Pexidartinib (PLX3397)
Pexidartinib (PLX3397) (CAS 1029044-16-3) is an orally bioavailable, selective ATP-competitive small molecule inhibitor, functioning as a potent antagonist of colony-stimulating factor 1 receptor (CSF1R) in various cellular systems and exhibiting inhibitory activity against related receptor tyrosine kinases in other cell types. Additionally, it demonstrates preferential inhibition of CSF1R compared to other kinases, supporting its selectivity in molecular targeting.
In preclinical experimental settings, Pexidartinib (PLX3397) elicits apoptosis in targeted cell populations, with IC50 values of 20 nM for CSF1R inhibition and 10 nM for additional relevant targets, when tested against pertinent cell lines. Comparative kinase profiling reveals selectivity margins of 10- to 100-fold over other kinases such as KDR (VEGFR2), FLT1 (VEGFR1), and NTRK3 (TRKC), with IC50 values reported at 160 nM, 350 nM, 860 nM, 880 nM, and 890 nM, respectively. It can also induce cellular apoptosis, contributing to its mechanism-based anti-tumor effects in vitro and in vivo.
In drug discovery and translational oncology research contexts, Pexidartinib (PLX3397) is widely used for its ability to inhibit CSF1R-mediated signaling pathways, explore macrophage dynamics within tumor microenvironments, and assess therapeutic strategies for tumor growth inhibition.
- 1. Shiyong Zhang, Yuting Zhou, Yue Ren. "Microglial activation drives neuronal dysregulation in alcohol-induced seizure susceptibility." Sci Rep. 2025 Nov 3;15(1):38389 PMID: 41184409
- 2. Jinchao Gao, Qingxiang Song, et al. "Intracerebral fate of organic and inorganic nanoparticles is dependent on microglial extracellular vesicle function." Nat Nanotechnol. 2024 Mar;19(3):376-386 PMID: 38158436
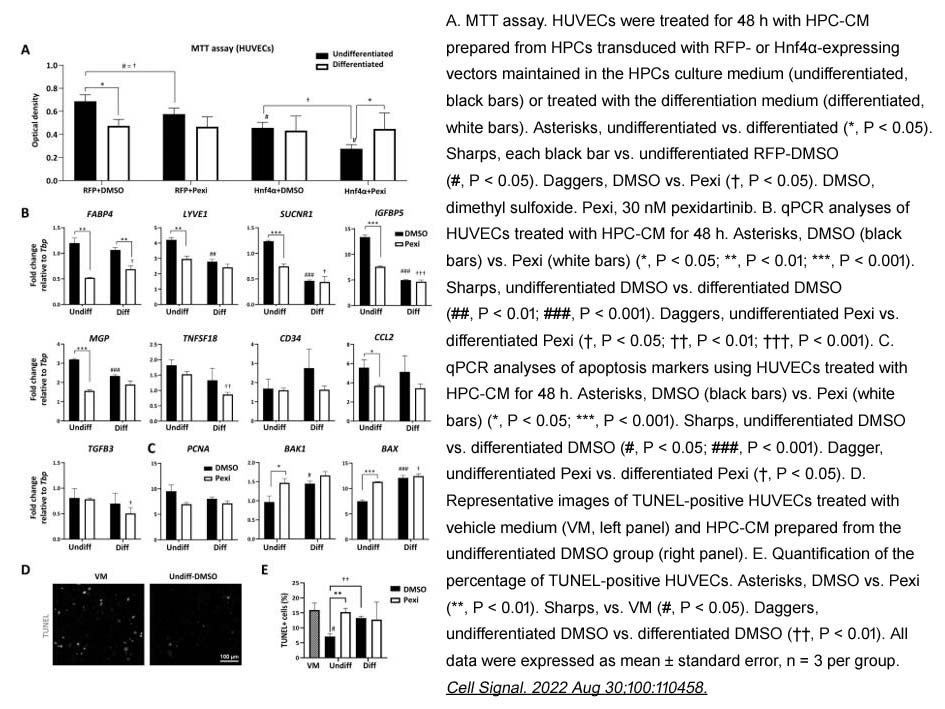
- 3. Sanghoon Lee, Rebekah Karns, et al. "Mechanism of paracrine communications between hepatic progenitor cells and endothelial cells." Cell Signal. 2022 Aug 30;100:110458 PMID: 36055565
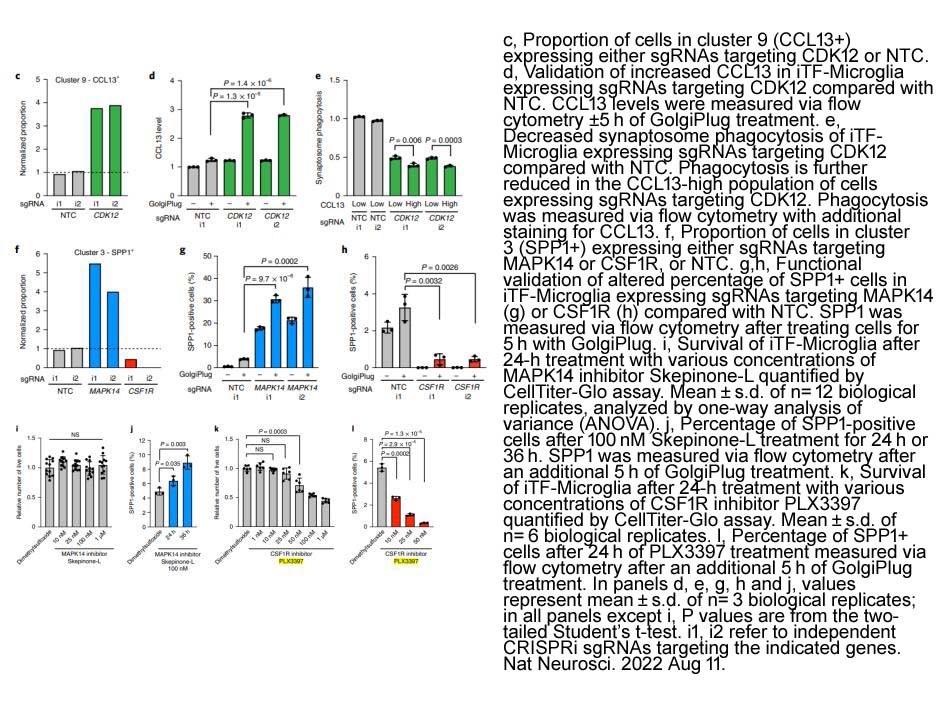
- 4. Nina M. Dräger, Sydney M. Sattler, et al. "A CRISPRi/a platform in human iPSC-derived microglia uncovers regulators of disease states." Nat Neurosci. 2022 Sep;25(9):1149-1162 PMID: 35953545
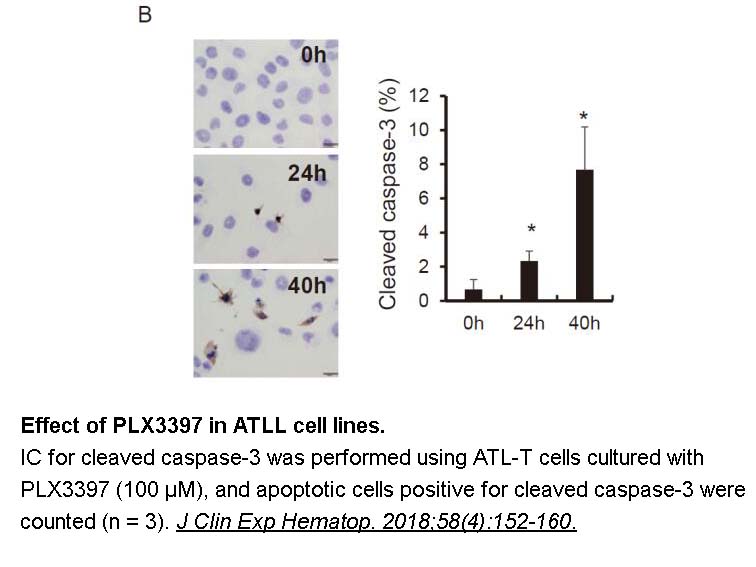
- 5. Komohara Y, Noyori O, et al. "Potential anti-lymphoma effect of M-CSFR inhibitor in adult T-cell leukemia/lymphoma." J Clin Exp Hematop. 2018;58(4):152-160 PMID: 30541986
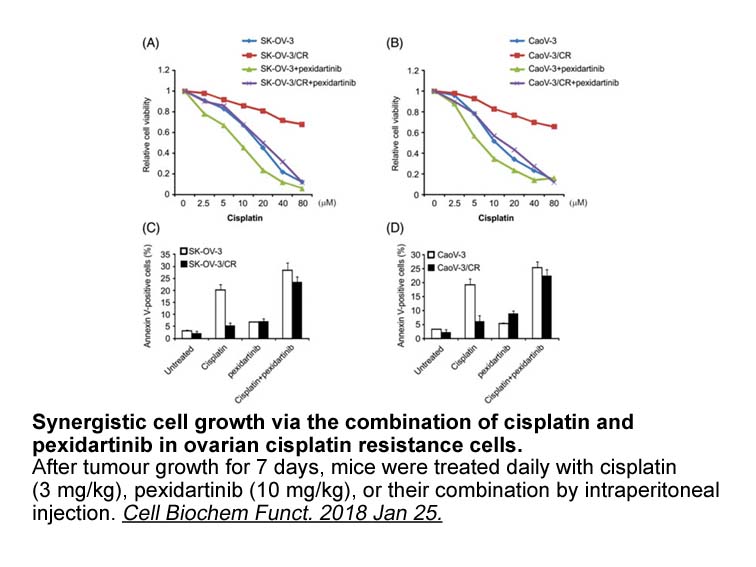
- 6. Yu R, Jin H, et al. "Inhibition of the CSF-1 receptor sensitizes ovarian cancer cells to cisplatin." Cell Biochem Funct. 2018 Jan 25 PMID: 29372560
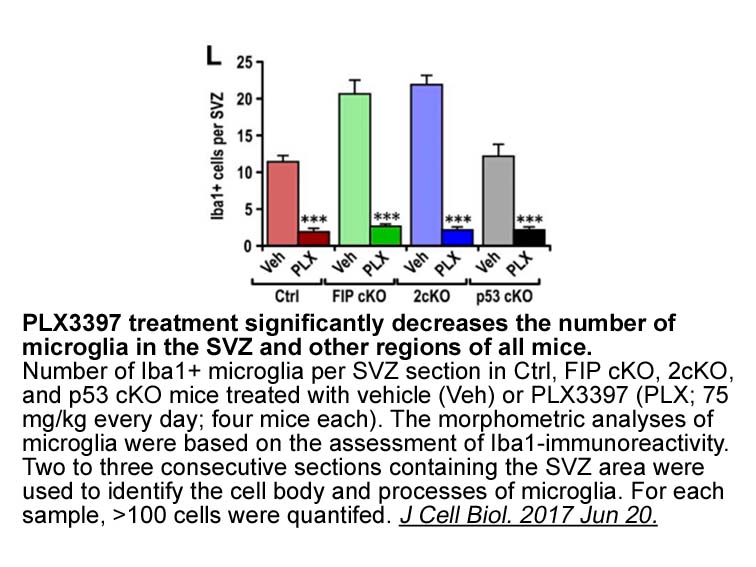
- 7. Wang C, Yeo S, et al. "Autophagy gene FIP200 in neural progenitors non-cell autonomously controls differentiation by regulating microglia." J Cell Biol. 2017 Jun 20. pii: jcb.201609093 PMID: 28634261
| Physical Appearance | A solid |
| Storage | Store at -20°C |
| M.Wt | 417.81 |
| Cas No. | 1029044-16-3 |
| Formula | C20H15ClF3N5 |
| Synonyms | PLX3397 |
| Solubility | insoluble in EtOH; insoluble in H2O; ≥20.9 mg/mL in DMSO |
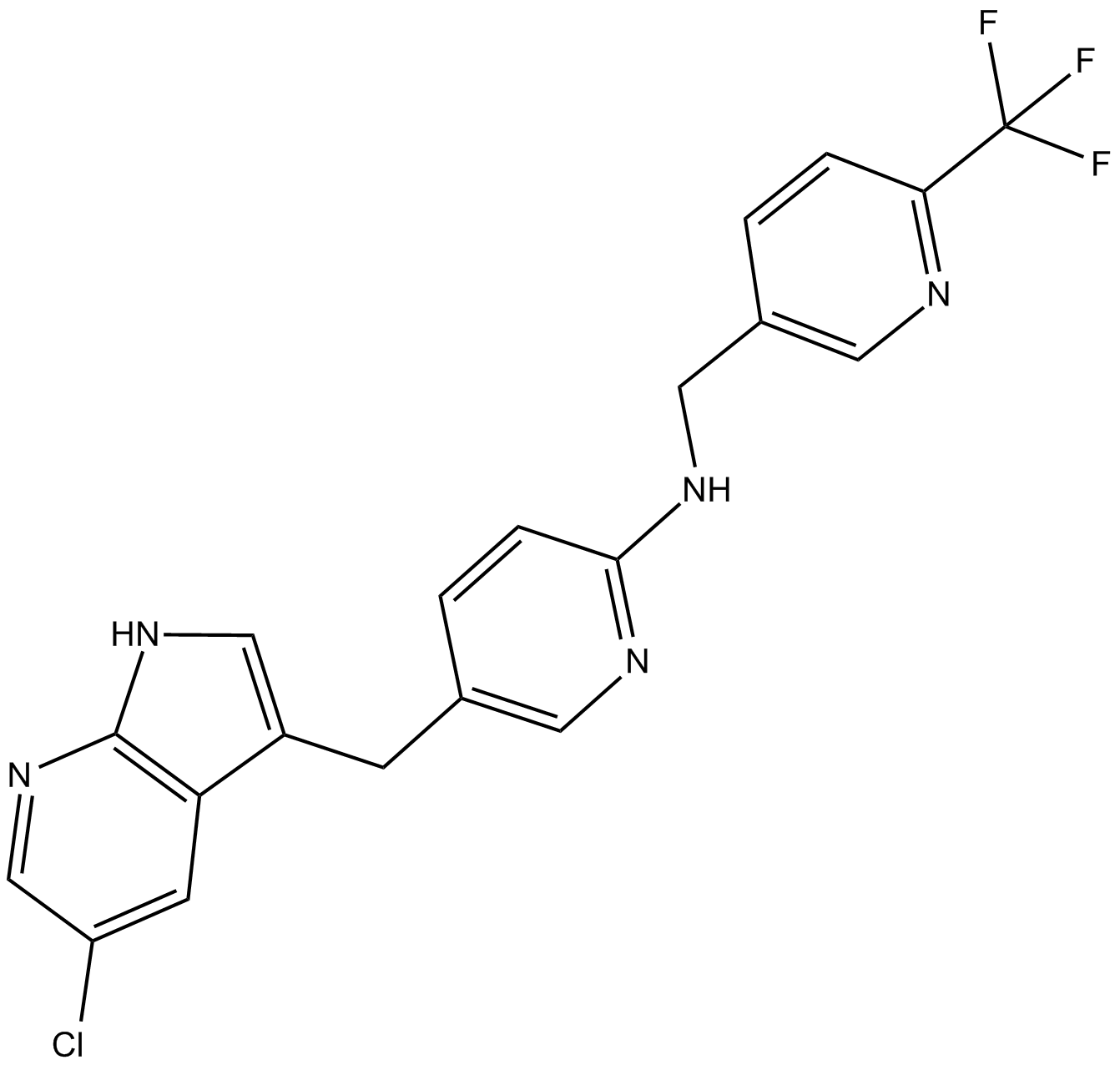
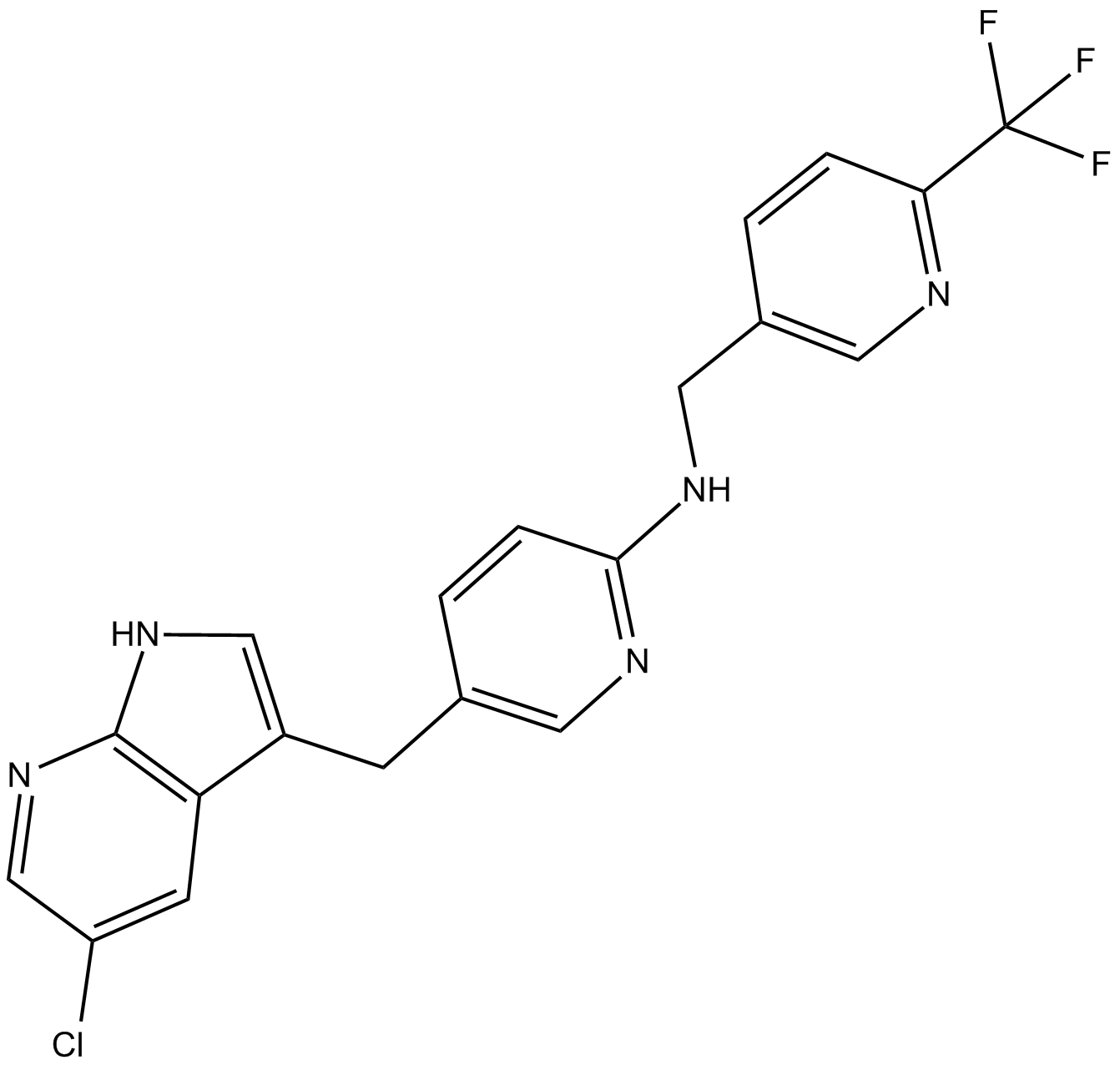
| Chemical Name | 5-((5-chloro-1H-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridin-3-yl)methyl)-N-((6-(trifluoromethyl)pyridin-3-yl)methyl)pyridin-2-amine |
| SDF | Download SDF |
| Canonical SMILES | FC(c1ncc(CNc2ncc(Cc(c3c4)c[nH]c3ncc4Cl)cc2)cc1)(F)F |
| Shipping Condition | Small Molecules with Blue Ice, Modified Nucleotides with Dry Ice. |
| General tips | We do not recommend long-term storage for the solution, please use it up soon. |
| Cell experiment [1]: | |
|
Cell lines |
SK-N-SH cells |
|
Preparation method |
The solubility of this compound in DMSO is >20.9mg/mL. General tips for obtaining a higher concentration: Please warm the tube at 37℃ for 10 minutes and/or shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while. Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. |
|
Reacting condition |
IC50: 10 μM |
|
Applications |
Pexidartinib weakly inhibited the growth of SK-N-SH cells with an IC50 of 10 μM. PLX3397 had little or no effect on the growth of MDA-MB-231 human tumor cells grown as xenografts. |
| Animal experiment [1,2]: | |
|
Animal models |
C57BL/6 mice xenografted with B16F10 melanoma cells, Female nude mice bearing MDA-MB-468 human breast tumor cells xenografts |
|
Dosage form |
Oral administration, daily doses of approximately 45 mg/kg |
|
Application |
Pexidartinib predominantly affected F4/80+ Ly6C- blood macrophages and strongly decreased the CSF-1R expression levels on F4/80+ Ly6C+ ‘inflammatory’ monocytes. Oral dosing of PLX3397 prevented the rise in osteoclasts and the loss of bone. |
|
Other notes |
Please test the solubility of all compounds indoor, and the actual solubility may slightly differ with the theoretical value. This is caused by an experimental system error and it is normal. |
|
References: [1] West B L, DeNardo D G, Tsai J, et al. Efficacy of the selective CSF-1R kinase inhibitor PLX3397 in mouse models of tumor growth and bone metastasis[J]. 2010. [2] Sluijter M, van der Sluis T C, van der Velden P A, et al. Inhibition of CSF-1R supports T-cell mediated melanoma therapy[J]. PloS one, 2014, 9(8): e104230. |
|
Quality Control & MSDS
- View current batch:
Chemical structure
Related Biological Data
Related Biological Data
Related Biological Data
Related Biological Data
Related Biological Data