Golgicide A
Golgicide A is a potent, reversible and highly specific GBF1 inhibitor.
GBF1, the ArfGEF responsible for Arf1 activation and COPI recruitment to cis-Golgi membranes, plays an important role in coordinating bidirectional transport and maintaining structural integrity of the Golgi [1].
Golgicide A inhibits the effect of shiga toxin on protein synthesis with an IC50 of 3.3 μM in Vero cells. Immunofluoresence experiments demonstrates that Golgicide A causes complete dispersal of the medial-Golgi markers giantin and the cis-Golgi marker GM130 and results in a rapid redistribution of COPI from the Golgi. Also, Golgicide A causes a decrease in GBF1-mediated Arf1 activation, impairs retrograde toxin transport and arrests secretion of soluble and membrane-anchored proteins [1]. Golgicide A decreases HCV RNA levels and causes redistribution of NS5A in FLRP1 cells and J6/JFH1 cells. In addition, Golgicide A causes accumulation of infectious viral particles in J6/JFH1 cells [2].
References:
[1] Sáenz JB, Sun WJ, Chang JW, et al. Golgicide A reveals essential roles for GBF1 in Golgi assembly and function. Nat Chem Biol, 2009, 5(3): 157-165.
[2] Matto M, Sklan EH, David N, et al. Role for ADP ribosylation factor 1 in the regulation of hepatitis C virus replication. J Virol, 2011, 85(2): 946-956.
- 1. Emily R. Derbyshire, et al. "Toxoplasma and Plasmodium associate with host Arfs during infection." mSphere. 2024 Mar 26;9(3):e0077023. PMID: 38349168
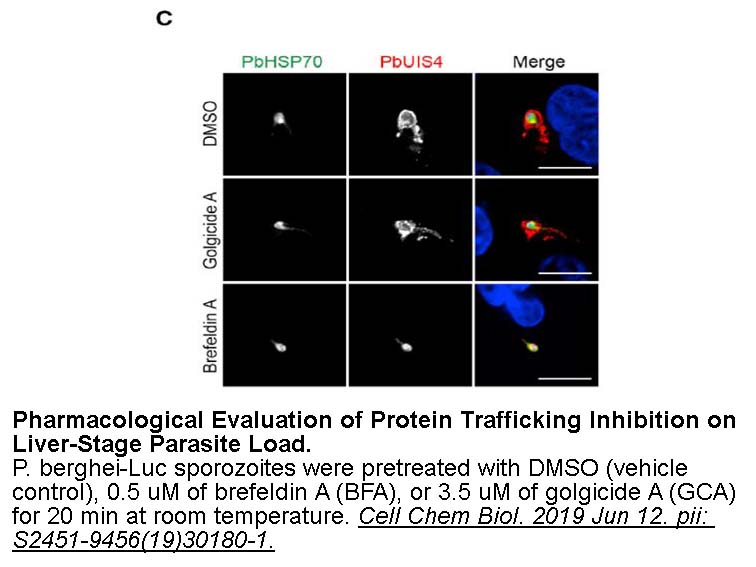
- 2. Raphemot R, Toro-Moreno M, et al. "Discovery of Druggable Host Factors Critical to Plasmodium Liver-Stage Infection." Cell Chem Biol. 2019 Jun 12. pii: S2451-9456(19)30180-1. PMID: 31257182
| Physical Appearance | A solid |
| Storage | Store at -20°C |
| M.Wt | 284.3 |
| Cas No. | 1139889-93-2 |
| Formula | C17H14F2N2 |
| Solubility | insoluble in H2O; ≥12.95 mg/mL in DMSO; ≥2.27 mg/mL in EtOH with ultrasonic |
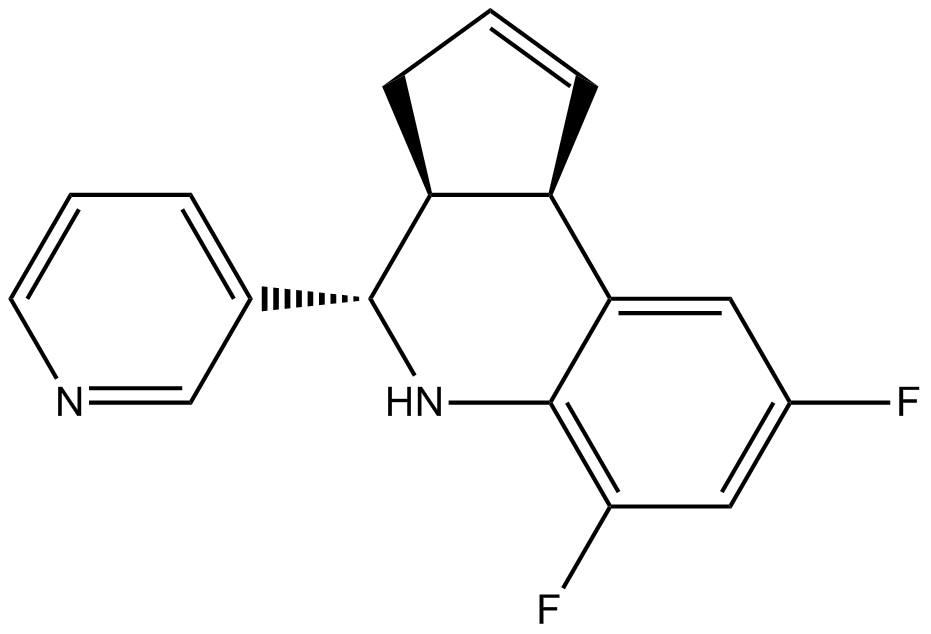
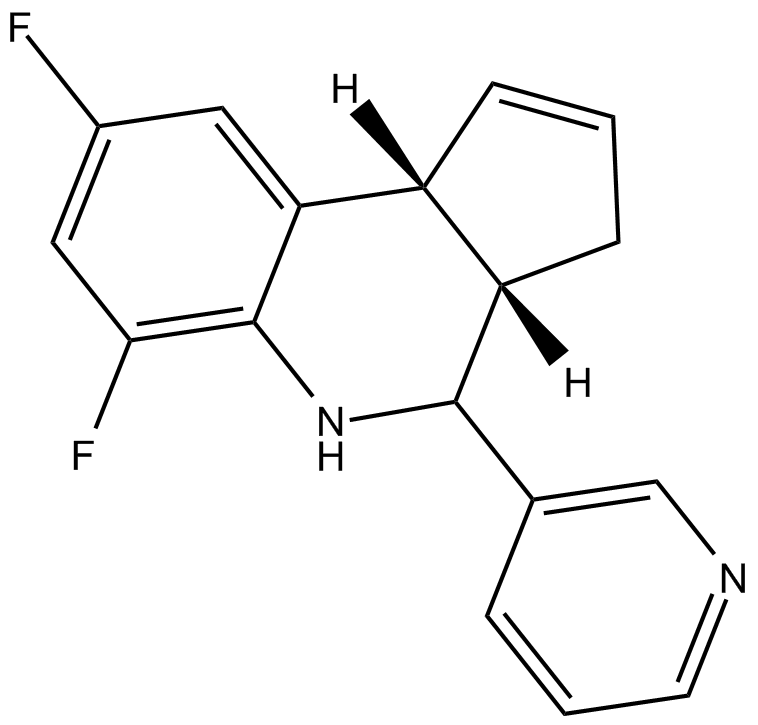
| Chemical Name | (3aS,9bR)-6,8-difluoro-4-(pyridin-3-yl)-3a,4,5,9b-tetrahydro-3H-cyclopenta[c]quinoline |
| SDF | Download SDF |
| Canonical SMILES | Fc(cc1[C@@H]2C=CC[C@@H]22)cc(F)c1NC2c1cnccc1 |
| Shipping Condition | Small Molecules with Blue Ice, Modified Nucleotides with Dry Ice. |
| General tips | We do not recommend long-term storage for the solution, please use it up soon. |
| Cell experiment [1]: | |
|
Cell lines |
The human hepatoma cell line Huh7 (Huh7.5 cells were electroporated with the J6/JFH1 RNA and were transfected with an NS5A-encoding plasmid.) |
|
Preparation method |
The solubility of this compound in DMSO is >13mg/mL. General tips for obtaining a higher concentration: Please warm the tube at 37℃ for 10 minutes and/or shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while. Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. |
|
Reacting condition |
10μM for 4, 24, and 48 h. |
|
Applications |
Treatment of cells with golgicide A, a drug that specifically inhibits GBF1, had been shown to decrease HCV (hepatitis C virus) RNA replication. Thus, golgicide A treatments diminished Arf1 (ADP-ribosylation factor 1) and HCV RNA levels in the JFH1-HCVcc cell system. In J6/JFH1 cells, some of the viral NS proteins migrated from speckle-like organelles to the peripheries of LDs in response to Arf1 inhibition by golgicide A treatment. Golgicide A treatments also decreased HCV RNA levels and cause redistribution of NS5A (a nonstructural protein) and accumulation of infectious viral particles. |
|
References: [1]. Matto M, Sklan EH, David N., et al.Role for ADP ribosylation factor 1 in the regulation of hepatitis C virus replication. J Virol, 2011, 85(2): 946-956. |
|
Quality Control & MSDS
- View current batch:
-
Purity = 98.00%
- COA (Certificate Of Analysis)
- MSDS (Material Safety Data Sheet)
- Datasheet
Chemical structure
Related Biological Data