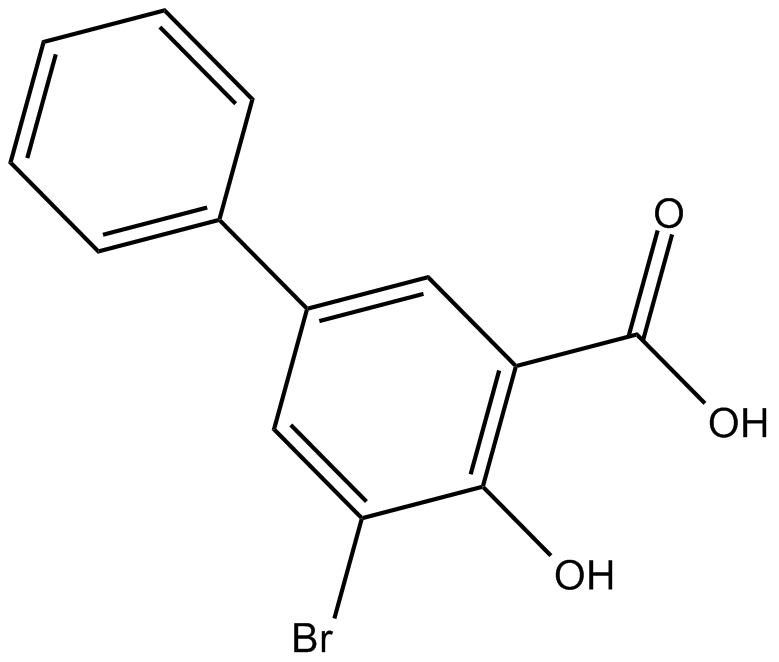
3-bromo-5-phenyl Salicylic Acid
Ki: 140 nM for AKR1C1; 1.97 μM for AKR1C2; 21 μM for AKR1C3
3-bromo-5-phenyl Salicylic acid is an AKR1C1 inhibitor.
The aldo-keto reductase (AKR) enzymes are a family of related NADP-dependent oxidoreductases, in which The 1C subfamily (AKR1C) has 4 human hydroxysteroid dehydrogenases (HSD), a 20α-HSD and the other three being 3α-HSDs. AKR1C1 has been found to metabolize progesterone to 20α-hydroxy progesterone, its inactive progestin.
In vitro: In previous screening study, the additional phenyl group of 3-bromo-5-phenylsalicylic acid, targeting a nonconserved hydrophobic pocket in the active site of AKR1C1, resulted in 21-fold improved potency over the structurally similar 3alpha-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase isoform (AKR1C2). 3-bromo-5-phenyl Salicylic acid was found to be hydrogen bonded to His117, Tyr55, and His222, and the phenyl ring could form additional van der Waals interactions with residues Phe311, Leu308, and Leu54. In addition, the metabolism of progesterone in AKR1C1-overexpressed cells could be potently inhibited by 3-bromo-5-phenylsalicylic acid, which was effective from 10 nM to 460 nM [1].
In vivo: Up to now, there is no animal in vivo data reported.
Clinical trial: So far, no clinical study has been conducted.
Reference:
[1] El-Kabbani, O. ,Scammells, P.J.,Gosling, J., et al. Structure-guided design, synthesis, and evaluation of salicylic acid-based inhibitors targeting a selectivity pocket in the active site of human 20α-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase (AKR1C1). Journal of Medicinal Chemistry 52, 3259-3264 (2009).
| Physical Appearance | A crystalline solid |
| Storage | Store at -20°C |
| M.Wt | 293.1 |
| Cas No. | 4906-68-7 |
| Formula | C13H9BrO3 |
| Synonyms | NSC 109116 |
| Solubility | ≥50.5 mg/mL in DMSO;≥50.4 mg/mL in EtOH;insoluble in H2O |
| Chemical Name | 5-bromo-4-hydroxy-[1,1'-biphenyl]-3-carboxylic acid |
| SDF | Download SDF |
| Canonical SMILES | OC(c1cc(-c2ccccc2)cc(Br)c1O)=O |
| Shipping Condition | Small Molecules with Blue Ice, Modified Nucleotides with Dry Ice. |
| General tips | We do not recommend long-term storage for the solution, please use it up soon. |
Quality Control & MSDS
- View current batch:
Chemical structure