Caspase
Caspases (cysteine-dependent aspartate specific ptotease) are a family of cysteine proteases that play an essential role in cell apoptosis. Caspases contain a conserved QACXG pentapeptide active site motif and are characterized by specificity for aspartic acid in the P1 position. The synthesis of caspases involves the activation of inactive proenzymes, which contain an N-terminal peptide (prodomain) together with two subunits (one small and one large), following cleavage at specific aspartate cleavage sites. Caspases can be classified into three subfamilies, due to phylogenetic analysis, including an ICE subfamily (caspases-1, -4 and -5), a CED-3/CPP32 subfamily (caspases-3, -6, -7, -8, -9 and -10) and an ICH-1/Nedd2 subfamily (caspase-2).
-
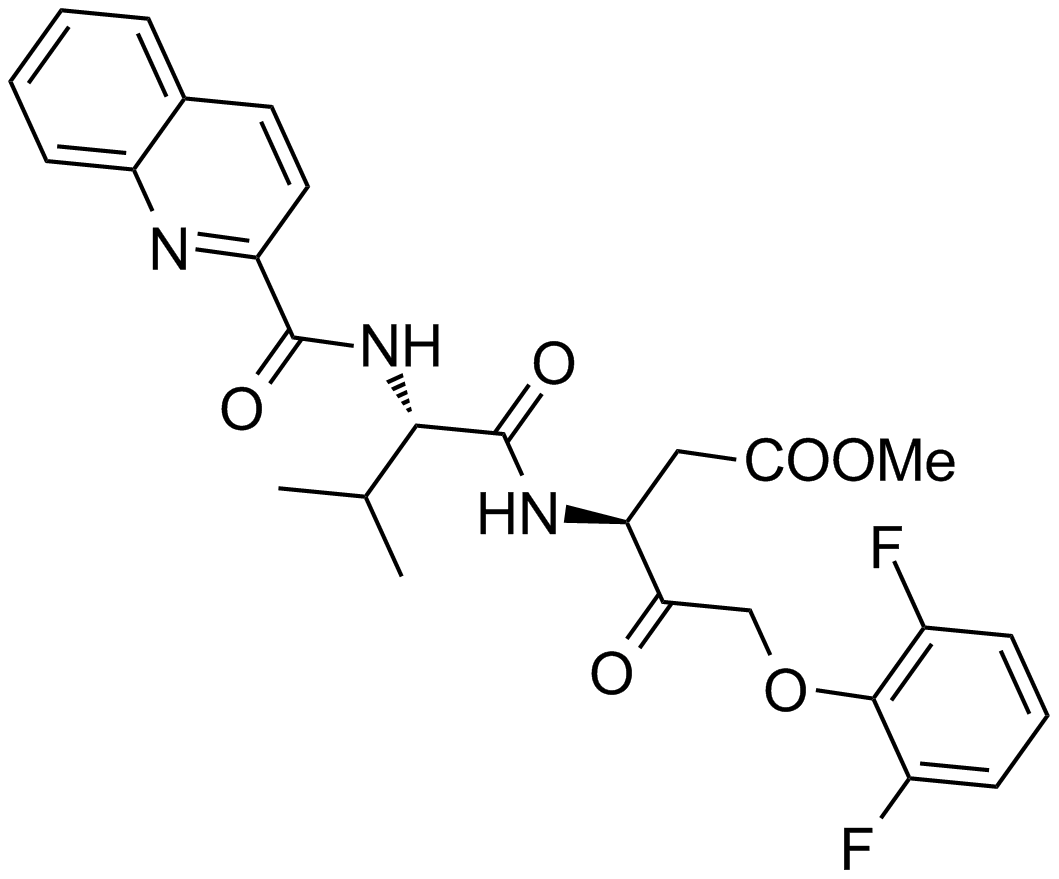 A8165 Q-VD(OMe)-OPh6 CitationTarget: CaspasesSummary: Pan-caspase inhibitor
A8165 Q-VD(OMe)-OPh6 CitationTarget: CaspasesSummary: Pan-caspase inhibitor -
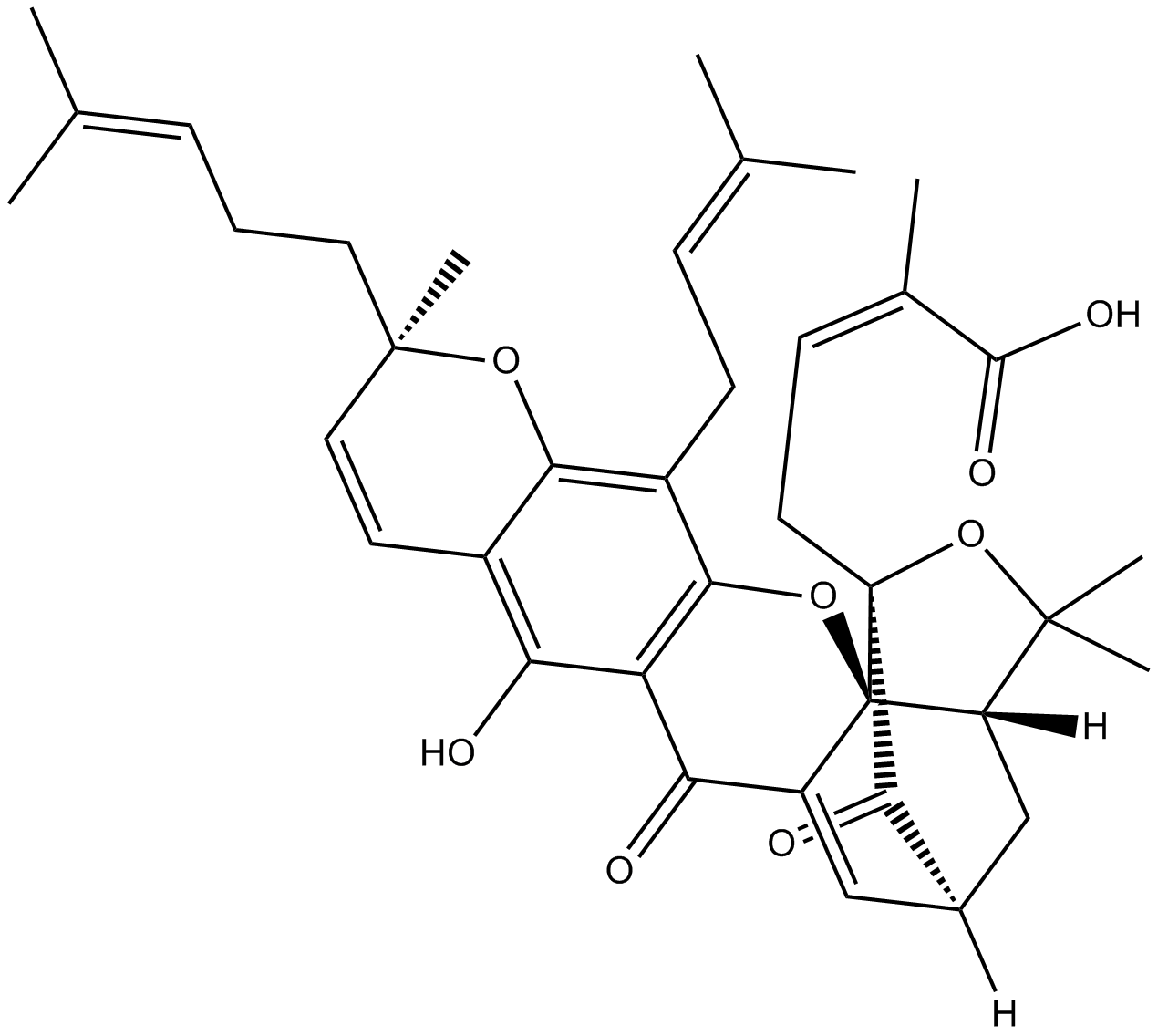 A3424 Gambogic AcidSummary: Caspase activator and apoptosis inducer
A3424 Gambogic AcidSummary: Caspase activator and apoptosis inducer -
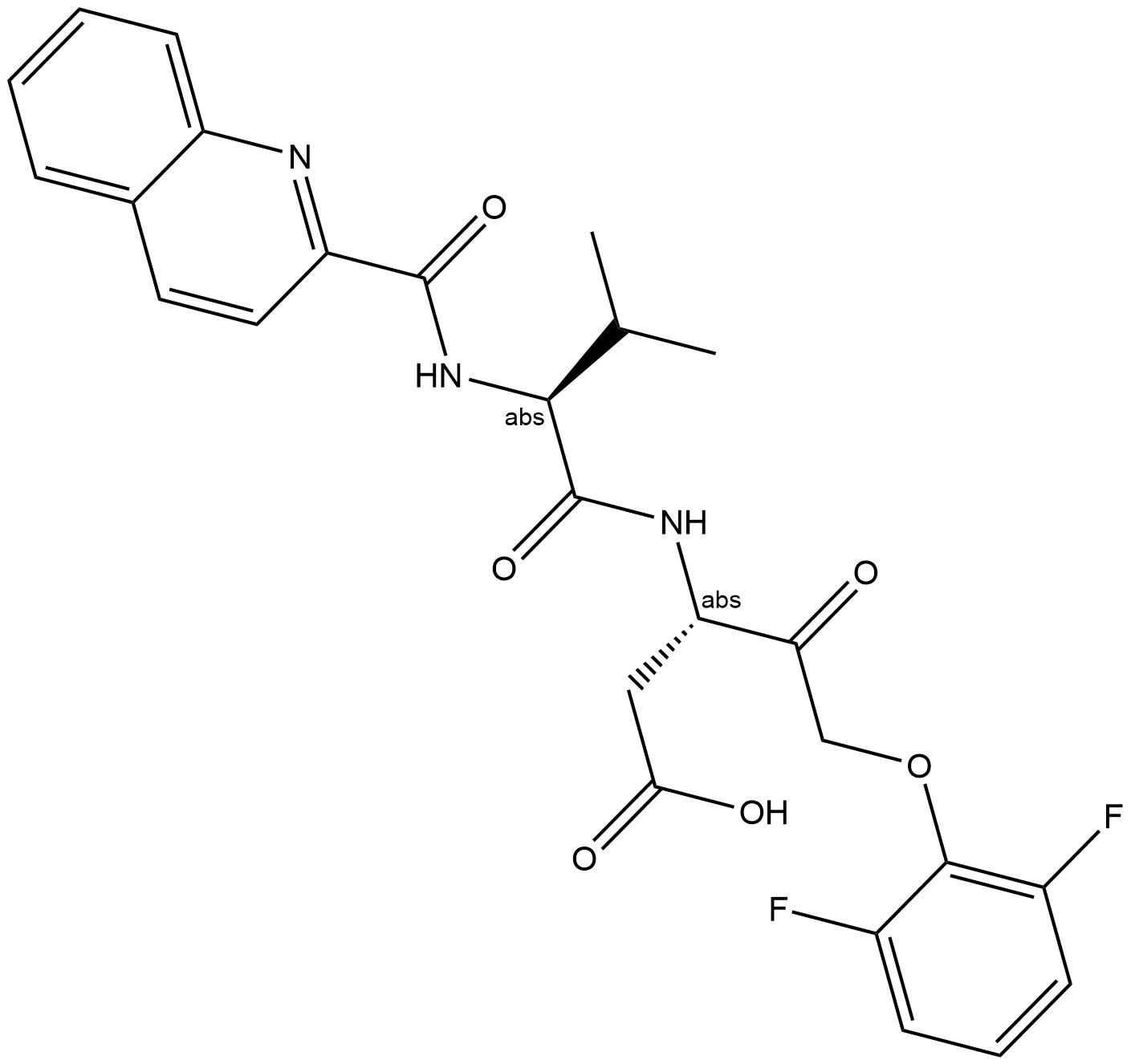 A1901 Q-VD-OPh83 CitationTarget: CaspasesSummary: pan-caspase inhibitor
A1901 Q-VD-OPh83 CitationTarget: CaspasesSummary: pan-caspase inhibitor -
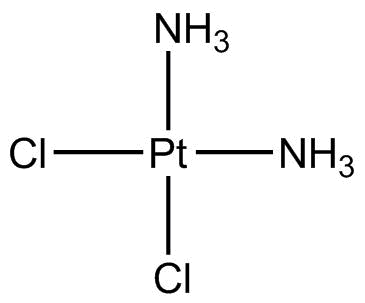 A8321 Cisplatin32 CitationSummary: chemotherapeutic compound
A8321 Cisplatin32 CitationSummary: chemotherapeutic compound -
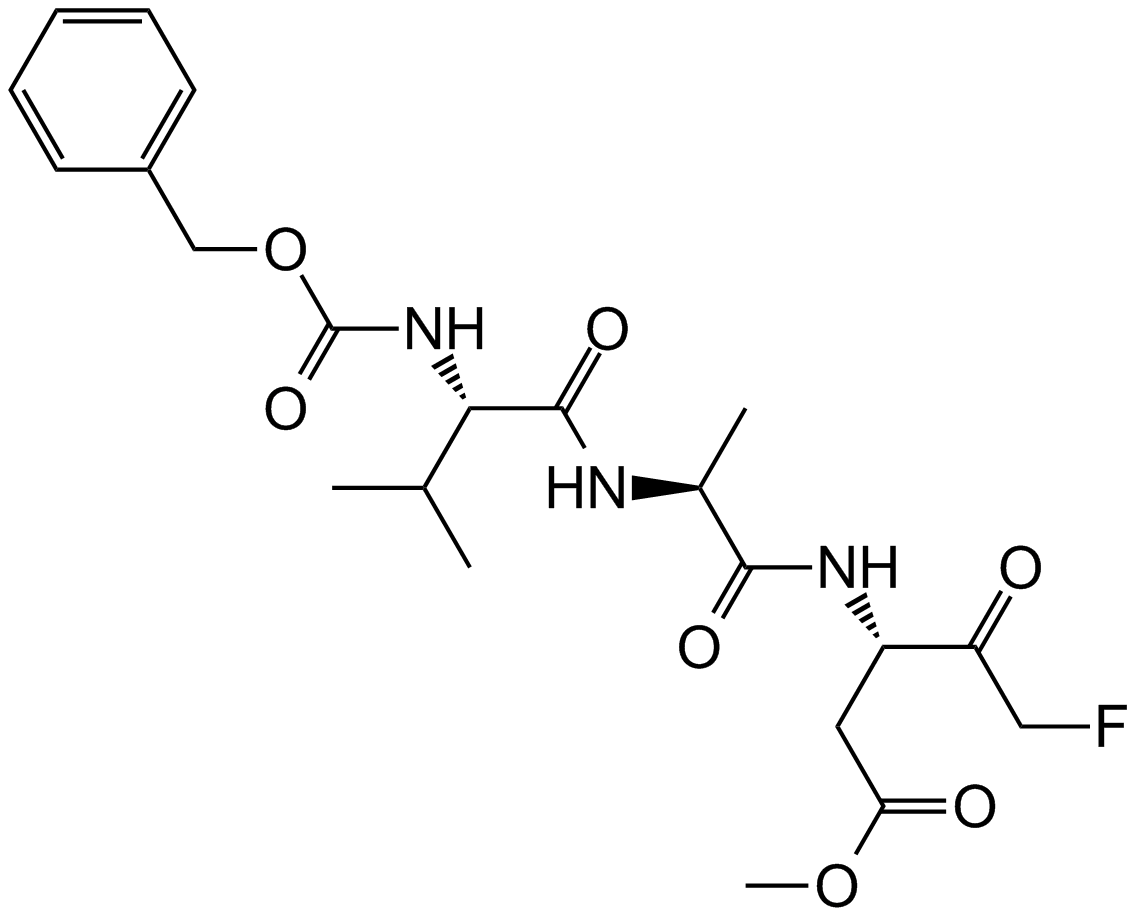 A1902 Z-VAD-FMK200 CitationTarget: CaspasesSummary: pan-caspase inhibitor
A1902 Z-VAD-FMK200 CitationTarget: CaspasesSummary: pan-caspase inhibitor

