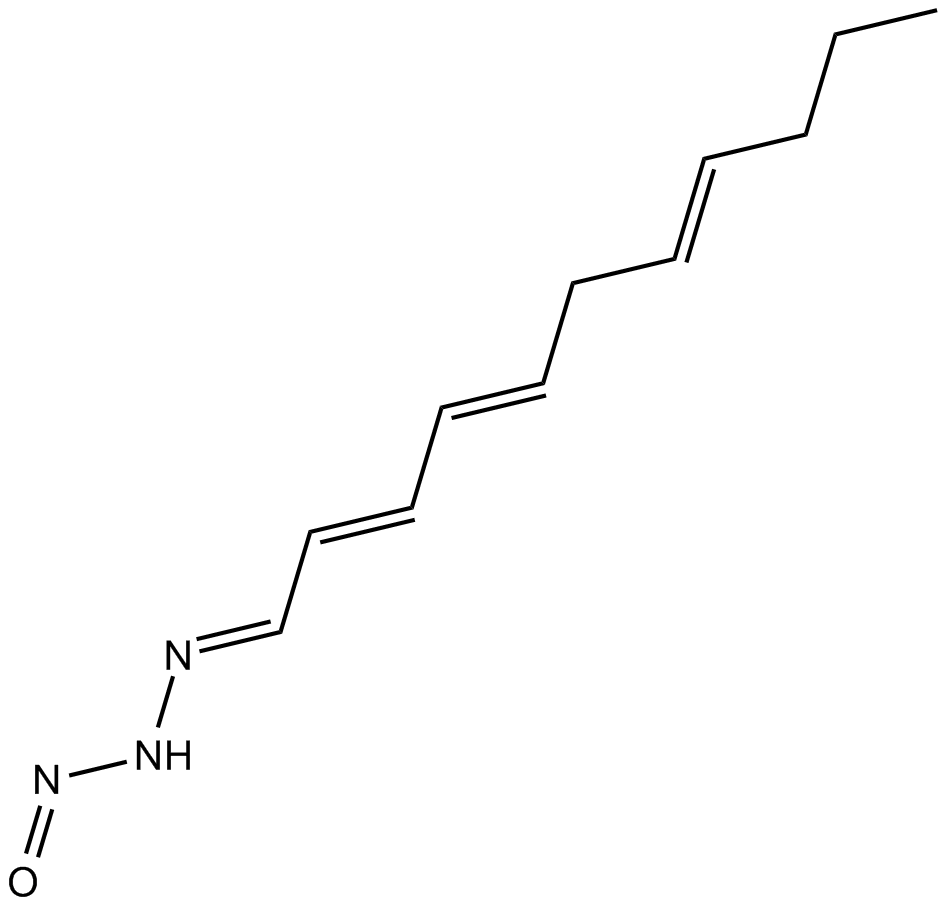
Triacsin C
Triacsin C is a potent inhibitor of long chain acyl-CoA synthetase, with an IC50 value of 6.3 μM in Raji cell membrane fraction. Long chain acyl-CoA synthetase is essential for catalyzing the conversion of free fatty acids to acyl-CoAs. Inhibition of acyl-CoA synthetase has been shown to interfere lipid synthesis as well as cell proliferation in Raji lymphoma cells. Triacsin C also induces apoptosis in many cancer cell lines, such as human lung cancer cells. In addition, Triacsin C has been found to be highly effective against rotavirus replication.
References:
1. Tomoda H, Igarashi K, Cyong JC, et al. Evidence for an essential role of long chain acyl-CoA synthetase in animal cell proliferation. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 1991, 266(7): 4214-4219.
2. Mashima T, Oh-hara T, Sato S, et al. p53-defective tumors with a functional apoptosome-mediated pathway: a new therapeutic target. Journal of the National Cancer Institute, 2005, 97(10): 765-777.
3. Kim Y, George D, Prior AM, et al. Novel triacsin C analogs as potential antivirals against rotavirus infections. European Journal of Medicinal Chemistry, 2012, 50: 311-318.
| Physical Appearance | A crystalline solid |
| Storage | Store at -20°C |
| M.Wt | 207.27 |
| Cas No. | 76896-80-5 |
| Formula | C11H17N3O |
| Solubility | ≥5 mg/mL in DMSO; ≥5 mg/mL in EtOH |
| Chemical Name | (E)-N'-((2E,4E,7E)-undeca-2,4,7-trien-1-ylidene)nitrous hydrazide |
| SDF | Download SDF |
| Canonical SMILES | CCC/C=C/C/C=C/C=C/C=N/NN=O |
| Shipping Condition | Small Molecules with Blue Ice, Modified Nucleotides with Dry Ice. |
| General tips | We do not recommend long-term storage for the solution, please use it up soon. |
| Cell experiment:[1] | |
|
Cell lines |
Raji lymphoma cells |
|
Reaction Conditions |
0 ~ 5 μM Triacsin C for 1 ~ 5 days |
|
Applications |
Among Triacsins A, B, C and D, Triacsin C exhibited the highest inhibitory potency against Raji cell proliferation at day 2. With regard to the other two activities in Raji cells, i.e. lipid synthesis and long chain acyl-CoA synthetase activity, Triacsin C also turned out to be the most potent inhibitor. |
| Animal experiment:[2] | |
|
Animal models |
Nude mice bearing NCI-H23 human lung cancer cells |
|
Dosage form |
30 mg/kg Once daily by intratumoral injection from days 0 to 2 |
|
Applications |
Triacsin C significantly inhibited the growth of tumor xenografts, and did not induce any obvious body weight changes. |
|
Note |
The technical data provided above is for reference only. |
|
References: 1. Tomoda H, Igarashi K, Cyong JC, et al. Evidence for an essential role of long chain acyl-CoA synthetase in animal cell proliferation. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 1991, 266(7): 4214-4219. 2. Mashima T, Oh-hara T, Sato S, et al. p53-defective tumors with a functional apoptosome-mediated pathway: a new therapeutic target. Journal of the National Cancer Institute, 2005, 97(10): 765-777. 3. Kim Y, George D, Prior AM, et al. Novel triacsin C analogs as potential antivirals against rotavirus infections. European Journal of Medicinal Chemistry, 2012, 50: 311-318. |
|
Quality Control & MSDS
- View current batch:
-
Purity ≥95.00%
- COA (Certificate Of Analysis)
- MSDS (Material Safety Data Sheet)
Chemical structure