Metabolism
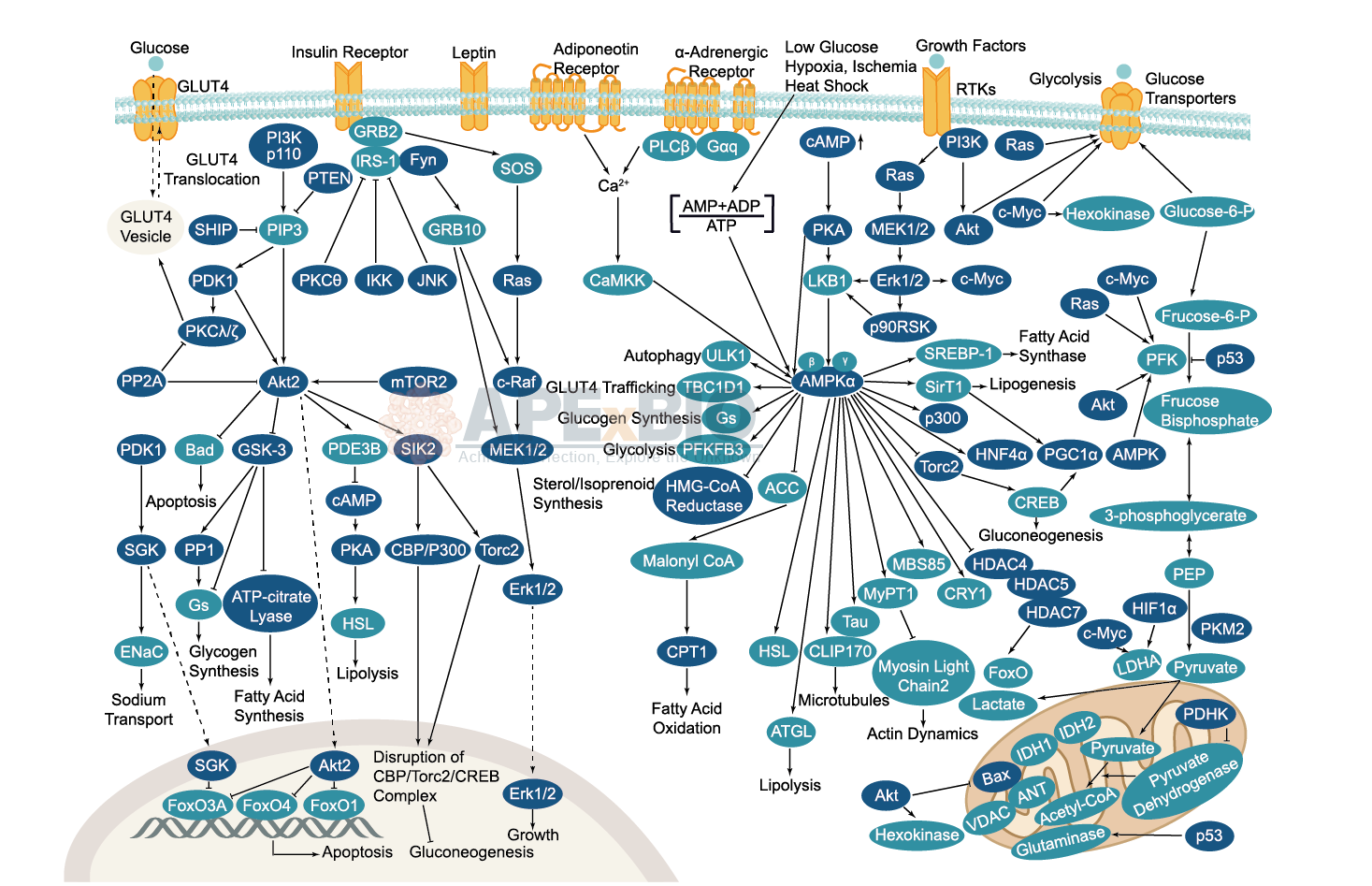
Serine/threonine kinase AMPK upregulates glucose uptake by promoting the expression and function of glucose transporters. AMPK is activated by increased AMP/ATP ratio, resulting from cellular and environmental stress, e.g. low glucose, heat shock, hypoxia and ischemia. AMPK activation positively modulates signaling transductions that refill ATP levels. Moreover, it also stimulates catabolic processes such as fatty acid oxidation and glycolysis through inhibition of ACC and activation of PFK2. AMPK negatively regulates various proteins which are important to ATP-consuming mechanisms, e.g. mTORC2, glycogen synthase, SREBP-1, and TSC2, causing the downregulation/inhibition of gluconeogenesis and glycogen, lipid and protein synthesis.
-
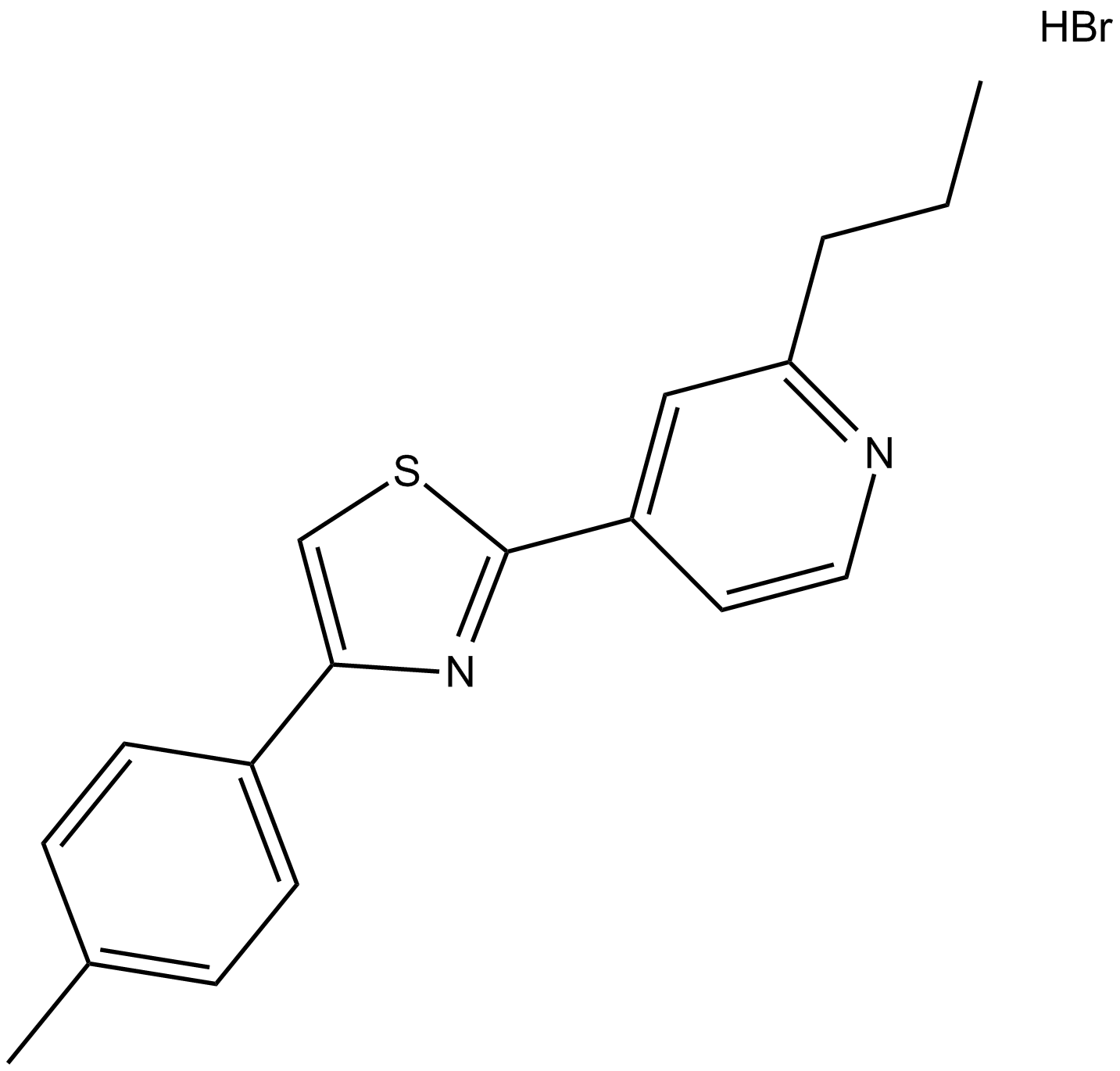 B5599 Fatostatin ASummary: sterol regulatory element binding protein (SREBP) inhibitor
B5599 Fatostatin ASummary: sterol regulatory element binding protein (SREBP) inhibitor -
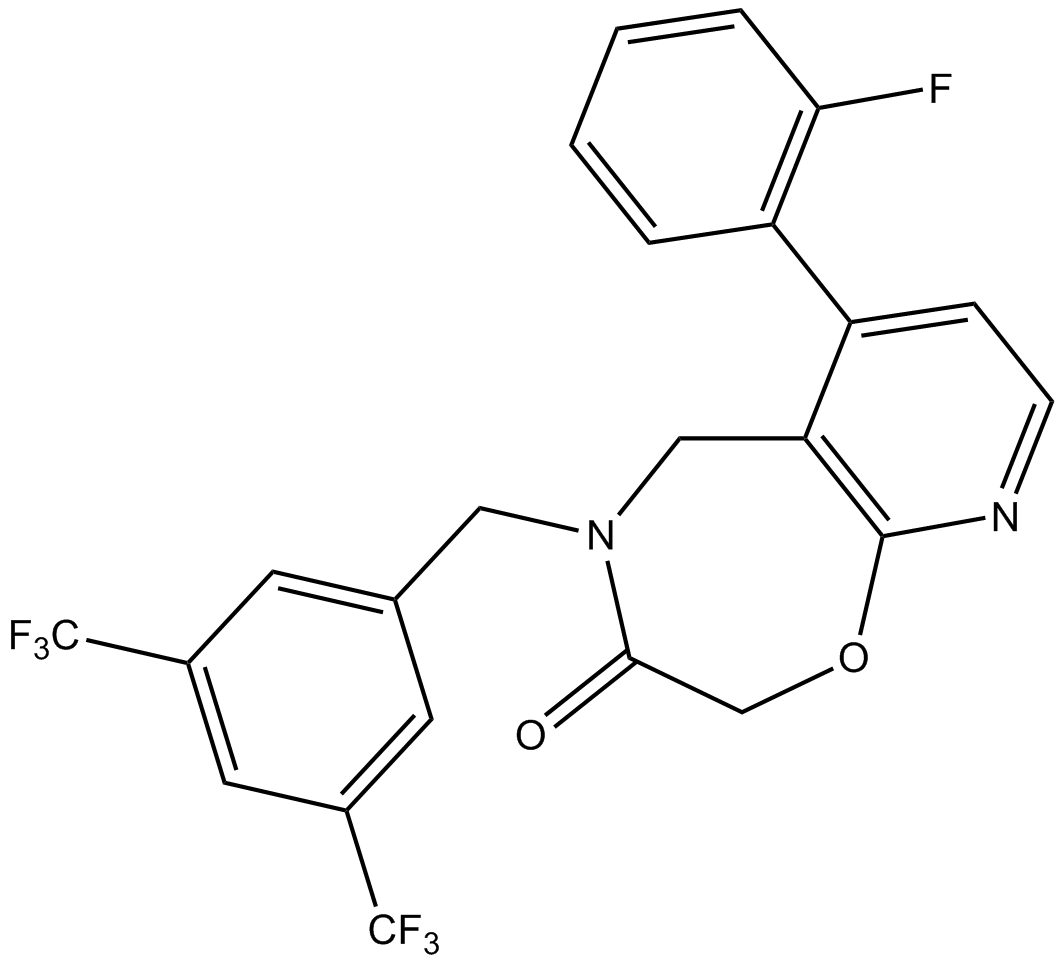 B5616 GPBAR-ASummary: agonist of bile acid receptor GPBAR1
B5616 GPBAR-ASummary: agonist of bile acid receptor GPBAR1 -
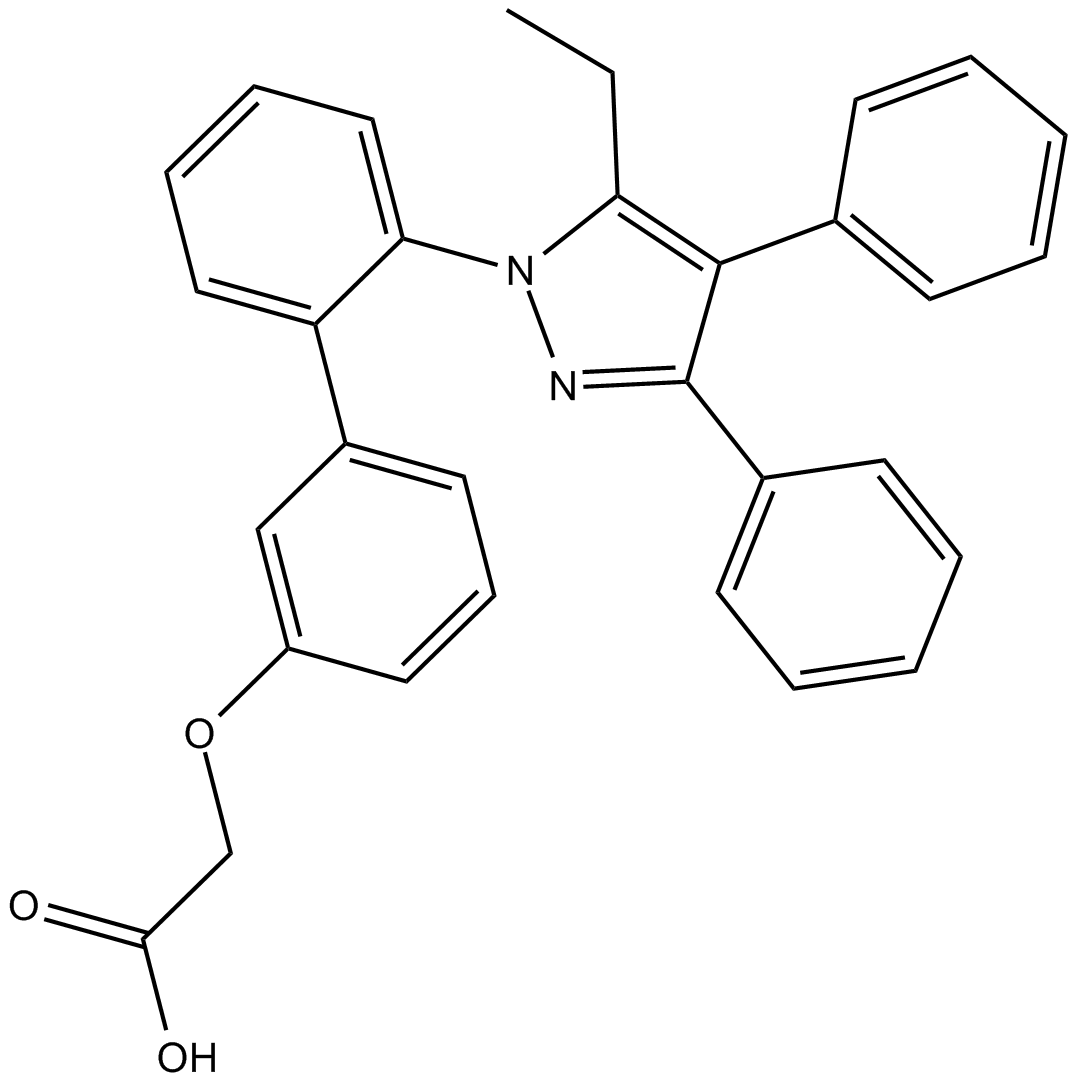 B7794 BMS 3094032 CitationTarget: Fatty-acid-binding proteins (FABPs)Summary: FABP4 inhibitor,potent and selective
B7794 BMS 3094032 CitationTarget: Fatty-acid-binding proteins (FABPs)Summary: FABP4 inhibitor,potent and selective -
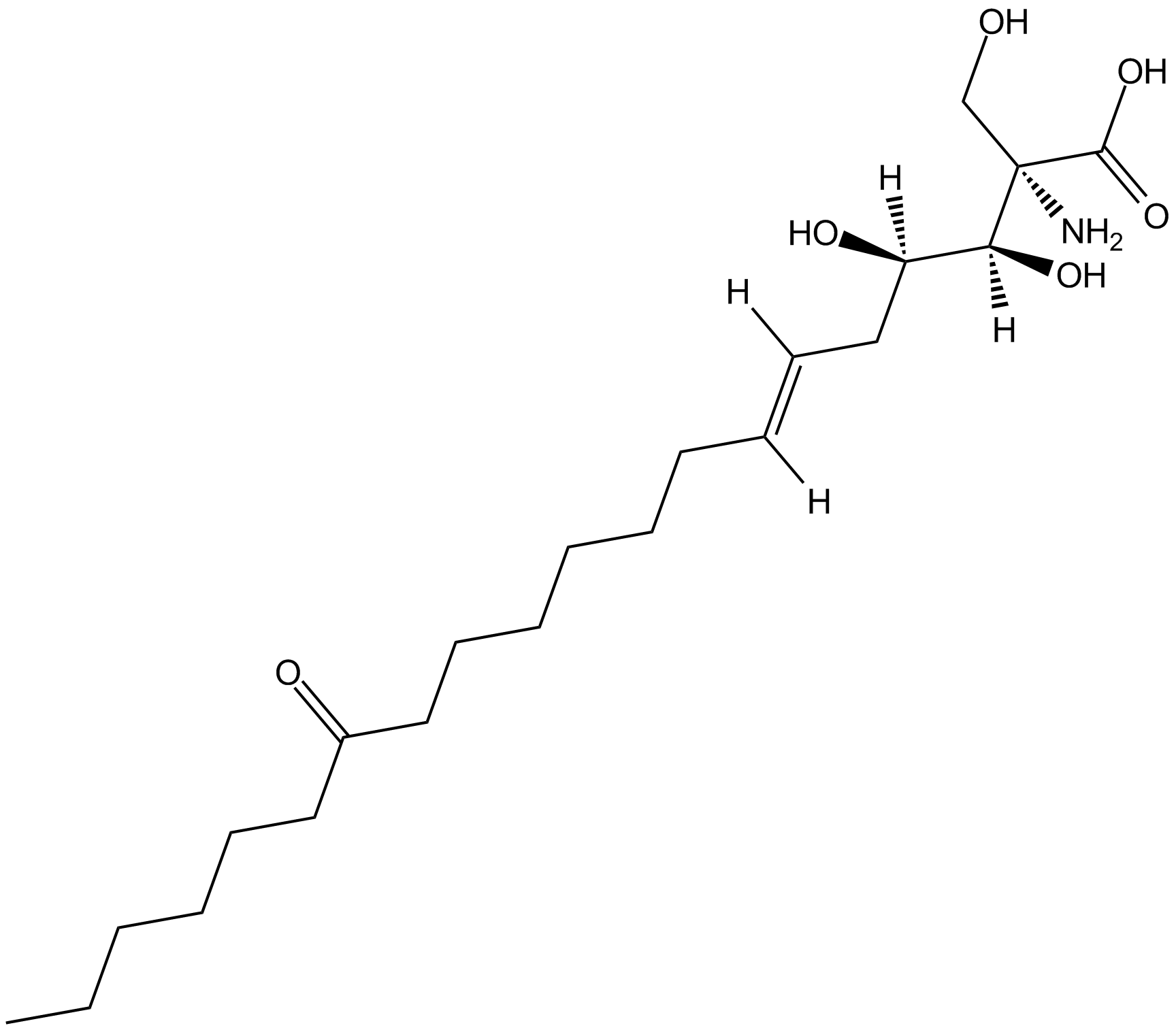 B6064 MyriocinSummary: immunosuppressant and specific serine palmitoyltransferase inhibitor
B6064 MyriocinSummary: immunosuppressant and specific serine palmitoyltransferase inhibitor -
 B6095 RSL31 CitationTarget: glutathione peroxidase 4Summary: glutathione peroxidase 4 inhibitor
B6095 RSL31 CitationTarget: glutathione peroxidase 4Summary: glutathione peroxidase 4 inhibitor -
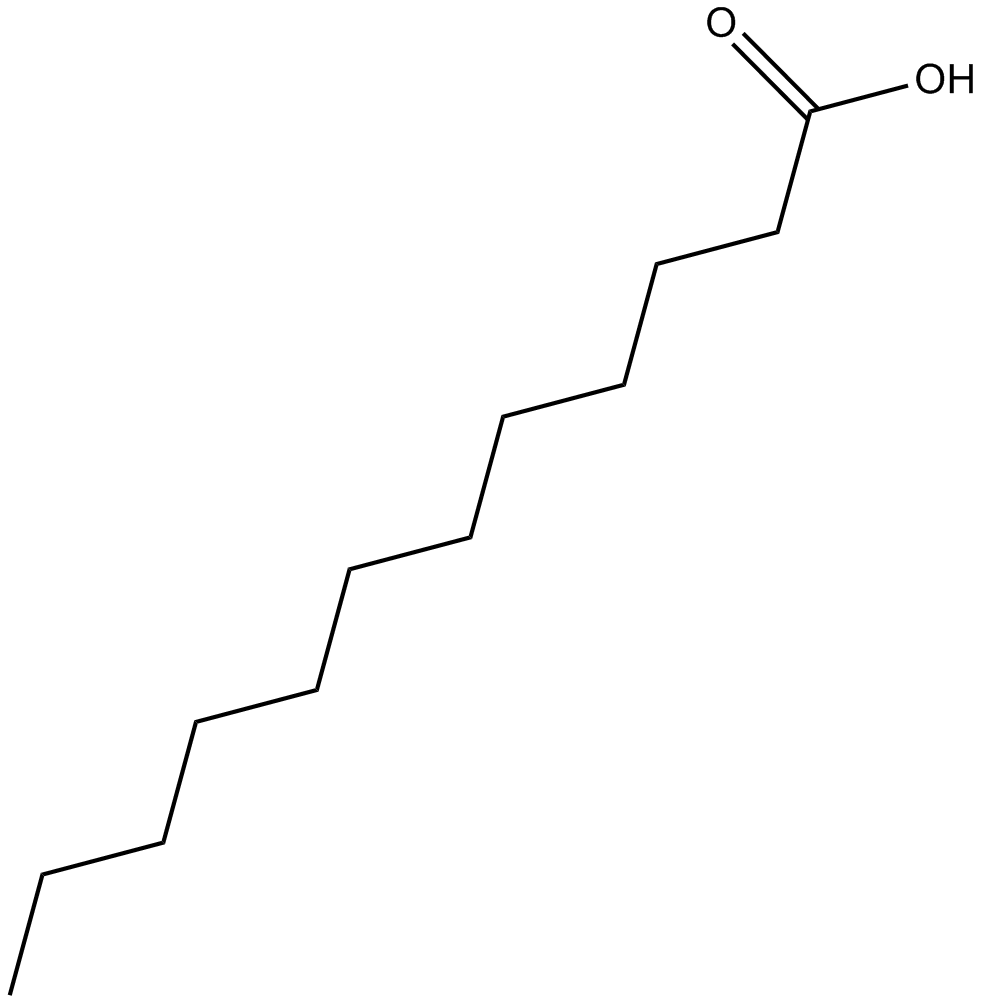 B6155 Lauric AcidSummary: saturated medium-chain fatty acid
B6155 Lauric AcidSummary: saturated medium-chain fatty acid -
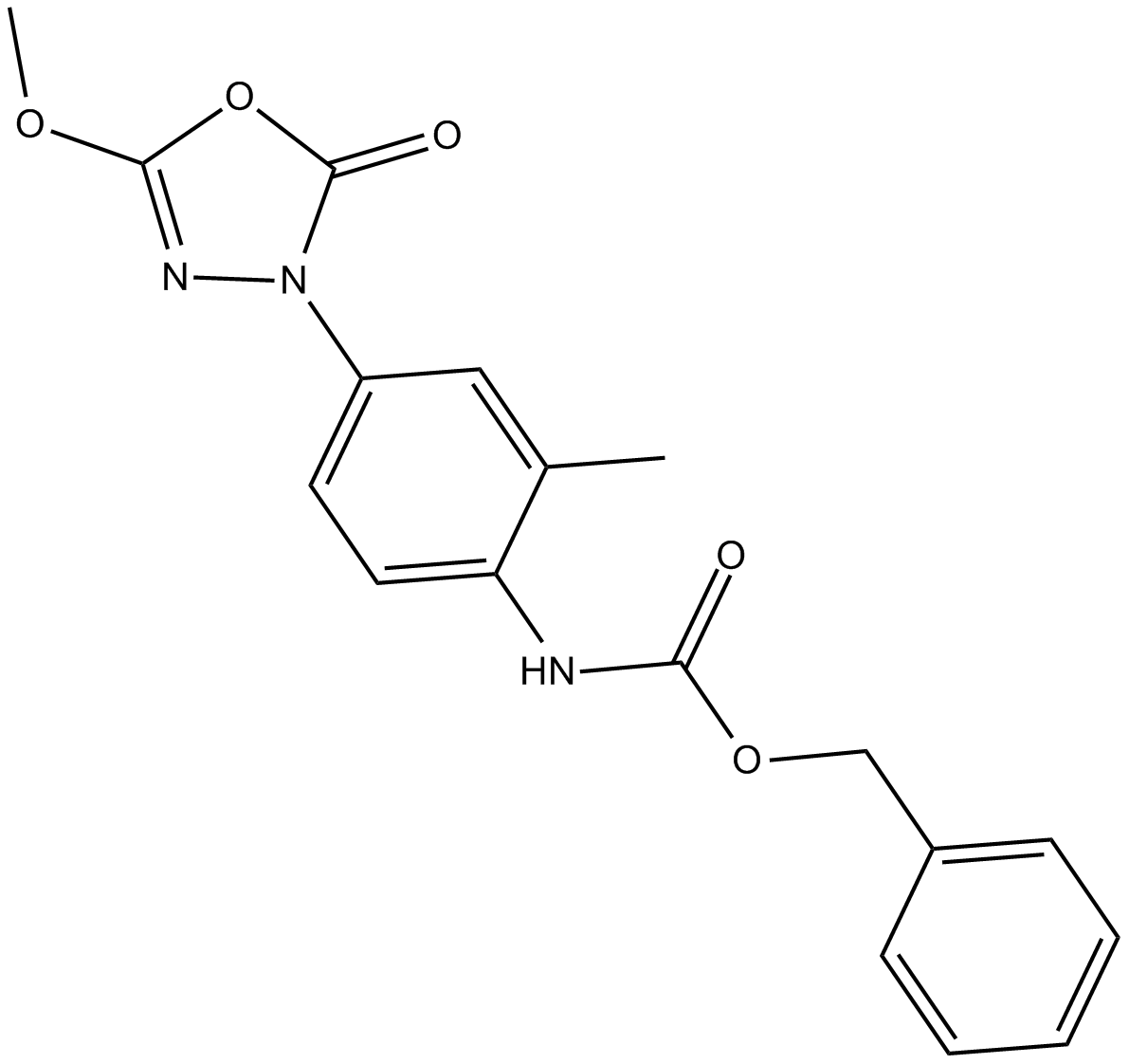 B7841 CAY10499Summary: inhibitor of human hormone sensitive lipase
B7841 CAY10499Summary: inhibitor of human hormone sensitive lipase -
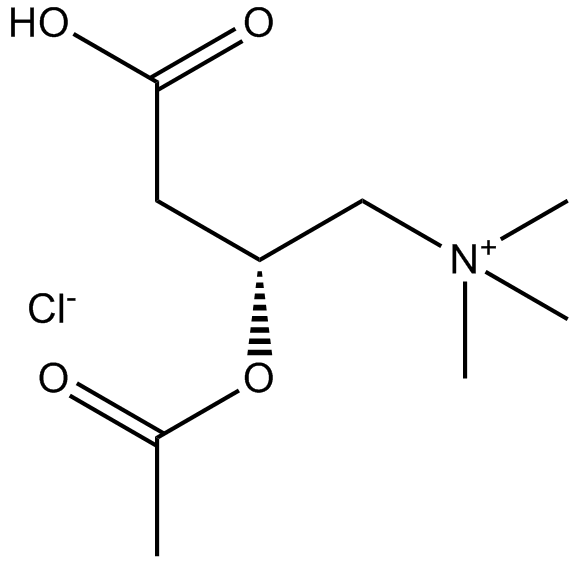 B6273 (±)-Acetylcarnitine chlorideSummary: weak cholinergic agonist; intermediates in lipid metabolism
B6273 (±)-Acetylcarnitine chlorideSummary: weak cholinergic agonist; intermediates in lipid metabolism -
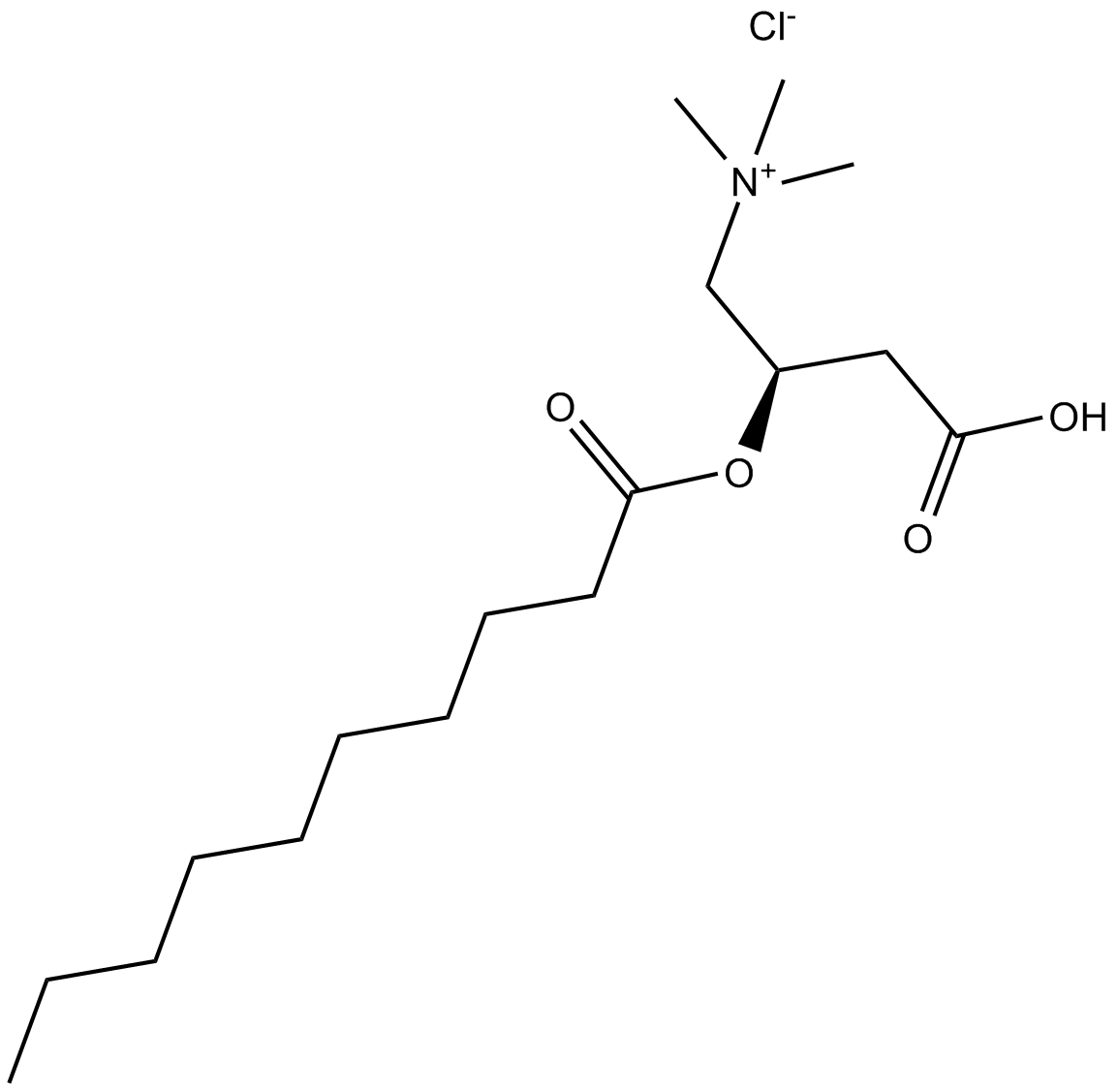 B6315 (±)-Decanoylcarnitine chlorideSummary: intermediate in lipid metabolism
B6315 (±)-Decanoylcarnitine chlorideSummary: intermediate in lipid metabolism -
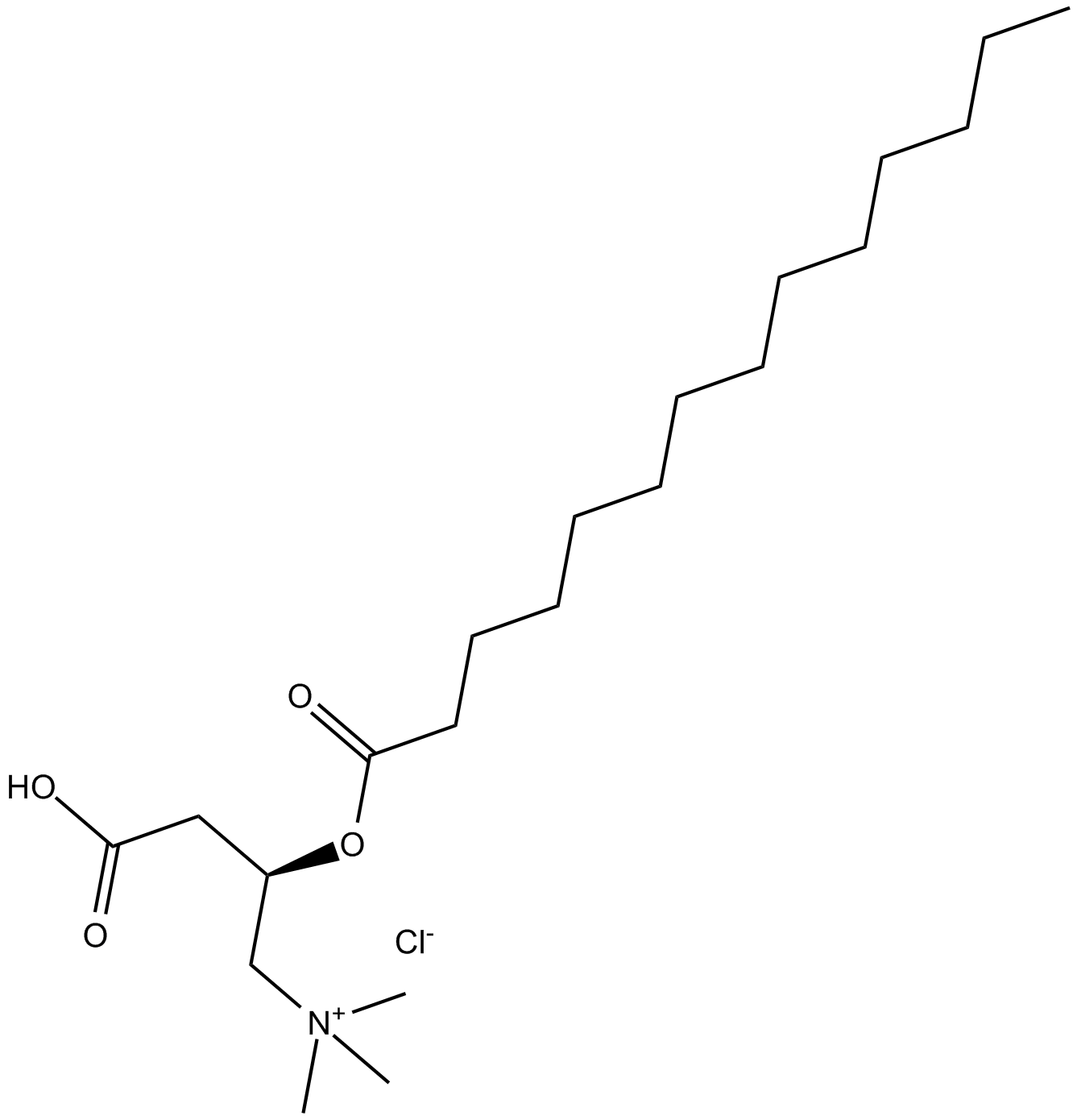 B6354 (±)-Myristoylcarnitine chlorideSummary: cholinergic agonist; important intermediates in lipid metabolism
B6354 (±)-Myristoylcarnitine chlorideSummary: cholinergic agonist; important intermediates in lipid metabolism

