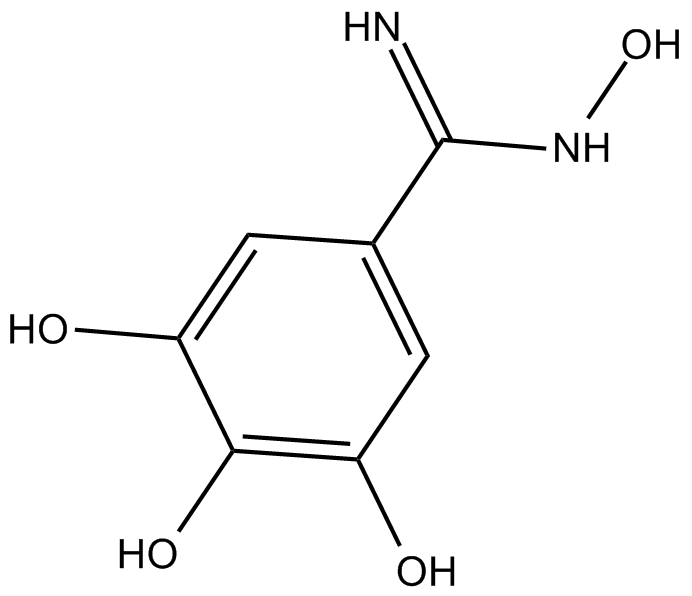
Trimidox
Trimidox (3.4.5-tri-hydroxybenzohydroxamidoxime) is a specific and patented ribonucleotide reductase (RNR) inhibitor [1].
Ribonucleotide reductase (RNR), also known as ribonucleoside diphosphate reductase, is an enzyme involved in catalyzing the formation of deoxyribonucleotides from ribonucleotides. RNR plays a vital role in regulating the total rate of DNA synthesis to DNA to maintain DNA cell mass a constant ratio during cell division and DNA repair. The substrates for RNR are ADP, GDP, CDP and UDP [2]. Increased ribonucleotide reductase (RNR) activity has been associated with malignant transformation and tumor cell growth [1].
In human promyelocytic leukemia HL-60 cells, trimidox inhibited the growth of with an IC50 of 35 pmol/L. Treatment with trimidox (50 pmol/L) for 24 hours decreased deoxyguanosine triphosphate (dGTP) and deoxycytidine triphosphate (dCTP) pools to 24% and 3946 of control values, respectively. Incubation of HL-60 cells with 20 to 80 pmol/L trimidox to 4 days showed no effects in the distribution of cells indifferent phases of cell cycle [1]. Trimidox in combination with tiazofurin was useful in the treatment of leukemia [1].
References:
[1] Szekeres T, Fritzer M, Strobl H, et al. Synergistic growth inhibitory and differentiating effects of trimidox and tiazofurin in human promyelocytic leukemia HL-60 cells[J]. Blood, 1994, 84(12): 4316-4321.
[2] Elledge S J, Zhou Z, Allen J B. Ribonucleotide reductase: regulation, regulation, regulation[J]. Trends in biochemical sciences, 1992, 17(3): 119-123.
| Physical Appearance | A crystalline solid |
| Storage | Store at -20°C |
| M.Wt | 184.2 |
| Cas No. | 95933-74-7 |
| Formula | C7H8N2O4 |
| Synonyms | VF 233 |
| Solubility | ≤20mg/ml in DMSO;20mg/ml in dimethyl formamide |
| Chemical Name | N,3,4,5-tetrahydroxy-benzenecarboximidamide |
| SDF | Download SDF |
| Canonical SMILES | N=C(c(cc1O)cc(O)c1O)NO |
| Shipping Condition | Small Molecules with Blue Ice, Modified Nucleotides with Dry Ice. |
| General tips | We do not recommend long-term storage for the solution, please use it up soon. |
Quality Control & MSDS
- View current batch:
-
Purity = 98.00%
- COA (Certificate Of Analysis)
- MSDS (Material Safety Data Sheet)
Chemical structure