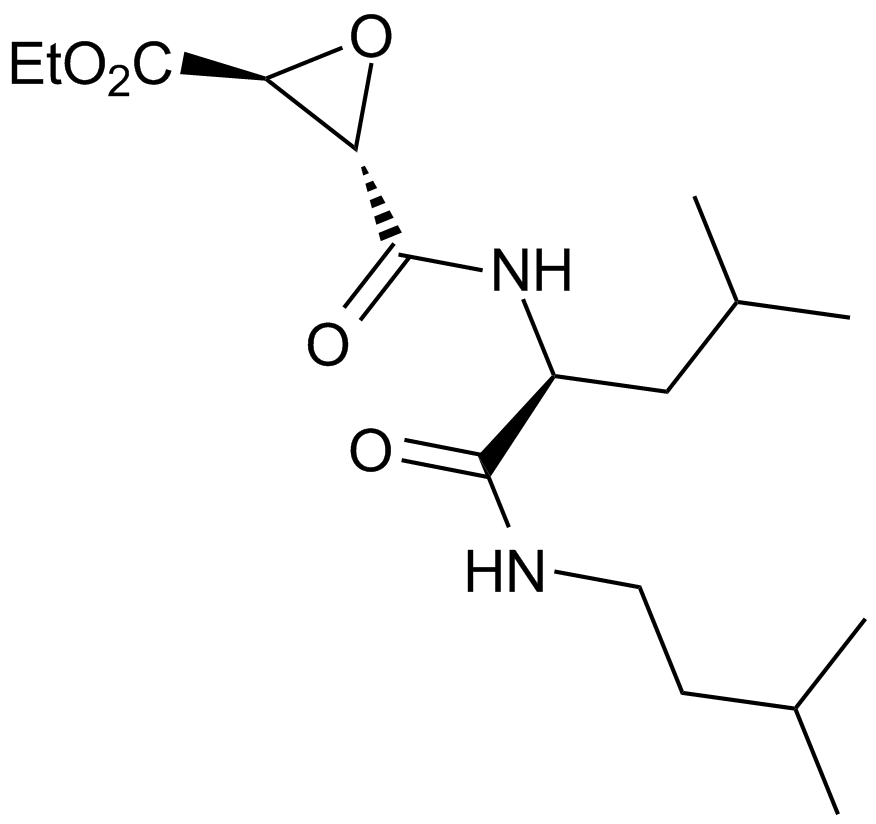
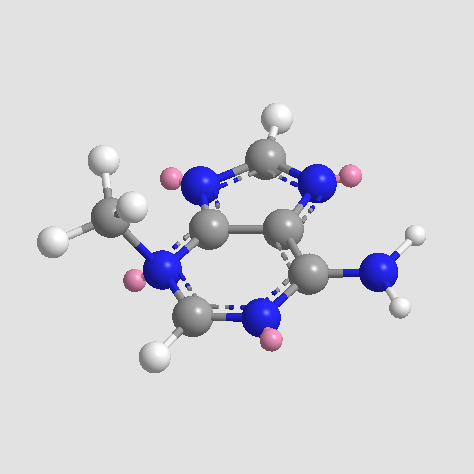
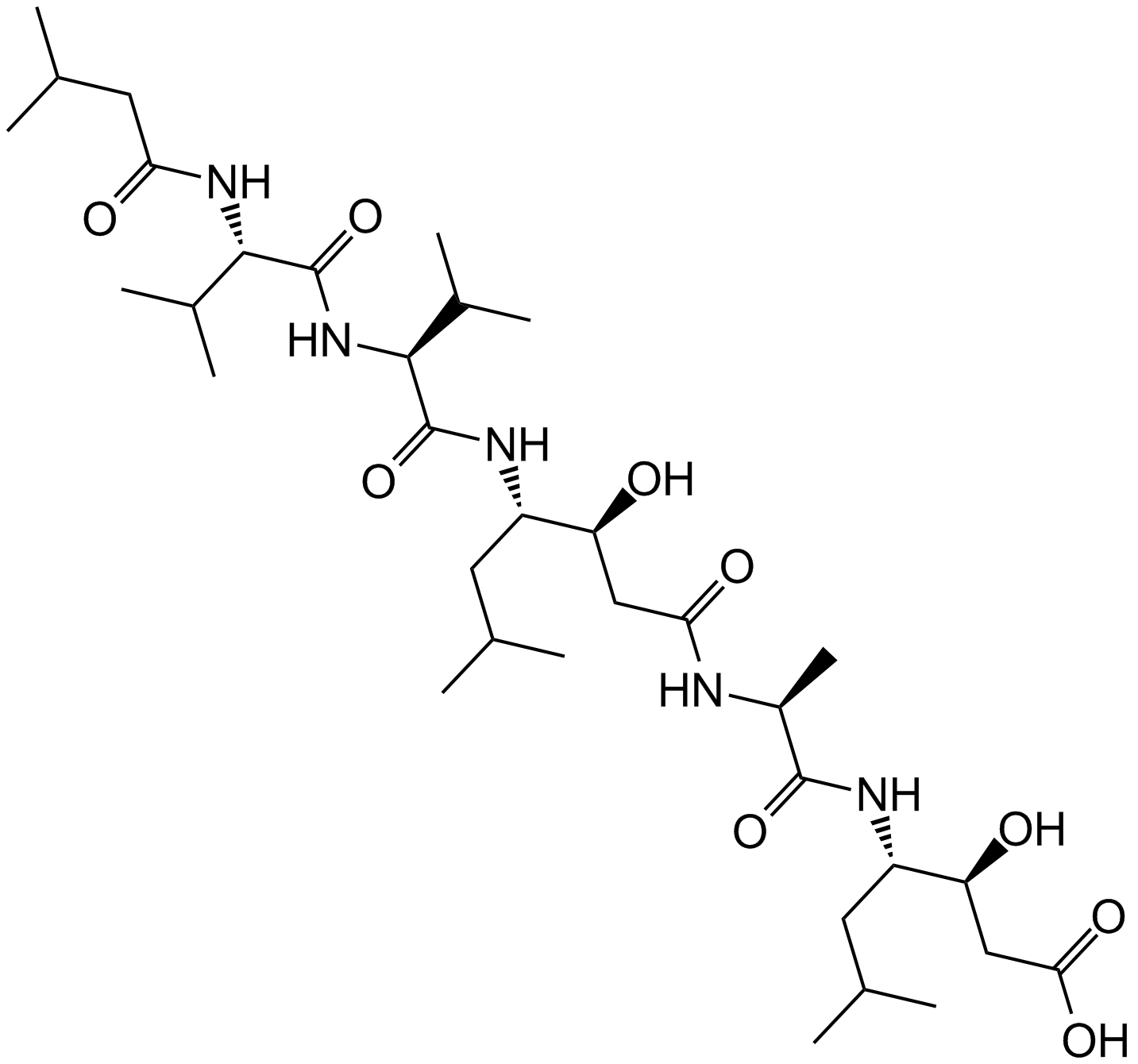
Pepstatin A
Pepstatin A (CAS 26305-03-3) is a pentapeptide functioning as an inhibitor targeting aspartic proteases, including pepsin, renin, HIV protease, and cathepsin D. It inhibits human renin and HIV protease with IC50 values of approximately 15 μM and 2 μM, respectively, and shows inhibitory activity toward pepsin and cathepsin D at IC50 values below 5 μM and 40 μM. Mechanistically, Pepstatin A acts through binding to the catalytic site of aspartic proteases, restricting proteolytic activity. In biomedical research, it is utilized to study viral protein processing, osteoclast differentiation mediated by cathepsins, and as a standard tool in enzyme inhibition assays examining aspartic protease function.
References:
1. Eid M, Evin G, Castro B, et al.New renin inhibitors homologous with pepstatin.Biochem. J, 1981, 197: 465-471.
2. Sarubbi E, Seneci P F, Angelastro M R, et al. Peptide aldehydes as inhibitors of HIV protease. FEBS letters, 1993, 319(3): 253-256.
3. von der Helm K, Gürtler L, Eberle J, et al. Inhibition of HIV replication in cell culture by the specific aspartic protease inhibitor pepstatin A. FEBS letters, 1989, 247(2): 349-352.
4. Yoshida H, Okamoto K, Iwamoto T, et al. Pepstatin A, an aspartic proteinase inhibitor, suppresses RANKL-induced osteoclast differentiation. Journal of biochemistry, 2006, 139(3): 583-590.
- 1. Shuyuan Zhang, Zhou-Li Cheng, et al. "Protocol for elucidating metabolite binding and regulation of TET2 dioxygenase." STAR Protoc. 2025 Aug 6;6(3):104015. PMID: 40773351
- 2. Qizhen Zhuang, Lu Chen, et al. "Scutellarin ameliorates ischemia/reperfusion-mediated endothelial dysfunction by upregulating cathepsin D expression to rescue autophagy-lysosomal function." Front Pharmacol. 2025 Mar 3:16:1538697 PMID: 40098620
- 3. Cadence Lee, Rachel Khan, et al. "IL-1β-driven NF-κB transcription of ACE2 as a Mechanism of Macrophage Infection by SARS-CoV-2." bioRxiv. 2025 Feb 13:2024.12.24.630260. PMID: 39763770
- 4. Shuzhen Liu, Preston Perez, et al. "MLKL polymerization-induced lysosomal membrane permeabilization promotes necroptosis." Cell Death Differ. 2023 Nov 23. PMID: 37996483
- 5. Banghao Yuan, Caroline Hatchett-Walker, et al. "Control of cell surface expression of GABAA receptors by a conserved region at the end of the N-terminal extracellular domain of receptor subunits." J Biol Chem. 2022 Oct 13;102590. PMID: 36244453
- 6. Yan Chen, Jiafu Zhu, et al. "Protocol for affordable and efficient profiling of nascent RNAs in bread wheat using GRO-seq." STAR Protoc. 2022 Sep 16;3(3):101657. PMID: 36097381
- 7. Adams MK, Belyaeva OV, et al. "Generation and isolation of recombinant retinoid oxidoreductase complex." Methods Enzymol. 2020;637:77-93. PMID: 32359661
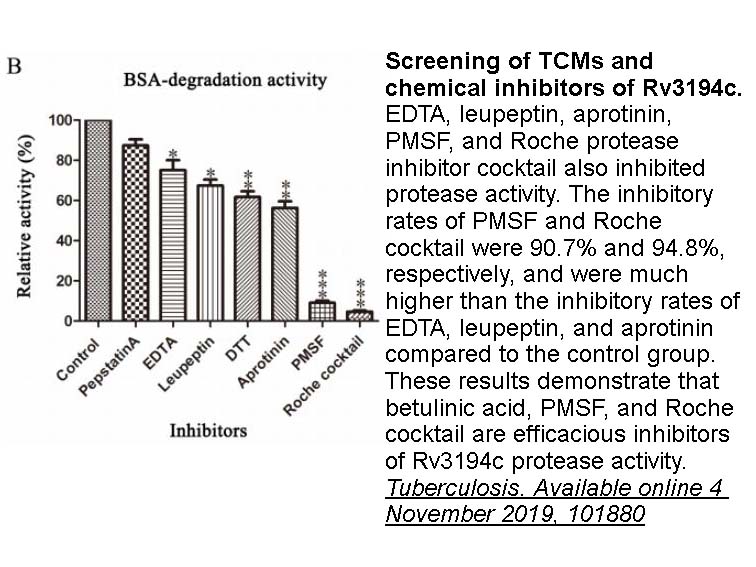
- 8. HeLia, GuanghuiDanga, et al. "Characterization of a novel Mycobacterium tuberculosis serine protease (Rv3194c) activity and pathogenicity." Tuberculosis. Available online 4 November 2019, 101880.
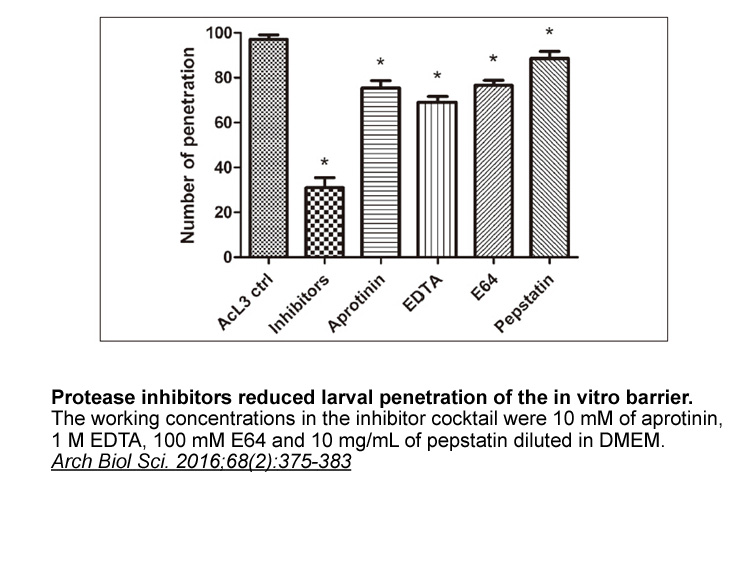
- 9. Ying Long, Xuri Zhang, et al. "Initial events in the breakthrough of the epithelial barrier of the small intestine by Angiostrongylus cantonensis." Arch Biol Sci. 2016;68(2):375-383.
| Physical Appearance | A solid |
| Storage | Store at -20°C |
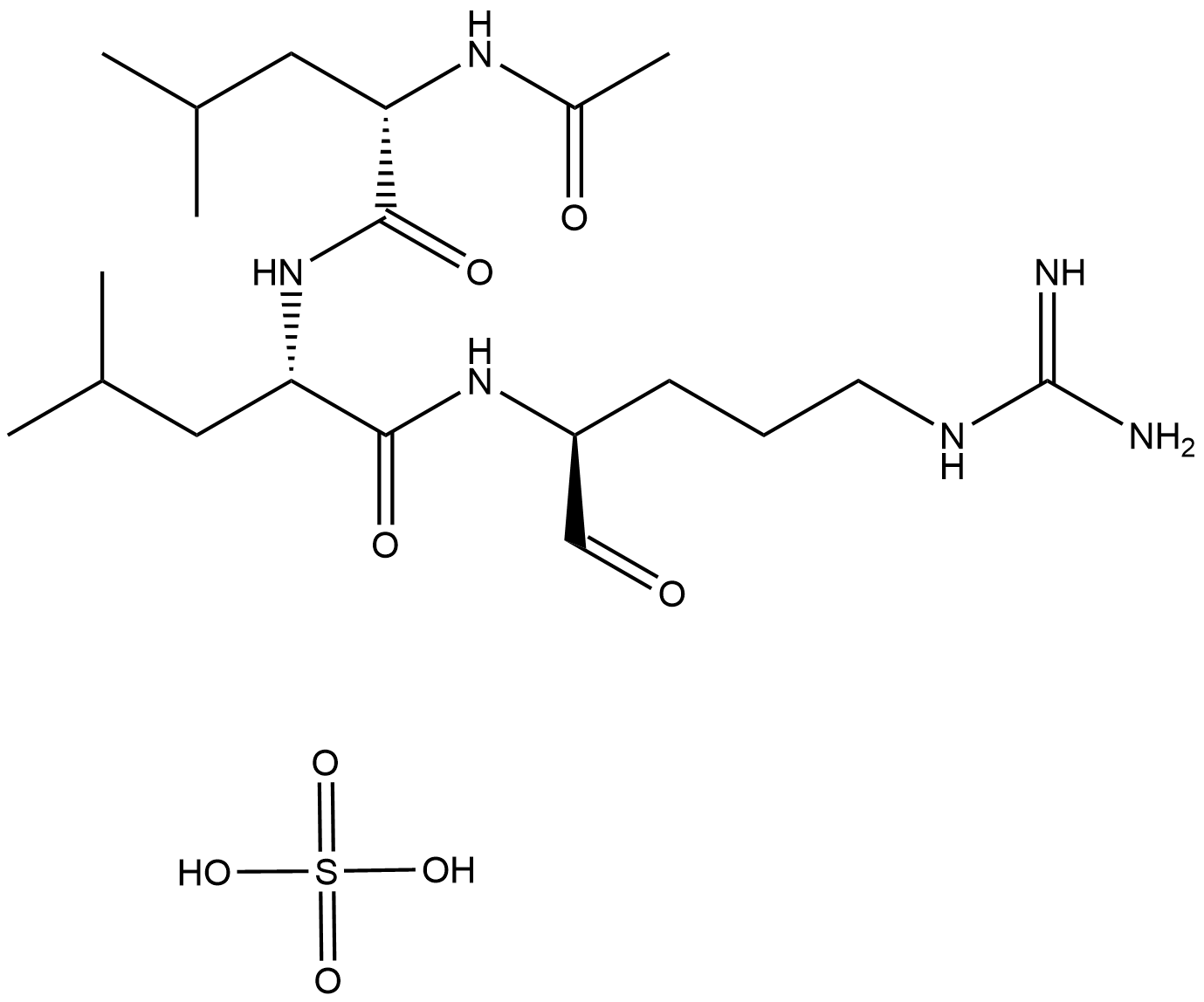
| M.Wt | 685.9 |
| Cas No. | 26305-03-3 |
| Formula | C34H63N5O9 |
| Synonyms | Pepstatin A,NSC272671,Isoval-Val-Val-Sta-Ala-Sta |
| Solubility | ≥34.3 mg/mL in DMSO; insoluble in H2O; insoluble in EtOH |
| Chemical Name | 3-hydroxy-4-[2-[[3-hydroxy-6-methyl-4-[[3-methyl-2-[[3-methyl-2-(3-methylbutanoylamino)butanoyl]amino]butanoyl]amino]heptanoyl]amino]propanoylamino]-6-methylheptanoic acid |
| SDF | Download SDF |
| Canonical SMILES | CC(C)CC(C(CC(=O)O)O)NC(=O)C(C)NC(=O)CC(C(CC(C)C)NC(=O)C(C(C)C)NC(=O)C(C(C)C)NC(=O)CC(C)C)O |
| Shipping Condition | Small Molecules with Blue Ice, Modified Nucleotides with Dry Ice. |
| General tips | We do not recommend long-term storage for the solution, please use it up soon. |
| Kinase experiment [1]: | |
|
Binding assays |
The inhibition of HIV protease, pepsin and cathepsin D activities was assayed using the solid-phase immunoassay at pH 5.6. After induction and harvesting, cells (50 g) were resuspended in 100 ml of 10 mM Tris-HCl buffer, pH 7.5, 1 mM EDTA, 1 mM DTT, 1 mM PMSF and 0.05% Triton X-100, sonicated and centrifuged at 10000g for 20 min, HIV-I protease activity in E. coli extracts was assayed by cleavage of a synthetic heptapeptide substrate and HPLC analysis of proctucts. |
| Cell experiment [2, 3]: | |
|
Cell lines |
H9 cells, Bone marrow cells |
|
Preparation method |
The solubility of this compound in DMSO is >34.3 mg/mL. General tips for obtaining a higher concentration: Please warm the tube at 37°C for 10 minutes and/or shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while. Stock solution can be stored below -20°C for several months. |
|
Reacting condition |
0.1 mM for 2, 4, or 11 days, 37°C |
|
Applications |
Pepstatin A inhibited the proteolytic processing of the HIV gag precursor in H9 cells. Pepstatin A inhibited the production of infectious HIV in H9 cell cultures. Pepstatin A (15–120 μM) dose-dependently suppressed the formation of TRAP-positive multinuclear cells. Pepstatin A dose-dependently suppressed the RANKL-induced osteoclastogenesis from stromal cell–deprived bone marrow cells in the co-culture system and bone marrow culture. Pepstatin A (15 μM) substantially inhibited the aspartic proteinase activity in bone marrow cells, while complete inhibition was seen at 90 μM. |
|
Other notes |
Please test the solubility of all compounds indoor, and the actual solubility may slightly differ with the theoretical value. This is caused by an experimental system error and it is normal. |
|
References: [1]. Sarubbi E, Seneci P F, Angelastro M R, et al. Peptide aldehydes as inhibitors of HIV protease. FEBS letters, 1993, 319(3): 253-256. [2]. von der Helm K, Gürtler L, Eberle J, et al. Inhibition of HIV replication in cell culture by the specific aspartic protease inhibitor pepstatin A. FEBS letters, 1989, 247(2): 349-352. [3] Yoshida H, Okamoto K, Iwamoto T, et al. Pepstatin A, an aspartic proteinase inhibitor, suppresses RANKL-induced osteoclast differentiation. Journal of biochemistry, 2006, 139(3): 583-590. > |
|
Quality Control & MSDS
- View current batch:
Chemical structure
Related Biological Data
Related Biological Data