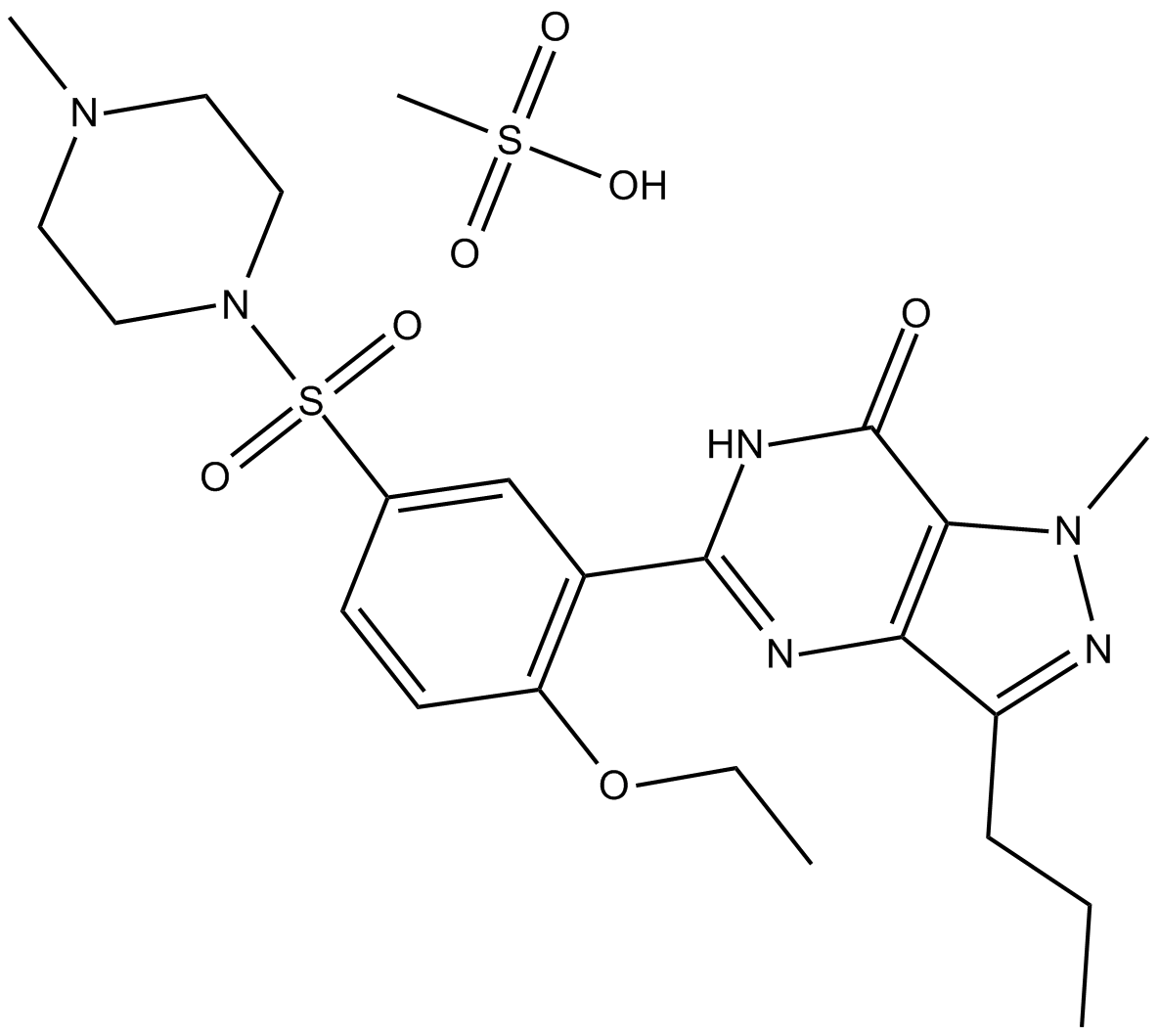
Sildenafil mesylate
IC50: 3.5 nM
Sildenafil mesylate is an inhibitor of cyclic guanosine monophosphate (cGMP)-specific phosphodiesterase type 5 (PDE5).
PDE5 is the predominant phosphodiesterase in the corpus cavernosum. The catalytic site of PDE5 degrades cGMP, and PDE5 inhibitors can potentiate endogenous increases in cGMP.
In vitro: Sildenafil mesylate had been identified as a potent PDE5 reversible and selective inhibitor. Sildenafil enhanced sodium nitroprusside- or transmural electrical stimulation-induced relaxation of precontracted corpus cavernosum muscle strips in organ baths. Sildenafil also increased intracellular cGMP concentrations in cultured smooth muscle cells treated with sodium nitroprusside [1].
In vivo: In anesthetized dogs, sildenafil could enhance the erectile function following pelvic nerve stimulation as measured by increased intracavernosal pressure [1].
Clinical trial: Ten previous randomised controlled trials had been conducted. Dose optimisation resulted in >60% of attempts at sexual intercourse, which was successful in 49% of men. Sildenafil treatment related adverse events occurred in 30% of men compared with 11% on placebo. Dose optimisation of sildenafil showed efficacy equivalent to the highest fixed doses, and adverse events equivalent to the lowest fixed doses [2].
References:
[1] Nehra A,Colreavy F,Khandheria BK,Chandrasekaran K. Sildenafil citrate, a selective phosphodiesterase type 5 inhibitor: urologic and cardiovascular implications. World J Urol.2001 Feb;19(1):40-5.
[2] Moore RA,Edwards JE,McQuay HJ. Sildenafil (Viagra) for male erectile dysfunction: a meta-analysis of clinical trial reports. BMC Urol.2002 May 22;2:6.
| Physical Appearance | A solid |
| Storage | Store at -20°C |
| M.Wt | 570.68 |
| Cas No. | 1308285-21-3 |
| Formula | C23H34N6O7S2 |
| Solubility | ≥57.1 mg/mL in DMSO; insoluble in EtOH; ≥25.95 mg/mL in H2O |
| Chemical Name | 5-(2-ethoxy-5-((4-methylpiperazin-1-yl)sulfonyl)phenyl)-1-methyl-3-propyl-1H-pyrazolo[4,3-d]pyrimidin-7(6H)-one methanesulfonate |
| SDF | Download SDF |
| Canonical SMILES | CCCC(C(N=C(N1)C2=C(OCC)C=CC(S(N3CCN(CC3)C)(=O)=O)=C2)=C4C1=O)=NN4C.CS(O)(=O)=O |
| Shipping Condition | Small Molecules with Blue Ice, Modified Nucleotides with Dry Ice. |
| General tips | We do not recommend long-term storage for the solution, please use it up soon. |
Quality Control & MSDS
- View current batch:
Chemical structure