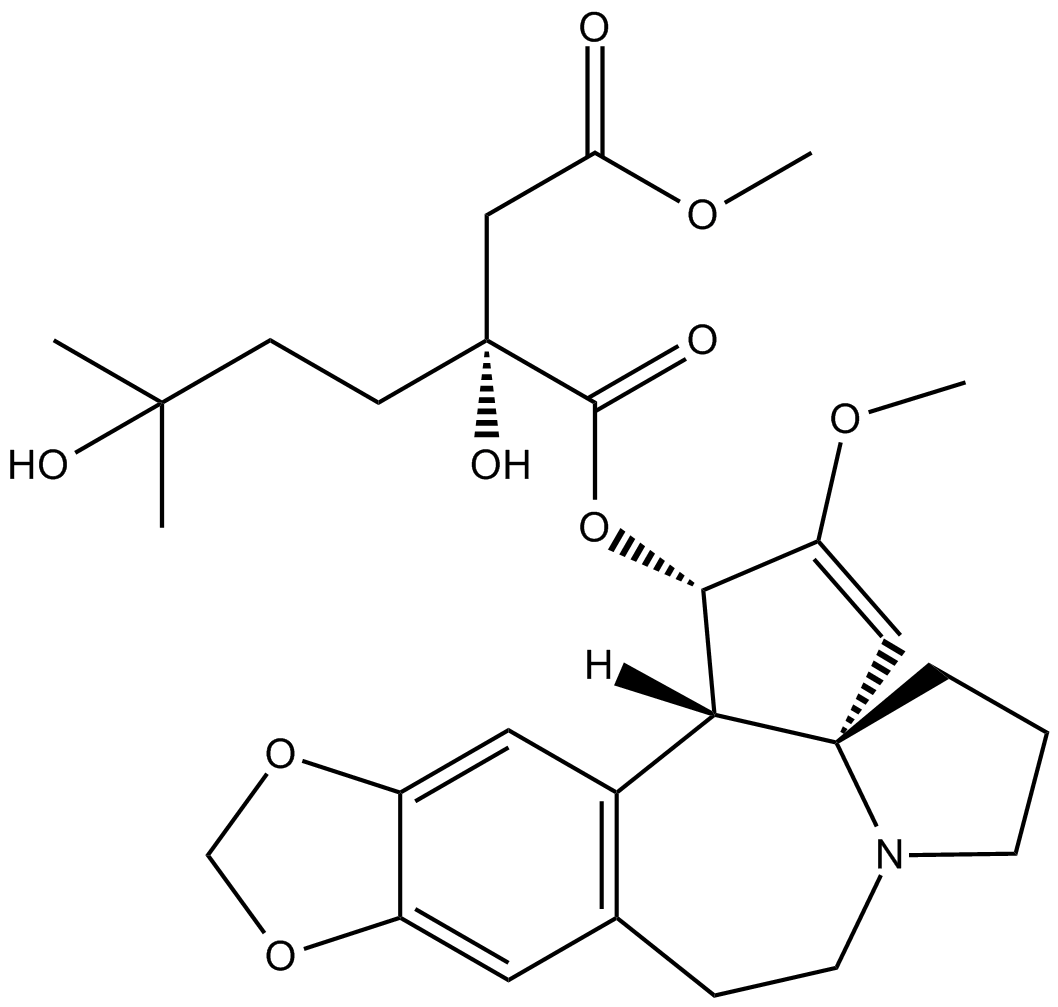
Harringtonine
Harringtonine (CAS 26833-85-2) is a natural alkaloid isolated from Cephalotaxus harringtonia, functioning primarily as an inhibitor of eukaryotic protein synthesis. It exerts its inhibitory effects by blocking translation initiation, specifically disrupting aminoacyl-tRNA binding and peptide bond formation during the early stages of polypeptide elongation. In ribosome profiling studies, harringtonine immobilizes ribosomes immediately following initiation, enabling capture and analysis of ribosome-protected mRNA fragments. Due to these mechanisms, harringtonine serves as a valuable experimental tool for investigating translation dynamics and holds potential in anti-cancer research, particularly against hematological malignancies.
| Physical Appearance | A crystalline solid |
| Storage | Store at -20°C |
| M.Wt | 531.6 |
| Cas No. | 26833-85-2 |
| Formula | C28H37NO9 |
| Synonyms | NSC 124147 |
| Solubility | ≥48 mg/mL in DMSO; ≥49.9 mg/mL in EtOH; insoluble in H2O |
| Chemical Name | 3-[4-methyl (2R)-2-hydroxy-2-(3-hydroxy-3-methylbutyl)butanedioate]cephalotaxine |
| SDF | Download SDF |
| Canonical SMILES | O=C(OC)C[C@@](CCC(C)(O)C)(O)C(O[C@H]1[C@](C(C=C(OCO2)C2=C3)=C3CCN4CCC5)([H])[C@]45C=C1OC)=O |
| Shipping Condition | Small Molecules with Blue Ice, Modified Nucleotides with Dry Ice. |
| General tips | We do not recommend long-term storage for the solution, please use it up soon. |
Quality Control & MSDS
- View current batch:
Chemical structure