U 18666A
U 18666A is an inhibitor of cholesterol transport and synthesis [1] [2].
Cholesterol is a sterol that biosynthesized by all animal cells and is an essential component of all animal cell membranes that is required to maintain membrane fluidity and structural integrity.
U 18666A is an inhibitor of cholesterol transport and synthesis. In rat brain, U 18666A inhibited sterols production in a concentration-dependent way [1]. In cultured Chinese hamster ovary (CHO) cells, U18666A inhibited cholesterol esterification stimulated by low density lipoprotein (LDL)-derived cholesterol and also inhibited LDL receptor activities and 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-coenzyme A reductase. U18666A caused the accumulation of LDL-derived cholesterol in the lysosomes, suggesting the inhibition of LDL-derived cholesterol transport [2]. In cultured baby hamster kidney cells and human skin fibroblasts (HSF), U18666A reversibly and rapidly inhibited acyl-CoA cholesterol acyl transferase (ACAT) activated by sphingomyelinase in a dose dependent way. In sphingomyelinase-treated HSF cells, U18666A significantly and reversibly reduced the translocation of plasma membrane cholesterol. In mouse Leydig tumor cells, U18666A inhibited steroid hormones secretion stimulated by cyclic AMP in a dose dependent way [3]. In primary cortical neurons, U18666A caused cellular injury and caspase-3 activation. U18666A also caused the accumulation of cholesterol [4].
References:
[1]. Cenedella RJ. Concentration-dependent effects of AY-9944 and U18666A on sterol synthesis in brain. Variable sensitivities of metabolic steps. Biochem Pharmacol, 1980, 29(20): 2751-2754.
[2]. Liscum L, Faust JR. The intracellular transport of low density lipoprotein-derived cholesterol is inhibited in Chinese hamster ovary cells cultured with 3-beta-[2-(diethylamino)ethoxy]androst-5-en-17-one. J Biol Chem, 1989, 264(20): 11796-11806.
[3]. Härmälä AS, Pörn MI, Mattjus P, Slotte JP. Cholesterol transport from plasma membranes to intracellular membranes is inhibited by 3 beta-[2-(diethylamino)ethoxy]androst-5-en-17-one. Biochim Biophys Acta, 1994, 1211(3): 317-325.
[4]. Cheung NS, Koh CH, Bay BH, et al. Chronic exposure to U18666A induces apoptosis in cultured murine cortical neurons. Biochem Biophys Res Commun, 2004, 315(2): 408-417.
| Physical Appearance | A crystalline solid |
| Storage | Store at -20°C |
| M.Wt | 424.07 |
| Cas No. | 3039-71-2 |
| Formula | C25H41NO2·HCl |
| Solubility | Soluble in H2O |
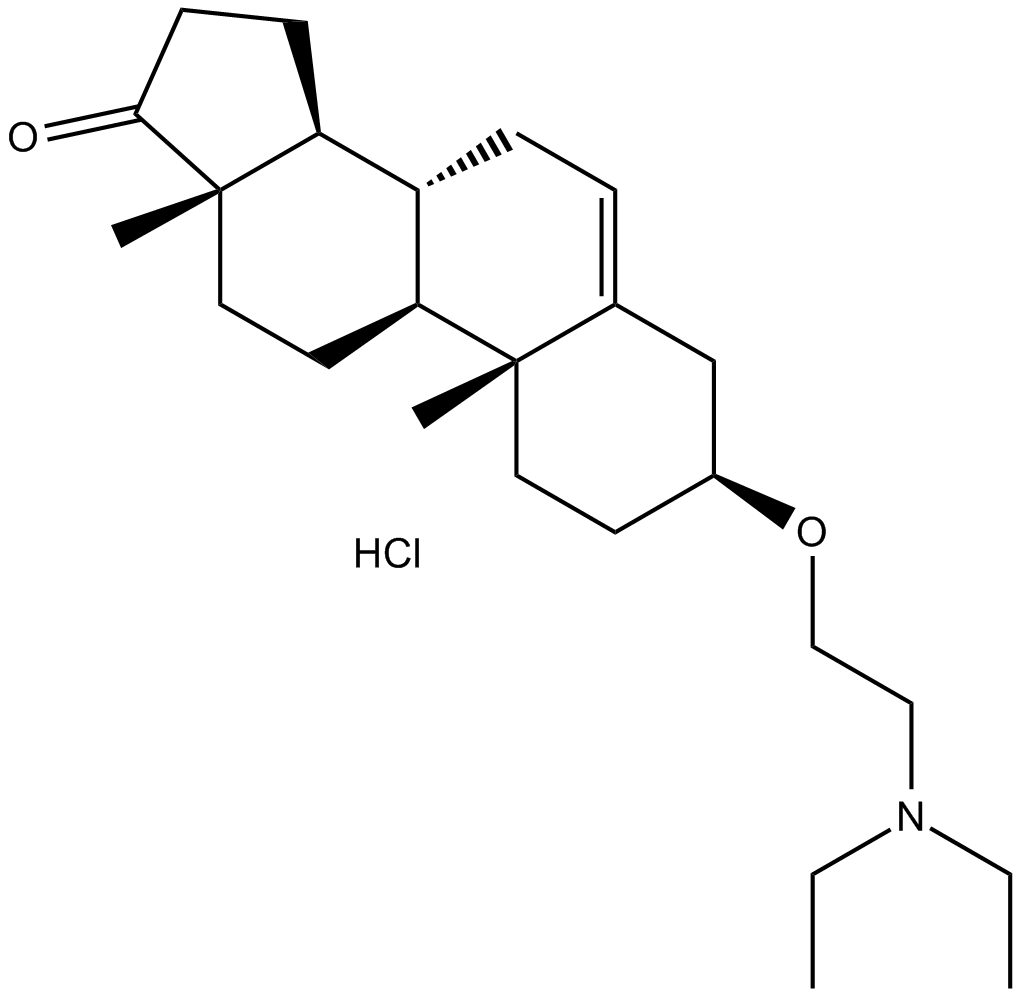
| Chemical Name | (3S,8R,9S,10R,13S,14S)-3-(2-(diethylamino)ethoxy)-10,13-dimethyl-3,4,7,8,9,10,11,12,13,14,15,16-dodecahydro-1H-cyclopenta[a]phenanthren-17(2H)-one hydrochloride |
| SDF | Download SDF |
| Canonical SMILES | CCN(CC)CCO[C@@H]1CC2=CC[C@@H]([C@H](CC3)[C@](C)(CC4)C3=O)[C@H]4[C@@]2(C)CC1.Cl |
| Shipping Condition | Small Molecules with Blue Ice, Modified Nucleotides with Dry Ice. |
| General tips | We do not recommend long-term storage for the solution, please use it up soon. |
| Cell experiment [1]: | |
|
Cell lines |
Primary cortical neurons |
|
Preparation method |
Soluble to 100 mM in sterile water. General tips for obtaining a higher concentration: Please warm the tube at 37 ℃ for 10 minutes and/or shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while. Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. |
|
Reacting condition |
0.1–2.5 μg/ml, 37°C, 72 h |
|
Applications |
U18666A (2.5 μg/ml, 72 h) induced cytotoxicity in primary cortical neurons. U18666A resulted in significant loss of more than 50% of cell survival and major morphological changes characterized by cell shrinkage and membrane blebbing in cortical neuron. U18666A (0.1–2.5 μg/ml, 72 h) induced cell injury and apoptosis in primary cortical neurons. |
| Animal experiment [2]: | |
|
Animal models |
Sprague-Dawley rats |
|
Dosage form |
Subcutaneous injection, 10 mg/kg, every fourth or seventh day |
|
Application |
Weekly injection of U 18666A (10 mg/kg, s.c.) into neonatal rats for 4 consecutive weeks caused a reduction in the seizure threshold of male rats to the convulsant flurothyl. |
|
Other notes |
Please test the solubility of all compounds indoor, and the actual solubility may slightly differ with the theoretical value. This is caused by an experimental system error and it is normal. |
|
References: [1]. Cheung N S, Koh C H V, Bay B H, et al. Chronic exposure to U18666A induces apoptosis in cultured murine cortical neurons[J]. Biochemical and biophysical research communications, 2004, 315(2): 408-417. [2]. Bierkamper G G, Cenedella R J. Induction of chronic epileptiform activity in the rat by an inhibitor of cholesterol synthesis, U18666A[J]. Brain research, 1978, 150(2): 343-351. | |
Quality Control & MSDS
- View current batch:
Chemical structure