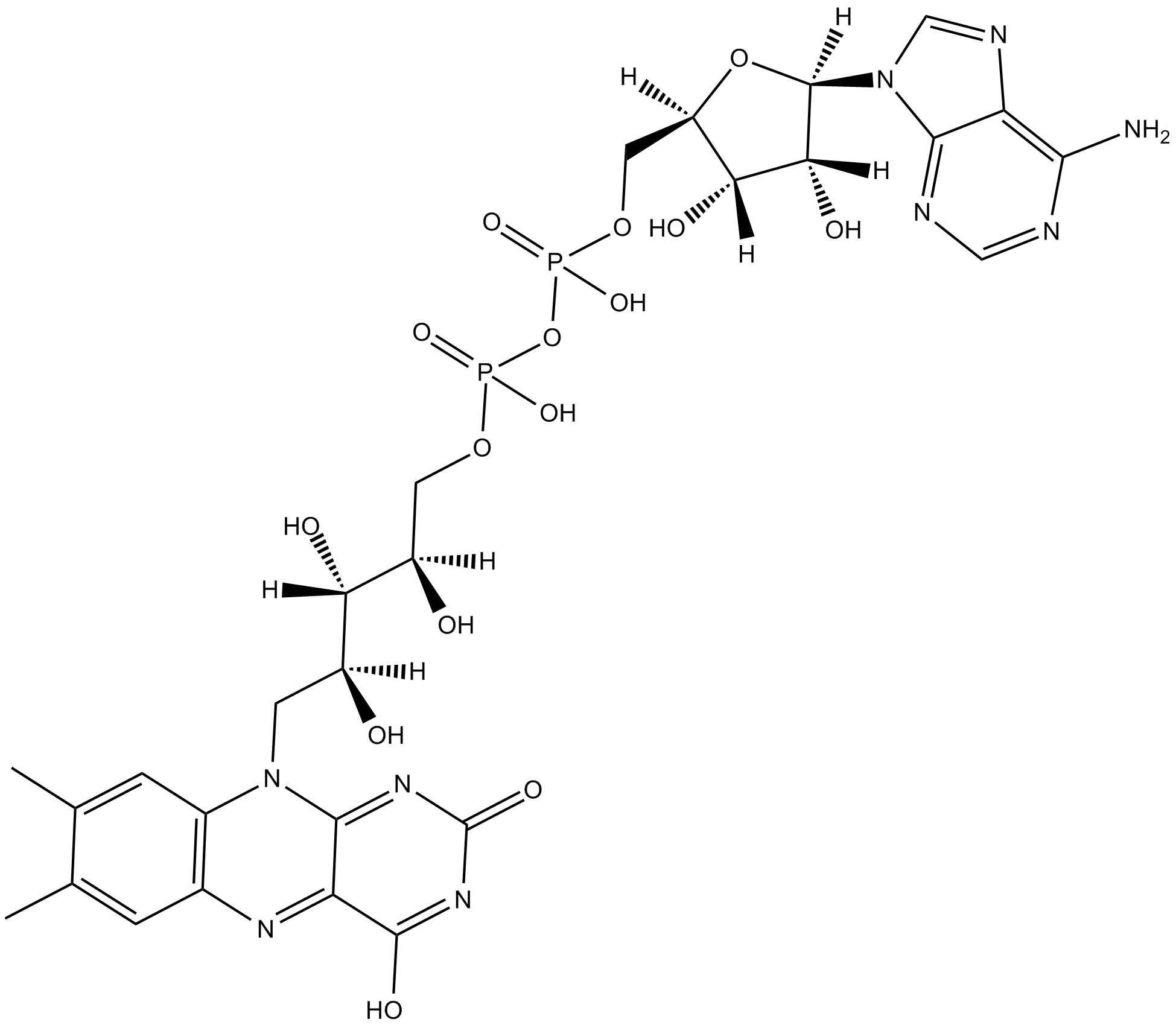
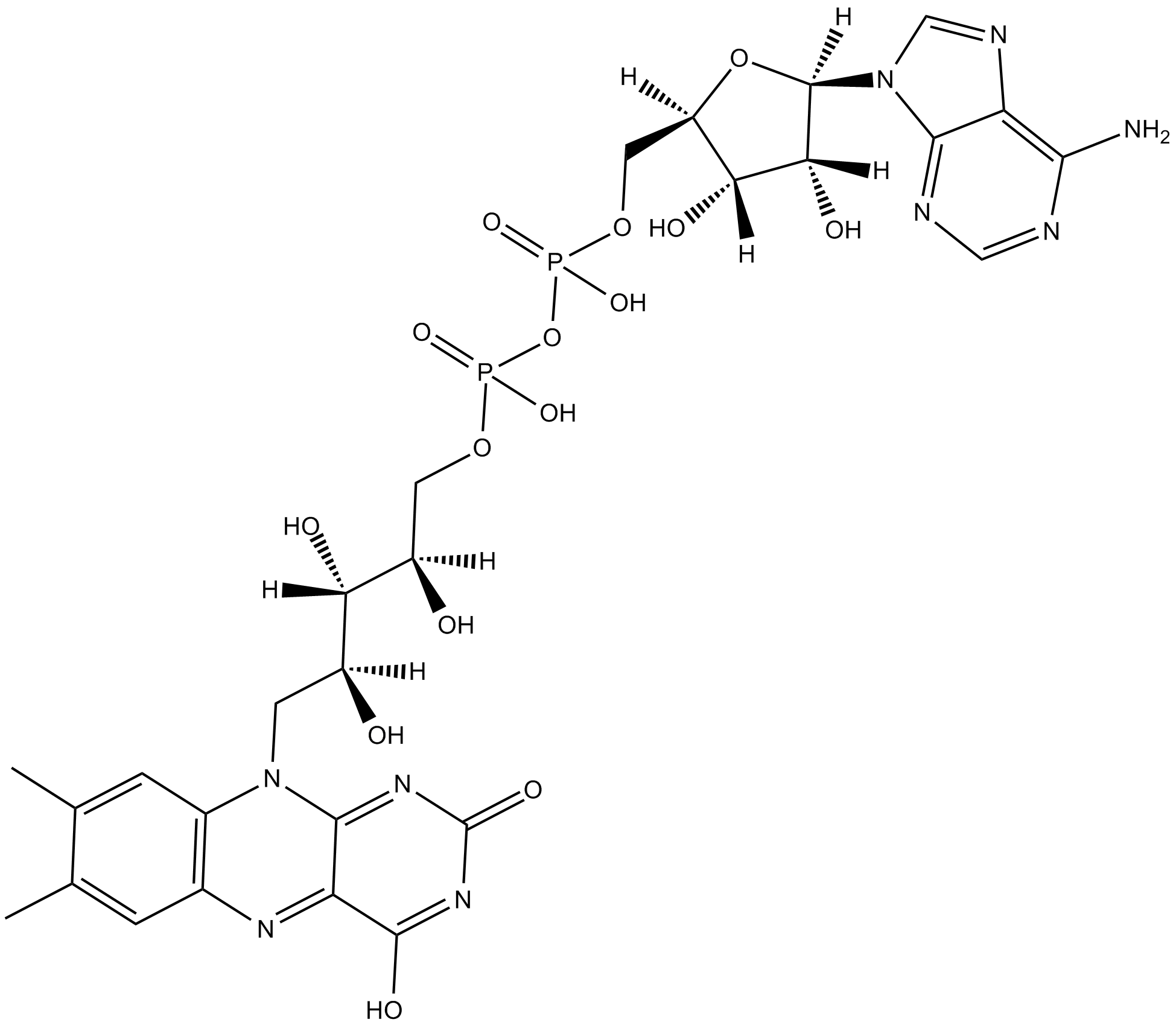
Flavin adenine dinucleotide
Flavin adenine dinucleotide is used as a redox cofactor by a variety of proteins involved in several important enzymatic reactions in metabolism. In human, most flavoproteins contain one or more loosely bound flavin adenine dinucleotide moieties. Flavoproteins include the succinate dehydrogenase complex, α-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase, folate/FAD-dependent tRNA methyltransferases, N-hydroxylating flavoprotein monooxygenases, and apoptosis-inducing factor 2. Flavoproteins are predominately located in the mitochondria due to their redox power. Of all flavoproteins, more than 90% perform redox reactions and ~ 10% are lyases, transferases, isomerases and ligases involved in nonredox reactions.
References:
1. Kohlmeier M. Chapter 10 - Water-Soluble Vitamins and Nonnutrients. Nutrient Metabolism (Second Edition), 2015, 567-671.
2. Lienhart WD, Gudipati V, Macheroux P. The human flavoproteome. Archives of Biochemistry and Biophysics, 2013, 535(2): 150-162.
3. Macheroux P, Kappes B, Ealick SE. Flavogenomics--a genomic and structural view of flavin-dependent proteins. The FEBS Journal, 2011, 278(15): 2625-2634.
4. Sugiyama S, Ozawa T. Protection of chlorpromazine-induced arrhythmia by flavin-adenine-dinucleotide in canine heart. Japanese Heart Journal, 1979, 20(5): 657-665.
| Physical Appearance | A solid |
| Storage | Store at -20°C |
| M.Wt | 785.55 |
| Cas No. | 146-14-5 |
| Formula | C27H33P2N9O15 |
| Solubility | insoluble in EtOH; insoluble in DMSO; ≥196.5 mg/mL in H2O |
| SDF | Download SDF |
| Canonical SMILES | CC1=CC(N=C(C(O)=N2)C3=NC2=O)=C(N3C[C@@](O)([H])[C@@](O)([H])[C@@](O)([H])COP(O)(OP(O)(OC[C@](O4)([H])[C@](O)([H])[C@](O)([H])[C@]4([H])N5C=NC(C5=NC=N6)=C6N)=O)=O)C=C1C |
| Shipping Condition | Small Molecules with Blue Ice, Modified Nucleotides with Dry Ice. |
| General tips | We do not recommend long-term storage for the solution, please use it up soon. |
| Animal experiment:[4] | |
|
Animal models |
Dogs |
|
Dosage form |
2 mg/kg Intravenous injection |
|
Applications |
Flavin adenine dinucleotide significantly canceled the chlorpromazine (CPZ)-induced decrease in ventricular fibrillation threshold (VFT). Also, flavin adenine dinucleotide counteracted the effects of CPZ on canine heart mitochondria. Thus, flavin adenine dinucleotide might be useful in the treatment of the cardiac disturbances associated with overdosage of CPZ. |
|
Note |
The technical data provided above is for reference only. |
|
References: 1. Kohlmeier M. Chapter 10 - Water-Soluble Vitamins and Nonnutrients. Nutrient Metabolism (Second Edition), 2015, 567-671. 2. Lienhart WD, Gudipati V, Macheroux P. The human flavoproteome. Archives of Biochemistry and Biophysics, 2013, 535(2): 150-162. 3. Macheroux P, Kappes B, Ealick SE. Flavogenomics--a genomic and structural view of flavin-dependent proteins. The FEBS Journal, 2011, 278(15): 2625-2634. 4. Sugiyama S, Ozawa T. Protection of chlorpromazine-induced arrhythmia by flavin-adenine-dinucleotide in canine heart. Japanese Heart Journal, 1979, 20(5): 657-665. |
|
Quality Control & MSDS
- View current batch:
Chemical structure