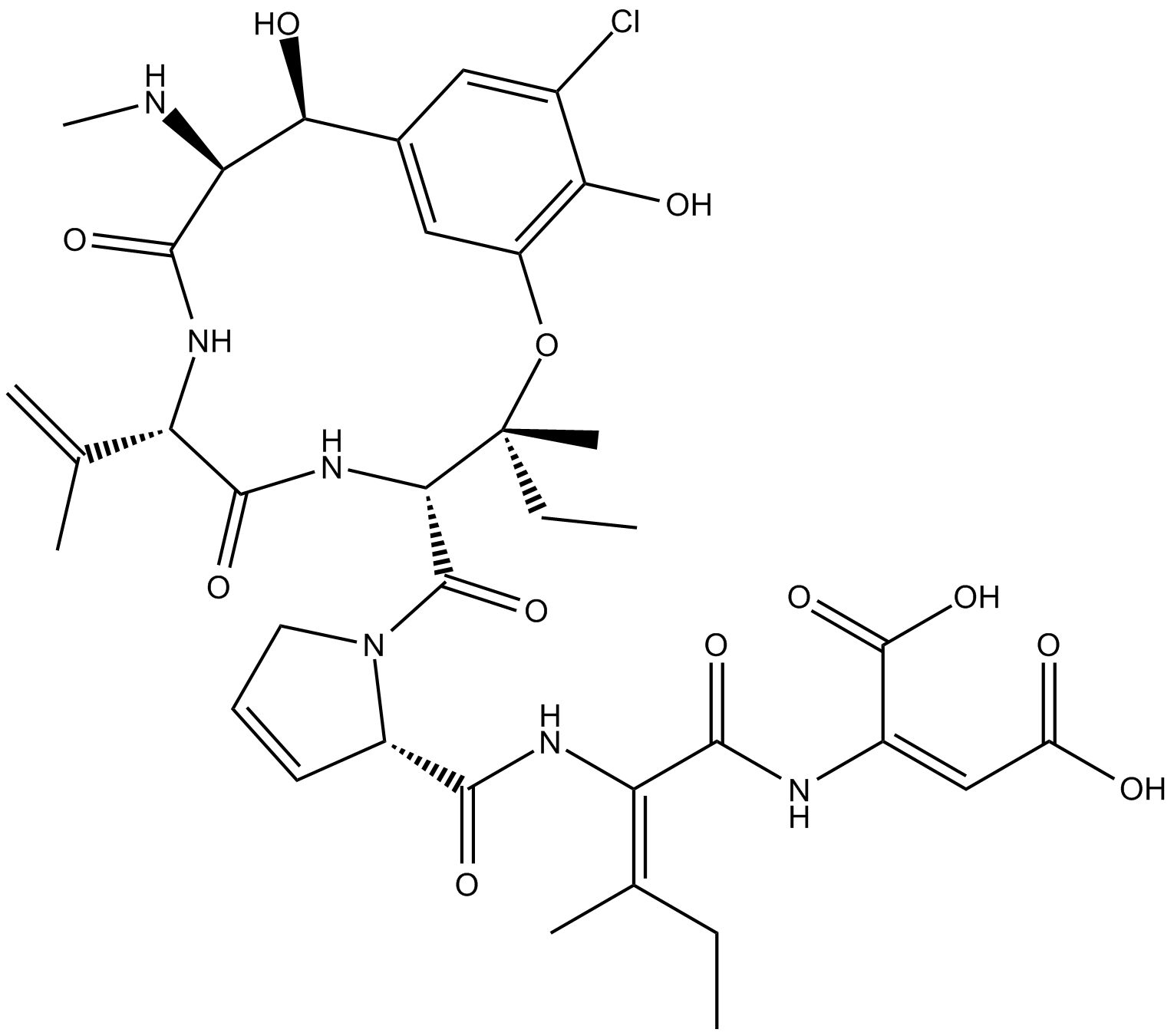
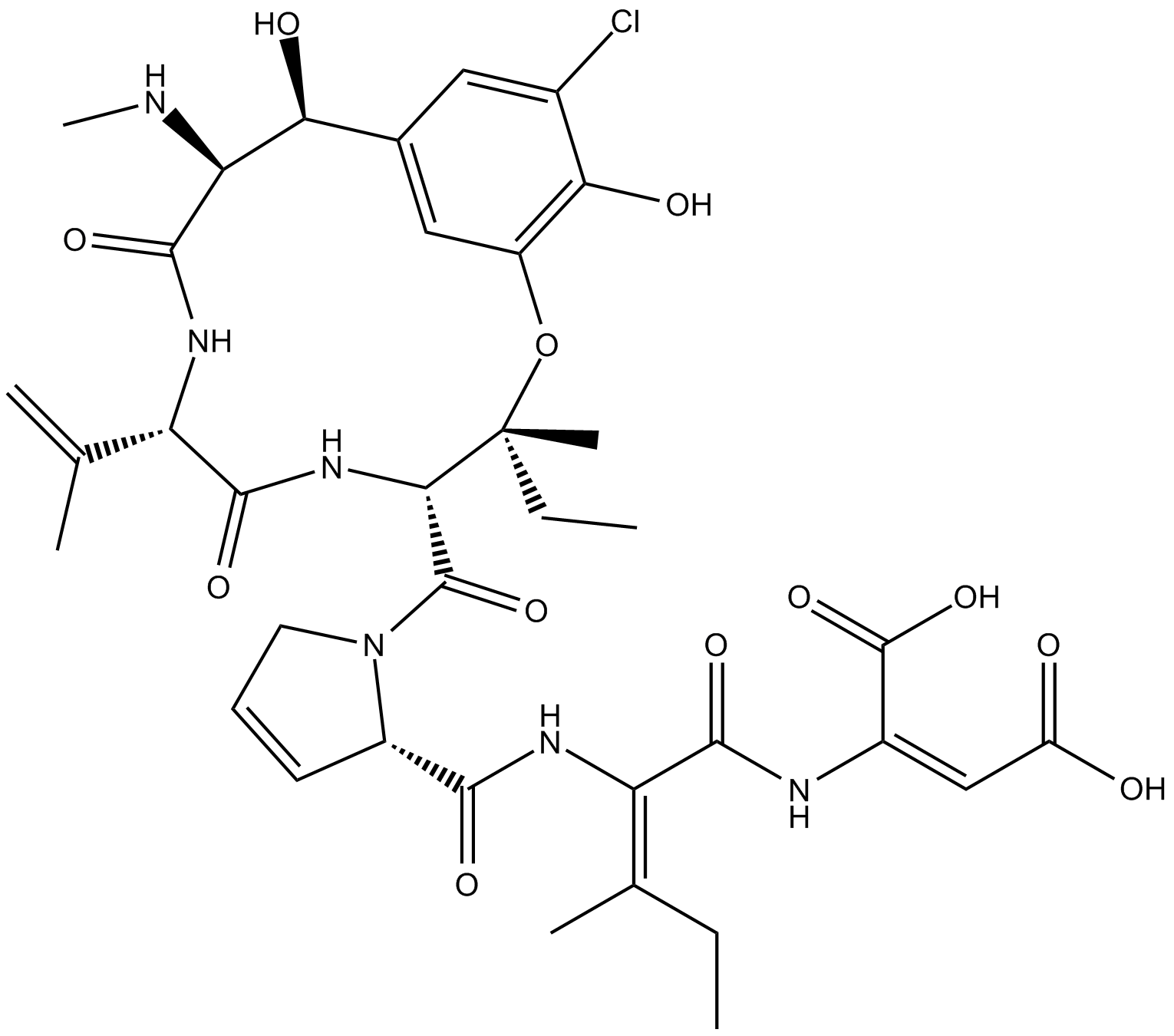
Phomopsin A
Phomopsin A is a cyclic hexapeptide mycotoxin that inhibits β-tubulin.
Phomopsins are a family of mycotoxins produced by the fungus Phomopsis leptostomiformis grows on lupins, which cause lupinosis, a severe liver disease of grazing animals [1][2].
Microtubules are one of the major components of the cytoskeleton that are essential in several cellular functions such as cell division and morphogenesis. α- and β-tubulins polymerize into microtubules.
Phomopsin A is a cyclic hexapeptide mycotoxin that binds β-tubulin in a vinca domain, partly overlapping with the site targeted by vinblastine and other tubulin inhibitors [2][3]. Phomopsin A noncompetitively inhibited the binding of radiolabeled vinblastine to tubulin with IC50 and Ki values of 0.8 μM and 2.8 μM, respectively. Phomopsin A potently inhibited tubulin-dependent GTP hydrolysis and nucleotide exchange on tubulin [2]. Phomopsin A, a vinca domain antimitotic peptide, also inhibited microtubule assembly [3][4]. Phomopsin A inhibited microtubule growth, modulated the dynamics of microtubules, and induced the self-association of tubulin dimers into single-walled rings and spirals [4].
References:
[1]. Hamel E. Natural products which interact with tubulin in the vinca domain: maytansine, rhizoxin, phomopsin A, dolastatins 10 and 15 and halichondrin B. Pharmacol Ther. 1992;55(1):31-51.
[2]. Cormier A, Marchand M, Ravelli RB, et al. Structural insight into the inhibition of tubulin by vinca domain peptide ligands. EMBO Rep. 2008 Nov;9(11):1101-6.
[3]. Li Y, Kobayashi H, Hashimoto Y, et al. Binding selectivity of rhizoxin, phomopsin A, vinblastine, and ansamitocin P-3 to fungal tubulins: differential interactions of these antimitotic agents with brain and fungal tubulins. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1992 Sep 16;187(2):722-9.
[4]. Mitra A, Sept D. Localization of the antimitotic peptide and depsipeptide binding site on beta-tubulin. Biochemistry. 2004 Nov 9;43(44):13955-62.
| Physical Appearance | A solid |
| Storage | Store at -20°C |
| M.Wt | 789.2 |
| Cas No. | 64925-80-0 |
| Formula | C36H45ClN6O12 |
| Synonyms | NSC 381839 |
| Solubility | Soluble in DMSO |
| Chemical Name | (2E)-(βS)-3-chloro-β,5-dihydroxy-N-methyl-L-tyrosyl-3,4-didehydro-L-valyl-3-hydroxy-L-isoleucyl-3,4-didehydro-L-prolyl-(2E)-2,3-didehydroisoleucyl-2,3-didehydro-aspartic acid, cyclic (15→3)-ether |
| SDF | Download SDF |
| Canonical SMILES | OC(/C(NC(/C(NC([C@H]1N(C([C@@H]2NC([C@H](C(C)=C)NC([C@@H](NC)[C@H](C3=CC(O[C@@]2(CC)C)=C(O)C(Cl)=C3)O)=O)=O)=O)CC=C1)=O)=C(CC)/C)=O)=C\C(O)=O)=O |
| Shipping Condition | Small Molecules with Blue Ice, Modified Nucleotides with Dry Ice. |
| General tips | We do not recommend long-term storage for the solution, please use it up soon. |
Quality Control & MSDS
- View current batch:
-
Purity = 98.00%
- COA (Certificate Of Analysis)
- MSDS (Material Safety Data Sheet)
- Datasheet
Chemical structure