FCCP
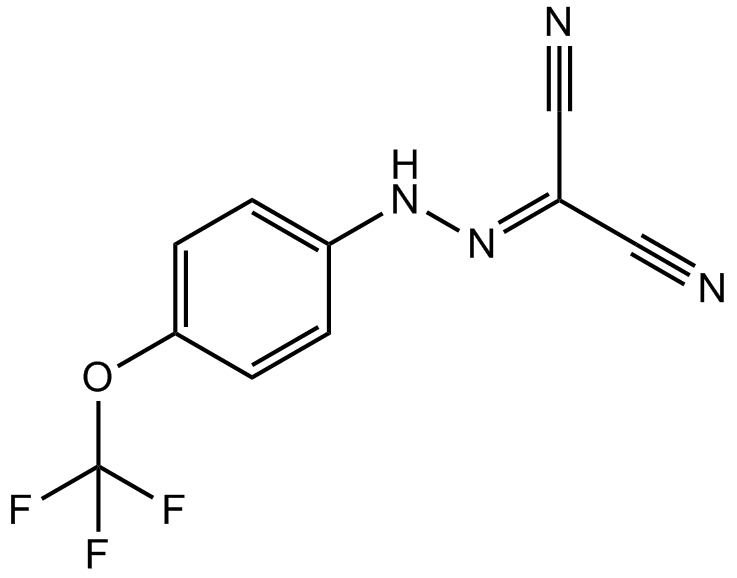
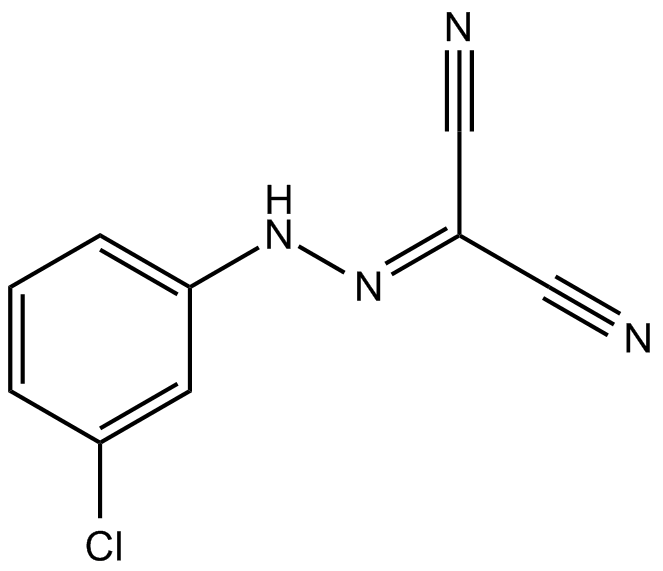
FCCP (CAS 370-86-5), chemically known as carbonyl cyanide p-trifluoromethoxyphenylhydrazone, is a lipophilic mitochondrial uncoupler frequently used in cellular biology research. It functions by transporting protons across mitochondrial membranes, dissipating the proton gradient essential for ATP synthesis. FCCP exhibits potent inhibitory activity (IC50 = 0.51 µM in T47D cells), effectively disrupting oxidative phosphorylation. Experimentally, FCCP increases cellular oxygen consumption and suppresses hypoxia-inducible factors (HIF-1α and HIF-2α), reducing downstream gene expression such as VEGF. In rodent embryos, FCCP impairs mitochondrial function, resulting in decreased ATP production, lower birth weight, and altered metabolic phenotypes in offspring, highlighting its utility in studying metabolic regulation and mitochondrial biology.
- 1. Jack Butler, Lowell Mott, et al. "Cell-to-cell signalling mediated via CO2: activity dependent CO2 production in the axonal node opens Cx32 in the Schwann cell paranode." bioRxiv. April 05, 2025.
- 2. Jiawei Yan, Xin Zhang, et al. "Macrophage NRF1 promotes mitochondrial protein turnover via the ubiquitin proteasome system to limit mitochondrial stress and inflammation." Cell Rep. 2024 Sep 25;43(10):114780 PMID: 39325625
- 3. Jun Xiao, Shuang Wang, et al. "25-Hydroxycholesterol regulates lysosome AMP kinase activation and metabolic reprogramming to educate immunosuppressive macrophages." Immunity. 2024 May 14;57(5):1087-1104.e7. PMID: 38640930
- 4. Jin-Long Pang, Fu-Hao Huang, et al. "Sodium cantharidate induces Apoptosis in breast cancer cells by regulating energy metabolism via the protein phosphatase 5-p53 axis." Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2021 Nov 1;430:115726. PMID: 34537213
| Physical Appearance | A crystalline solid |
| Storage | Store at RT |
| M.Wt | 254.17 |
| Cas No. | 370-86-5 |
| Formula | C10H5F3N4O |
| Solubility | insoluble in H2O; ≥25 mg/mL in EtOH with ultrasonic; ≥56.6 mg/mL in DMSO with ultrasonic |
| Chemical Name | (4-(trifluoromethoxy)phenyl)carbonohydrazonoyl dicyanide |
| SDF | Download SDF |
| Canonical SMILES | N#CC(C#N)=NNc(cc1)ccc1OC(F)(F)F |
| Shipping Condition | Small Molecules with Blue Ice, Modified Nucleotides with Dry Ice. |
| General tips | We do not recommend long-term storage for the solution, please use it up soon. |
| Cell experiment:[1] | |
|
Cell lines |
PC-3 and DU-145 prostate cancer cells |
|
Reaction Conditions |
10 μM FCCP for 24 h incubation |
|
Applications |
FCCP significantly decreased hypoxic as well as normoxic HIF-1 transcriptional activity which was in part mediated by down-regulation of the oxygen labile HIF-1α and HIF-2α protein levels in PC-3 and DU-145 prostate cancer cells. FCCP also decreased the expression of HIF target genes, VEGF and VEGF receptor-2. The mitochondrial uncoupler FCCP may be useful in the inhibition of HIF pathway in tumors. |
|
Note |
The technical data provided above is for reference only. |
|
References: 1. Thomas R, Kim MH. Targeting the hypoxia inducible factor pathway with mitochondrial uncouplers. Molecular and Cellular Biochemistry, 2007, 296(1-2): 35-44. |
|
Quality Control & MSDS
- View current batch:
Chemical structure