CID 755673
IC50: Selective protein kinase D (PKD) antagonist with the IC50 of 0.182, 0.280, 0.227, >10, 15.3, 20.3, 40.5 and >50 μM for PKD1, PKD2, PKD3, PKC, CAK, PLK1, CAMKIIα and Akt respectively.
CID755673, benzoxoloazepinolone, is the first identified cell-active small molecule PKD antagonist. It inhibits the activity of PKD1 with an IC50 of 182 nM and demonstrates highest selectivity to PKD1 when compared with AKT, PLK1, CAK, CAMKIIα, PKD2 and PKD3. Moreover, it was not competitive with ATP for enzyme inhibition. [1]
In vitro: In cell based assays, CID755673 dose-dependently suppressed PKD1 activation induced by phorbol ester endogenous in LNCaP cells. It was also reported to reverse biological actions of PKD1 including class IIa histone deacetylase 5 nuclear exclusion, vesicular stomatitis, virus glycoprotein delivery from the Golgi to the plasma membrane as well as the ilimaquinone-induced Golgi fragmentation. Moreover, CID755673 suppressed prostate cancer cell proliferation, cell migration, and invasion. [1]
In vivo: Experimental models of acute pancreatitis were developed to study the effect of CID755673 on acute pancreatitis in vivo. Results demonstrated that this compound suppressed PKD1/2 and therefore significantly offset necrosis and severity of pancreatitis. [2]
Clinical trial: So far, no clinical trial has been conducted.
References:
[1]Sharlow ER, Giridhar KV, LaValle CR, Chen J, Leimgruber S, Barrett R, Altamirano KB, Wipf P, Lazo JS and Wang QJ. Potent and selective disruption of protein kinase D functionality by a benzoxoloazepinolone. J Biol Chem. 2008 Nov. 283(48): 3351246.
[2]Yuan JZ, Liu YN, Tan TY, Guha S, Gukovsky I, Gukovskaya A and Pandol SJ. Protein kinase D regulates cell death pathways in experimental pancreatitis. Front Physiol. 2012 Mar. 3: DOI: 10.3389/fphys.2012.00060.
| Physical Appearance | A solid |
| Storage | Store at -20°C |
| M.Wt | 217.22 |
| Cas No. | 521937-07-5 |
| Formula | C12H11NO3 |
| Solubility | insoluble in H2O; ≥4.94 mg/mL in EtOH with ultrasonic; ≥5.55 mg/mL in DMSO |
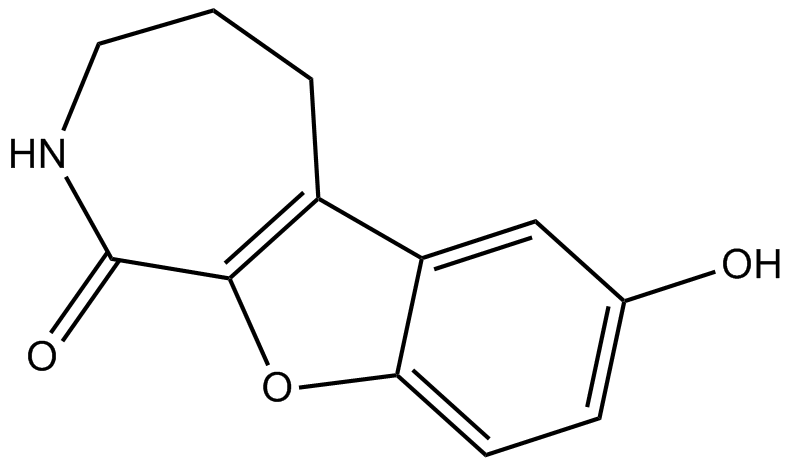
| Chemical Name | 7-hydroxy-2,3,4,5-tetrahydro-[1]benzofuro[2,3-c]azepin-1-one |
| SDF | Download SDF |
| Canonical SMILES | Oc(cc1)cc2c1[o]c1c2CCCNC1=O |
| Shipping Condition | Small Molecules with Blue Ice, Modified Nucleotides with Dry Ice. |
| General tips | We do not recommend long-term storage for the solution, please use it up soon. |
Quality Control & MSDS
- View current batch:
Chemical structure