Metabolism
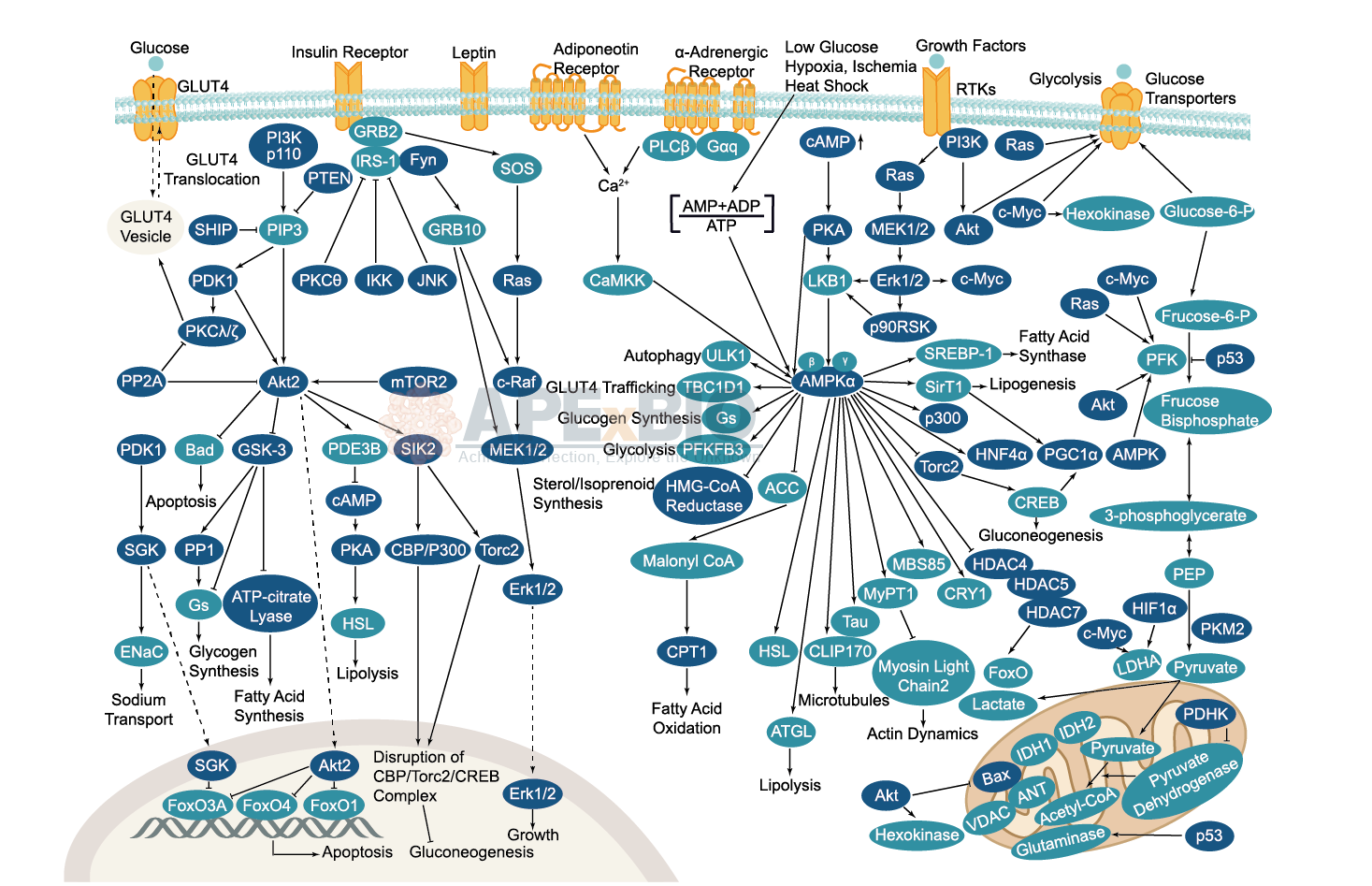
Serine/threonine kinase AMPK upregulates glucose uptake by promoting the expression and function of glucose transporters. AMPK is activated by increased AMP/ATP ratio, resulting from cellular and environmental stress, e.g. low glucose, heat shock, hypoxia and ischemia. AMPK activation positively modulates signaling transductions that refill ATP levels. Moreover, it also stimulates catabolic processes such as fatty acid oxidation and glycolysis through inhibition of ACC and activation of PFK2. AMPK negatively regulates various proteins which are important to ATP-consuming mechanisms, e.g. mTORC2, glycogen synthase, SREBP-1, and TSC2, causing the downregulation/inhibition of gluconeogenesis and glycogen, lipid and protein synthesis.
-
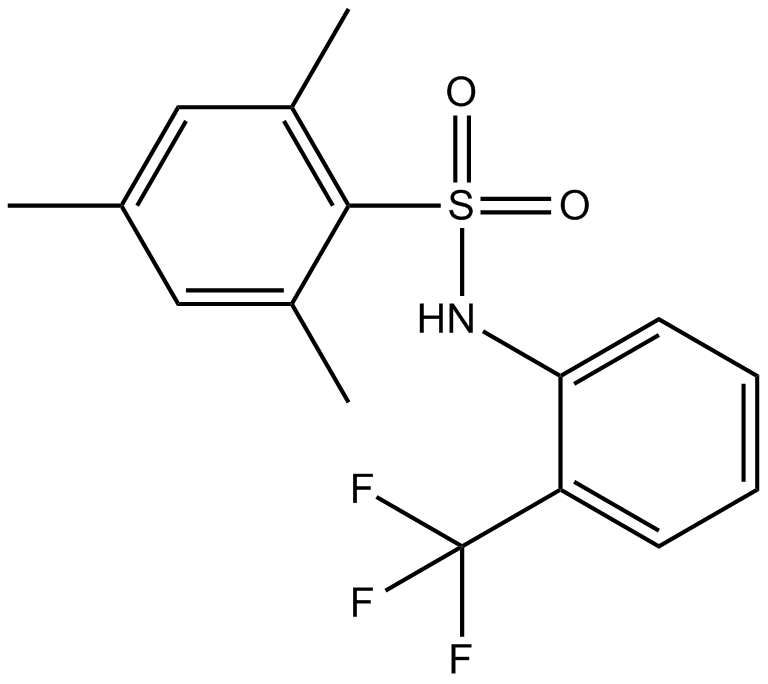 B6894 o-3M3FBSSummary: Inactive analog of m-3M3FBS (PLC activator)
B6894 o-3M3FBSSummary: Inactive analog of m-3M3FBS (PLC activator) -
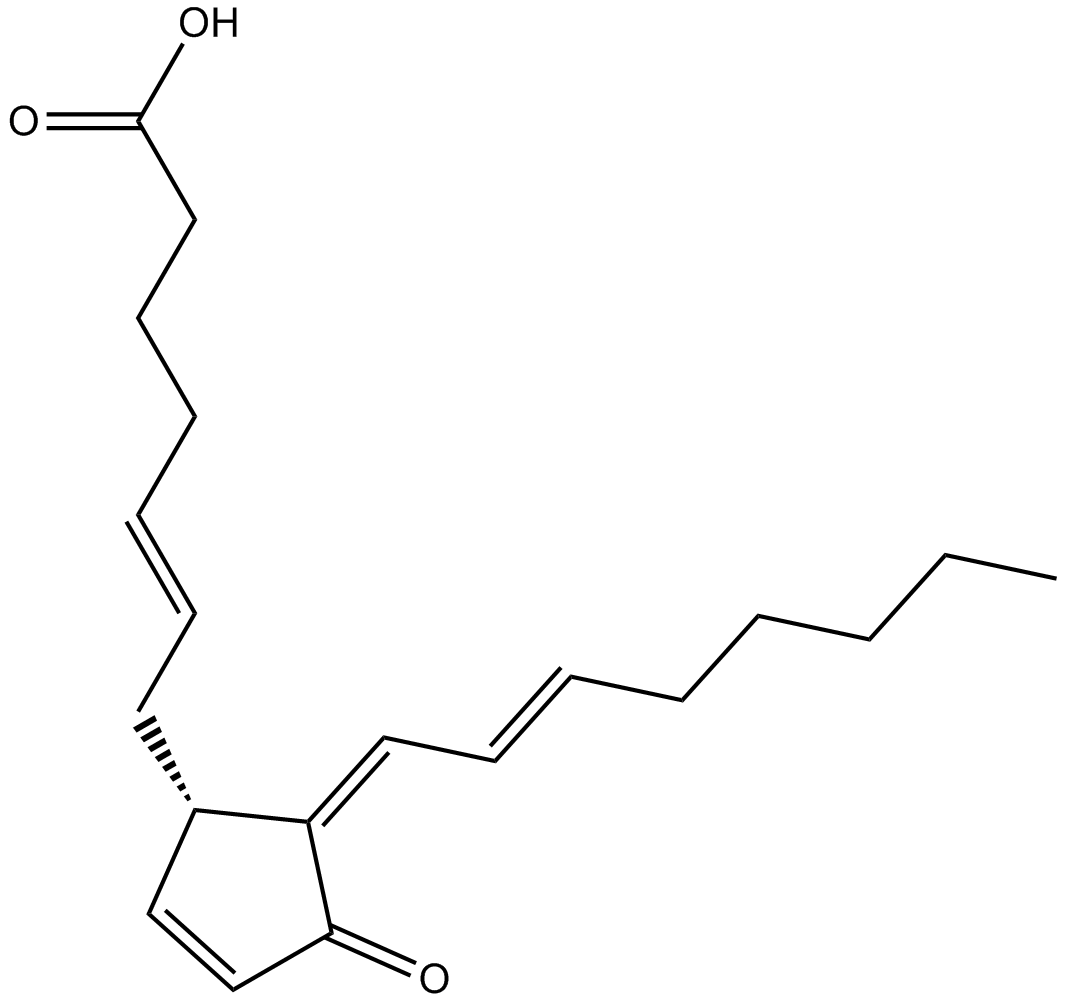 B7010 15-deoxy-Δ-12,14-Prostaglandin J2Target: PPARSummary: PPARγ agonist
B7010 15-deoxy-Δ-12,14-Prostaglandin J2Target: PPARSummary: PPARγ agonist -
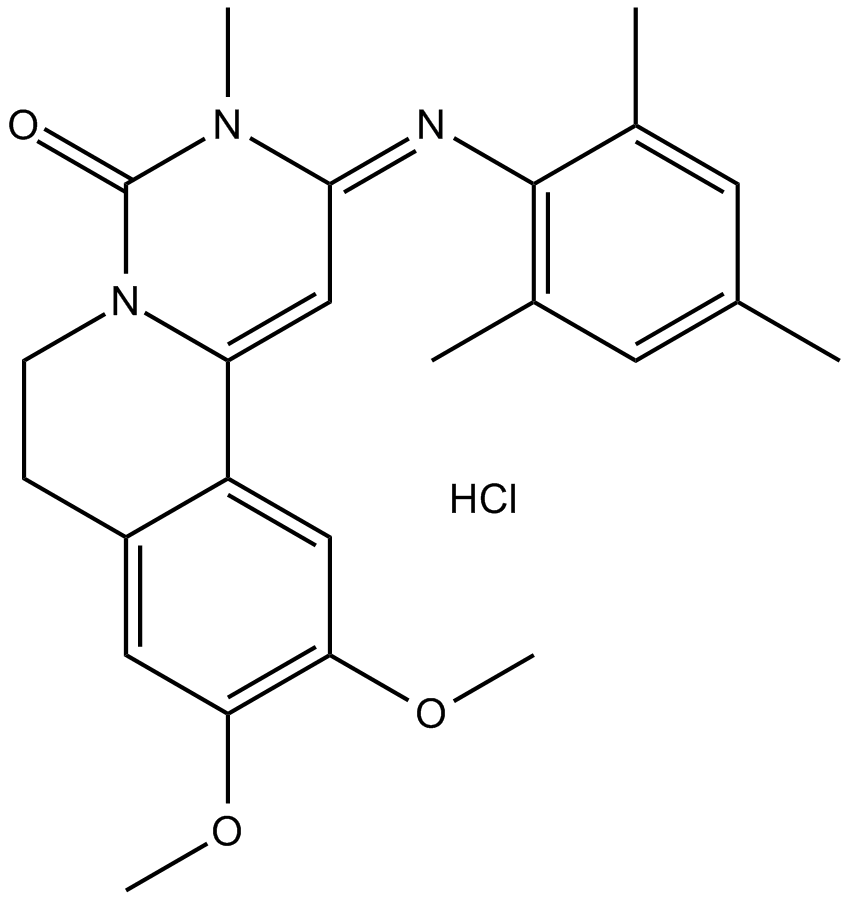 B7022 Trequinsin hydrochlorideSummary: PDE3 inhibitor
B7022 Trequinsin hydrochlorideSummary: PDE3 inhibitor -
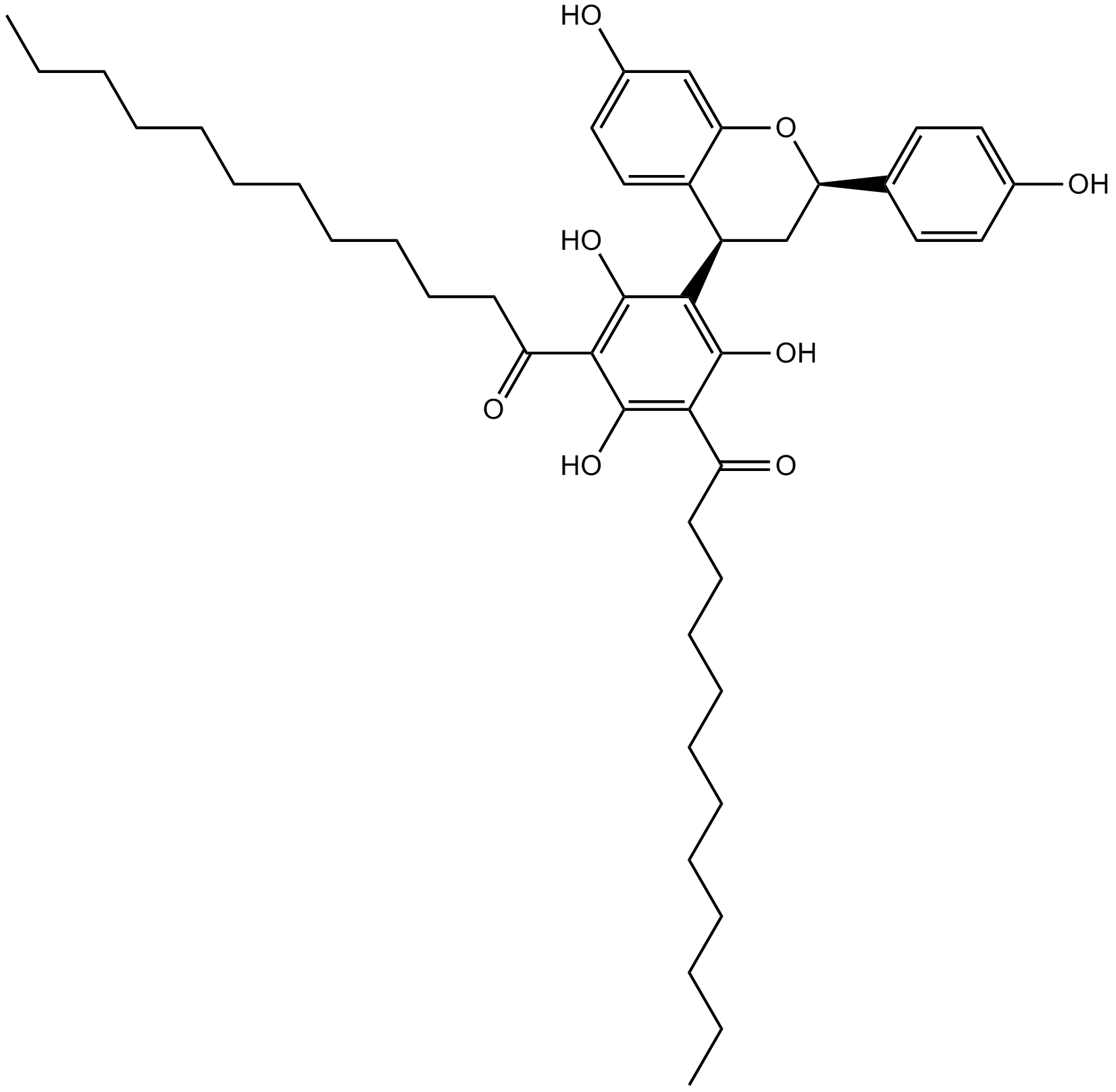 B7091 YM 26734Summary: Competitive inhibitor of secretory phospholipase A2 (sPLA2)
B7091 YM 26734Summary: Competitive inhibitor of secretory phospholipase A2 (sPLA2) -
 B7206 IBMX1 CitationSummary: Phosphodiesterase inhibitor
B7206 IBMX1 CitationSummary: Phosphodiesterase inhibitor -
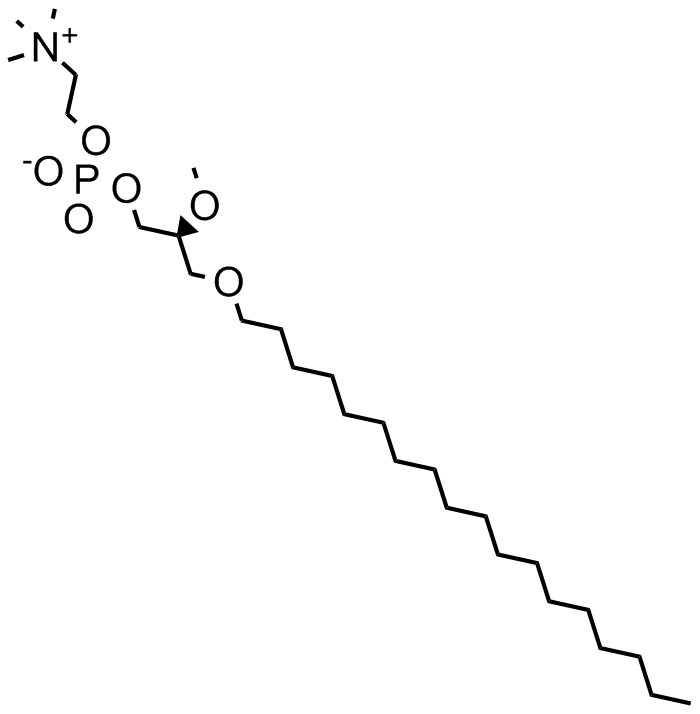 B7245 EdelfosineSummary: inhibits phosphatidylinositol phospholipase C
B7245 EdelfosineSummary: inhibits phosphatidylinositol phospholipase C -
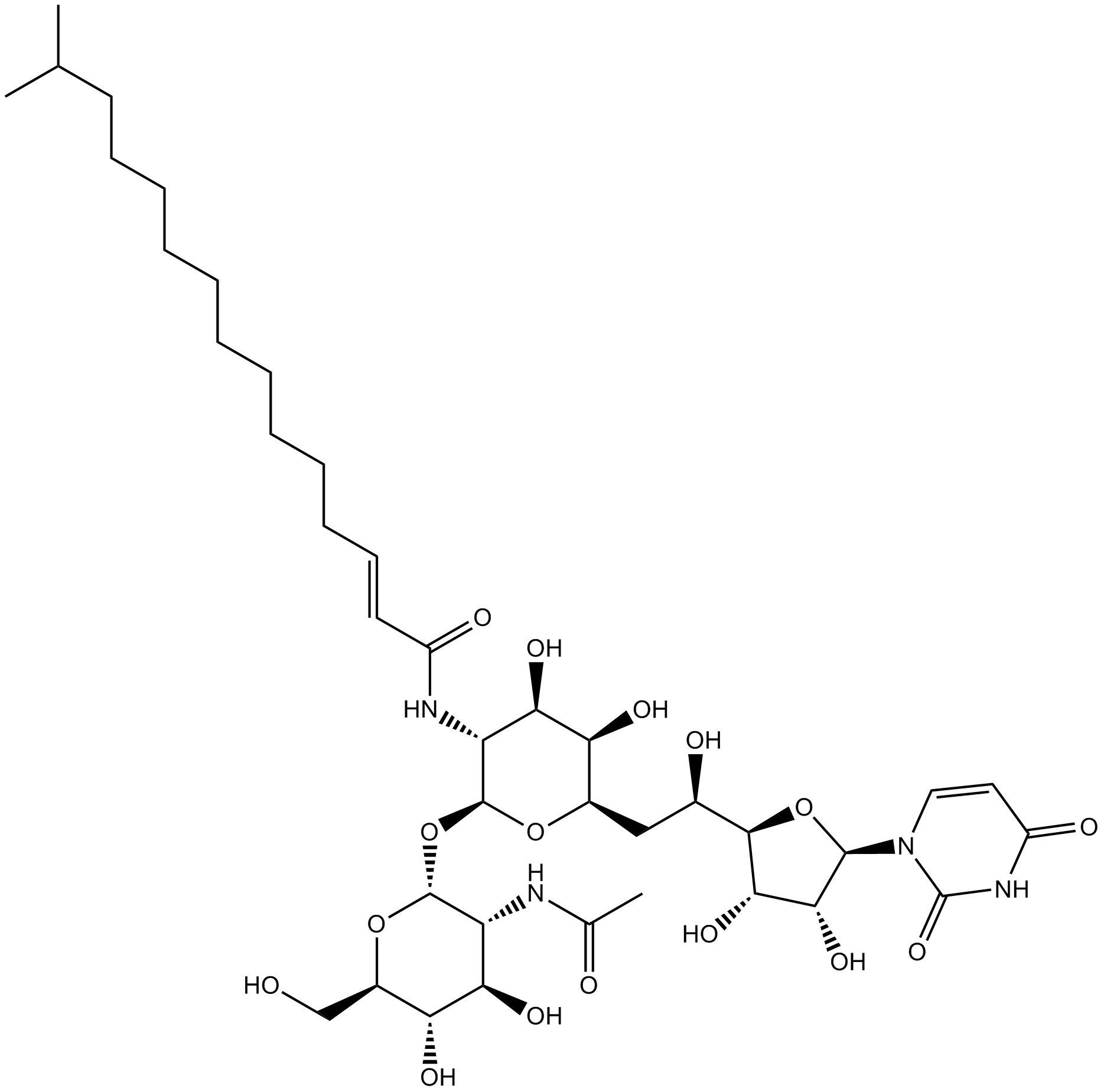 B7417 Tunicamycin15 CitationSummary: antibiotic,inhibits GlcNAc phosphotransferase (GPT)
B7417 Tunicamycin15 CitationSummary: antibiotic,inhibits GlcNAc phosphotransferase (GPT) -
 B7447 LY 311727Summary: secreted phospholipase A2 (sPLA2) inhibitor
B7447 LY 311727Summary: secreted phospholipase A2 (sPLA2) inhibitor -
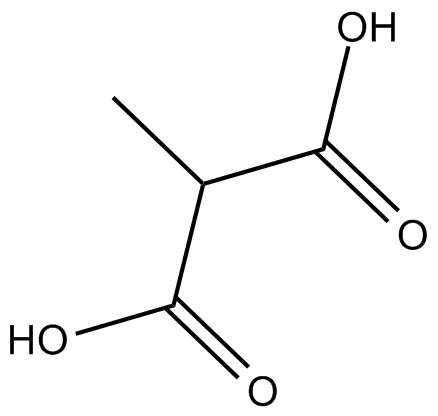 B7725 MethylmalonateSummary: reversible succinate dehydrogenase inhibitor
B7725 MethylmalonateSummary: reversible succinate dehydrogenase inhibitor -
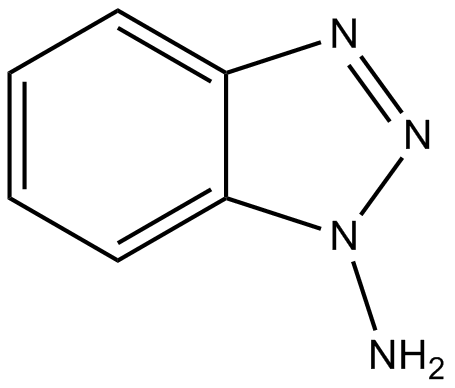 B7737 ABTSummary: Cytochrome P450 inhibitor
B7737 ABTSummary: Cytochrome P450 inhibitor

