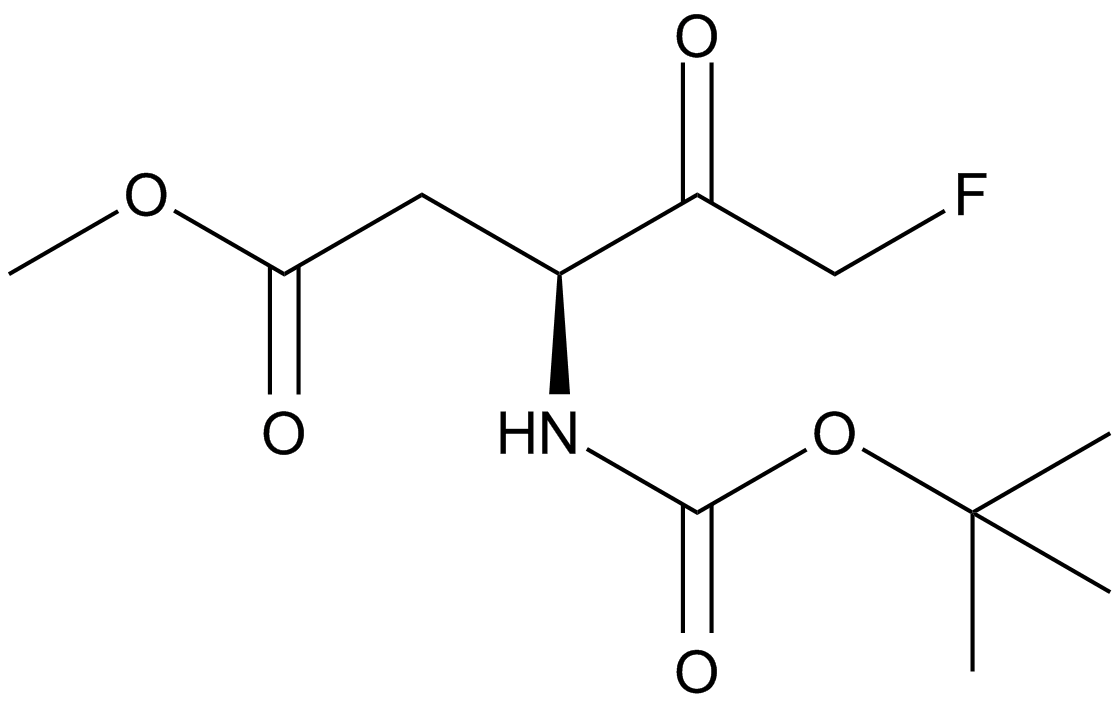
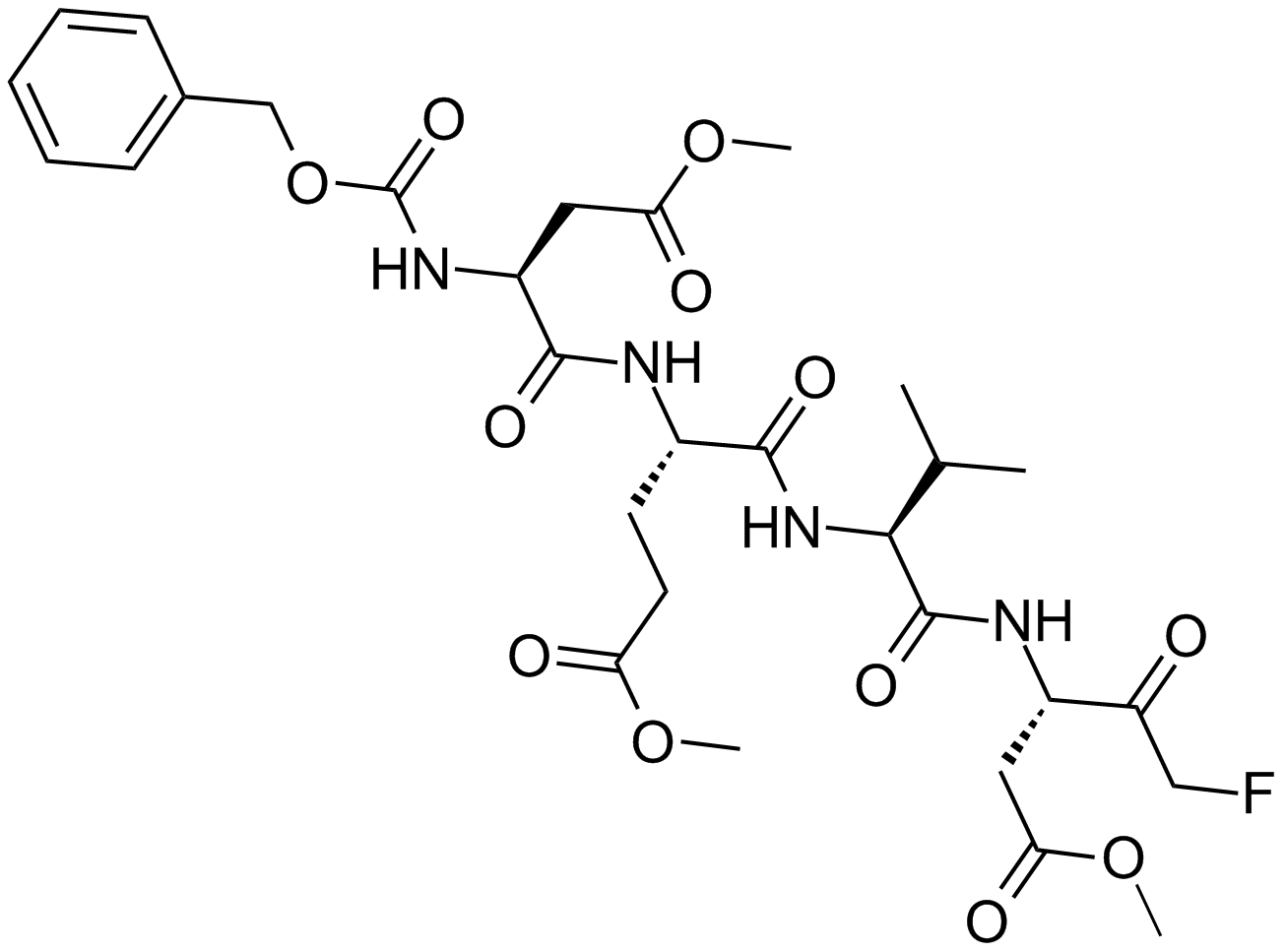
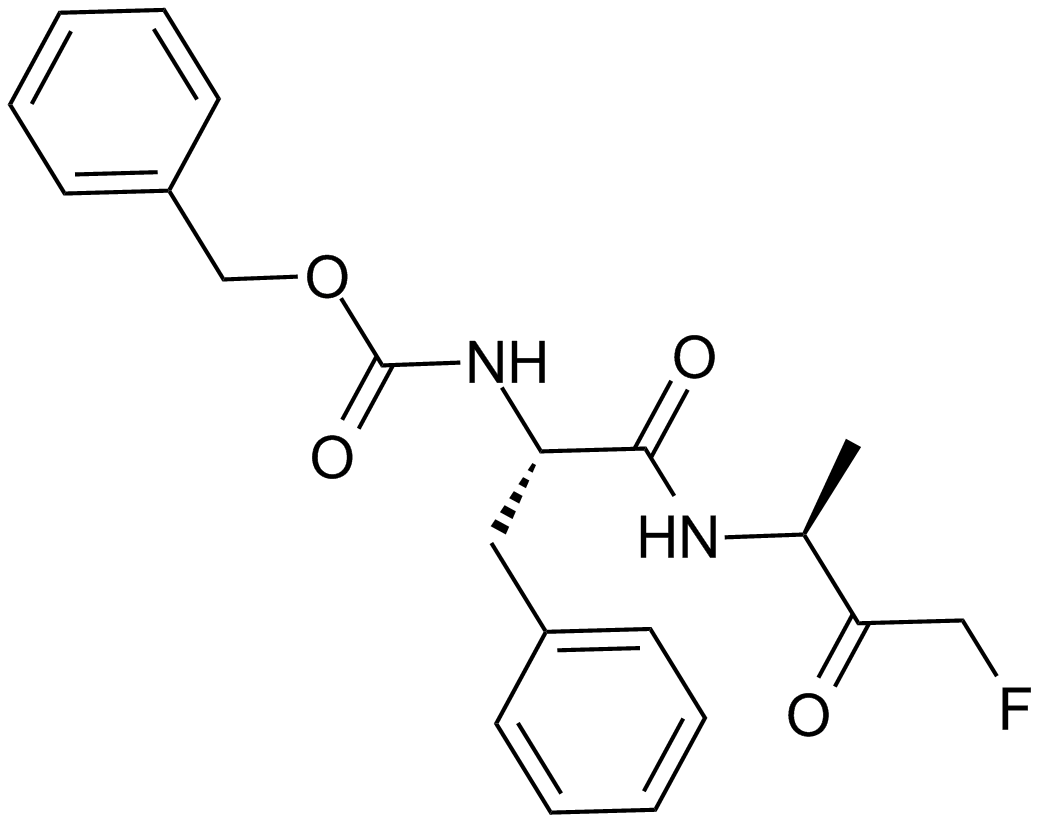
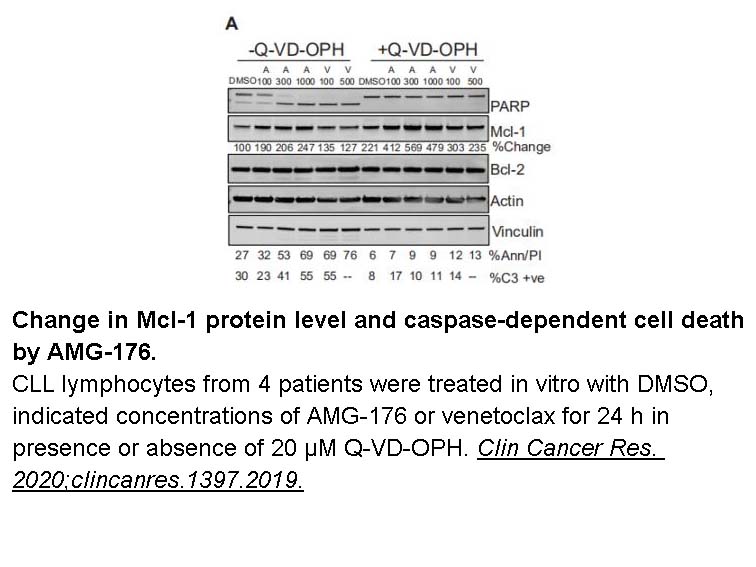
Q-VD(OMe)-OPh
Q-VD-OPh (quinolyl-valyl-O-methylaspartyl-[-2,6-difluorophenoxy]-methyl ketone) is a broad spectrum caspase inhibitor, provides a cost effective, non toxic, and highly specific means of apoptotic inhibition and provides new insight into the design of new inhibitors. [1] It is significantly more effective in preventing apoptosis than the widely used inhibitors, ZVAD-fmk and Boc-D-fmk. Q-VD-OPh is also equally effective in preventing apoptosis mediated by the three major apoptotic pathways, caspase 9/3, caspase 8/10, and caspase 12. In addition to the increased effectiveness, Q-VD-OPh was not toxic to cells, even at high concentrations. Q-VD-OPh is equally effective at inhibiting the three major apoptotic pathways, it can inhibit recombinant caspases 1, 3, 8, and 9 with IC50 values ranging from 25 to 400 nM2. The effectiveness of Q-VD-OPh as an apoptotic inhibitor is evidenced by the complete suppression of an apoptotic inducer capable of inducing substantial cell death in less than 4 hours. [2] Q-VD-OPh protected against the substantial apoptosis induced by actinomycin D. In addition, Q-VD-OPh alone exhibited little or no toxicity, even at extremely high concentrations.
Ref:
- 1. T. M. Caserta, A. N. Smith, A. D. Gultice, M. A. Reedy and T. L. Brown, Q-VD-OPh, a broad spectrum caspase inhibitor with potent antiapoptotic properties, Apoptosis 2003; 8: 345–352
- Yin XM. Signal transduction mediated by Bid, a pro-death Bcl-2 family proteins, connects the death receptor and mitochondria apoptosis pathways. Cell Res 2000; 10: 161–167
- 1. Aabdin, Zainul, Abbas, Muhammad, et al. "Characterization of the architecture of BAK apoptotic foci and mitochondria-ER membrane contact sites" 2024-08-01
- 2. Sergio Espinosa-Gil, Saska Ivanova, et al. "MAP kinase ERK5 modulates cancer cell sensitivity to extrinsic apoptosis induced by death-receptor agonists." Cell Death Dis. 2023 Nov 2;14(11):715. PMID: 37919293
- 3. Mingchao Mu, Qin Zhang, et al. "3-Bromopyruvate overcomes cetuximab resistance in human colorectal cancer cells by inducing autophagy-dependent ferroptosis." Cancer Gene Ther. 2023 Aug 9. PMID: 37558749
- 4. Collins Waguia Kontchou, Ian E Gentle, et al. "Chlamydia trachomatis inhibits apoptosis in infected cells by targeting the pro-apoptotic proteins Bax and Bak." Cell Death Differ. 2022 Oct;29(10):2046-2059. PMID: 35397654
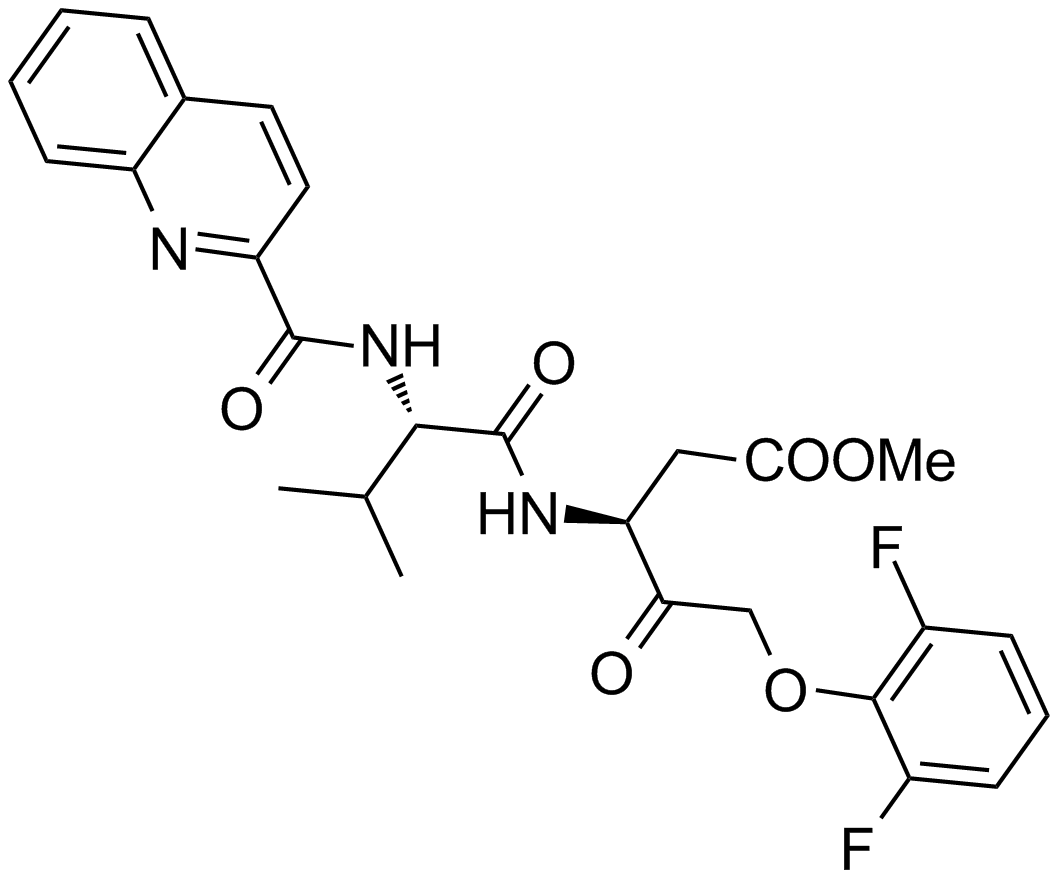
- 5. Rocío Mora-Molina, Daniela Stöhr, et al. "cFLIP downregulation is an early event required for endoplasmic reticulum stress-induced apoptosis in tumor cells." Cell Death Dis. 2022 Feb 3;13(2):111. PMID: 35115486
- 6. Pin Li, Qin Li, et al. "LIF, a mitogen for choroidal endothelial cells, protects the choriocapillaris: implications for prevention of geographic atrophy." EMBO Mol Med. 2022 Jan 11;14(1):e14511. PMID: 34779136
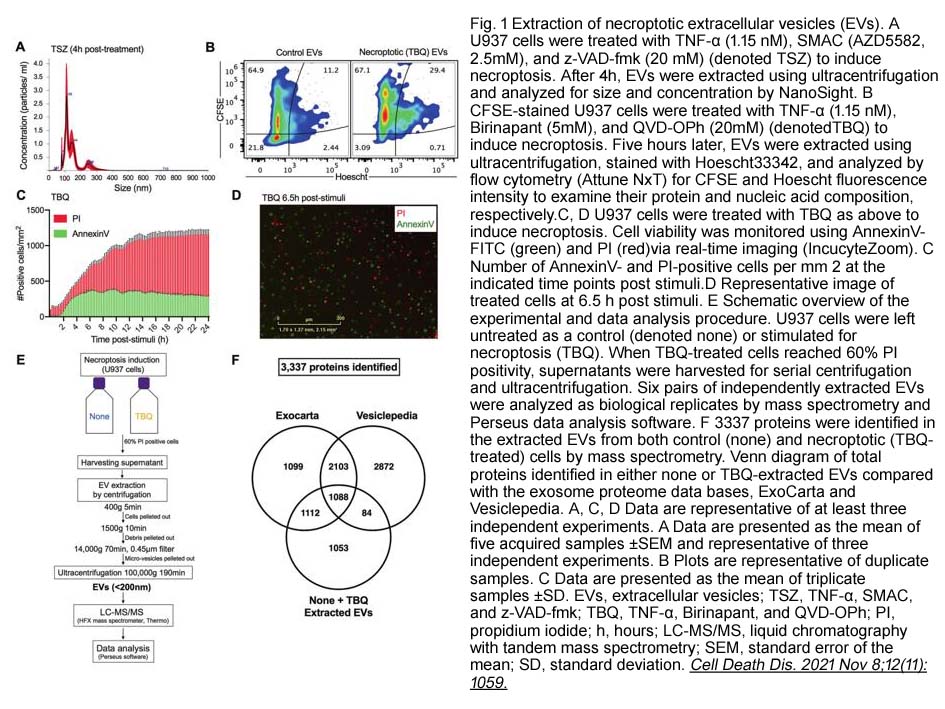
- 7. Inbar Shlomovitz, Ziv Erlich, et al. "Proteomic analysis of necroptotic extracellular vesicles." Cell Death Dis. 2021 Nov 8;12(11):1059. PMID: 34750357
- 8. Lioba Klaas, Juliane Vier, et al. "Diversity of cell death signaling pathways in macrophages upon infection with modified vaccinia virus Ankara (MVA)." Cell Death Dis. 2021 Oct 28;12(11):1011. PMID: 34711816
- 9. PIUS REYDERG AGYEMANG. "Profifiling of FDA-Approved and Clinical Trial Drugs Revealed Shared Cytotoxicity And Collateral Sensitivity In Resistant (H69ar) And Non-Resistant (H69) Small Cell Lung Cancer Cells. (Drug Repurposing in Cancer Chemotherapy)." South Dakota State University 2021.
- 10. Martens AWJ, Janssen SR, et al. "CD3xCD19 DART molecule treatment induces non-apoptotic killing and is efficient against high-risk chemotherapy and venetoclax-resistant chronic lymphocytic leukemia cells." J Immunother Cancer. 2020;8(1):e000218. PMID: 32581054
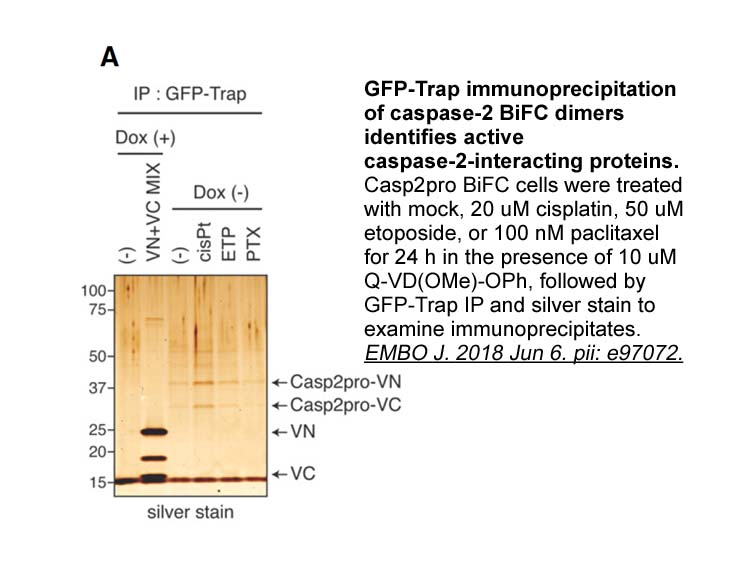
- 11. Yi X, Sarkar A, et al. "AMG-176, an Mcl-1 antagonist, shows preclinical efficacy in chronic lymphocytic leukemia." Clin Cancer Res. 2020;clincanres.1397.2019. PMID: 31937611
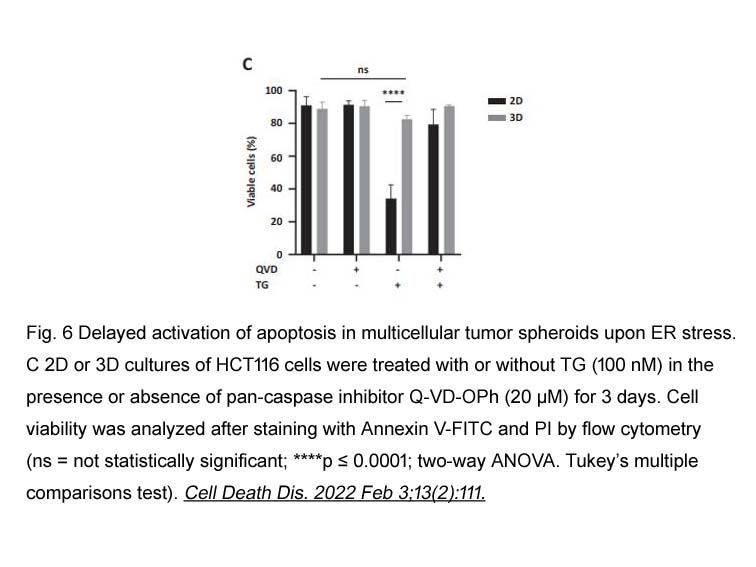
- 12. Robeson AC, Lindblom KR, et al. "Dimer-specific immunoprecipitation of active caspase-2 identifies TRAF proteins as novel activators." EMBO J. 2018 Jun 6. pii: e97072. PMID: 29875129
- 13. Burman JL, Pickles S, et al. "Mitochondrial fission facilitates the selective mitophagy of protein aggregates." J Cell Biol. 2017 Oct 2;216(10):3231-3247. PMID: 28893839
- 14. Gong YN, Guy C, et al. "ESCRT-III Acts Downstream of MLKL to Regulate Necroptotic Cell Death and Its Consequences." Cell. 2017 Apr 6;169(2):286-300.e16. PMID: 28388412
- 15. Wang L, Mehta S, et al. "Inhibition of Murine Pulmonary Microvascular Endothelial Cell Apoptosis Promotes Recovery of Barrier Function under Septic Conditions." Mediators Inflamm. 2017;2017:3415380. PMID: 28250575
- 16. Milasta S, Dillon CP, et al. "Apoptosis-Inducing-Factor-Dependent Mitochondrial Function Is Required for T Cell but Not B Cell Function." Immunity. 2016 Jan 19;44(1):88-102. PMID: 26795252
- 17. Rodriguez, D. A, et al. "Characterization of RIPK3-mediated phosphorylation of the activation loop of MLKL during necroptosis." Cell Death & Differentiation (2015). PMID: 26024392
| Physical Appearance | A solid |
| Storage | Store at -20°C |
| M.Wt | 527 |
| Cas No. | 402592-44-3 |
| Formula | C26H25F2N3O6 |
| Synonyms | Q-VD(OMe)-OPh |
| Solubility | ≥26.35 mg/mL in DMSO; insoluble in H2O; ≥97.4 mg/mL in EtOH |
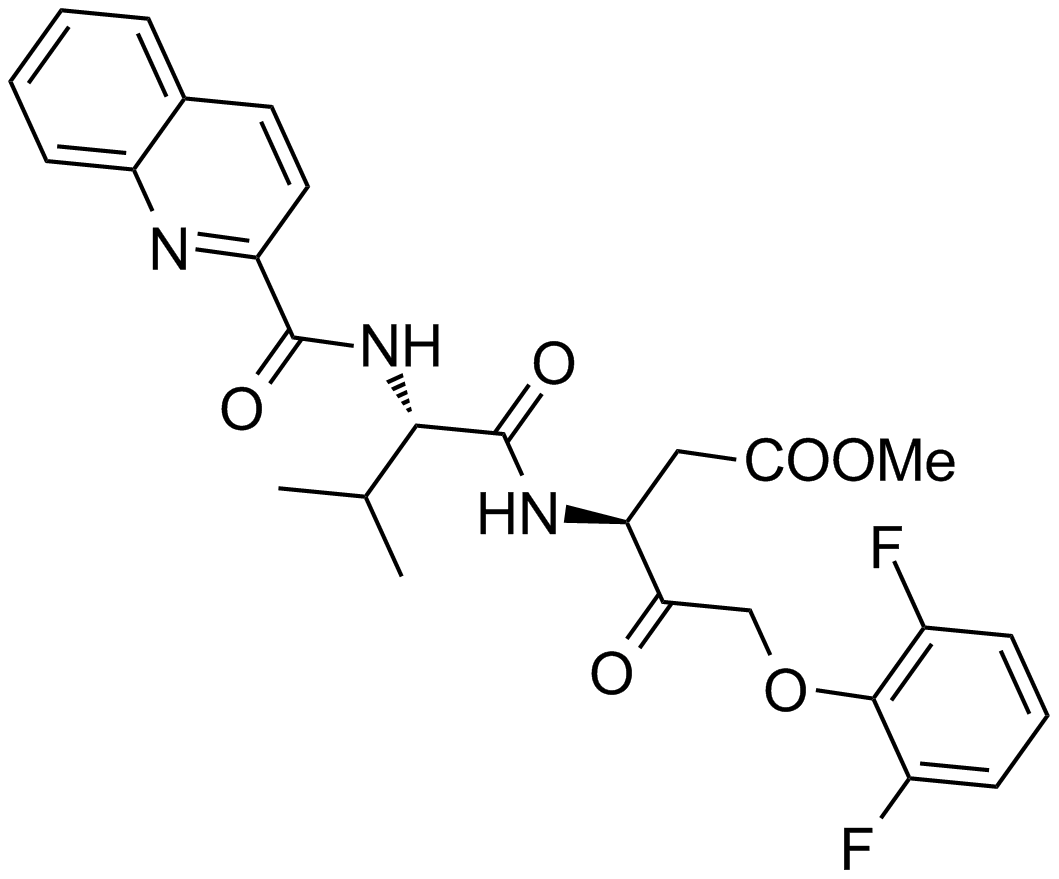
| Chemical Name | (S)-methyl 5-(2,6-difluorophenoxy)-3-((S)-3-methyl-2-(quinoline-2-carboxamido)butanamido)-4-oxopentanoate |
| SDF | Download SDF |
| Canonical SMILES | O=C(N[C@@H](C(C)C)C(N[C@@H](CC(OC)=O)C(COC1=C(F)C=CC=C1F)=O)=O)C2=NC3=CC=CC=C3C=C2 |
| Shipping Condition | Small Molecules with Blue Ice, Modified Nucleotides with Dry Ice. |
| General tips | We do not recommend long-term storage for the solution, please use it up soon. |
| Cell experiment:[1] | |
|
Cell lines |
Acute myeloid leukemia (AML) blasts |
|
Reaction Conditions |
5 μM Q-VD-OPh for 7 d incubation |
|
Applications |
Caspase inhibitor Q-VD-OPh induced cell differentiation, and further enhanced differentiation of AML blasts when combined with vitamin D derivatives. Q-VD-OPh alone was also able to increase the expression of differentiation markers in these AML blasts. |
| Animal experiment:[2] | |
|
Animal models |
A murine model of stroke induced by middle cerebral artery occlusion (MCAO) |
|
Dosage form |
500 μg Administered intraperitoneally |
|
Applications |
Q-VD-OPh reduced ischemic brain damage and stroke-induced programmed cell death in thymus and spleen, decreased susceptibility to post-stroke bacteremia, and improved survival. |
|
Note |
The technical data provided above is for reference only. |
|
References: 1. Chen-Deutsch X, Kutner A, Harrison JS, et al. The pan-caspase inhibitor Q-VD-OPh has anti-leukemia effects and can interact with vitamin D analogs to increase HPK1 signaling in AML cells. Leukemia Research, 2012, 36(7): 884-888. 2. Braun JS, Prass K, Dirnagl U, et al. Protection from brain damage and bacterial infection in murine stroke by the novel caspase-inhibitor Q-VD-OPH. Experimental Neurology, 2007, 206(2): 183-191. |
|
Quality Control & MSDS
- View current batch:
Chemical structure
Related Biological Data
Related Biological Data
Related Biological Data
Related Biological Data
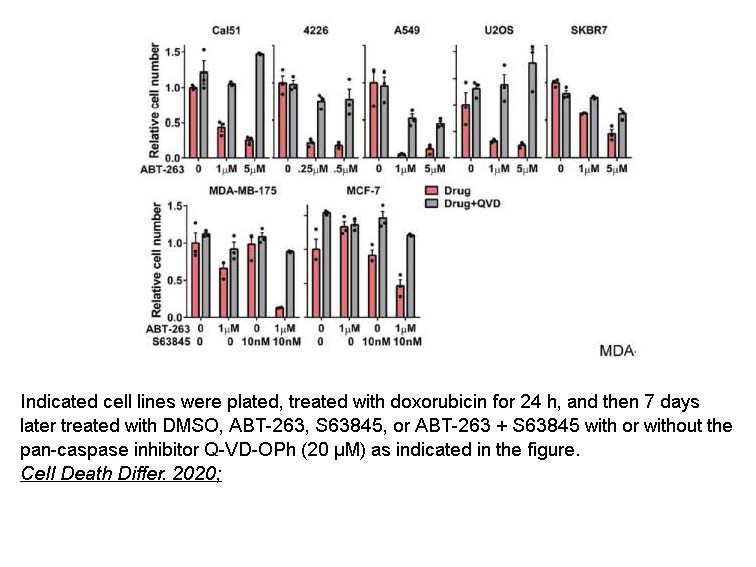
Related Biological Data
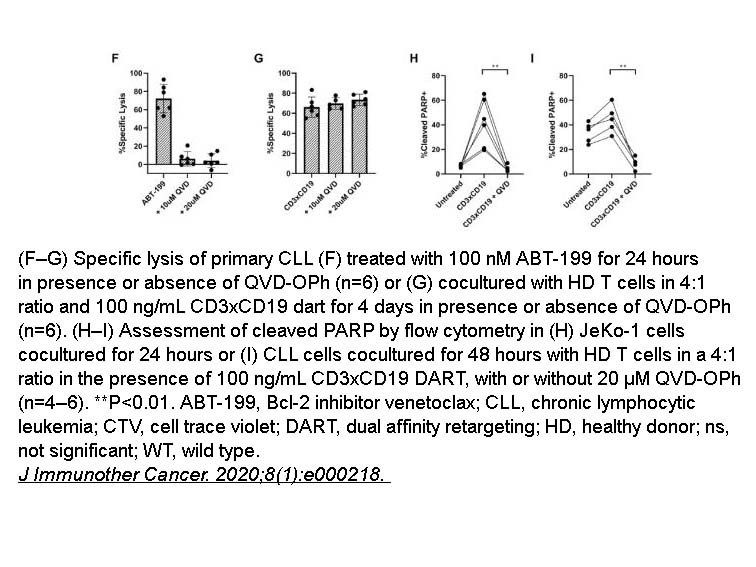
Related Biological Data
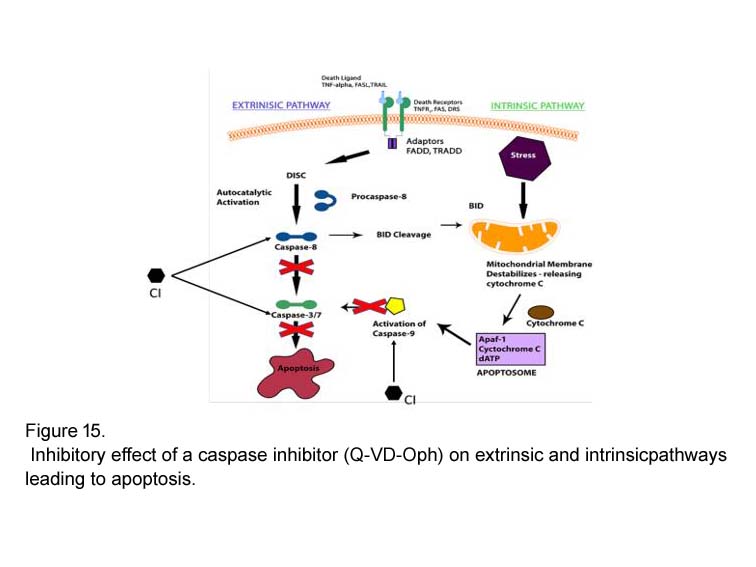
Related Biological Data