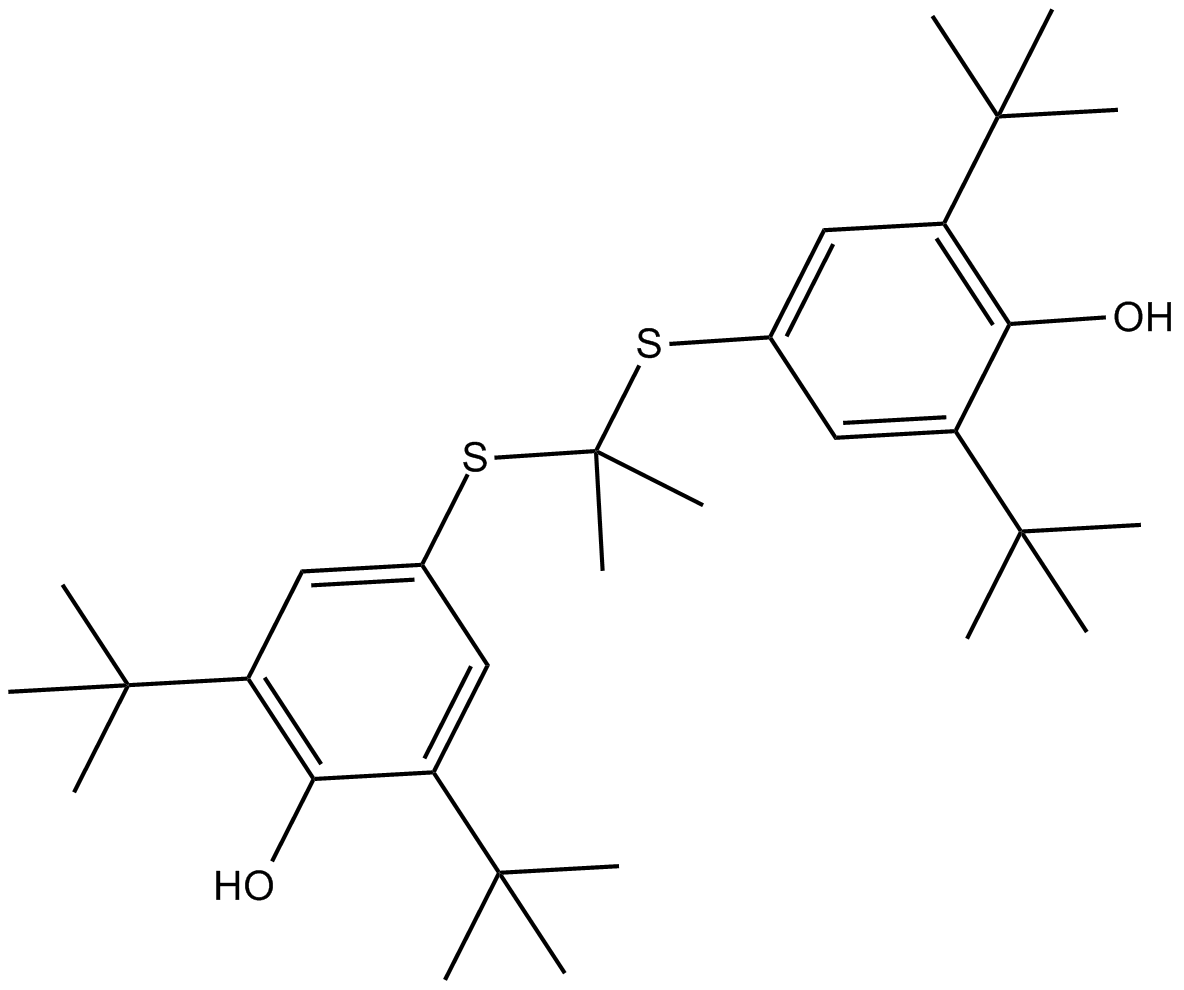
Probucol
Probucol is a lipid-lowering agent with anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties [1-3].
Probucol inhibits the oxidation of cholesterol in low-density lipoprotein, preventing the formation of macrophage-derived foam cells which lead to atherosclerotic vascular lesions. However, the application of probucol is limited, because it leads to the reduction of high-density lipoprotein cholesterol as well [1].
In J774 macrophages, probucol at 10 μmol/L inhibited cholesterol efflux up to 80% by impairing the translocation of ATP-binding cassette transporter A1 (ABCA1) from intracellular compartments to the plasma membrane. Probucol also suppressed the formation of an ABCA1-linked cholesterol oxidase sensitive plasma membrane domain [2].
In a mouse model of Huntington’s disease, long-term probucol treatment (3.5 mg/kg/day, p.o., for 2 months) protected against behavioral and striatal biochemical changes induced by 3-nitropropionic acid (3-NP), attenuating 3-NP-induced motor impairments and striatal oxidative stress, without rescuing complex II inhibition. Furthermore, probucol was able to increase activity of glutathione peroxidase, an enzyme involved in mediating the detoxification of peroxides in the central nervous system [3].
References:
[1]. Yamamoto A. A uniqe antilipidemic drug--probucol. Journal of Atherosclerosis and Thrombosis, 2008, 15(6): 304-305.
[2]. Favari E, Zanotti I, Zimetti F, et al. Probucol inhibits ABCA1-mediated cellular lipid efflux. Arteriosclerosis, Thrombosis, and Vascular Biology, 2004, 24(12): 2345-2350.
[3]. Colle D, Santos D B, Moreira E L, et al. Probucol increases striatal glutathione peroxidase activity and protects against 3-nitropropionic acid-induced pro-oxidative damage in rats. PLoS One, 2013, 8(6): e67658.
| Physical Appearance | A solid |
| Storage | Store at -20°C |
| M.Wt | 516.84 |
| Cas No. | 23288-49-5 |
| Formula | C31H48O2S2 |
| Solubility | insoluble in H2O; ≥17.45 mg/mL in DMSO; ≥64.2 mg/mL in EtOH |
| Chemical Name | 2,6-ditert-butyl-4-[2-(3,5-ditert-butyl-4-hydroxyphenyl)sulfanylpropan-2-ylsulfanyl]phenol |
| SDF | Download SDF |
| Canonical SMILES | CC(C)(C)C1=CC(=CC(=C1O)C(C)(C)C)SC(C)(C)SC2=CC(=C(C(=C2)C(C)(C)C)O)C(C)(C)C |
| Shipping Condition | Small Molecules with Blue Ice, Modified Nucleotides with Dry Ice. |
| General tips | We do not recommend long-term storage for the solution, please use it up soon. |
Quality Control & MSDS
- View current batch:
Chemical structure