RG7112
RG7112(CAS 939981-39-2) is a selective inhibitor of p53-MDM2 binding that frees p53 from negative control, activating the p53 pathway in cancer cells, leading to cell cycle arrest and apoptosis. [1]
P53 is a potent tumor suppressor that activates the transcription of a subset of genes controlling cell-cycle progression and apoptosis. MDM2 is a negative regulator of p53 that binds the transactivation domain of p53 and inhibits its ability to activate transcription. MDM2 is also an E3 ubiquitin ligase that targets p53 for proteosomal degradation. MDM2 overexpression is one of the mechanisms by which the wild-type p53 function is impaired. [2]
RG7112 has been profiled extensively in many cell lines. In 15 cancer cell lines expressing wild-type p53, shows IC50 is in the range of 0.18 - 2.2 μM. However, the inhibition is much less in seven cancer cell lines with p53 mutation, IC50 5.7 - 20.3 μM. The overall selectivity is 14-fold.
In the animal models, RG7112-induced thrombocytopenia occurred rather late during the treatment period and persisted after drug discontinuation, suggesting that the drug acts on early hematopoietic progenitor cells. This is supported by the RG7112 ability to inhibit CFU-MK colony formation by the CD34t cells in vitro. Administration of RG7112 in rats and monkeys reduces WBC counts and, to a lesser extent, hemoglobin levels. In patients treated with RG7112, neutropenia is among the serious adverse events while anemia occurred only in 2 of 20 patients. Interestingly, when tested in vitro, the same concentration of RG7112 that reduced CFU-MK colony formation do not significantly affect the formation of BFU-E and CFU-GM derived colonies.
References:
[1] Hernan Carol, C. Patrick Reynolds, Min H. Kang et al. Initial Testing of the MDM2 Inhibitor RG7112 by the Pediatric Preclinical Testing Program. Pediatr Blood Cancer 2013;60:633–641
[2] Binh Vu, Peter Wovkulich, Giacomo Pizzolato et al. Discovery of RG7112: A Small-Molecule MDM2 Inhibitor in Clinical Development. ACS Med. Chem. Lett. 2013, 4, 466?469
[3] Camelia Iancu-Rubina, Goar Mosoyana, Kelli Glenn et al. Activation of p53 by the MDM2 inhibitor RG7112 impairs thrombopoiesis. Experimental Hematology 2014;42:137–145
- 1. Makii C, Ikeda Y, et al. ”Anti-tumor activity of dual inhibition of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase and MDM2 against clear cell ovarian carcinoma." Gynecol Oncol. 2019 Nov;155(2):331-339. PMID:31493899
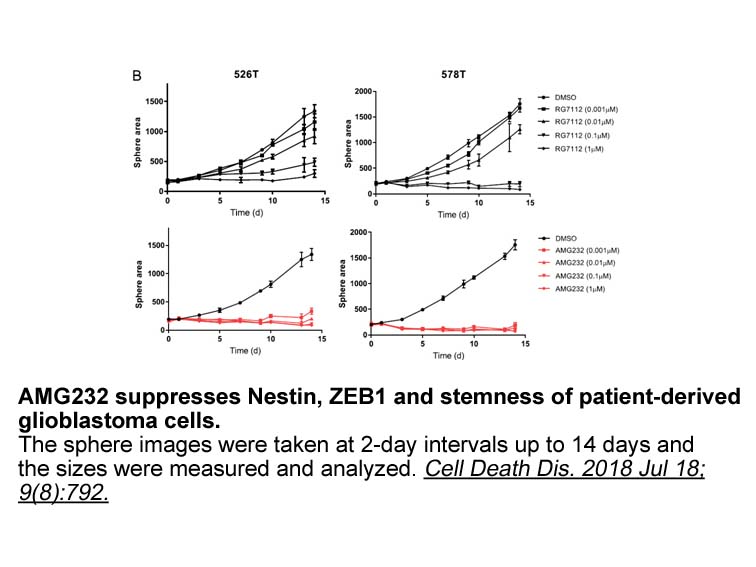
- 2. Her NG, Oh JW, et al. "Potent effect of the MDM2 inhibitor AMG232 on suppression of glioblastoma stem cells." Cell Death Dis. 2018 Jul 18;9(8):792. PMID:30022047
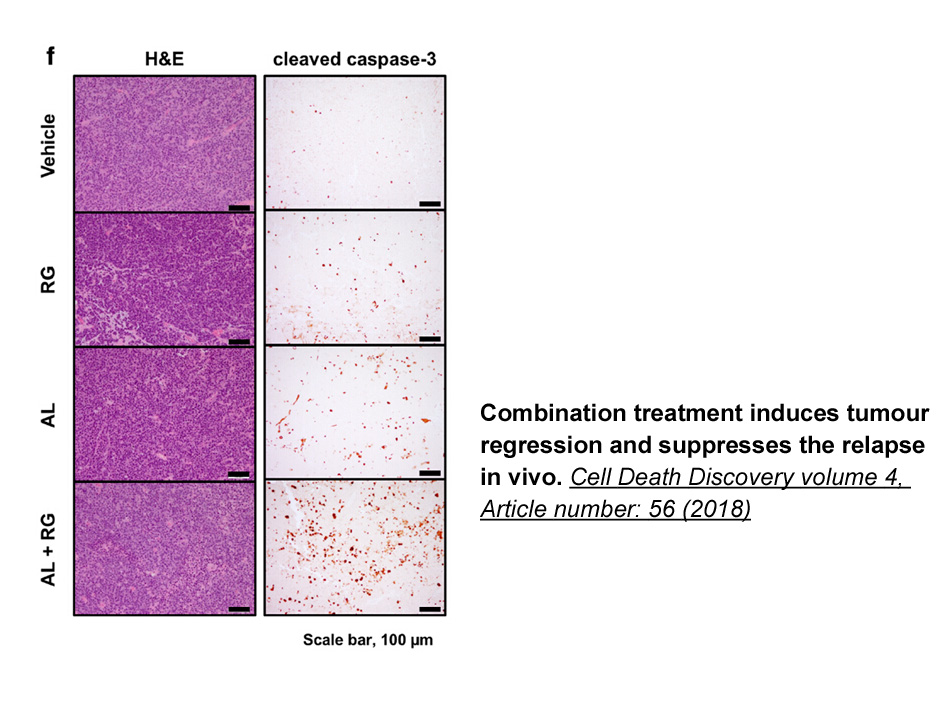
- 3. Miyazaki M, Otomo R, et al. "The p53 activator overcomes resistance to ALK inhibitors by regulating p53-target selectivity in ALK-driven neuroblastomas." Cell Death Discov. 2018 May 10;4:56. PMID:29760954
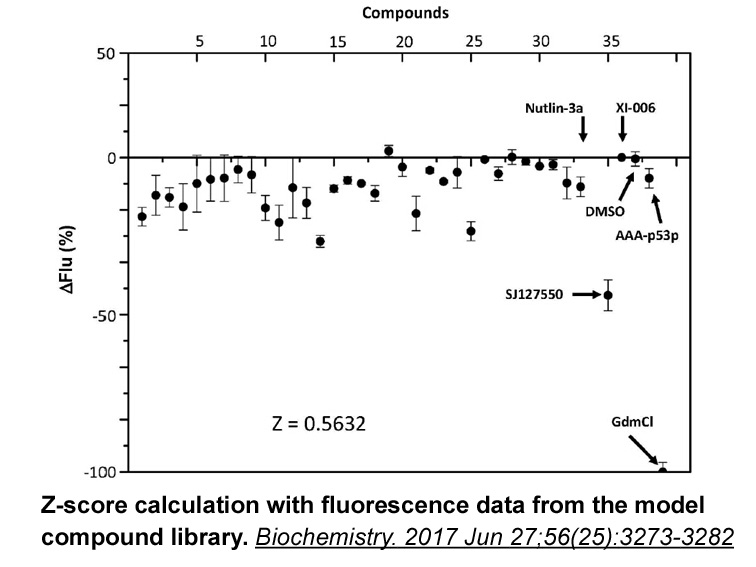
- 4. Chen R, Zhou J, et al. "A Fusion Protein of the p53 Transaction Domain and the p53-Binding Domain of the Oncoprotein MdmX as an Efficient System for High-Throughput Screening of MdmX Inhibitors." Biochemistry. 2017 Jun 27;56(25):3273-3282. PMID:28581721
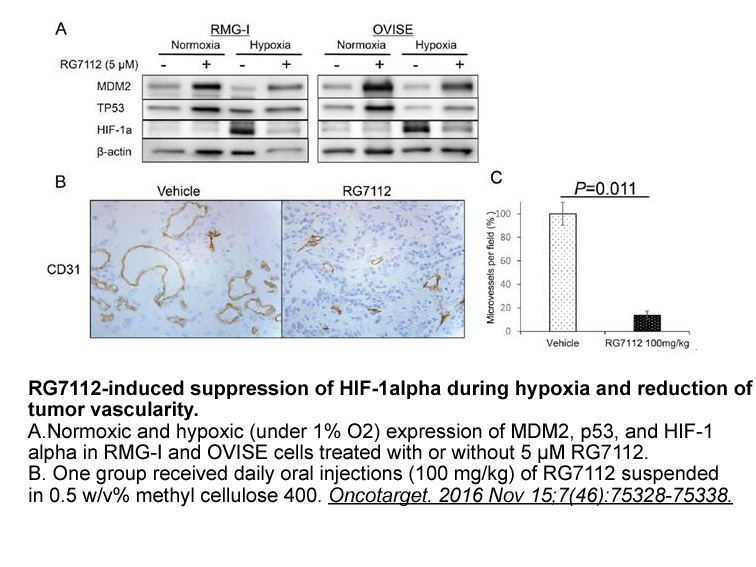
- 5. Makii C, Oda K, et al. "MDM2 is a potential therapeutic target and prognostic factor for ovarian clear cell carcinomas with wild type TP53." Oncotarget. 2016 Nov 15;7(46):75328-75338. PMID:27659536
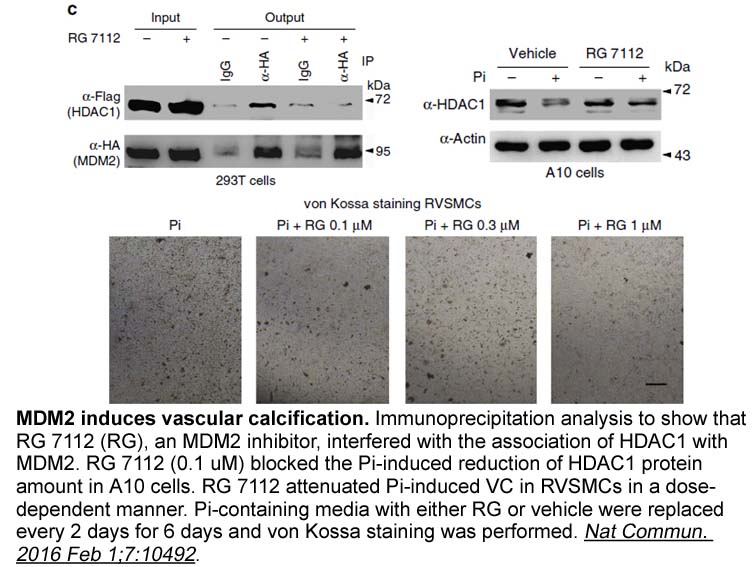
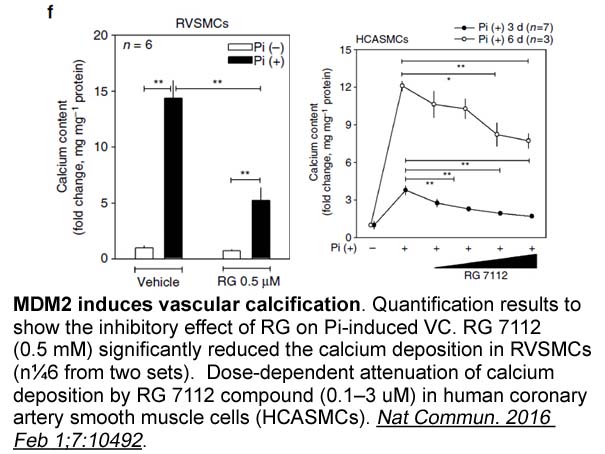
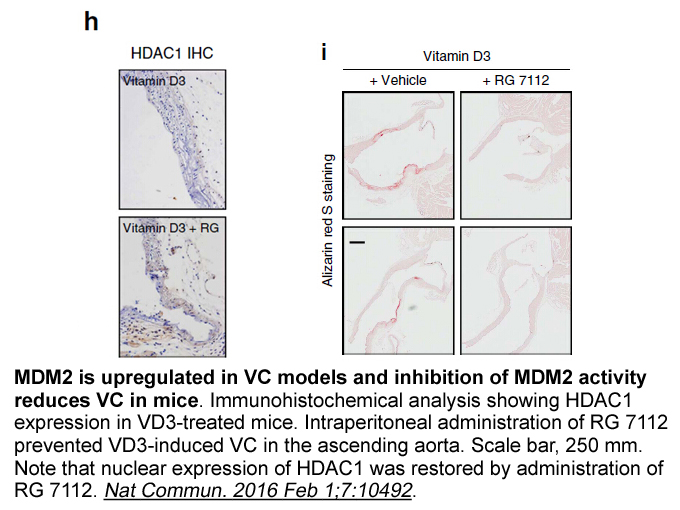
- 6. Kwon DH, Eom GH, et al. "MDM2 E3 ligase-mediated ubiquitination and degradation of HDAC1 in vascular calcification." Nat Commun.2016 Feb 1;7:10492. PMID:26832969
| Physical Appearance | A solid |
| Storage | Store at -20°C |
| M.Wt | 727.78 |
| Cas No. | 939981-39-2 |
| Formula | C38H48Cl2N4O4S |
| Synonyms | RG-7112;RG 7112 |
| Solubility | ≥36.4 mg/mL in DMSO; insoluble in H2O; ≥31.87 mg/mL in EtOH |
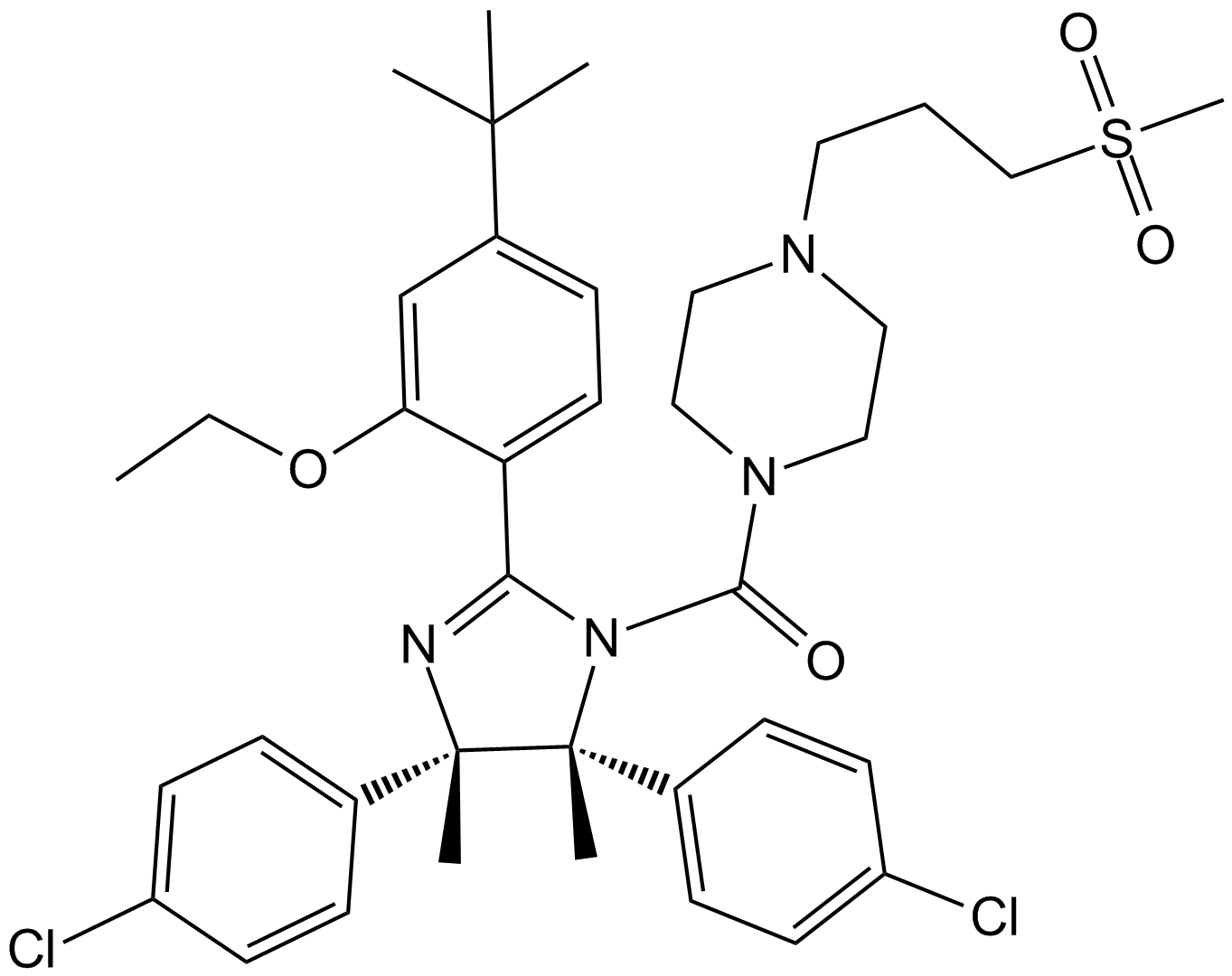
| Chemical Name | [(4S,5R)-2-(4-tert-butyl-2-ethoxyphenyl)-4,5-bis(4-chlorophenyl)-4,5-dimethylimidazol-1-yl]-[4-(3-methylsulfonylpropyl)piperazin-1-yl]methanone |
| SDF | Download SDF |
| Canonical SMILES | CCOC1=C(C=CC(=C1)C(C)(C)C)C2=NC(C(N2C(=O)N3CCN(CC3)CCCS(=O)(=O)C)(C)C4=CC=C(C=C4)Cl)(C)C5=CC=C(C=C5)Cl |
| Shipping Condition | Small Molecules with Blue Ice, Modified Nucleotides with Dry Ice. |
| General tips | We do not recommend long-term storage for the solution, please use it up soon. |
| Cell experiment [1]: | |
|
Cell lines |
SJSA1 osteosarcoma cells |
|
Preparation method |
The solubility of this compound in DMSO is >10 mM. General tips for obtaining a higher concentration: Please warm the tube at 37 °C for 10 minutes and/or shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20°C for several months. |
|
Reaction Conditions |
24 h; 10 μM |
|
Applications |
Treatment of cultured cancer cells with RG7112 led to concentration-dependent accumulation of p53 protein and its transcriptional targets, p21 and MDM2. RG7112 dose dependently inhibited the growth and killed SJSA1 osteosarcoma cells expressing high-levels of MDM2 protein due to MDM2 gene ampli fication |
| Animal experiment [1]: | |
|
Animal models |
Female Balb/c nude mice |
|
Dosage form |
200 mg/kg; oral taken |
|
Applications |
Pharmocodynamic effects of RG7112 were assessed in the SJSA1 xenograft model. To assess the ability of RG7112 to activate p53 response in vivo, SJSA1 tumor-bearing mice were treated with a single dose of vehicle or 50 to 200 mg/kg RG7112 for 4 to 24 hours. Western blot analysis showed a dose-dependent increase in p53 protein and its targets, p21 and MDM2. The p53 protein levels were highest at 4 hours after dose and continue to persist at 24 hours at the highest dose level (200 mg/kg), whereas the duration of p53 modulation was shorter at lower dose levels. |
|
Other notes |
Please test the solubility of all compounds indoor, and the actual solubility may slightly differ with the theoretical value. This is caused by an experimental system error and it is normal. |
|
References: [1] Tovar C, Graves B, Packman K, et al. MDM2 small-molecule antagonist RG7112 activates p53 signaling and regresses human tumors in preclinical cancer models[J]. Cancer research, 2013, 73(8): 2587-2597. |
|
| Description | RG7112 is the first clinical small-molecule inhibitor of MDM2. | |||||
| Targets | MDM2 | |||||
| IC50 | ||||||
Quality Control & MSDS
- View current batch:
Chemical structure
Related Biological Data
Related Biological Data
Related Biological Data
Related Biological Data
Related Biological Data
Related Biological Data
Related Biological Data