Ubiquitination/ Proteasome
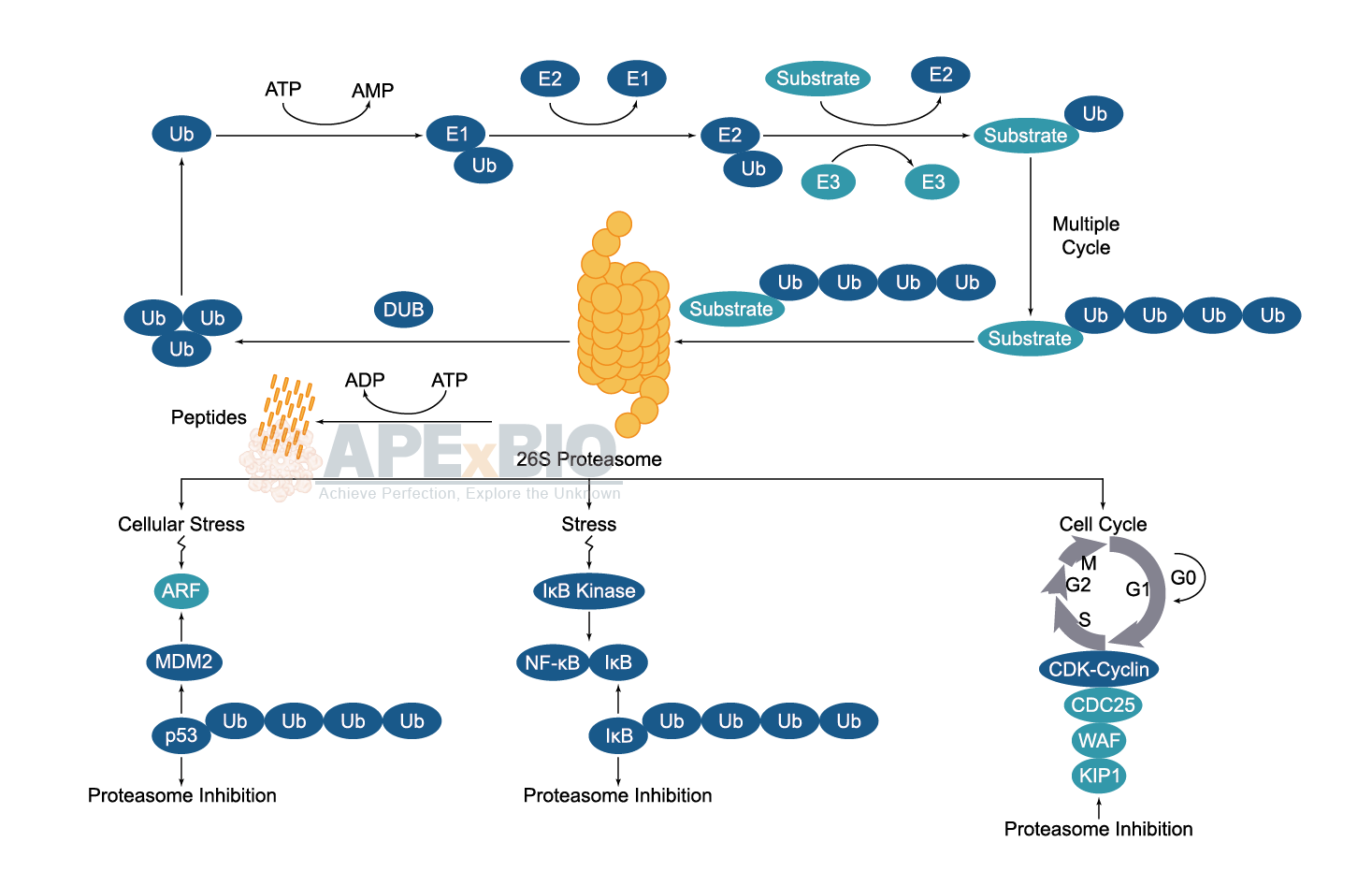
Once the substrate protein is labeled, proteasome will bind to a polyubiquitin chain, allowing the degradation of the labeled protein. The polyubiquitinated target protein is then recognized and degraded by the 26S proteasome. Deubiquitinating enzymes (DUBs) reverse the process of ubiquitination by removing ubiquitin from its substrate protein. Dysregulation of the ubiquitin-proteasome system has been linked to cancer, diabetes, cardiovascular and neurodegenerative diseases etc.
-
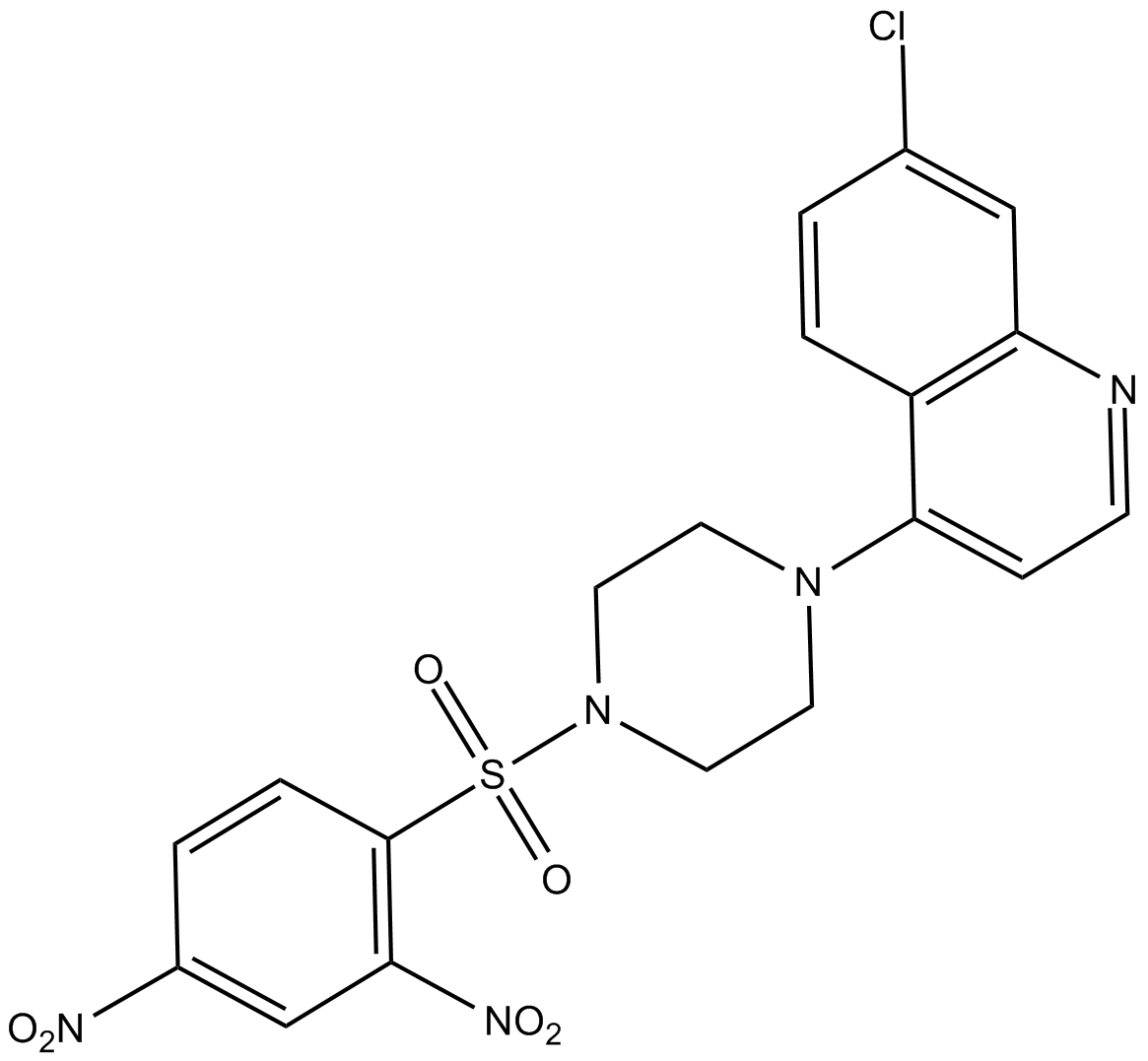 B6026 VR23Target: ProteasomeSummary: proteasome inhibitor
B6026 VR23Target: ProteasomeSummary: proteasome inhibitor -
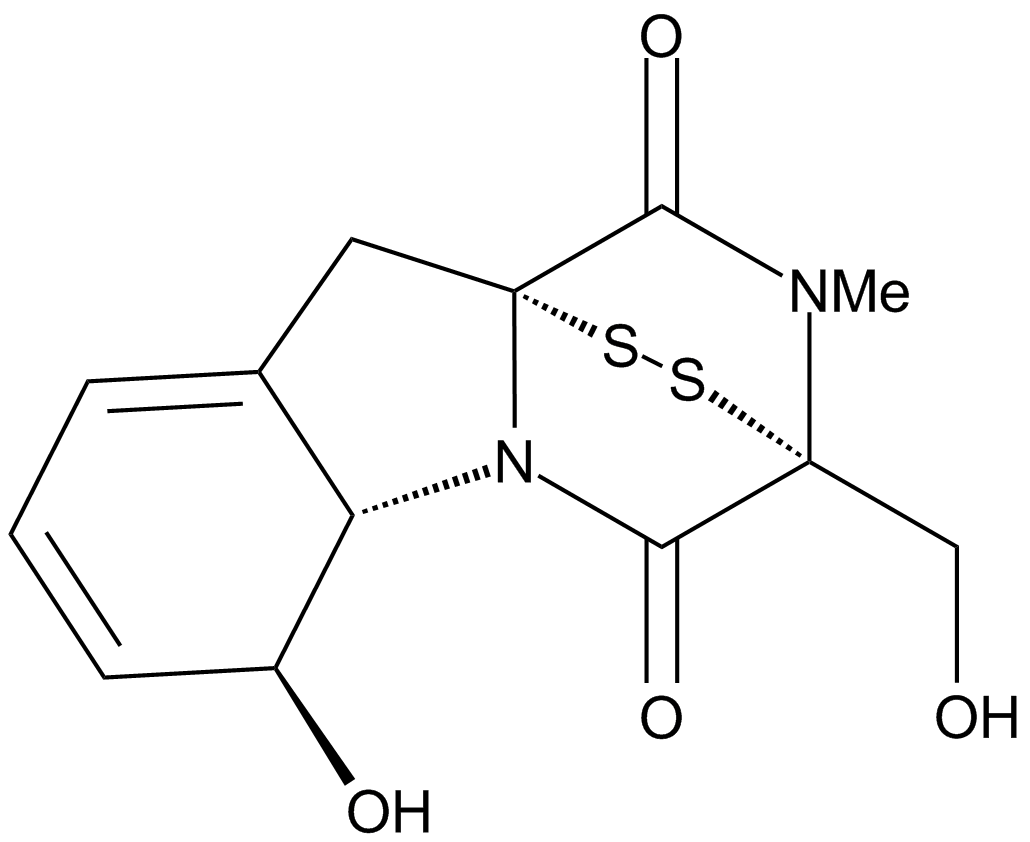 A4443 Gliotoxin1 CitationTarget: 20S proteasomal chymotrypsin|Geranylgeranyltransferase I|FarnesyltransferaseSummary: 20S proteasome inhibitor
A4443 Gliotoxin1 CitationTarget: 20S proteasomal chymotrypsin|Geranylgeranyltransferase I|FarnesyltransferaseSummary: 20S proteasome inhibitor -
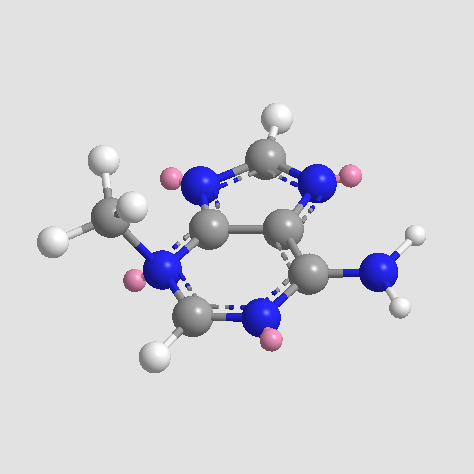 A8353 3-Methyladenine3 CitationTarget: PI3KSummary: Class III PI3K inhibitor
A8353 3-Methyladenine3 CitationTarget: PI3KSummary: Class III PI3K inhibitor -
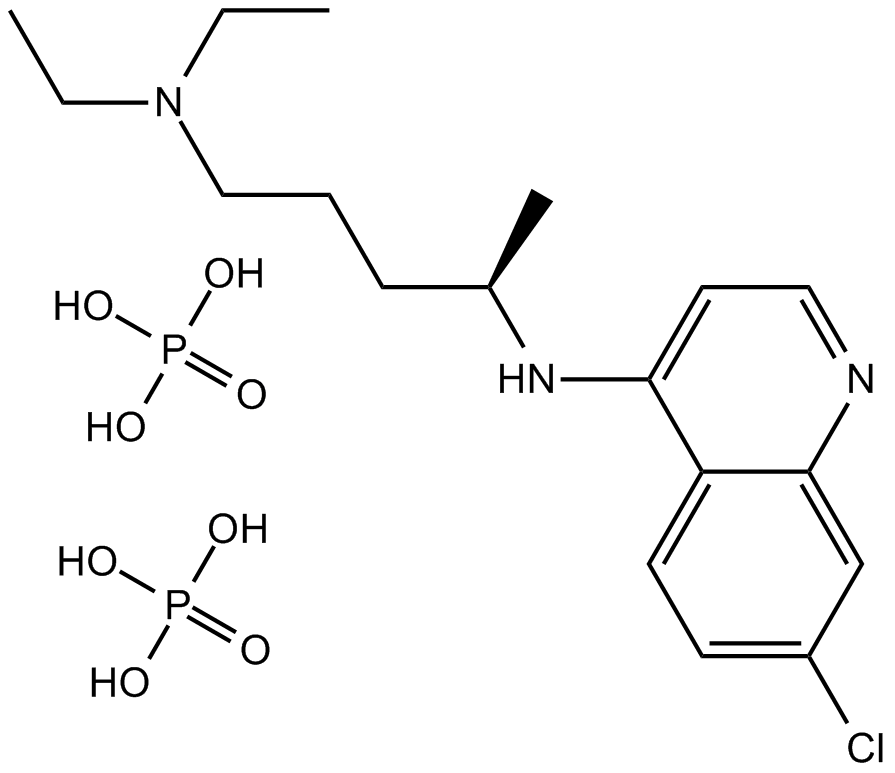 A8628 Chloroquine diphosphate1 CitationTarget: AutophagySummary: Antimalarial drug,TLR7 TLR9 inhibitor
A8628 Chloroquine diphosphate1 CitationTarget: AutophagySummary: Antimalarial drug,TLR7 TLR9 inhibitor -
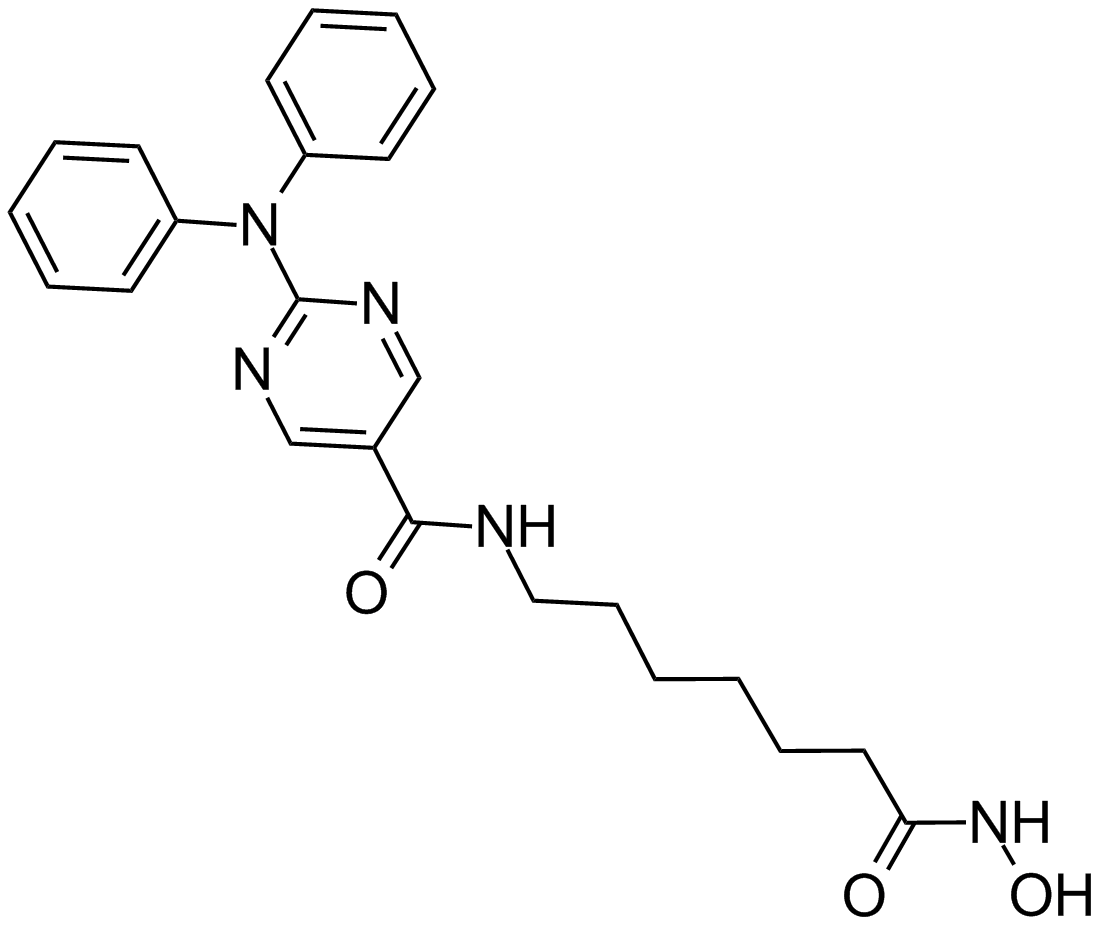 A4083 Rocilinostat (ACY-1215)1 CitationTarget: Histone Deacetylases (HDACs)Summary: Selective HDAC6 inhibitor
A4083 Rocilinostat (ACY-1215)1 CitationTarget: Histone Deacetylases (HDACs)Summary: Selective HDAC6 inhibitor -
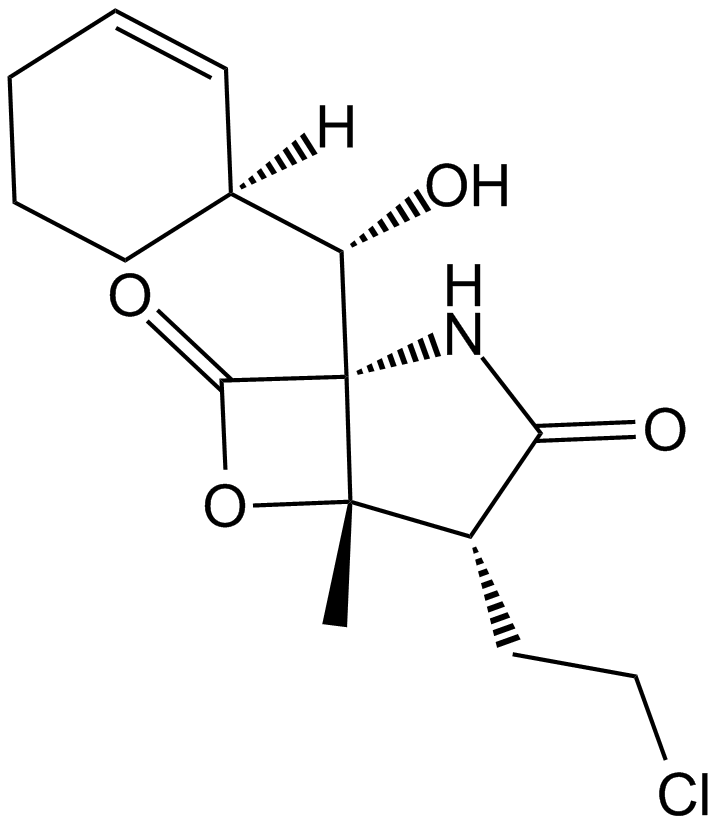 A4010 Salinosporamide A (NPI-0052, Marizomib)Target: ProteasomeSummary: 20S proteasome inhibitor
A4010 Salinosporamide A (NPI-0052, Marizomib)Target: ProteasomeSummary: 20S proteasome inhibitor -
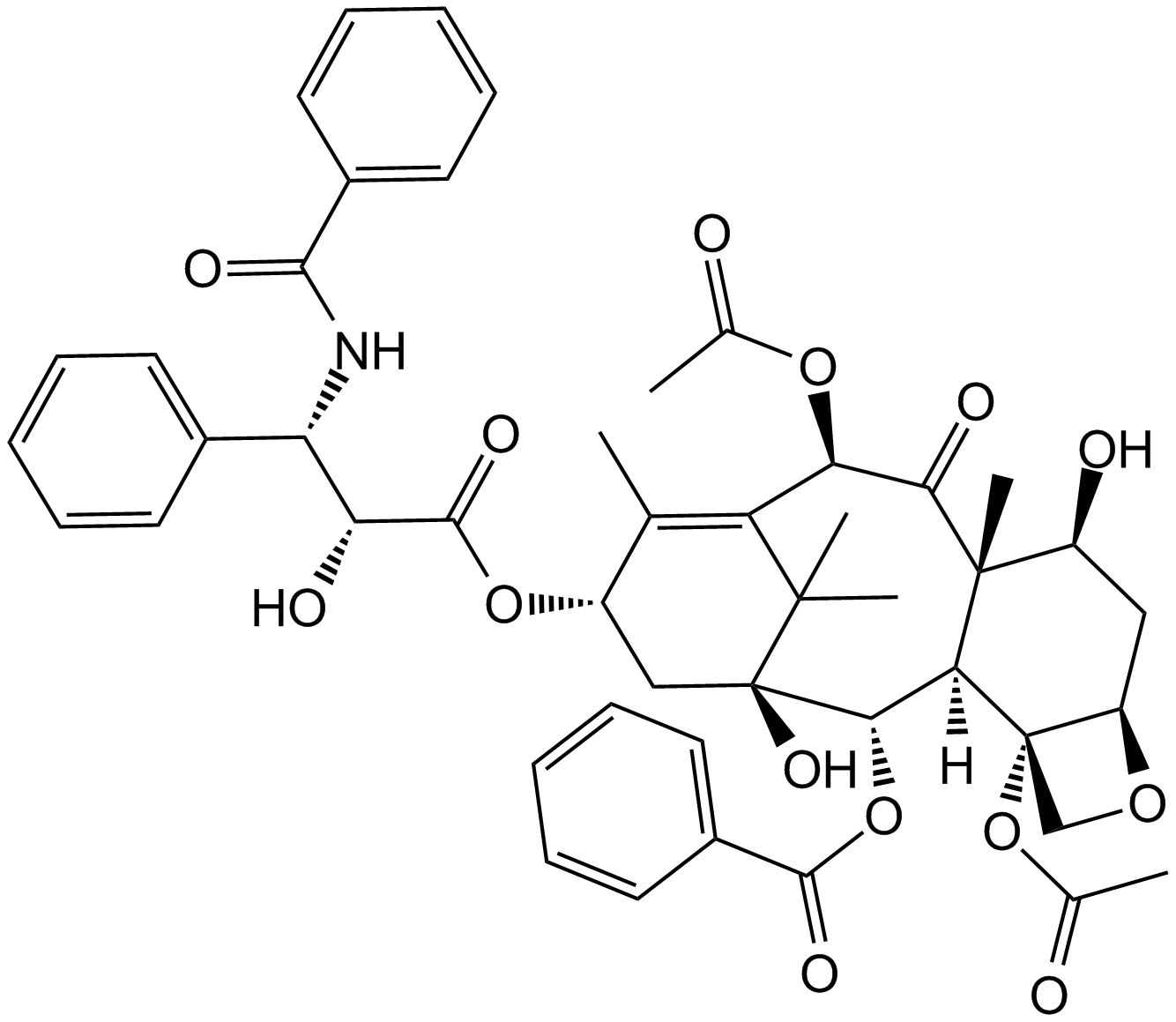 A4393 Paclitaxel (Taxol)4 CitationTarget: Microtubules/TubulinsSummary: Antineoplastic agent
A4393 Paclitaxel (Taxol)4 CitationTarget: Microtubules/TubulinsSummary: Antineoplastic agent

