Nifedipine
Nifedipine (BAY-a-1040) is an efficient calcium channel blocker which blocked L-type calcium current with an IC50 of 0.3 µM [1]. In the heart, it is also a drug of choice for cardiac insufficiency.
Nifedipine (BAY-a-1040) is wildly used as a dihydropyridine derivative. It forms a stable complex with the binding site of L-type calcium receptors. Nifedipine preferentially blocks various cell types’ Ca2+ channels and reduces cytosolic Ca2+ concentrations to prevent Ca2+ influx into the cells [2]. Nifedipine can decrease heart muscle sensitively during activation of beta 1-adrenergic receptors [3].
Nifedipine (BAY-a-1040) (100 µM) strongly reduce the viability of the WKPT-0293 Cl.2 Cells, and cell viability is significantly reduced when treated with nifedipine (10 or 100 µM) plus FAC, but there are no obvious differences in viability between the control cells and the cells treated with 100 µM of FAC or 1 and 10 µM of nifedipine. Iron level is considerably increased by treatment of Nifedipine (BAY-a-1040) (1, 10, or 100 µM) in WKPT-0293 Cl.2 cells. Nifedipine treatment also increases TfR1, DMT1+IRE and DMT1-IRE expression in WKPT-0293 Cl.2 cells. In addition, co-treatment with nifedipine (100 µM) and FAC (100 µM) increases expression of TfR1, DMT1+IRE and DMT1-IRE in WKPT-0293 Cl.2 cells [4]. Nifedipine plus ritodrine produces a significantly greater inhibition of contractility comparing with each drug alone in the midrange of concentrations. Nifedipine plus NS-1619 (Ca2+-activated K+ [BKCa] channel opener) combination decreases the inhibitory effect of each drug [5]. Nifedipine (BAY-a-1040) (2 µM) strongly inhibits the growth and sporulation of P. capsici mycelial. Nifedipine (BAY-a-1040)-induced mycelial growth inhibition is calcium-dependent [6].
In Nifedipine (BAY-a-1040) (50 mg/kg)- and CsA-treated rats, the BL dimensions (BLi and BLk), MD dimensions (MDk) and vertical dimensions (VHi and VHk) are significantly increased (P < 0.05) at the end of the 4th week [7].
References:
[1]. Jian-Bing Shen, Bin Jiang and Achilles J. Pappano. Comparison of L-Type Calcium Channel Blockade by Nifedipine and/or Cadmium in Guinea Pig Ventricular Myocytes. Journal of Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics August 2000, 294 (2) 562-570;
[2]. Nguemo F., Fleischmann B. K., Gupta M. K., Šarić T., Malan D., Liang H., et al. (2013). The L-type Ca 2+ channels blocker nifedipine represses mesodermal fate determination in murine embryonic stem cells. PLoS One. 2013;8(1):e53407.
[3]. Legssyer AK, Hove-Madsen L, Hoerter J, Fischmeister R. Sympathetic modulation of the effect of nifedipine on myocardial contraction and Ca current in the rat. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 1997 Feb;29(2):579-91.
[4]. Yu SS, et al. Nifedipine Increases Iron Content in WKPT-0293 Cl.2 Cells via Up-Regulating Iron Influx Proteins. Front Pharmacol. 2017 Feb 13;8:60
[5]. Carvajal JA, et al. The Synergic In Vitro Tocolytic Effect of Nifedipine Plus Ritodrine on Human Myometrial Contractility. Reprod Sci. 2017 Apr;24(4):635- 640.
[6]. Liu P, et al. The L-type Ca2+ Channel Blocker Nifedipine Inhibits Mycelial Growth, Sporulation, and Virulence of Phytophthora capsici. Front Microbiol. 2016 Aug 4;7:1236.
[7]. Ratre MS, et al. Effect of azithromycin on gingival overgrowth induced by cyclosporine A + nifedipine combination therapy: A morphometric analysis in rats. J Indian Soc Periodontol. 2016 Jul-Aug;20(4):396-401.
- 1. Hüseyin Gül, Jamie A Davies, et al. "Targeting TRPM3 as a potential therapeutic approach for autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease." Sci Rep. 2025 Feb 8;15(1):4714. PMID: 39922884
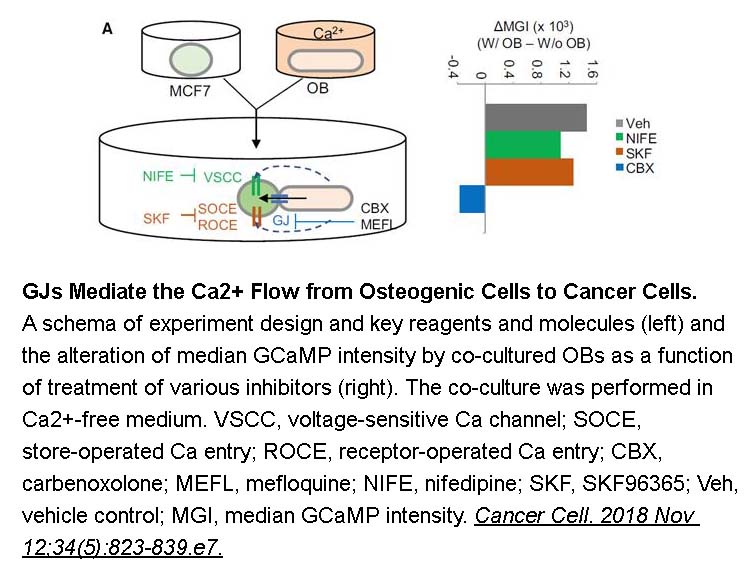
- 2. Wang H, Tian L, et al. "The Osteogenic Niche Is a Calcium Reservoir of Bone Micrometastases and Confers Unexpected Therapeutic Vulnerability." Cancer Cell. 2018 Nov 12;34(5):823-839.e7. PMID:30423299
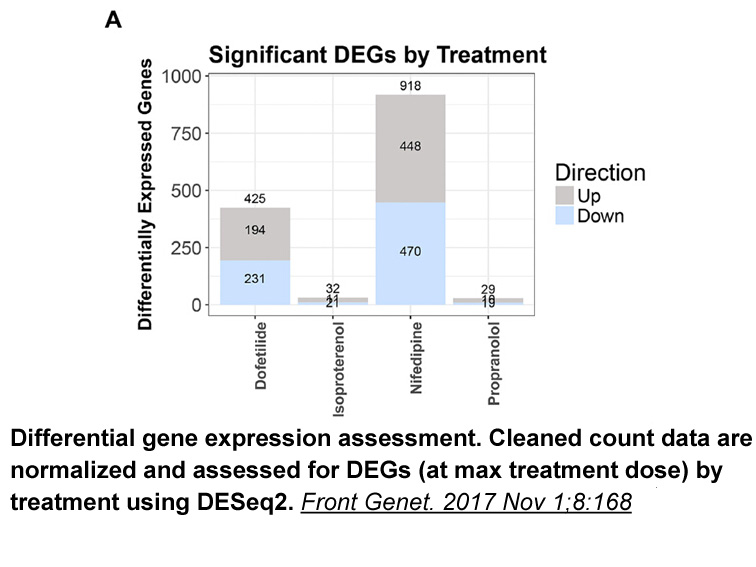
- 3 House JS, Grimm FA, Jet al. "A Pipeline for High-Throughput Concentration Response Modeling of Gene Expression for Toxicogenomics." Front Genet. 2017 Nov 1;8:168. PMID:29163636
| Storage | Store at -20°C |
| M.Wt | 346.33 |
| Cas No. | 21829-25-4 |
| Formula | C17H18N2O6 |
| Solubility | insoluble in H2O; ≥15.75 mg/mL in DMSO; ≥7.14 mg/mL in EtOH with ultrasonic |
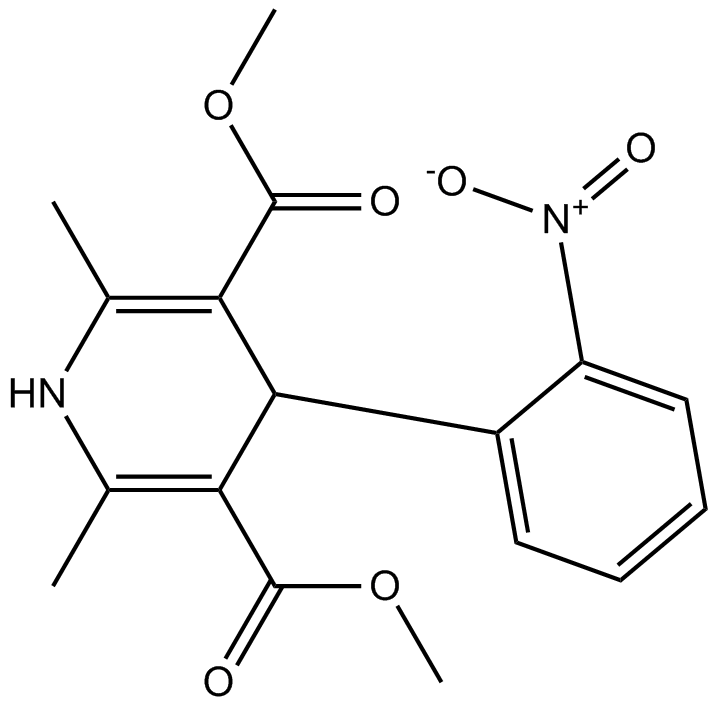
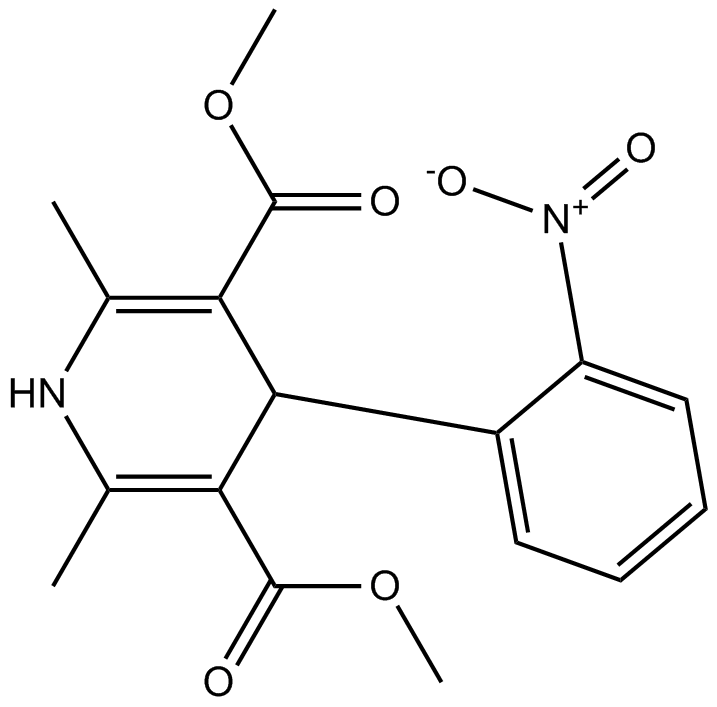
| Chemical Name | dimethyl 2,6-dimethyl-4-(2-nitrophenyl)-1,4-dihydropyridine-3,5-dicarboxylate |
| SDF | Download SDF |
| Canonical SMILES | CC(NC(C)=C(C1c(cccc2)c2[N+]([O-])=O)C(OC)=O)=C1C(OC)=O |
| Shipping Condition | Small Molecules with Blue Ice, Modified Nucleotides with Dry Ice. |
| General tips | We do not recommend long-term storage for the solution, please use it up soon. |
Quality Control & MSDS
- View current batch:
Chemical structure
Related Biological Data
Related Biological Data