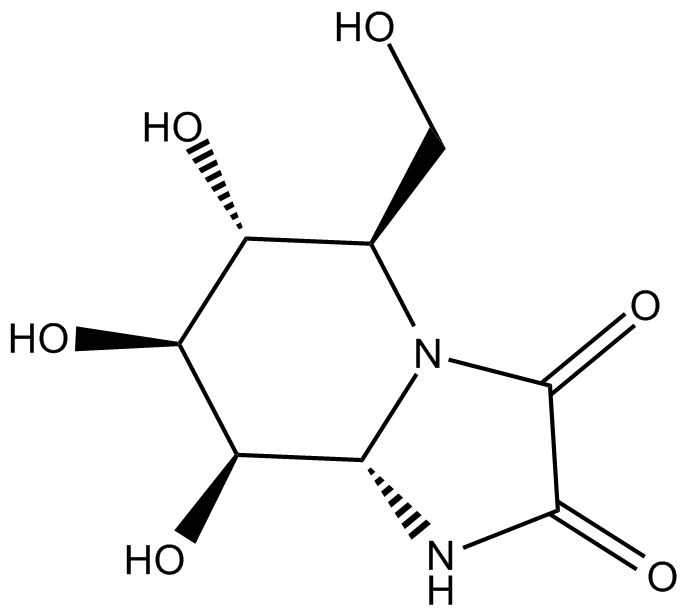
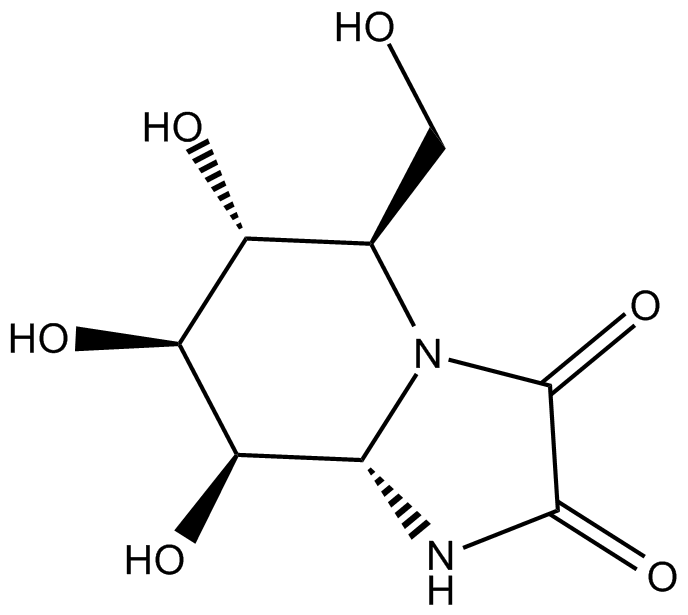
Kifunensine
Kifunensine is a potent and selective inhibitor of class I α-mannosidases and may serve as a key inhibitor of glycoprotein biosynthesis[1]. Kifunensine inhibits both human endoplasmic reticulum α-1,2-mannosidase I and members of the Golgi subfamily of the class I mannosidases (Golgi α-mannosidase IA, IB, and IC) exhibiting Ki values of 130 and 23 nM, respectively. It also inhibits mung bean α-1,2-mannosidase I with an IC50 value of 20-50 nM[1]. Kifunensine can be used to block α-mannosidase I activity at the endoplasmic reticulum (ER), preventing the removal of desired mutated proteins through ER quality control mechanisms[2,3].
References:
[1]. Hering K W, Karaveg K, Moremen K W, et al. A Practical Synthesis of Kifunensine Analogues as Inhibitors of Endoplasmic Reticulum alpha-Mannosidase I. Journal of Organic Chemistry, 2005, 70(24): p.9892-9904.
[2]. Bartoli M, Gicquel E, Barrault L, et al. Mannosidase I inhibition rescues the human α-sarcoglycan R77C recurrent mutation. Human Molecular Genetics, 2008, 17(9): 1214-1221.
[3]. Soheili T, Gicquel E, Poupiot J, et al. Rescue of sarcoglycan mutations by inhibition of endoplasmic reticulum quality control is associated with minimal structural modifications. Human Mutation, 2012, 33(2): 429-439.
| Physical Appearance | A crystalline solid |
| Storage | Store at -20°C |
| M.Wt | 232.19 |
| Cas No. | 109944-15-2 |
| Formula | C8H12N2O6 |
| Solubility | Soluble in H2O |
| Chemical Name | (5R,6R,7S,8R,8aS)-6,7,8-trihydroxy-5-(hydroxymethyl)hexahydroimidazo[1,2-a]pyridine-2,3-dione |
| SDF | Download SDF |
| Canonical SMILES | VO[C@@H]([C@H]1O)[C@@H](NC2=O)N(C2=O)[C@H](CO)[C@H]1O |
| Shipping Condition | Small Molecules with Blue Ice, Modified Nucleotides with Dry Ice. |
| General tips | We do not recommend long-term storage for the solution, please use it up soon. |
| Cell experiment:[1] | |
|
Cell lines |
Hybridoma cells expressing a human IgG1 monoclonal antibody against a tumor vascular associated antigen |
|
Reaction Conditions |
2 μg/mL kifunensine for 4 d incubation |
|
Applications |
Kifunensine treatment significantly reduced the lentil lectin binding. Furthermore, kifunensine was the most effective among the glycosylation inhibitors tested in producing antibodies containing oligomannose residues without fucose. |
| Animal experiment:[1] | |
|
Animal models |
BALB/c mice |
|
Dosage form |
5 mg/kg Injected via the tail vein |
|
Applications |
The serum levels of antibody in mice were not significantly altered up to 168 h following injection. The use of kifunensine provided a simple and rapid method for the production of antibodies with increased antibody-dependent cell mediated cytotoxicity (ADCC) without the time-consuming need to re-engineer either the antibody molecule or the host cell line. |
|
Note |
The technical data provided above is for reference only. |
|
References: 1. Zhou Q, Shankara S, Roy A, et al. Development of a simple and rapid method for producing non-fucosylated oligomannose containing antibodies with increased effector function. Biotechnology and Bioengineering, 2008, 99(3): 652-665. |
|
Quality Control & MSDS
- View current batch:
-
Purity = 98.00%
- COA (Certificate Of Analysis)
- MSDS (Material Safety Data Sheet)
Chemical structure