Vacuolin-1
Vacuolin-1 is a potent and cell-permeable inhibitor of Ca2+-dependent lysosomal exocytosis [1].
Exocytic fusion of lysosomes triggered by plasma membrane damage is the major source of the membrane required for resealing. Lysosomal markers appear at the cell surface or are released into the medium on transient elevation of cytosolic Ca2+, including that induced by plasma membrane disruption [1].
Vacuolin-1 is a cell-permeable blocker of Ca2+-dependent lysosomal exocytosis induced by ionomycin or plasma membrane wounding. In HeLa cells, 5 or 10 μM Vacuolin-1 reduced the release of lysosomal β-hexosaminidase. Vacuolin-1 also blocked the ionomycin-induced, Ca2+-dependent cell surface appearance of the luminal epitope from the lysosomal membrane protein, Lamp-1, a marker for fusion between the limiting membranes of lysosomes and the cell surface. Thus, vacuolin-1 blocks the Ca2+-dependent fusion of lysosomes with the plasma membrane and the release of lysosomal contents. While vacuolin-1 had no effect on the fusion of enlargeosomes with the plasma membrane. Other cell structures and membrane trafficking functions were also unaffected [1].
Reference:
[1]. Cerny J, Feng Y, Yu A, et al. The small chemical vacuolin-1 inhibits Ca2+-dependent lysosomal exocytosis but not cell resealing. EMBO Rep. 2004 Sep;5(9):883-8.
- 1. Heather Flanagan-Steet, et al. "Dysregulated lysosomal exocytosis drives protease-mediated cartilage pathogenesis in multiple lysosomal disorders." iScience. 2024 Feb 21;27(4):109293. PMID: 38495824
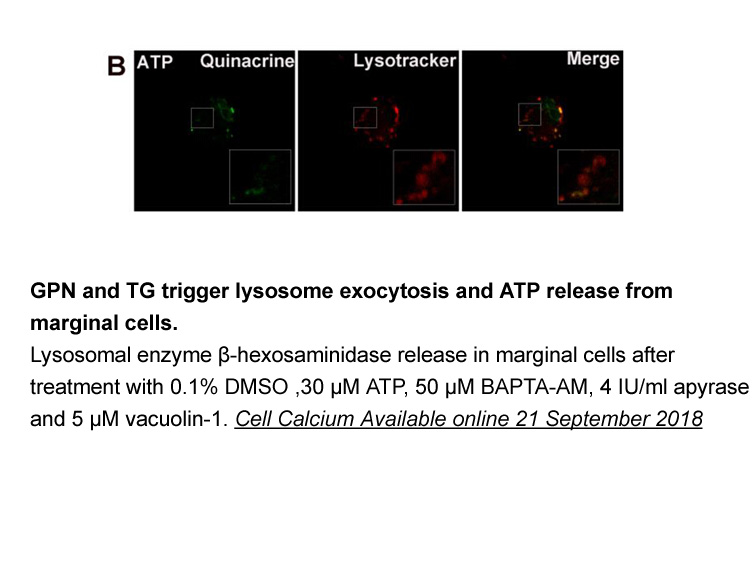
- 2.Liu B, Cao W, et al. "Lysosomal exocytosis of ATP is coupled to P2Y(2) receptor in marginal cells in the stria vascular in neonatal rats." Cell Calcium. 2018 Sep 21;76:62-71. PMID: 30273839
| Physical Appearance | A crystalline solid |
| Storage | Store at -20°C |
| M.Wt | 577.4 |
| Cas No. | 351986-85-1 |
| Formula | C26H24IN7O |
| Solubility | ≥7.28 mg/mL in DMSO with ultrasonic; insoluble in EtOH; insoluble in H2O |
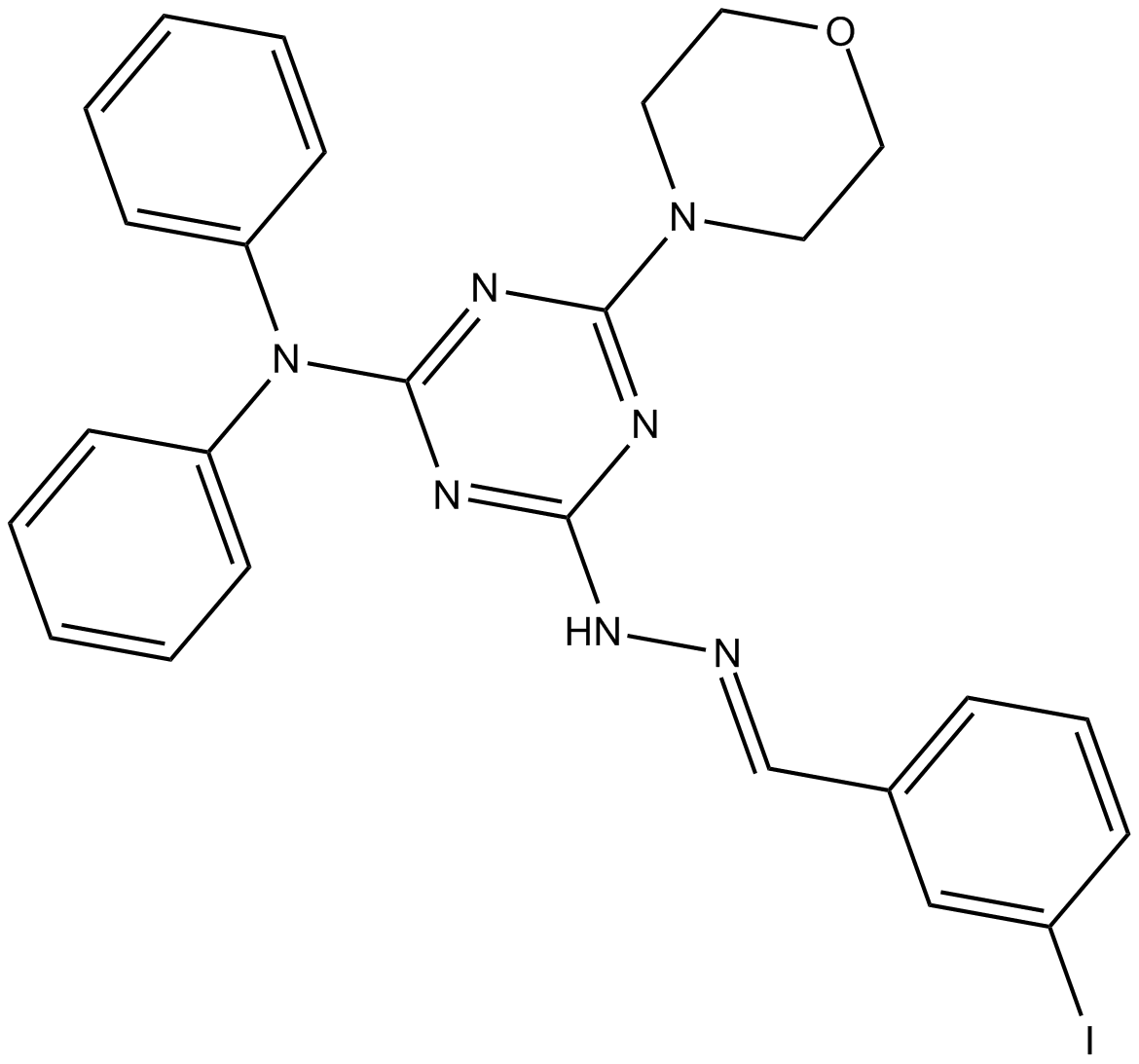
| Chemical Name | 3-iodo-2-[4-(diphenylamino)-6-(4-morpholinyl)-1,3,5-triazin-2-yl]hydrazone, benzaldehyde |
| SDF | Download SDF |
| Canonical SMILES | IC1=CC(/C=N/NC2=NC(N(C3=CC=CC=C3)C4=CC=CC=C4)=NC(N5CCOCC5)=N2)=CC=C1 |
| Shipping Condition | Small Molecules with Blue Ice, Modified Nucleotides with Dry Ice. |
| General tips | We do not recommend long-term storage for the solution, please use it up soon. |
| Cell experiment:[1] | |
|
Cell lines |
HeLa cells |
|
Reaction Conditions |
1, 5 or 10 μM vacuolin-1 for 1, 2 or 4 h incubation |
|
Applications |
In the absence of vacuolin-1, treatment of HeLa cells for 10 min with 5 μM ionomycin resulted in the expected release of 18 ~ 20% of lysosomal β-hexosaminidase. In contrast, cells that were pretreated with 5 or 10 μM vacuolin-1 for 2 h released no more β-hexosaminidase compared with cells that were not exposed to ionomycin (~ 4%). However, pretreatment of HeLa cells with 1 μM vacuolin-1 had no effect on the cell surface appearance of the enlargeosome marker in response to ionomycin. Thus, the inhibitory effect of vacuolin-1 on Ca2+-dependent exocytosis was not a general phenomenon. Rather, it seemed to be a specific effect for endosomes and lysosomes but not for enlargeosomes. |
|
Note |
The technical data provided above is for reference only. |
|
References: 1. Cerny J, Feng Y, Yu A, et al. The small chemical vacuolin-1 inhibits Ca(2+)-dependent lysosomal exocytosis but not cell resealing. EMBO Reports, 2004, 5(9): 883-888. |
|
Quality Control & MSDS
- View current batch:
Chemical structure
Related Biological Data