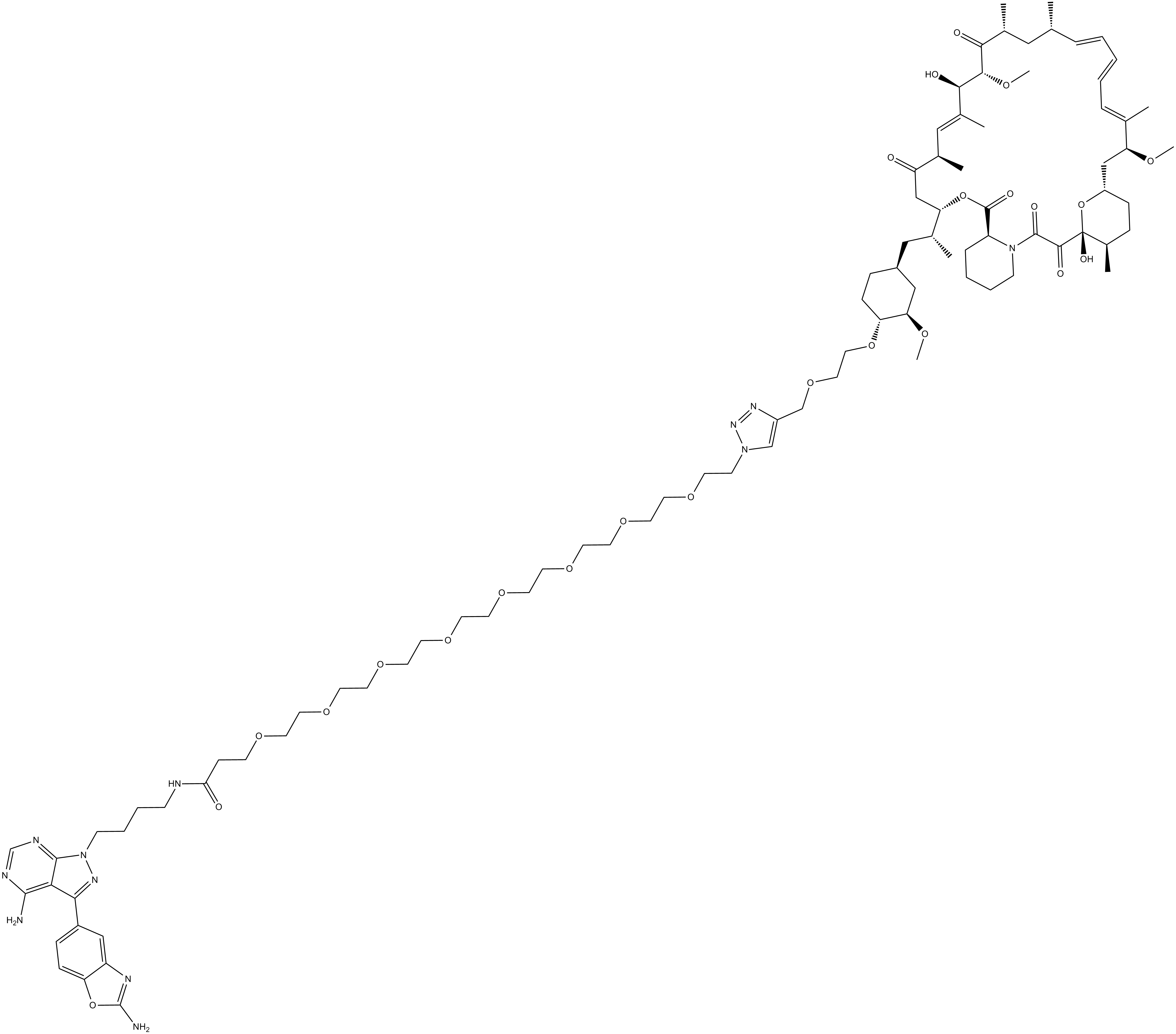
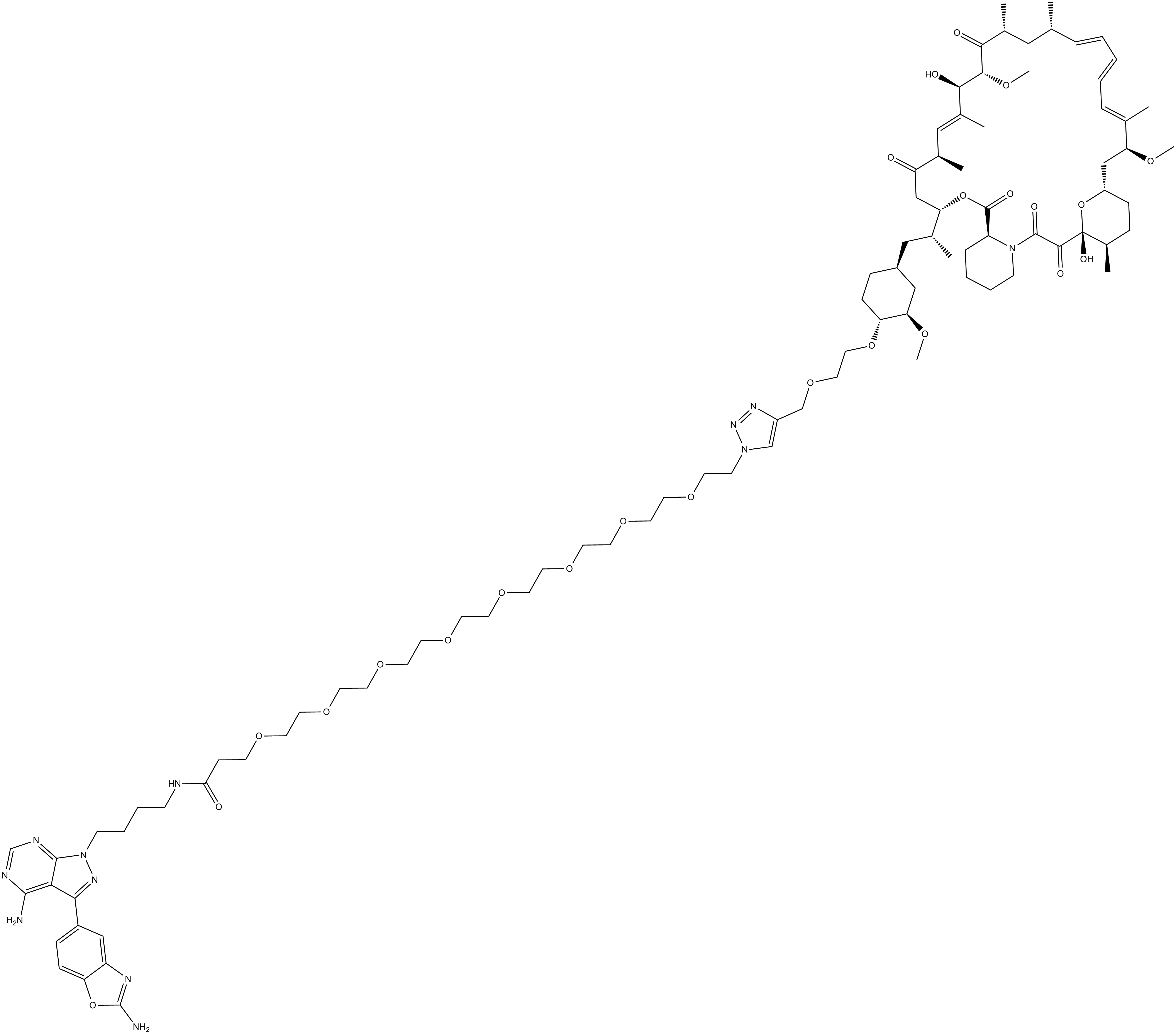
Rapalink-1
RapaLink-1 (CAS: 1887095-82-0) is a third-generation mTOR inhibitor. It uniquely combines the binding pockets of first- and second-generation mTOR kinase inhibitors, creating a bivalent interaction that enables it to inhibit mutations that are resistant to previous TORKi (mTOR kinase inhibitors).
The PIK3CA–AKT–mTOR signaling pathway is one of the most commonly activated pathways in human cancers, which has led to the development of small molecule inhibitors targeting multiple nodes of this pathway. Two generations of mTOR inhibitors have already been developed.
Compared to first- and second-generation mTOR inhibitors, RapaLink-1 is more potent. RapaLink-1 can more effectively reduce the levels of p-4EBP1 and inhibit cell proliferation. Researchers compared the efficacy of rapamycin, RapaLink-1, and MLN0128 in LN229 and U87MG cells. Compared to rapamycin or MLN0128, RapaLink-1 exhibited stronger growth inhibition and a greater ability to arrest cells in the G0/G1 phase. In vivo, RapaLink-1 demonstrated potent antitumor activity; in xenograft tumor models, it led to tumor regression and subsequent stabilization of tumor volume, whereas tumors in the vehicle, rapamycin, or MLN0128 groups continued to grow steadily.
RapaLink-1 can durably block mTORC1. RapaLink-1 is associated with FKBP12, an abundant mTOR-interacting protein, which allows RapaLink-1 to aggregate. Compared to rapamycin or other TORKi, RapaLink-1 shows better efficacy and can potently inhibit cancer-derived, mTOR-activating mutations.
- 1. Dhanur P Iyer, Heidar Heidari Khoei, et al. "mTOR activity paces human blastocyst stage developmental progression." Cell. 2024 Sep 18:S0092-8674(24)00977-2 PMID: 39332412
- 2. Chiyuan Ma, Qin Li, et al. "mTOR hypoactivity leads to trophectoderm cell failure by enhancing lysosomal activation and disrupting the cytoskeleton in preimplantation embryo." Cell Biosci. 2023 Nov 30;13(1):219. PMID: 38037142
- 3. Gangyin Zhao, Gabriel Forn-Cuní, et al. "Simultaneous targeting of AMPK and mTOR is a novel therapeutic strategy against prostate cancer" bioRxiv. August 16, 2023.
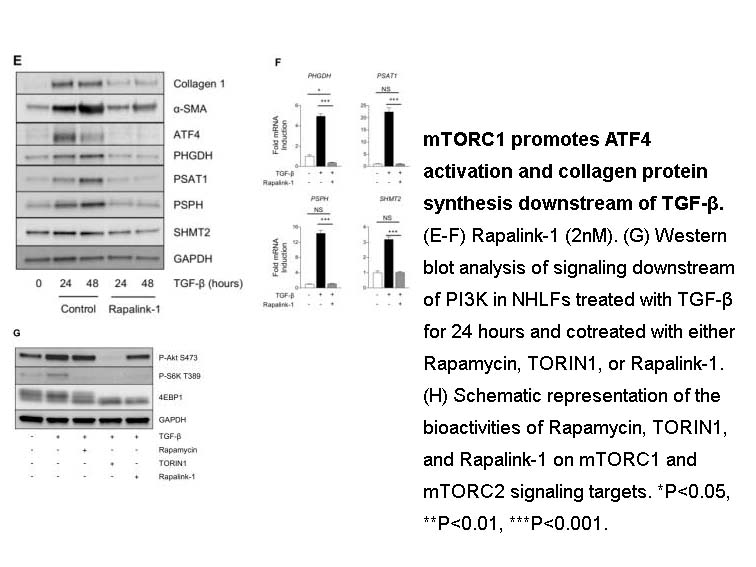
- 4. Erin M O'Leary, Yufeng Tian, et al. "TGF-β Promotes Metabolic Reprogramming in Lung Fibroblasts via mTORC1-dependent ATF4 Activation." Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2020 Nov;63(5):601-612. PMID:32668192
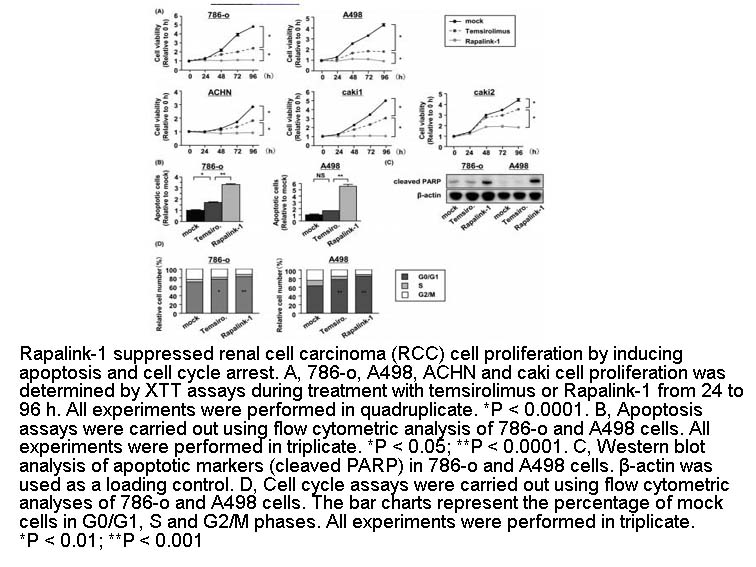
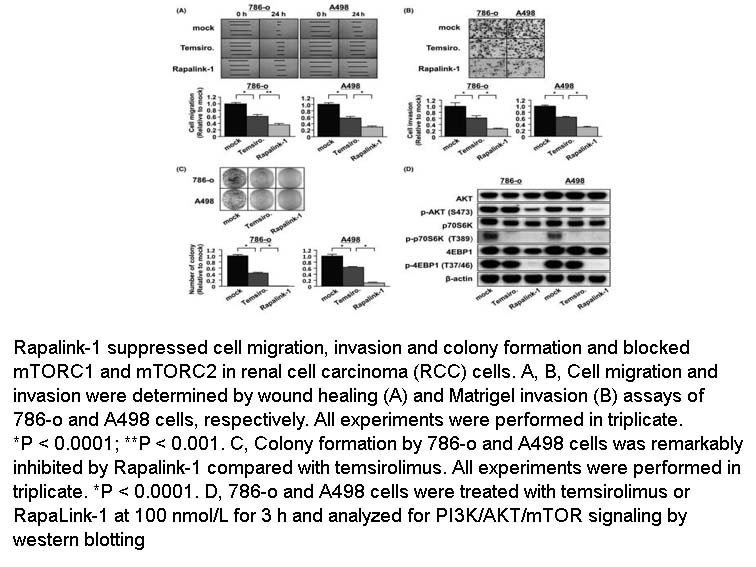
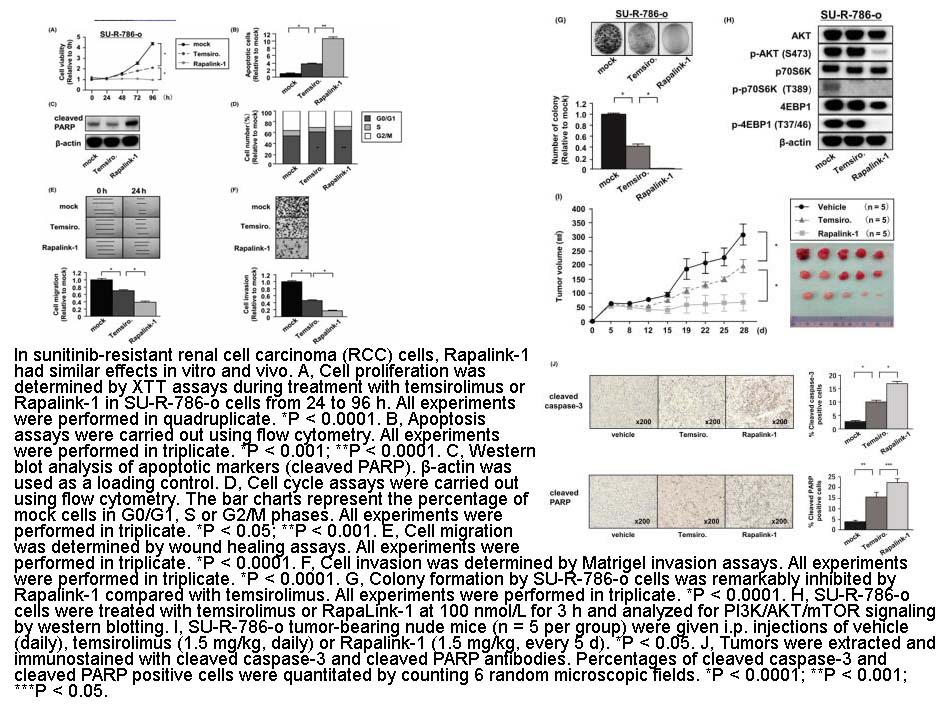
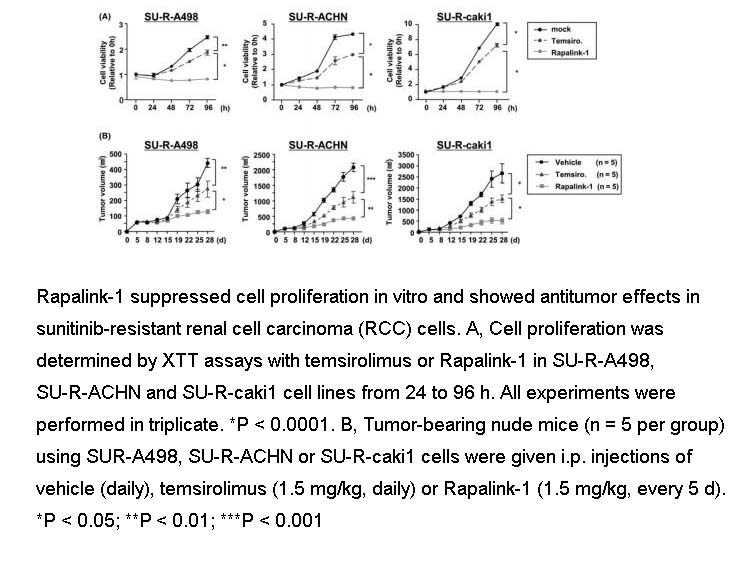
- 5. Kuroshima K, Yoshino H, et al. "Potential new therapy of Rapalink-1, a new generation mammalian target of rapamycin inhibitor, against sunitinib-resistant renal cell carcinoma." Cancer Sci. 2020;111(5):1607-1618. PMID:32232883
| Storage | Store at -20°C |
| M.Wt | 1784.14 |
| Cas No. | 1887095-82-0 |
| Formula | C91H138N12O24 |
| Solubility | ≥178.4 mg/mL in DMSO; insoluble in H2O; ≥24.85 mg/mL in EtOH |
| SDF | Download SDF |
| Canonical SMILES | O=C(NCCCCN1N=C(C2=CC=C(OC(N)=N3)C3=C2)C4=C(N)N=CN=C41)CCOCCOCCOCCOCCOCCOCCOCCOCCN5C=C(COCCO[C@@H]6CC[C@@H](C[C@H]([C@@H](OC([C@H](CCCC7)N7C(C([C@@]8(O)[C@H](C)CC[C@H](O8)C[C@H](OC)/C(C)=C/C=C/C=C/[C@@H](C)C[C@@H](C)C([C@H](OC)[C@H](O)/C(C)=C/[C@H]9C)=O)=O |
| Shipping Condition | Small Molecules with Blue Ice, Modified Nucleotides with Dry Ice. |
| General tips | We do not recommend long-term storage for the solution, please use it up soon. |
| Cell experiment:[1] | |
|
Cell lines |
Human glioma cell line U87MG |
|
Reaction Conditions |
0 ~ 200 nM Rapalink-1 for 3 days |
|
Applications |
In U87MG cells, both growth inhibition (0 ~ 200 nM Rapalink-1; 3 days) and arrest in G0/G1 (0 ~ 12.5 nM Rapalink-1; 48 hours) were more obvious in response to Rapalink-1, compared with Rapamycin or MLN0128. |
| Animal experiment:[1] | |
|
Animal models |
BALB/Cnu/nu mice bearing U87MG intracranial xenografts |
|
Dosage form |
1.5 mg/kg Injected intraperitoneally (i.p.) every 5 or 7 days |
|
Applications |
Rapalink-1 led to initial regression and subsequent stabilization of tumor size, while tumors treated with vehicle, Rapamycin, or MLN0128 grew steadily. Furthermore, Rapalink-1 was well tolerated and associated with significantly improved survival. |
|
Note |
The technical data provided above is for reference only. |
|
References: 1. Fan Q, Aksoy O, Wong RA, et al. A kinase inhibitor targeted to mTORC1 drives regression in glioblastoma. Cancer Cell, 2017, 31(3): 424-435. |
|
Quality Control & MSDS
- View current batch:
Chemical structure

Related Biological Data
Related Biological Data
Related Biological Data
Related Biological Data
Related Biological Data