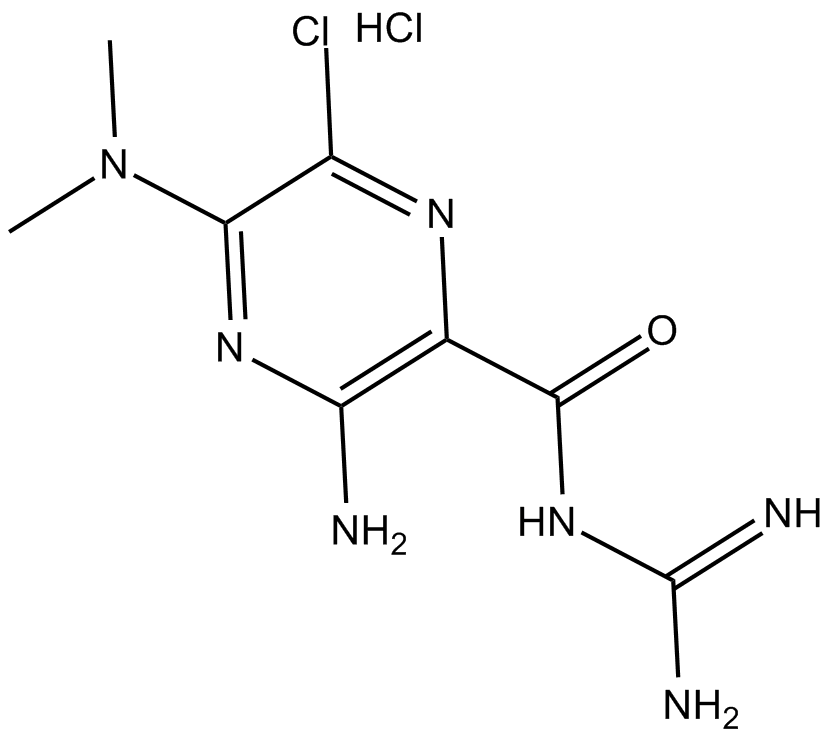
5-(N,N-dimethyl)-Amiloride (hydrochloride)
5-(N, N-dimethyl)-Amiloride (hydrochloride), a derivative of amiloride, is an inhibitor of NHE1, NHE2, and NHE3.
The Na+/H+ exchanger (NHE) is a protein that has been involved in intracellular pH homeostasis of many mammalian cell types. NHE is involved in regulating intracellular pH and cell volume by extruding protons from, and taking up sodium ions into cells [1].
5-(N, N-dimethyl)-Amiloride (DMA) inhibited NHE1, NHE2, and NHE3 with Ki values of 0.02, 0.25, and 14 μM, respectively. DMA showed little or no effects on NHE4, NHE5, and NHE7 [1]. DMA could effectively protect the right ventricular wall against ischemia-reperfusion dysfunction in the presence or absence of ouabain [2]. DMA protected against severe reperfusion-induced cardiac contractile dysfunction, appeared to act via a normalization of tissue sodium levels [2]. DMA (0.2 mM) completely inhibited pHi recovery after cell acidification and blocked EGF-induced cytoprotection against acid [3].
In primary rat hepatocyte cultures and rat liver plasma membranes, DMA increased steady-state Na+ content and inhibited ouabain-sensitive 86Rb+ uptake in a reversible, concentration-dependent, ouabain-like manner, with estimated IC50 of 5.2×10-4 M. DMA also inhibited ouabain-sensitive ATP hydrolysis in rat liver plasma membranes with IC50 value of 2.2 ×10-3 M. DMA (10-3 M) decreased the uptake into hepatocytes of alanine by 61% [4].
References:
[1] Masereel B, Pochet L, Laeckmann D. An overview of inhibitors of Na+/H+ exchanger[J]. European journal of medicinal chemistry, 2003, 38(6): 547-554.
[2] Meng H, Pierce G N. Involvement of sodium in the protective effect of 5-(N, N-dimethyl)-amiloride on ischemia-reperfusion injury in isolated rat ventricular wall[J]. Journal of Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics, 1991, 256(3): 1094-1100.
[3] Fujiwara Y, Higuchi K, Takashima T, et al. Roles of epidermal growth factor and Na+/H+ exchanger-1 in esophageal epithelial defense against acid-induced injury[J]. American Journal of Physiology-Gastrointestinal and Liver Physiology, 2006, 290(4): G665-G673.
[4] Renner E L, Lake J R, Cragoe E J, et al. Amiloride and amiloride analogs inhibit Na+/K+-transporting ATPase and Na+-coupled alanine transport in rat hepatocytes[J]. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA)-Biomembranes, 1988, 938(3): 386-394.
- 1. Yuanyuan Zeng, Jian Zhao, et al. "Targeting TYK2 alleviates Rab27A-induced malignant progression of non-small cell lung cancer via disrupting IFNα-TYK2-STAT-HSPA5 axis." NPJ Precis Oncol. 2024 Mar 23;8(1):74. PMID: 38521810
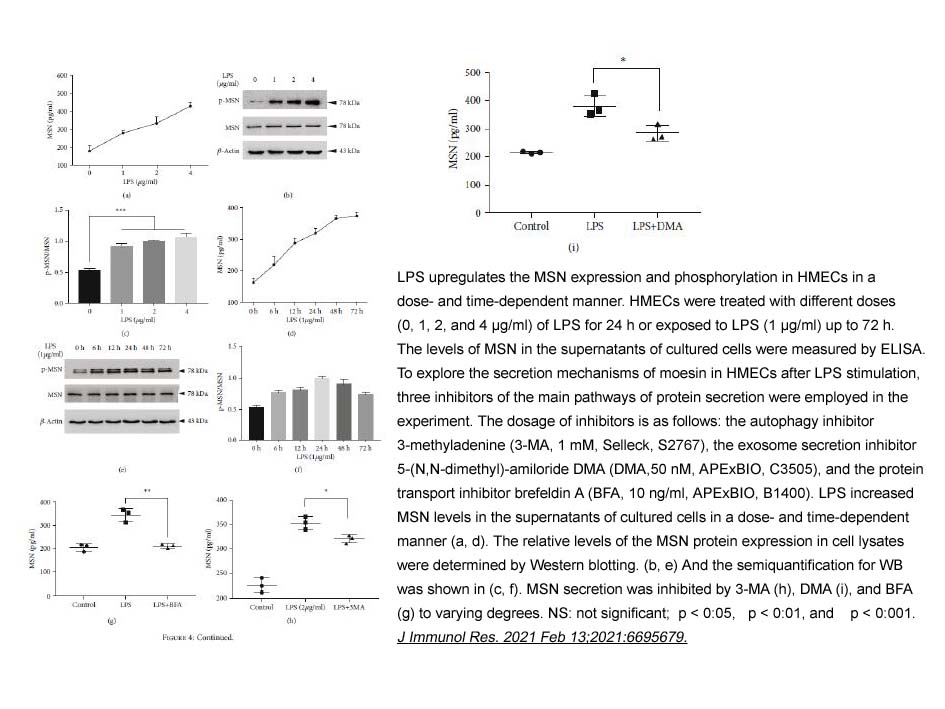
- 2. Yikun Chen, Jiajia Wang, et al. "Moesin Is a Novel Biomarker of Endothelial Injury in Sepsis." J Immunol Res. 2021 Feb 13;2021:6695679. PMID: 33628853
- 3. Yulong Fu, Yang Zhang, et al. "Abnormally activated OPN/integrin αVβ3/FAK signalling is responsible for EGFR-TKI resistance in EGFR mutant non-small-cell lung cancer." J Hematol Oncol. 2020 Dec 7;13(1):169. PMID: 33287873
- 4. Wenwen Du, Jianjie Zhu, et al. "KPNB1-mediated nuclear translocation of PD-L1 promotes non-small cell lung cancer cell proliferation via the Gas6/MerTK signaling pathway." Cell Death Differ. 2021 Apr;28(4):1284-1300. PMID: 33139930
| Physical Appearance | A crystalline solid |
| Storage | Store at -20°C |
| M.Wt | 294.1 |
| Cas No. | 2235-97-4 |
| Formula | C8H12ClN7O·HCl |
| Synonyms | DMA,L-591,605,MK-685 |
| Solubility | ≤30mg/ml in DMSO;30mg/ml in dimethyl formamide |
| Chemical Name | 3-amino-N-(aminoiminomethyl)-6-chloro-5-(dimethylamino)-2-pyrazinecarboxamide, monohydrochloride |
| SDF | Download SDF |
| Canonical SMILES | CN(C)C1=NC(N)=C(C(NC(N)=N)=O)N=C1Cl.Cl |
| Shipping Condition | Small Molecules with Blue Ice, Modified Nucleotides with Dry Ice. |
| General tips | We do not recommend long-term storage for the solution, please use it up soon. |
Quality Control & MSDS
- View current batch:
-
Purity = 98.00%
- COA (Certificate Of Analysis)
- MSDS (Material Safety Data Sheet)
- Datasheet
Chemical structure

Related Biological Data