Ubiquitination/ Proteasome
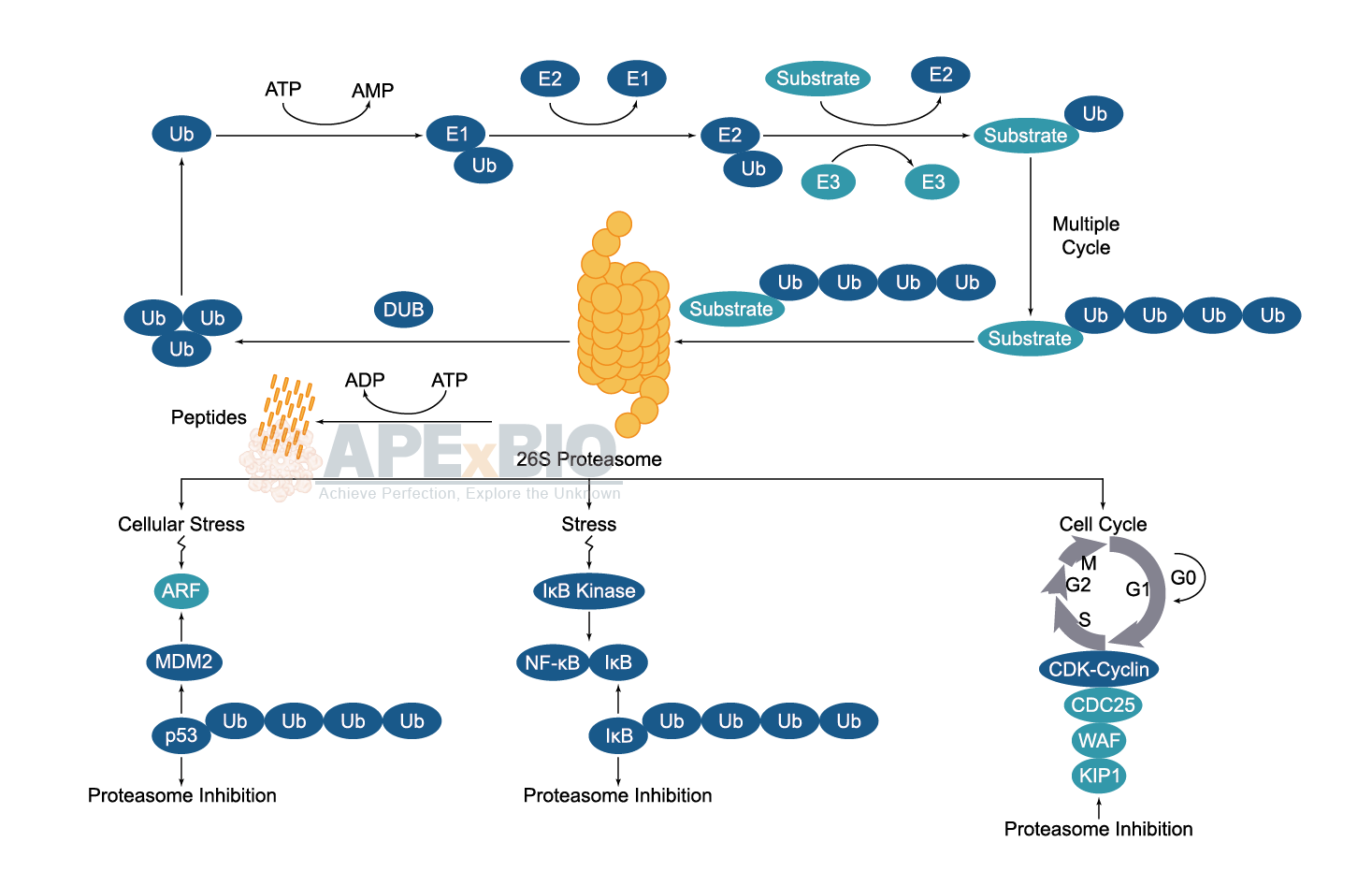
Once the substrate protein is labeled, proteasome will bind to a polyubiquitin chain, allowing the degradation of the labeled protein. The polyubiquitinated target protein is then recognized and degraded by the 26S proteasome. Deubiquitinating enzymes (DUBs) reverse the process of ubiquitination by removing ubiquitin from its substrate protein. Dysregulation of the ubiquitin-proteasome system has been linked to cancer, diabetes, cardiovascular and neurodegenerative diseases etc.
-
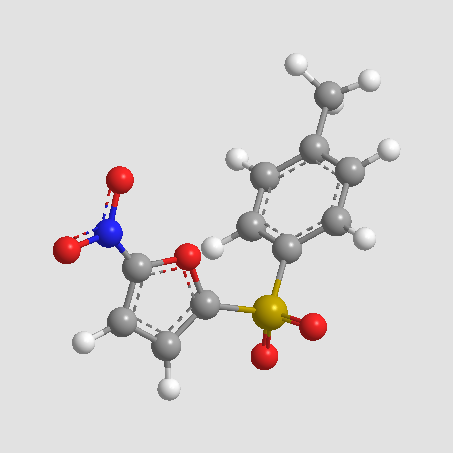 A8813 NSC697923Target: Ub-conjugating enzyme (E2) complexSummary: Inhibitor of E2 complex Ubc13-Uev1A,cell permeable and selective
A8813 NSC697923Target: Ub-conjugating enzyme (E2) complexSummary: Inhibitor of E2 complex Ubc13-Uev1A,cell permeable and selective -
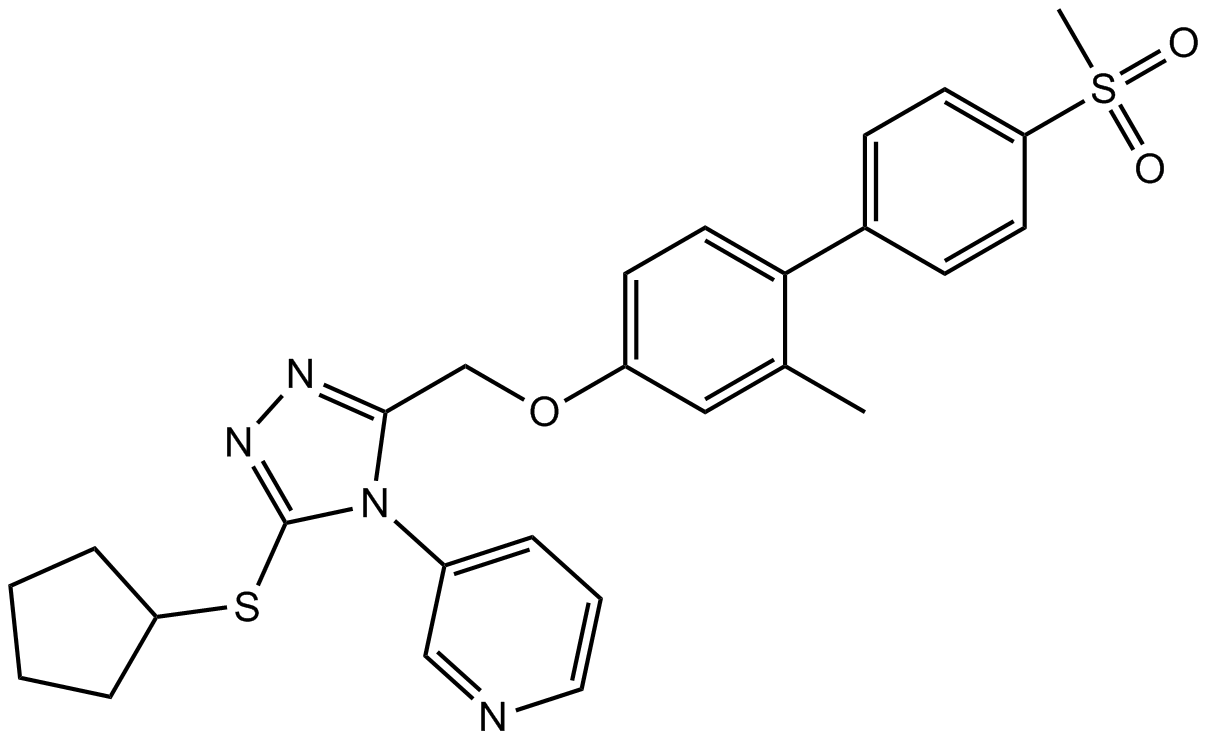 B2168 NMS-8733 CitationTarget: Valosin-containing protein (VCP)Summary: VCP/p97 inhibitor,selective and allosteric
B2168 NMS-8733 CitationTarget: Valosin-containing protein (VCP)Summary: VCP/p97 inhibitor,selective and allosteric -
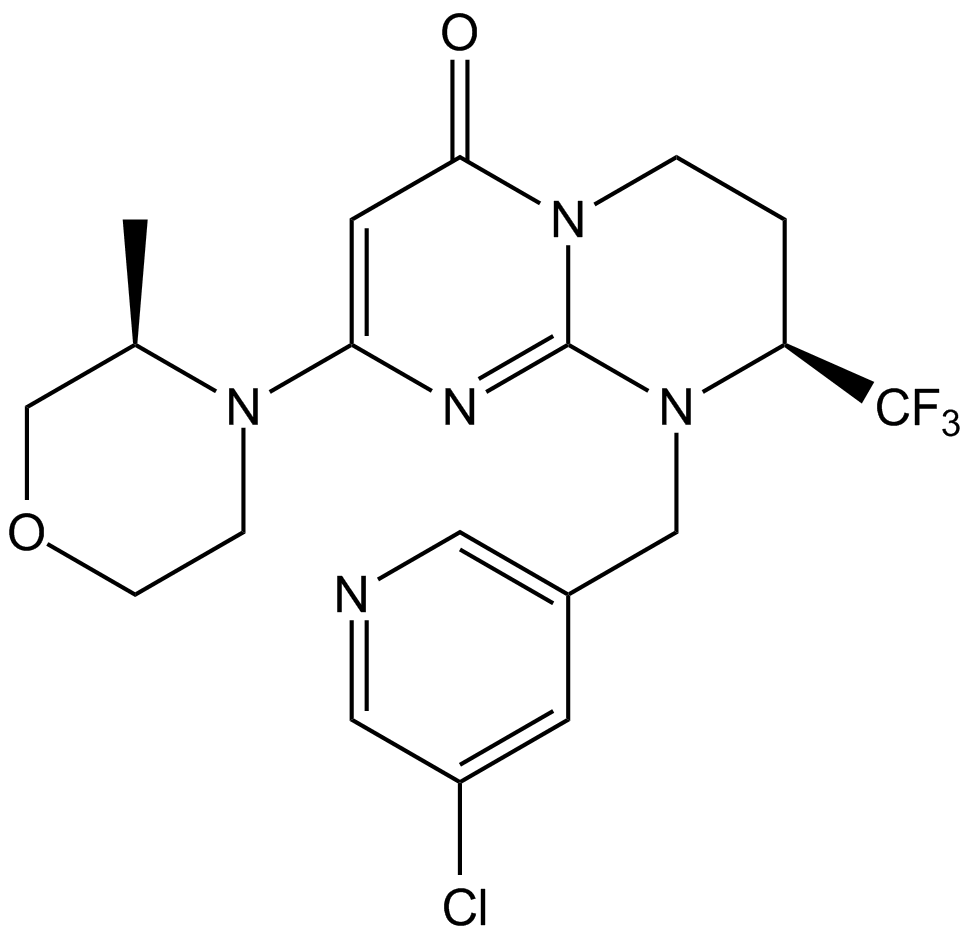 A8883 SAR40522 CitationSummary: Selective ATP-competitive inhibitor of Vps34
A8883 SAR40522 CitationSummary: Selective ATP-competitive inhibitor of Vps34 -
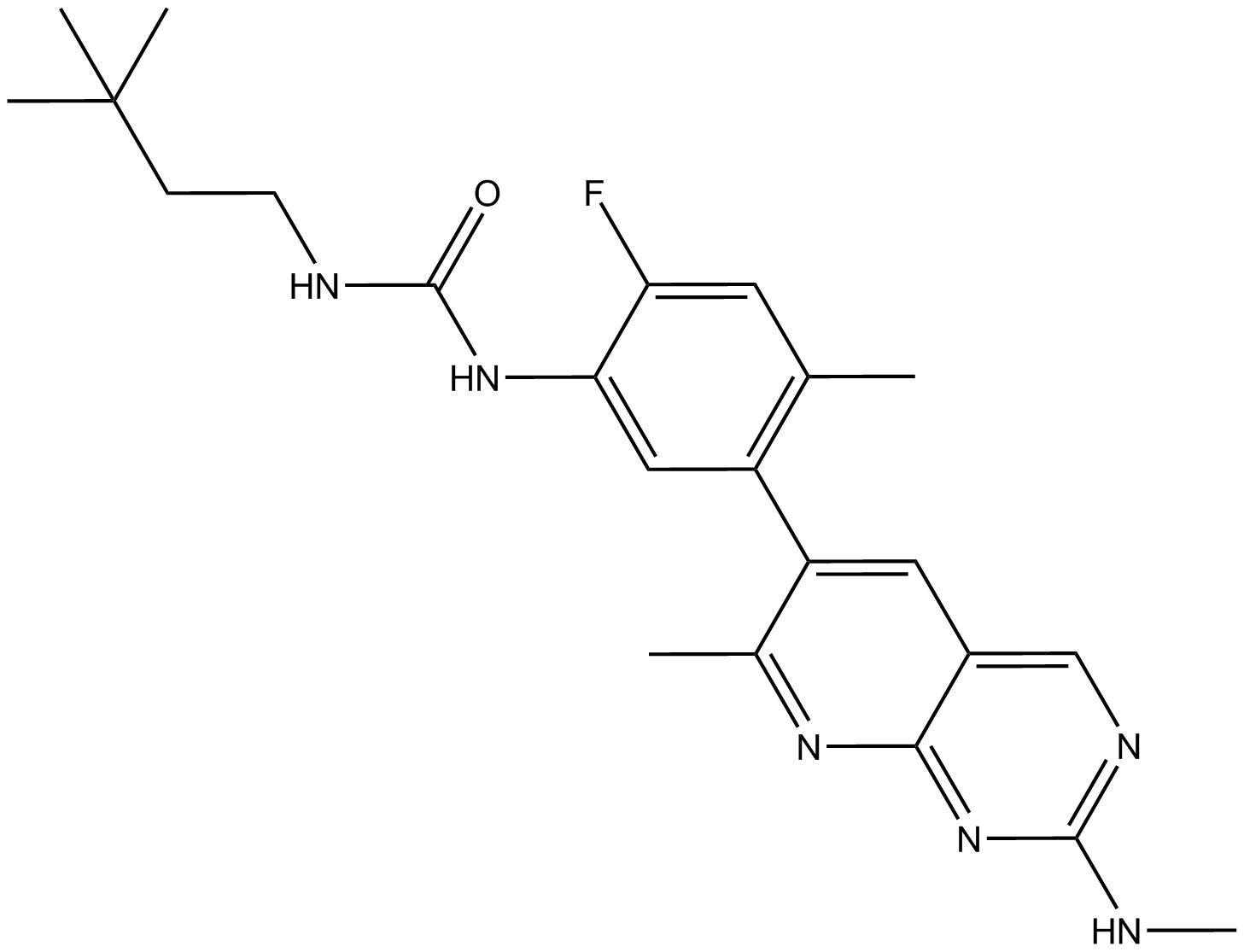 A8716 LY3009120Target: RafSummary: pan-RAF and RAF dimer inhibitor
A8716 LY3009120Target: RafSummary: pan-RAF and RAF dimer inhibitor -
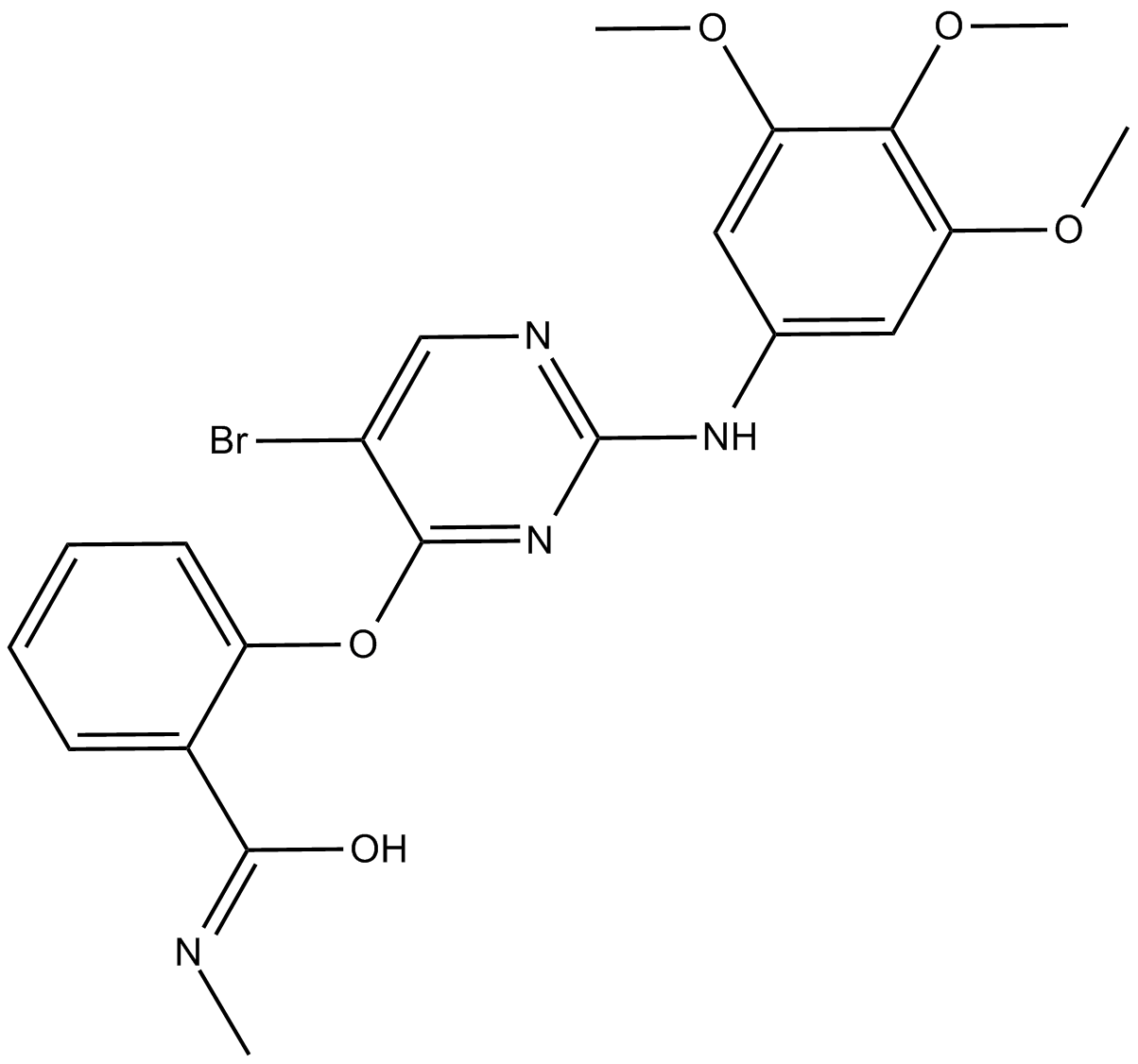 A8715 SBI-02069652 CitationTarget: ULK1Summary: ULK1 inhibitor
A8715 SBI-02069652 CitationTarget: ULK1Summary: ULK1 inhibitor -
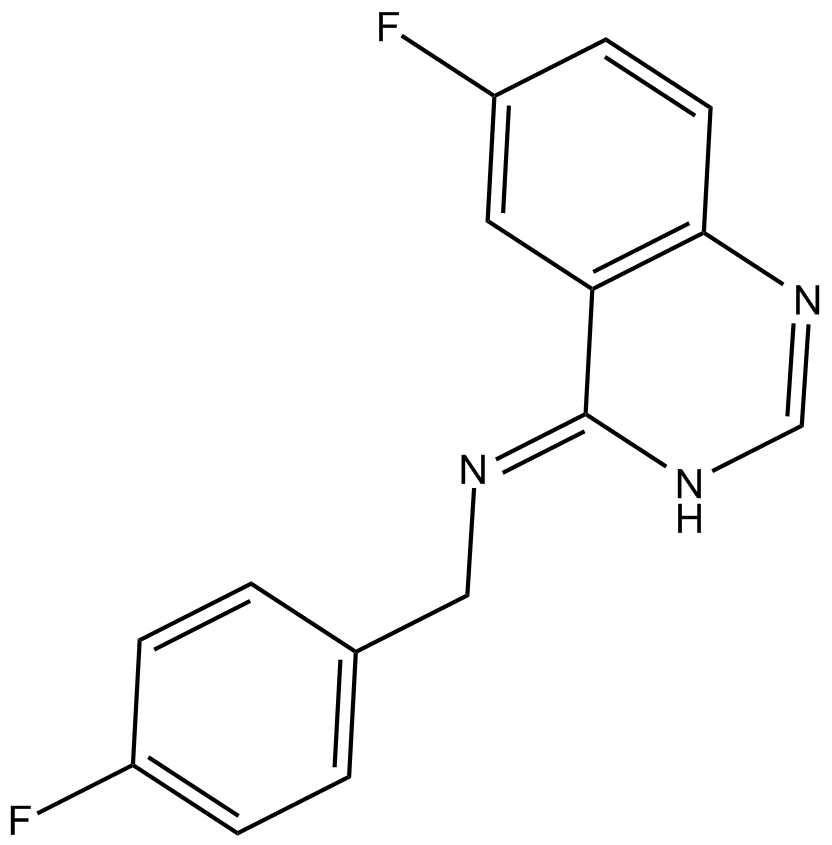 B5873 Spautin-11 CitationTarget: Deubiquitinating enzymes (DUBs)|AutophagySummary: Novel autophagy inhibitor
B5873 Spautin-11 CitationTarget: Deubiquitinating enzymes (DUBs)|AutophagySummary: Novel autophagy inhibitor -
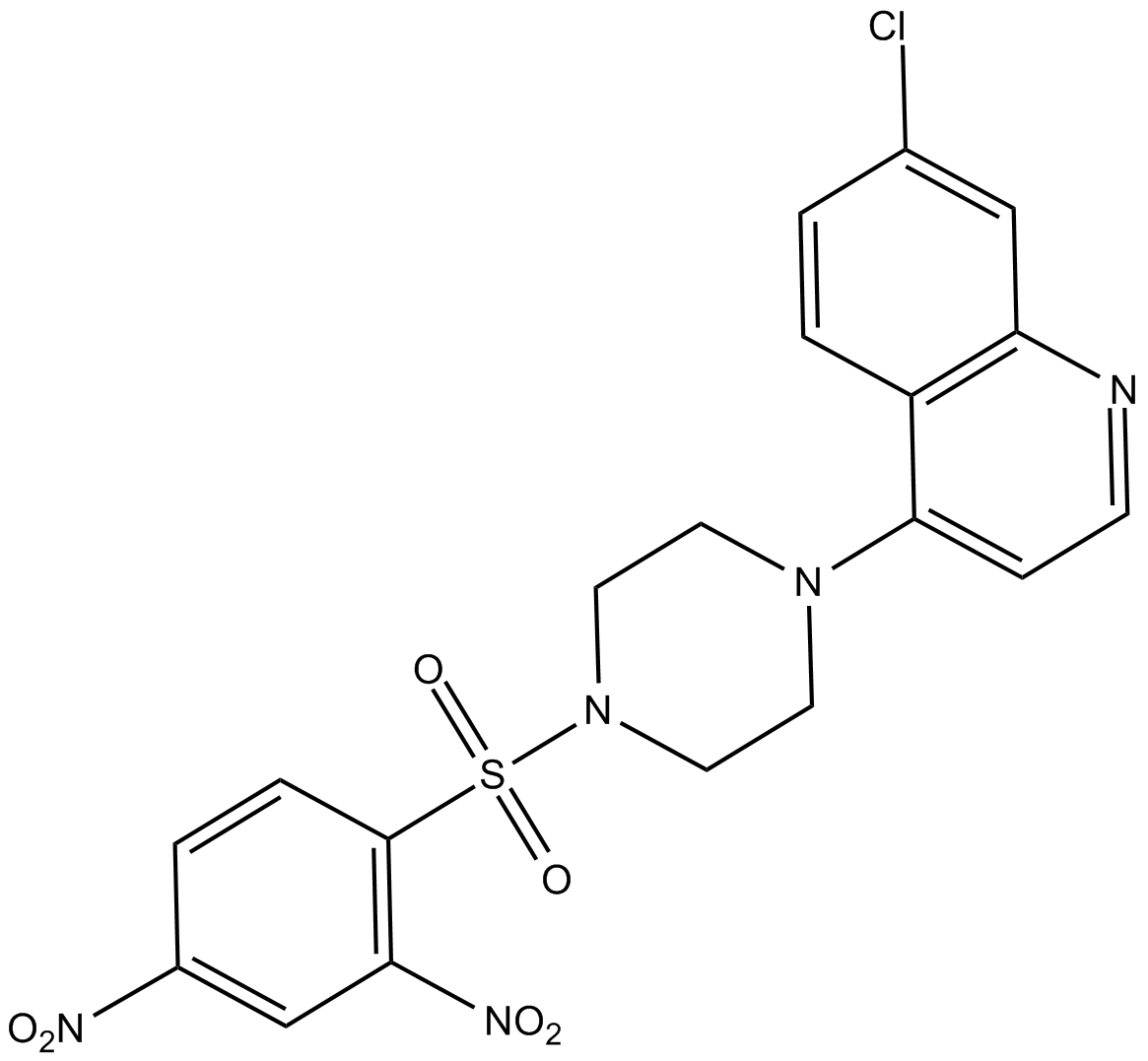 B6026 VR23Target: ProteasomeSummary: proteasome inhibitor
B6026 VR23Target: ProteasomeSummary: proteasome inhibitor -
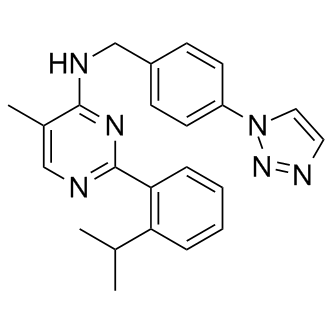 B1317 ML-323Target: Deubiquitinating enzymes (DUBs)Summary: USP1-UAF1 inhibitor
B1317 ML-323Target: Deubiquitinating enzymes (DUBs)Summary: USP1-UAF1 inhibitor -
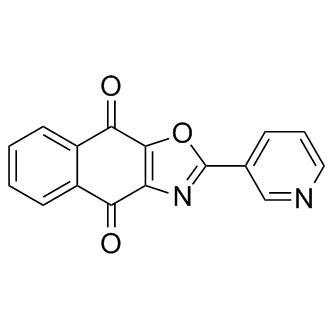 B1307 SJB3-019ATarget: USPSummary: Usp1 inhibitor
B1307 SJB3-019ATarget: USPSummary: Usp1 inhibitor -
 A2571 Pepstatin A1 CitationTarget: Cathepsins|Renin|HIV proteases|PepsinsSummary: Aspartic protease inhibitor
A2571 Pepstatin A1 CitationTarget: Cathepsins|Renin|HIV proteases|PepsinsSummary: Aspartic protease inhibitor

