tumor protein p53 binding protein fragment [Homo sapiens]/[Mus musculus]
P53 is a sequence-specific DNA-binding oligomeric protein that can activate transcription from promoters bearing p53-binding sites. Whereas the activation region of p53 has been identified within the amino terminus, the location of the specific DNA-binding domain has not been reported1.
Tumor protein p53 binding protein (53BP1) has been identified in a yeast two hybrid screen as a protein that interacts with the central DNA–binding domain of p532. Similar to breast cancer susceptibility gene 13, 4 (BRCA1; 53BP1 enhances p53-dependent transcription5. Interestingly, the COOH terminus of 53BP1 contains tandem BRCA1 COOH terminus (BRCT) motifs.
53BP1 becomes hyperphosphorylated and rapidly relocates to the sites of DNA strand breaks in response to ionizing radiation. 53BP1 foci formation is reduced in ATM-deficient cells and can be inhibited by wortmannin in ATM wild-type cells. Moreover, radiation-induced hyperphosphorylation of 53BP1 is absent in cells treated with wortmannin, as well as in ATM-deficient cells. 53BP1 participates in DNA damage–signaling pathways and is regulated by ATM after γ-radiation6.
Figure1. Tumor protein p53 binding protein 1
Figure2. Tumor protein p53 binding protein 2
Ref:
1.J.Bargonetti, J. J. Manfredi et al. A proteolytic fragment from the central region of p53 has marked sequence-specific DNA-binding activity wlien generated from wild-type but not from oncogenic mutant p53 protein, Genes Dev. 1993 7: 2565-2574
2.Iwabuchi, K., P.L. Bartel, B. Li, R. Marraccino, S. Fields (1994) Two cellular proteins that bind to wild-type but not mutant p53. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA91:6098–6102
3.Ouchi, T., A.N. Monteiro, A. August, S.A. Aaronson, H. Hanafusa (1998) BRCA1 regulates p53-dependent gene expression. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA95:2302–2306
4.Zhang, H., K. Somasundaram, Y. Peng, H. Tian, D. Bi, B.L. Weber, W.S. El-Deiry BRCA1 physically associates with p53 and stimulates its transcriptional activity Oncogene16199817131721
5.Iwabuchi, K., B. Li, H.F. Massa, B.J. Trask, T. Date, S. Fields(1998) Stimulation of p53-mediated transcriptional activation by the p53-binding proteins, 53BP1 and 53BP2. J. Biol. Chem 273:26061–2606
6.Irene Rappold, Kuniyoshi Iwabuchi, Takayasu Date, and Junjie Chen Tumor Suppressor P53 Binding Protein 1 (53bp1) Is Involved in DNA Damage–Signaling Pathways. JCB vol. 153 no. 3 613-620
| Physical Appearance | A solid |
| Storage | Store at -20°C |
| M.Wt | 1242.38 |
| Formula | C57H87N13O18 |
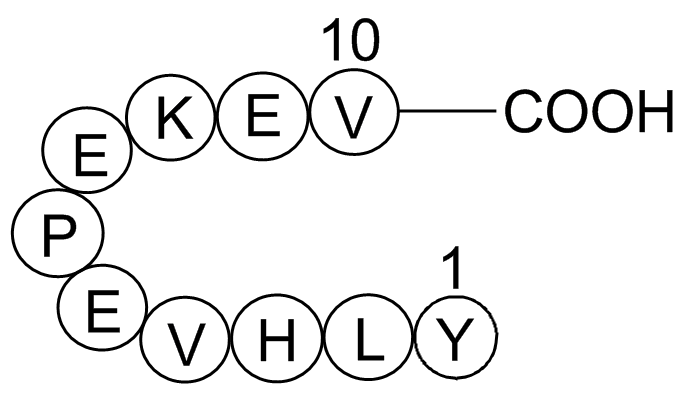
| Synonyms | H2N-Tyr-Leu-His-Val-Glu-Pro-Glu-Lys-Glu-Val-OH |
| Solubility | ≥124.2 mg/mL in DMSO; ≥49.2 mg/mL in H2O; ≥50 mg/mL in EtOH |
| SDF | Download SDF |
| Canonical SMILES | OC(C=C1)=CC=C1CC(N)C(NC(CC(C)C)C(NC(CC2=CN=CN2)C(NC(C(C)C)C(NC(CCC(O)=O)C(N3CCCC3C(NC(CCC(O)=O)C(NC(CCCCN)C(NC(CCC(O)=O)C(NC(C(C)C)C(O)=O)=O)=O)=O)=O)=O)=O)=O)=O)=O |
| Shipping Condition | Small Molecules with Blue Ice, Modified Nucleotides with Dry Ice. |
| General tips | We do not recommend long-term storage for the solution, please use it up soon. |
Quality Control & MSDS
- View current batch:
Chemical structure
![tumor protein p53 binding protein fragment [Homo sapiens]/[Mus musculus]](/media/diy/images/struct/A1094.png)