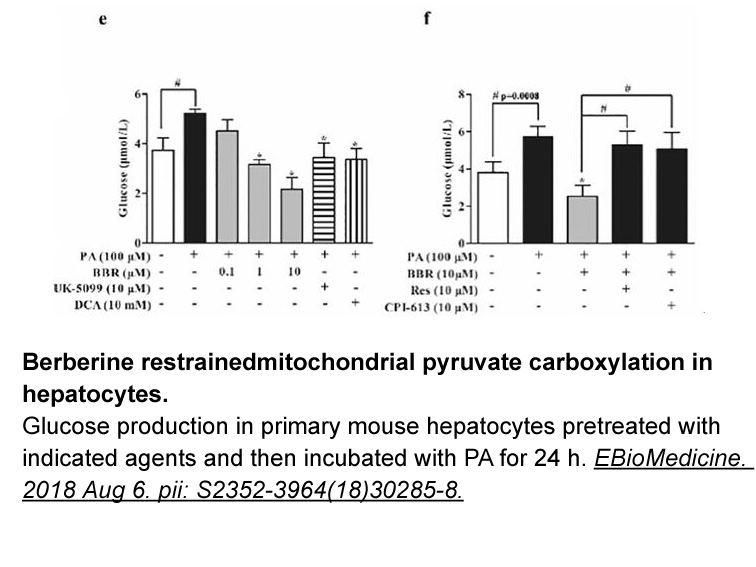
UK-5099
UK-5099 is a potent inhibitor of the mitochondrial pyruvate carrier [1].
The mitochondrial pyruvate carrier (MPC) facilitates pyruvate transport across the mitochondrial inner membrane and plays a critical role in carbohydrate, lipid and amino acid metabolism.
UK-5099 (1 mM) completely blocked pyruvate uptake with Ki value of 49 μM. Also, UK-5099 decreased the overall efflux rate in a concentration-dependant way [1]. In mitochondria isolated from S. Guttatum, UK-5099 (20 μM) inhibited pyruvate-dependent 02 consumption [2].
In rat heart mitochondria, UK-5099 inhibited pyruvate oxidation with a non-linear inhibition kinetics [2]. In glucagon-treated rats, UK-5099 inhibited pyruvate carboxylation and total pyruvate metabolism with a linear relationship [3]. In rat liver and heart mitochondria, UK-5099 inhibited pyruvate-dependent 02 consumption with IC50 value of 50 nM [4].
References:
[1]. Wiemer EA, Michels PA, Opperdoes FR. The inhibition of pyruvate transport across the plasma membrane of the bloodstream form of Trypanosoma brucei and its metabolic implications. Biochem J, 1995, 312 ( Pt 2): 479-484.
[2]. Halestrap AP. The mitochondrial pyruvate carrier. Kinetics and specificity for substrates and inhibitors. Biochem J, 1975, 148(1): 85-96.
[3]. Halestrap AP, Armston AE. A re-evaluation of the role of mitochondrial pyruvate transport in the hormonal control of rat liver mitochondrial pyruvate metabolism. Biochem J, 1984, 223(3): 677-685.
[4]. Proudlove MO, Beechey RB, Moore AL. Pyruvate transport by thermogenic-tissue mitochondria. Biochem J, 1987, 247(2): 441-447.
| Physical Appearance | A crystalline solid |
| Storage | Store at -20°C |
| M.Wt | 288.3 |
| Cas No. | 56396-35-1 |
| Formula | C18H12N2O2 |
| Synonyms | PF-1005023;UK5099;UK 5099;PF1005023;PF 1005023 |
| Solubility | insoluble in EtOH; insoluble in H2O; ≥28.8 mg/mL in DMSO |
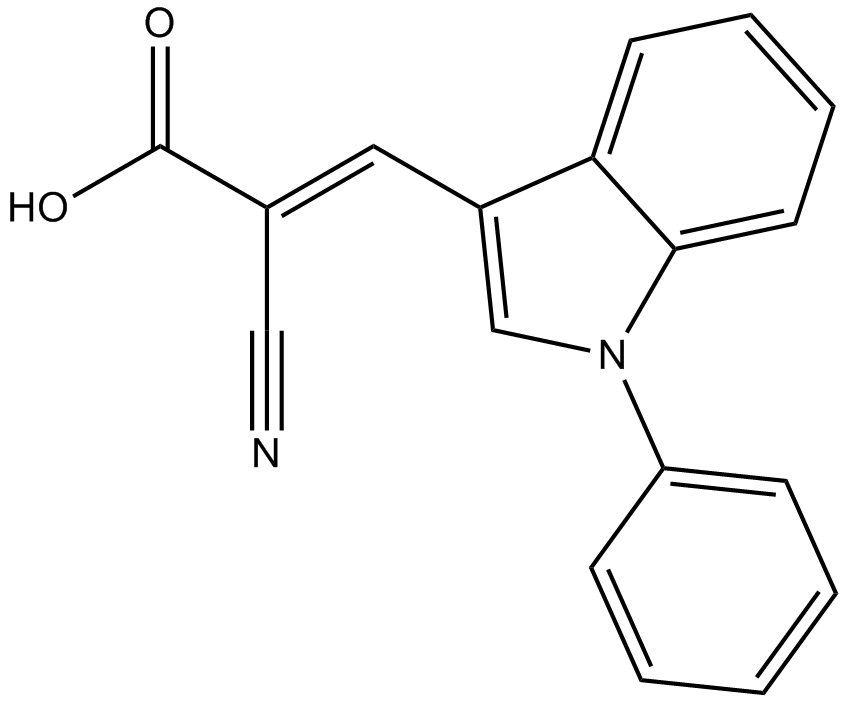
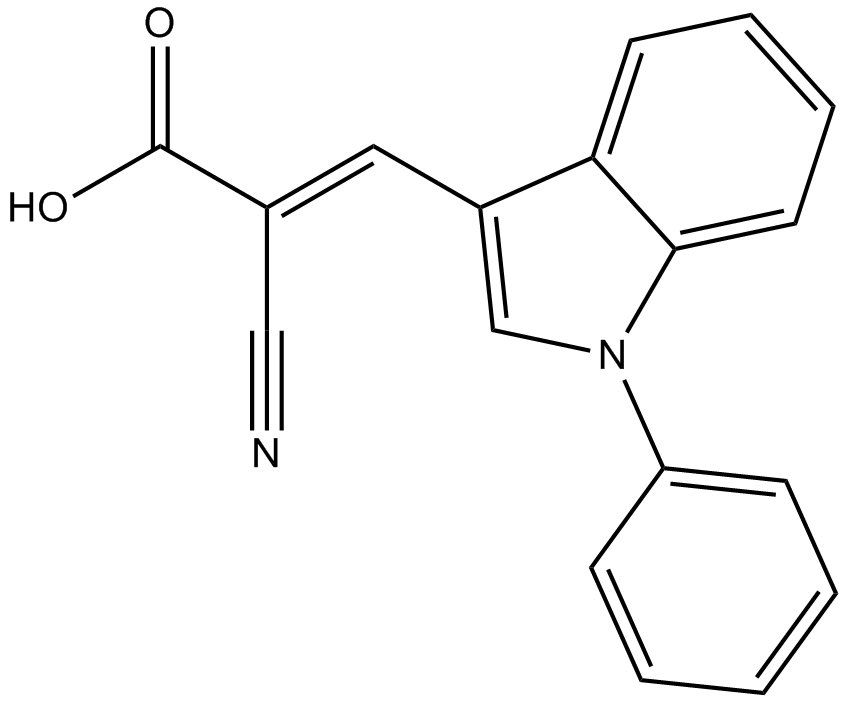
| Chemical Name | (E)-2-cyano-3-(1-phenylindol-3-yl)prop-2-enoic acid |
| SDF | Download SDF |
| Canonical SMILES | C1=CC=C(C=C1)N2C=C(C3=CC=CC=C32)C=C(C#N)C(=O)O |
| Shipping Condition | Small Molecules with Blue Ice, Modified Nucleotides with Dry Ice. |
| General tips | We do not recommend long-term storage for the solution, please use it up soon. |
| Cell experiment:[1] | |
|
Cell lines |
832/13 cells derived from INS-1 rat insulinoma cells |
|
Reaction Conditions |
50 ~ 150 μM UK-5099 for 30 ~ 65 min incubation |
|
Applications |
UK-5099 significantly inhibited the glucose-stimulated rise in oxygen consumption in a dose-dependent manner and at 150 μM reduced oxygen consumption below basal levels. Moreover, UK-5099 (150 μM) reduced ATP levels and increased ADP and AMP levels in 832/13 cells. |
| Animal experiment:[1] | |
|
Animal models |
C57BLK mice |
|
Dosage form |
32 μmol/kg Injected intraperitoneally 30 min before the glucose challenge |
|
Applications |
UK-5099 caused a significantly greater glucose excursion at 30, 60, and 120 min as compared with DMSO control mice. The area under the curve was also significantly increased by UK-5099 as compared with DMSO control mice. Thus, UK-5099 resulted in impaired glucose tolerance in vivo. |
|
Note |
The technical data provided above is for reference only. |
|
References: 1. Patterson JN, Cousteils K, Lou JW, et al Mitochondrial metabolism of pyruvate is essential for regulating glucose-stimulated insulin secretion. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 2014, 289(19): 13335-13346. |
|
Quality Control & MSDS
- View current batch:
Chemical structure
Related Biological Data