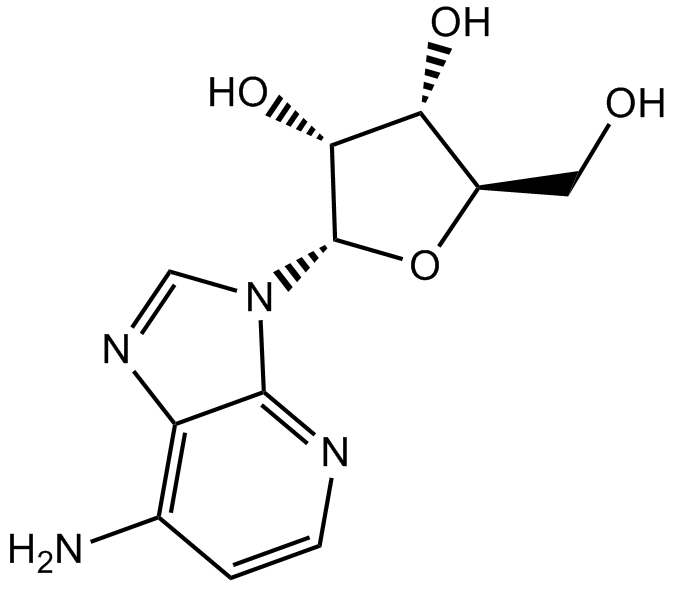 B5619 1-DeazaadenosineSummary: adenosine deaminase inhibitor
B5619 1-DeazaadenosineSummary: adenosine deaminase inhibitor -
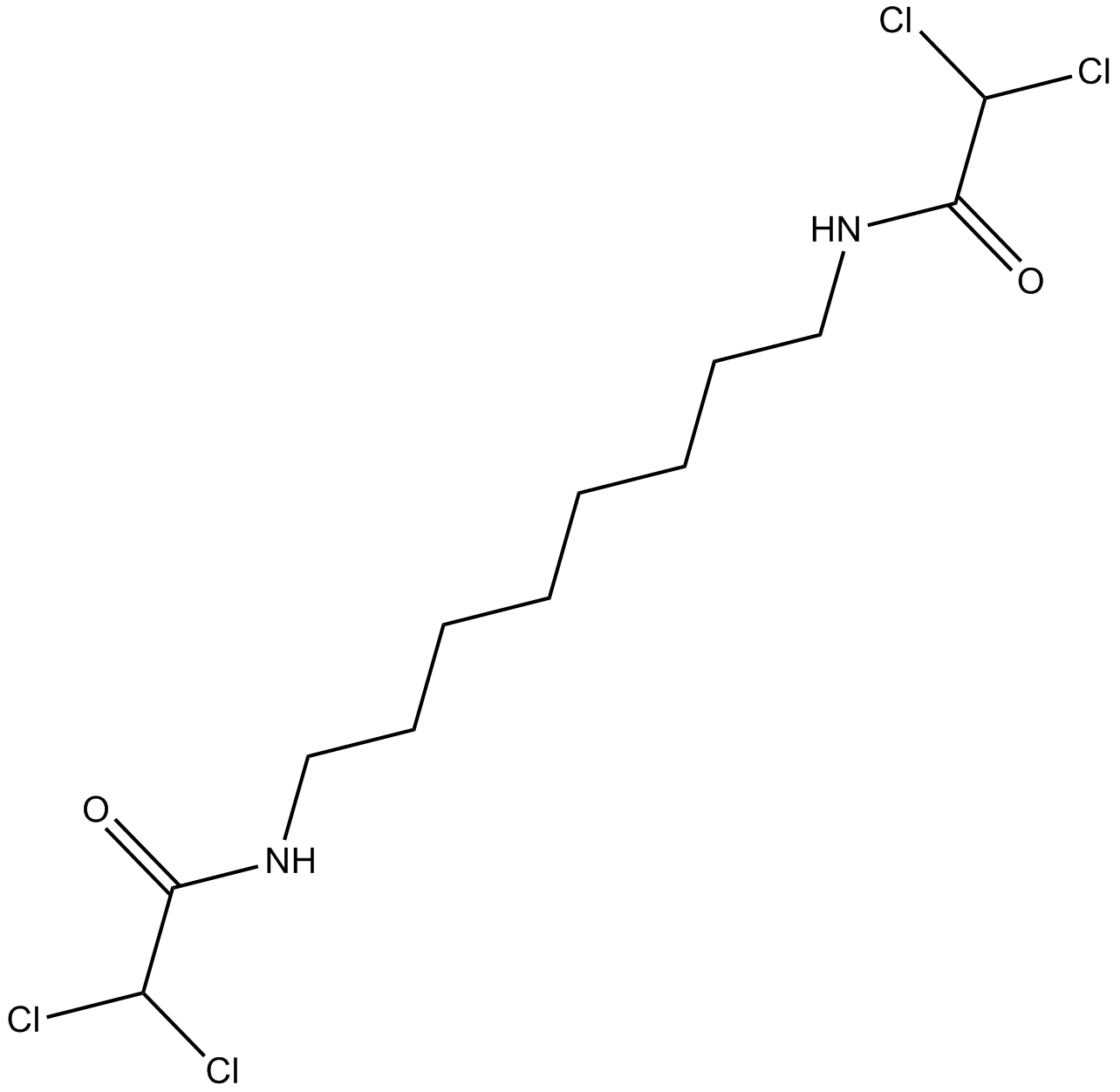 B5697 WIN 18446Summary: inhibitor of aldehyde dehydrogenase 1a2 (ALDH1a2)
B5697 WIN 18446Summary: inhibitor of aldehyde dehydrogenase 1a2 (ALDH1a2) -
 B5716 GalloflavinSummary: human lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) inhibitor
B5716 GalloflavinSummary: human lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) inhibitor

