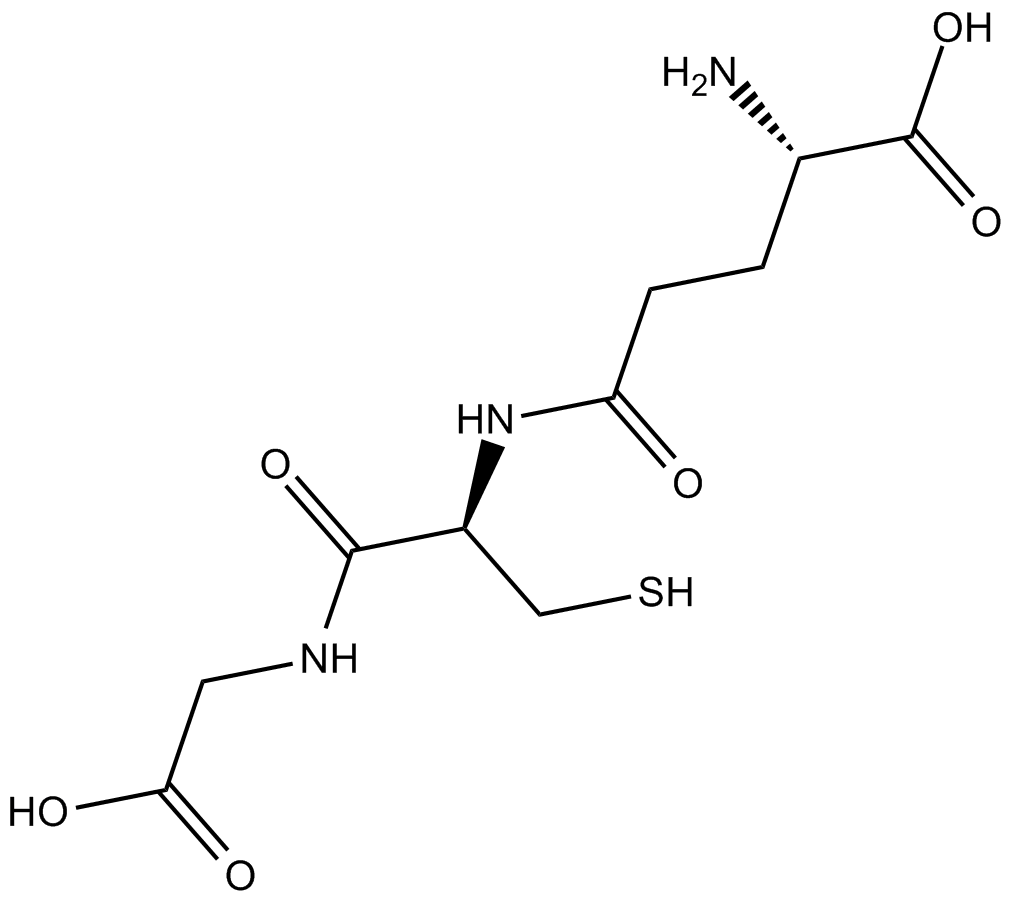
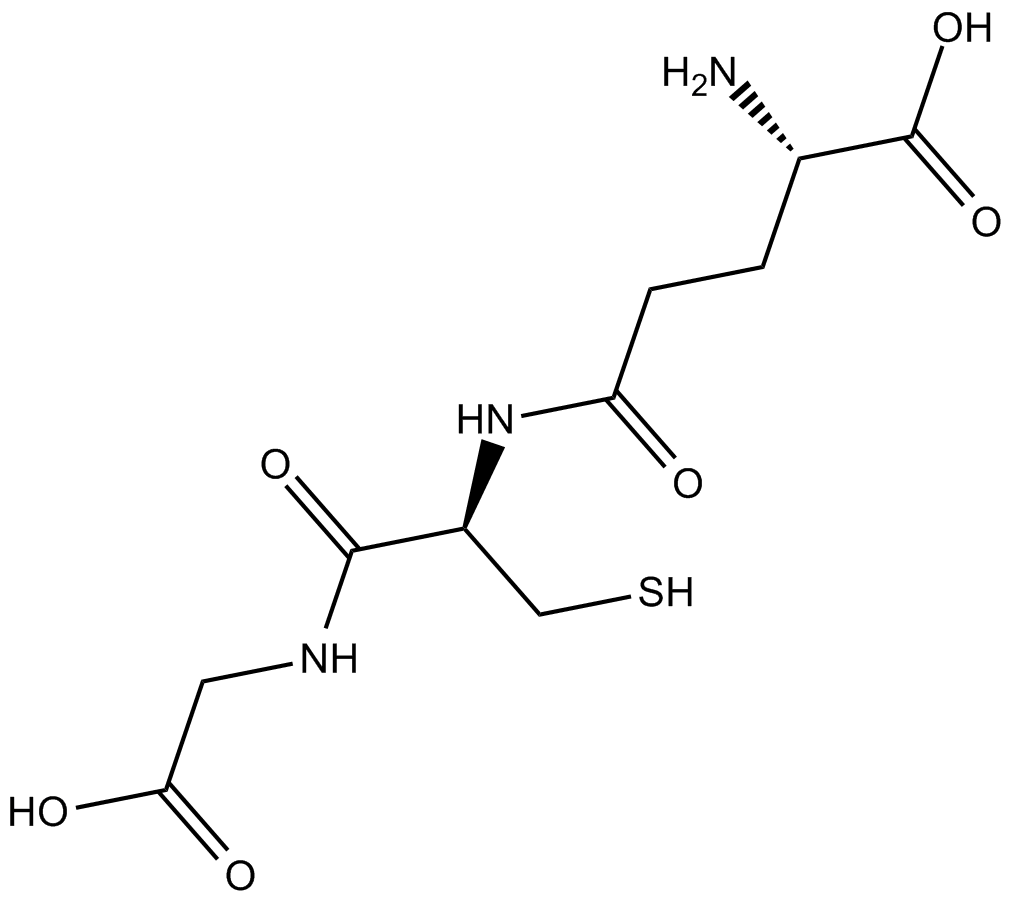
L-Glutathione Reduced
L-Glutathione Reduced (70-18-8) is an endogenous tripeptide antioxidant composed of glutamic acid, cysteine, and glycine. It functions by scavenging oxygen-derived free radicals and serves as a critical detoxifying agent in cellular systems. L-Glutathione Reduced exerts its biological activity mainly through redox reactions involving its thiol group, contributing to processes such as protein and DNA synthesis, enzyme regulation, and cellular protection.
No specific experimental model, activity type, or key metric such as IC50/EC50 is provided. L-Glutathione Reduced holds research potential in studies of oxidative stress, detoxification, and as an eluting agent for glutathione S-transferase (GST) in affinity chromatography.
- 1. Ziyi Dong, Qin Zhang, et al. "Enhancing tumor penetration: GSH-sensitive paclitaxel liposomes modified with Dermaseptin-PP." Materials & Design Volume 246, October 2024, 113323
- 2. Mengting Zhang, Wanhong Wu, et al. "Interaction of Bmal1 and eIF2α/ATF4 pathway was involved in Shuxie compound alleviation of circadian rhythm disturbance-induced hepatic endoplasmic reticulum stress." J Ethnopharmacol. 2023 Aug 10:312:116446. PMID: 37019162
| Physical Appearance | A solid |
| Storage | Store at -20°C |
| M.Wt | 307.32 |
| Cas No. | 70-18-8 |
| Formula | C10H17N3O6S |
| Solubility | insoluble in EtOH; insoluble in DMSO; ≥14.25 mg/mL in H2O |
| Chemical Name | (S)-2-amino-5-(((R)-1-((carboxymethyl)amino)-3-mercapto-1-oxopropan-2-yl)amino)-5-oxopentanoic acid |
| SDF | Download SDF |
| Canonical SMILES | N[C@@H](CCC(N[C@@H](CS)C(NCC(O)=O)=O)=O)C(O)=O |
| Shipping Condition | Small Molecules with Blue Ice, Modified Nucleotides with Dry Ice. |
| General tips | We do not recommend long-term storage for the solution, please use it up soon. |
| Animal experiment [1]: | |
|
Animal models |
Male Hypothyroidism Wistar rats |
|
Dosage form |
0.0012%, oral administration |
|
Application |
Compared with the control group, no significant effects were observed in the rates of lipid peroxidation and vitamin E in hepatic and cardiac tissues of hypothyroidism rats, while the thyroid function of hyperthyroidism rats was significantly enhanced. |
|
Other notes |
Please test the solubility of all compounds indoor, and the actual solubility may slightly differ with the theoretical value. This is caused by an experimental system error and it is normal. |
|
References: [1]. Messarah M, Boulakoud MS, Boumendjel A, Abdennour C, El Feki A. The impact of thyroid activity variations on some oxidizing-stress parameters in rats. C R Biol. 2007 Feb;330(2):107-12. Epub 2006 Dec 12. PubMed PMID: 17303537. |
|
Quality Control & MSDS
- View current batch:
Chemical structure