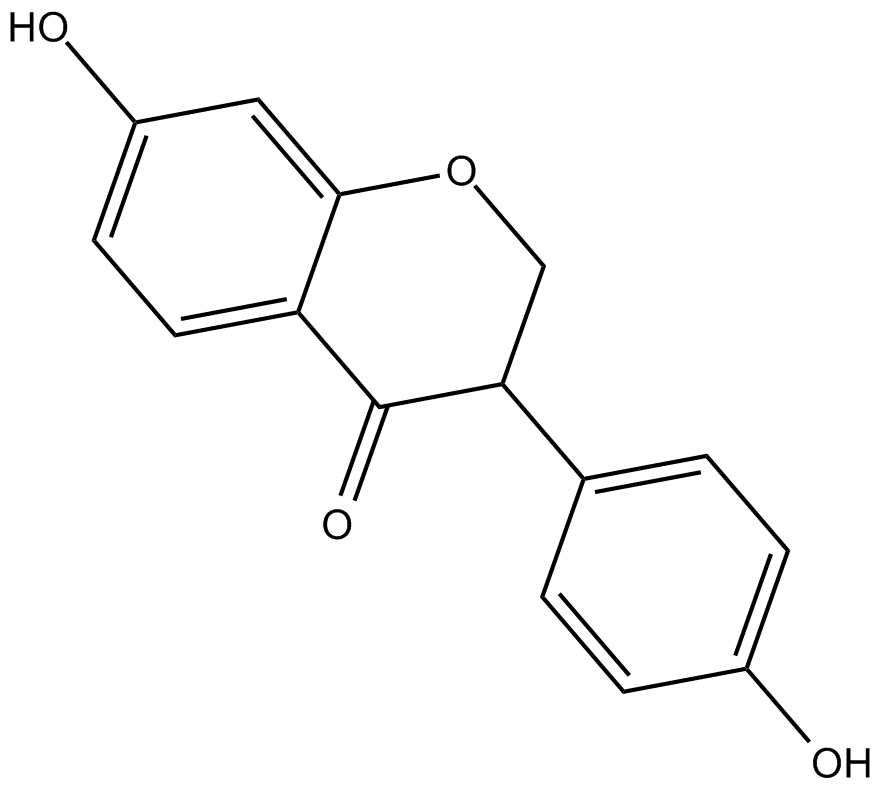
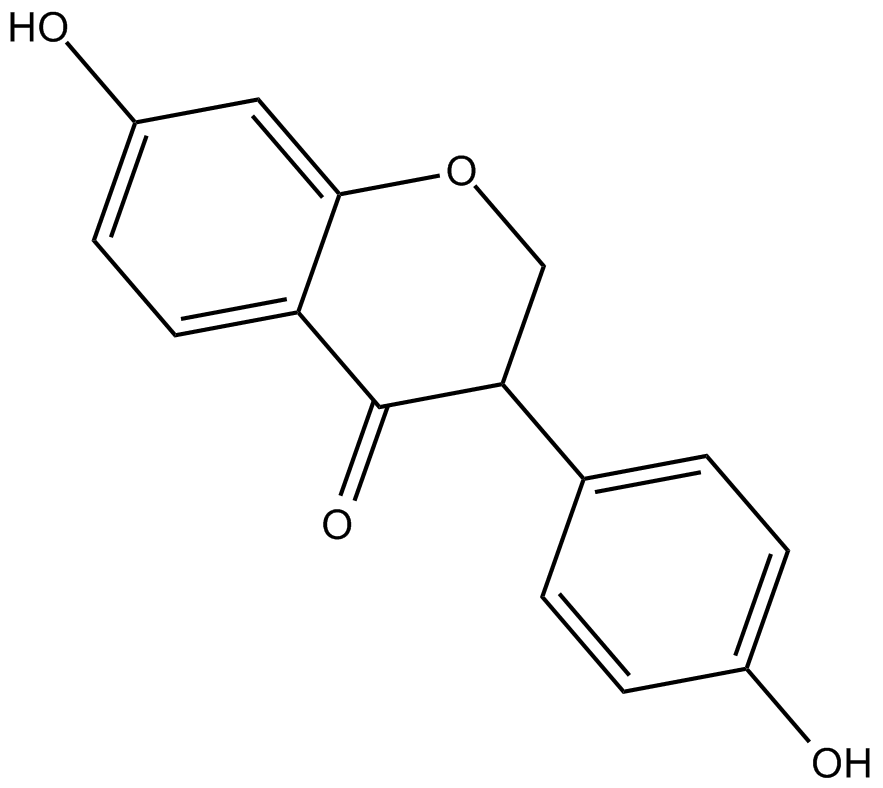
Dihydrodaidzein
Dihydrodaidzein, an active, estrogenic metabolite of daidzein in colonic bacteria, probably is further metabolized to various bioactive compounds including equol. As an estrogen receptor agonist, dihydrodaidzein, at micromolar concentrations, activates the estrogen receptor-dependent growth of breast cancer cells. Daidzein, an isoflavonoid phytoestrogenic compound, is found in soybeans, clover, kudzu, and other legumes.
In vitro: Prostatic fluid and plasma concentrations of dihydrodaidzein were sufficient to block the growth of benign human prostatic epithelial cells (PrEC). Dihydrodaidzein showed a significant inhibitory effect on the growth of prostate cancer cell line LNCaP. Additionally, dihydrodaidzein slightly triggered the apoptosis of PrEC. In addition to affecting apoptosis, dihydrodaidzein decreased proliferation, which was associated with the changes in cell cycle distribution and Caspase 3 activation [1].
In vivo: Male C57B1/6 wild type mice were administered orally with dihydrodaidzein at a dose of 25 mg/kg/day for 4 weeks. Compared to the control groups, the neointima of mice treated with dihydrodaidzein was thickened. In dihydrodaidzein-treated mice, the intimal thickness in the non-injured right iliac artery was not altered. Moreover, neointimal proliferation was selectively blocked by dihydrodaidzein via suppressing the migration and proliferation of vascular smooth muscle cell and dampening the endothelial apoptosis [2].
References:
[1]. Hedlund, T., Bokhoven, A., Johannes, W., Nordeen, S., & Ogden, L. Prostatic fluid concentrations of isoflavonoids in soy consumers are sufficient to inhibit growth of benign and malignant prostatic epithelial cells in vitro. The Prostate. 2006; 66(5): 557-566.
[2]. Shen, J., White, M., Husband, A., Hambly, B., & Bao, S. Phytoestrogen derivatives differentially inhibit arterial neointimal proliferation in a mouse model. European Journal of Pharmacology. 2006; 548(1-3): 123-128.
| Physical Appearance | A crystalline solid |
| Storage | Store at -20°C |
| M.Wt | 256.3 |
| Cas No. | 17238-05-0 |
| Formula | C15H12O4 |
| Synonyms | (±)-Dihydrodaidzein,4',7-dihydroxy Isoflavanone |
| Solubility | ≤0.1mg/ml in ethanol;30mg/ml in DMSO;10mg/ml in dimethyl formamide |
| Chemical Name | 2,3-dihydro-7-hydroxy-3-(4-hydroxyphenyl)-4H-1-benzopyran-4-one |
| SDF | Download SDF |
| Canonical SMILES | OC(C=C1)=CC=C1C2C(C3=CC=C(O)C=C3OC2)=O |
| Shipping Condition | Small Molecules with Blue Ice, Modified Nucleotides with Dry Ice. |
| General tips | We do not recommend long-term storage for the solution, please use it up soon. |
Quality Control & MSDS
- View current batch:
-
Purity = 98.00%
- COA (Certificate Of Analysis)
- MSDS (Material Safety Data Sheet)
- Datasheet
Chemical structure