Proteases
Proteases, also known as peptidases or proteolytic enzymes, consists of a large number of enzymes catalyzing the hydrolysis of peptide bonds and subsequently resulting in the degradation of protein substrates into amino acids. Proteases are involved in a wide range of human diseases, including cancer, neurodegenerative disorders, inflammatory diseases and cardiovascular diseases. Thus numerous proteases inhibitors (small molecules and proteins) have been identified to block activity of proteases. Proteases inhibitors can be classified into different types based on the class of proteases they inhibit through two general mechanisms, irreversible “trapping” reactions and reversible tight-binding reactions. Proteases inhibitors have been used as diagnostic or therapeutic agents for the treatment of proteases-related diseases.
-
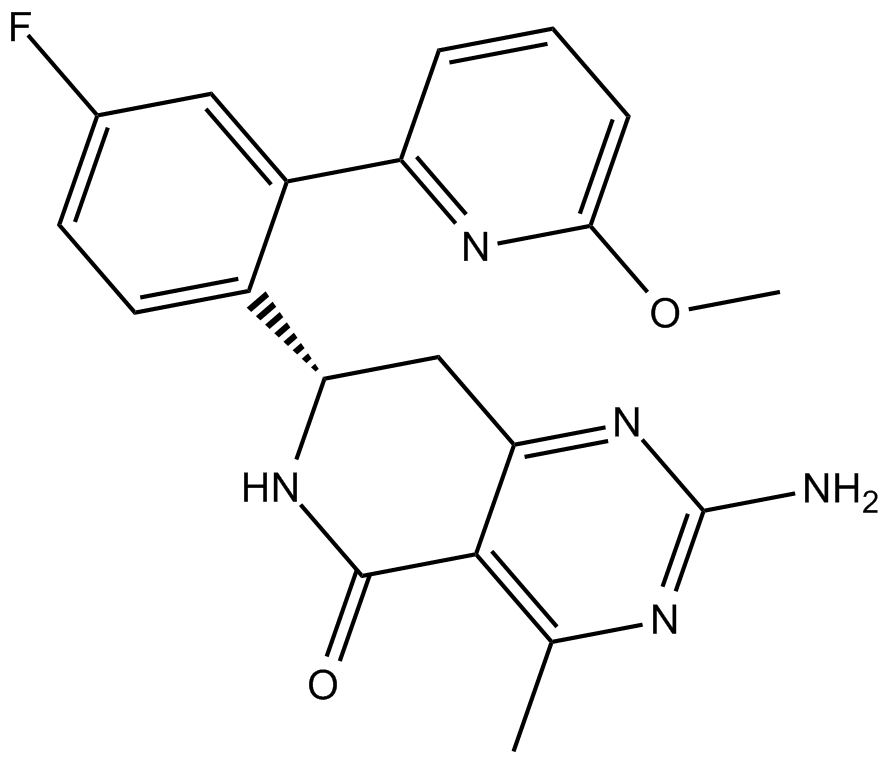 B4797 HSP990 (NVP-HSP990)Target: HSP90Summary: Hsp90 inhibitor, potent and selective
B4797 HSP990 (NVP-HSP990)Target: HSP90Summary: Hsp90 inhibitor, potent and selective -
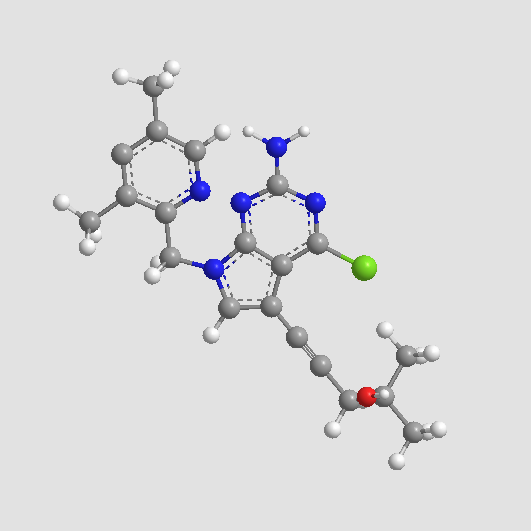 B4920 EC 144Target: HSP90Summary: High affinity, potent and selective Hsp90 inhibitor
B4920 EC 144Target: HSP90Summary: High affinity, potent and selective Hsp90 inhibitor -
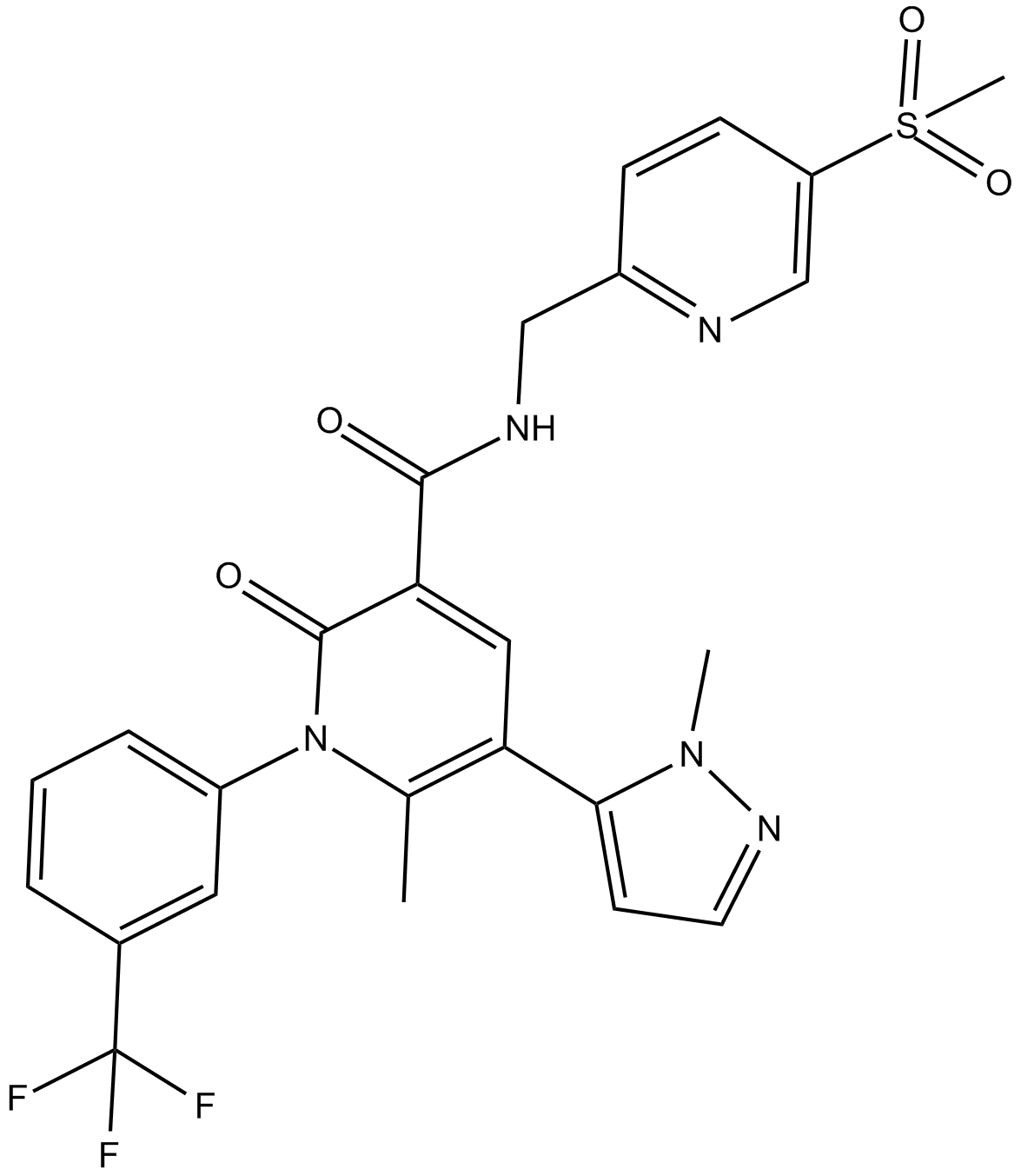 B1037 AlvelestatTarget: NESummary: NE inhibitor
B1037 AlvelestatTarget: NESummary: NE inhibitor -
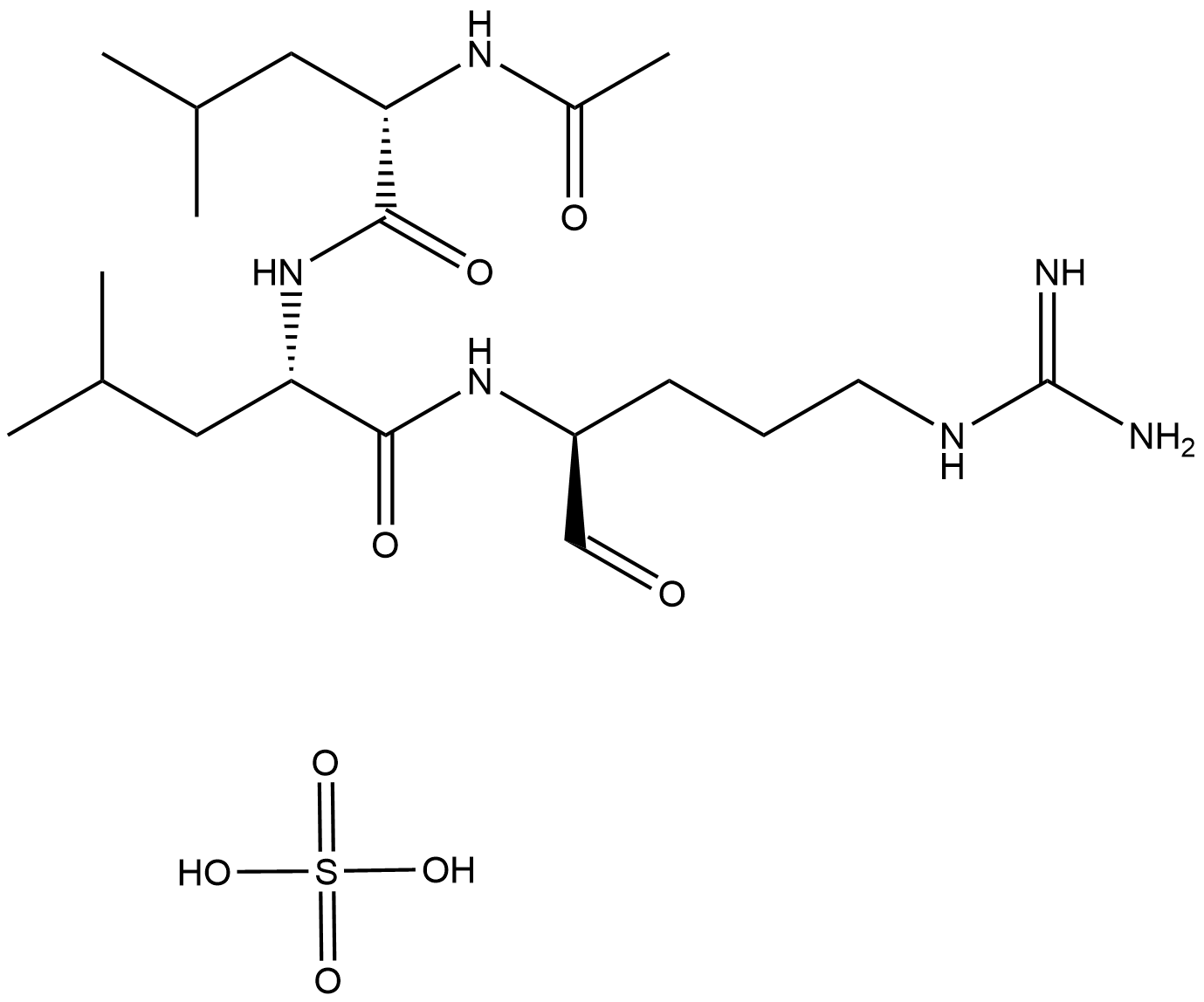 A2570 Leupeptin, MicrobialTarget: Cathepsins|Calpains|TrypsinsSummary: Inhibitor of serine and cysteine proteases
A2570 Leupeptin, MicrobialTarget: Cathepsins|Calpains|TrypsinsSummary: Inhibitor of serine and cysteine proteases -
 A2571 Pepstatin A1 CitationTarget: Cathepsins|Renin|HIV proteases|PepsinsSummary: Aspartic protease inhibitor
A2571 Pepstatin A1 CitationTarget: Cathepsins|Renin|HIV proteases|PepsinsSummary: Aspartic protease inhibitor -
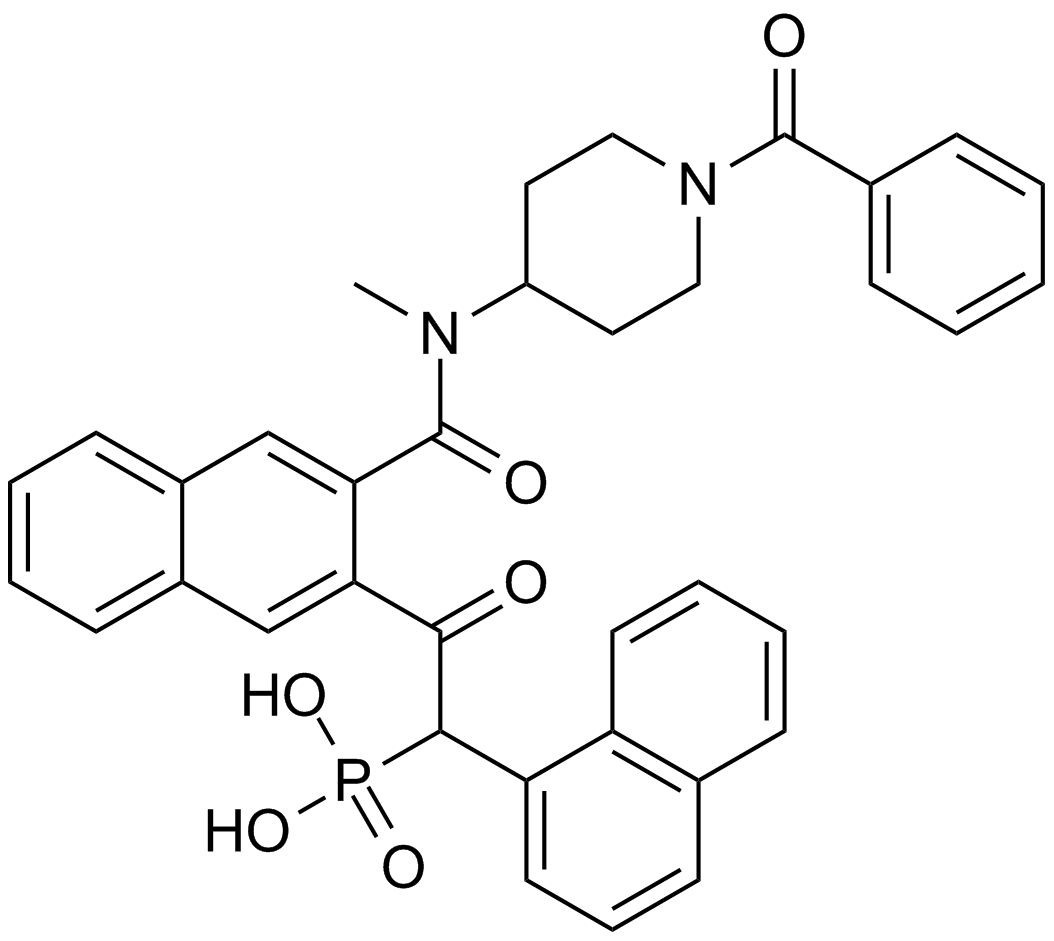 A8174 Cathepsin G Inhibitor ITarget: CathepsinsSummary: Cathepsin G inhibitor
A8174 Cathepsin G Inhibitor ITarget: CathepsinsSummary: Cathepsin G inhibitor -
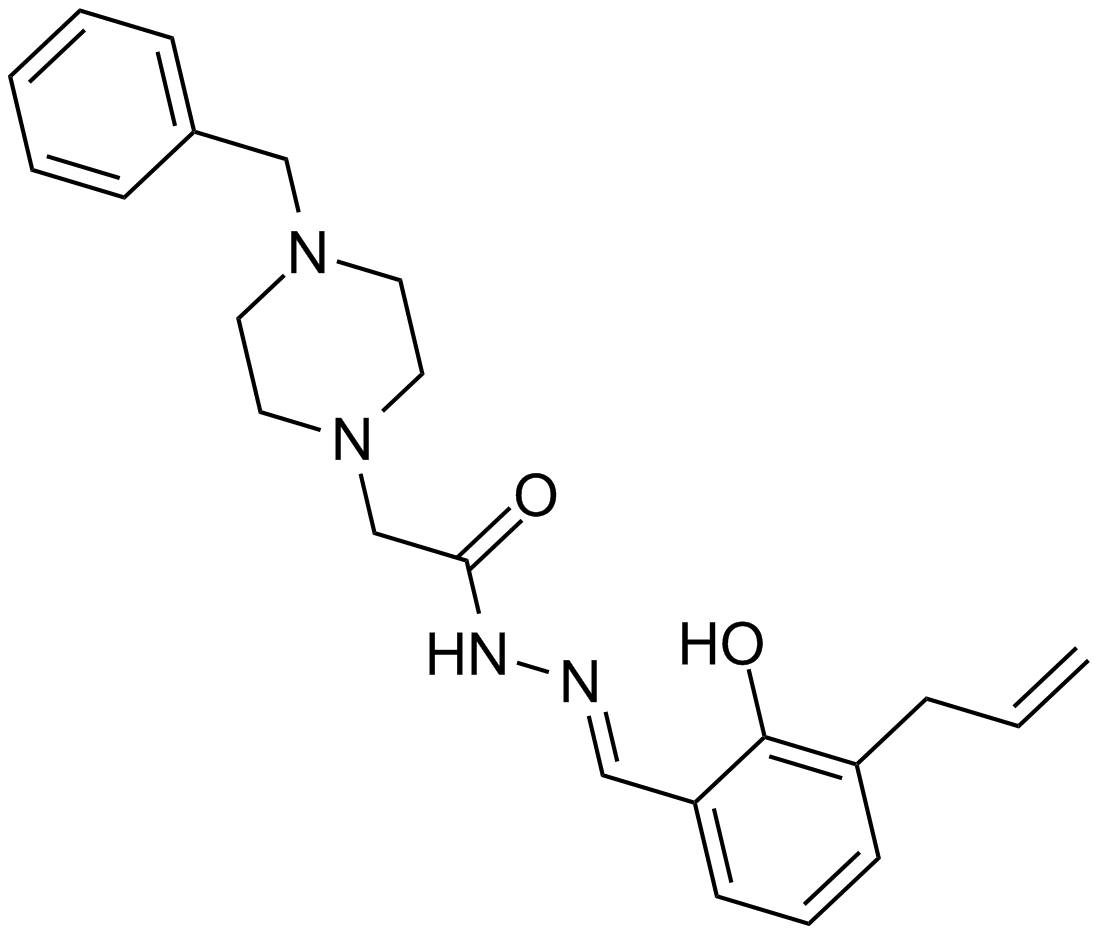 A8177 PAC-11 CitationTarget: CaspasesSummary: Procaspase-3 activator
A8177 PAC-11 CitationTarget: CaspasesSummary: Procaspase-3 activator -
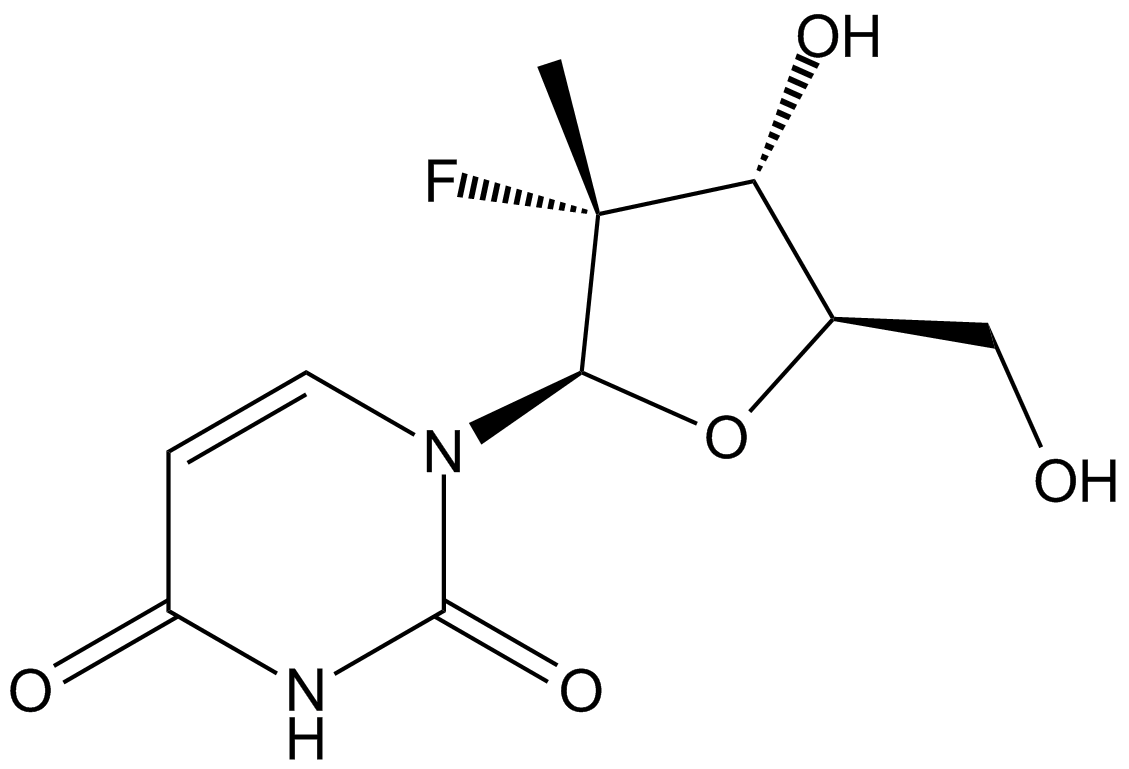 A8189 PSI-62063 CitationTarget: HCV polymeraseSummary: Inhibitor of HCV RNA polymerase,potent and selective
A8189 PSI-62063 CitationTarget: HCV polymeraseSummary: Inhibitor of HCV RNA polymerase,potent and selective -
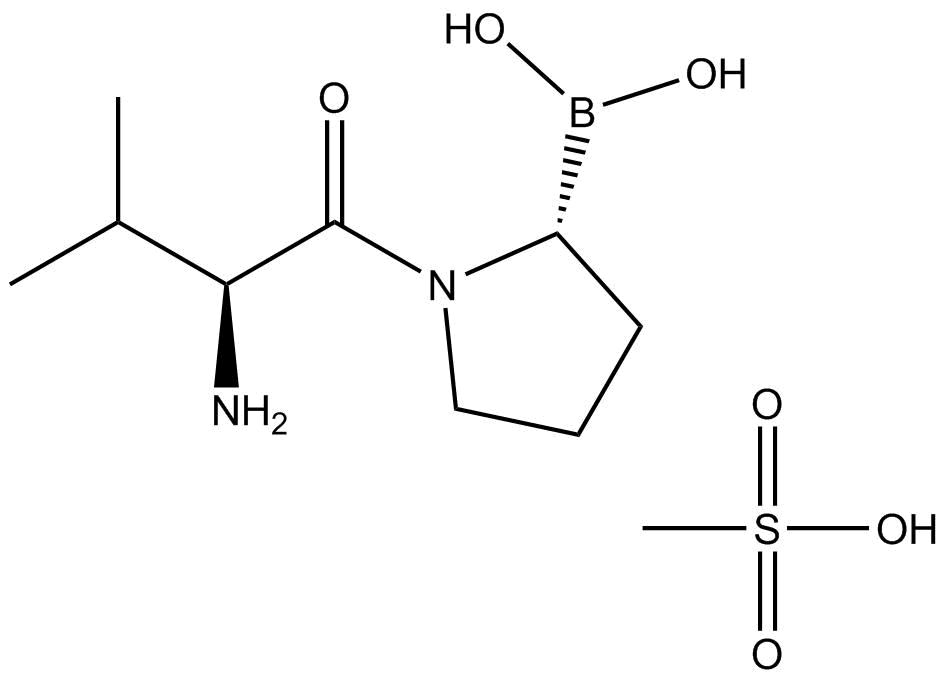 B3941 Talabostat mesylate2 CitationTarget: DPP-4Summary: orally active, specific inhibitor of DPP4
B3941 Talabostat mesylate2 CitationTarget: DPP-4Summary: orally active, specific inhibitor of DPP4 -
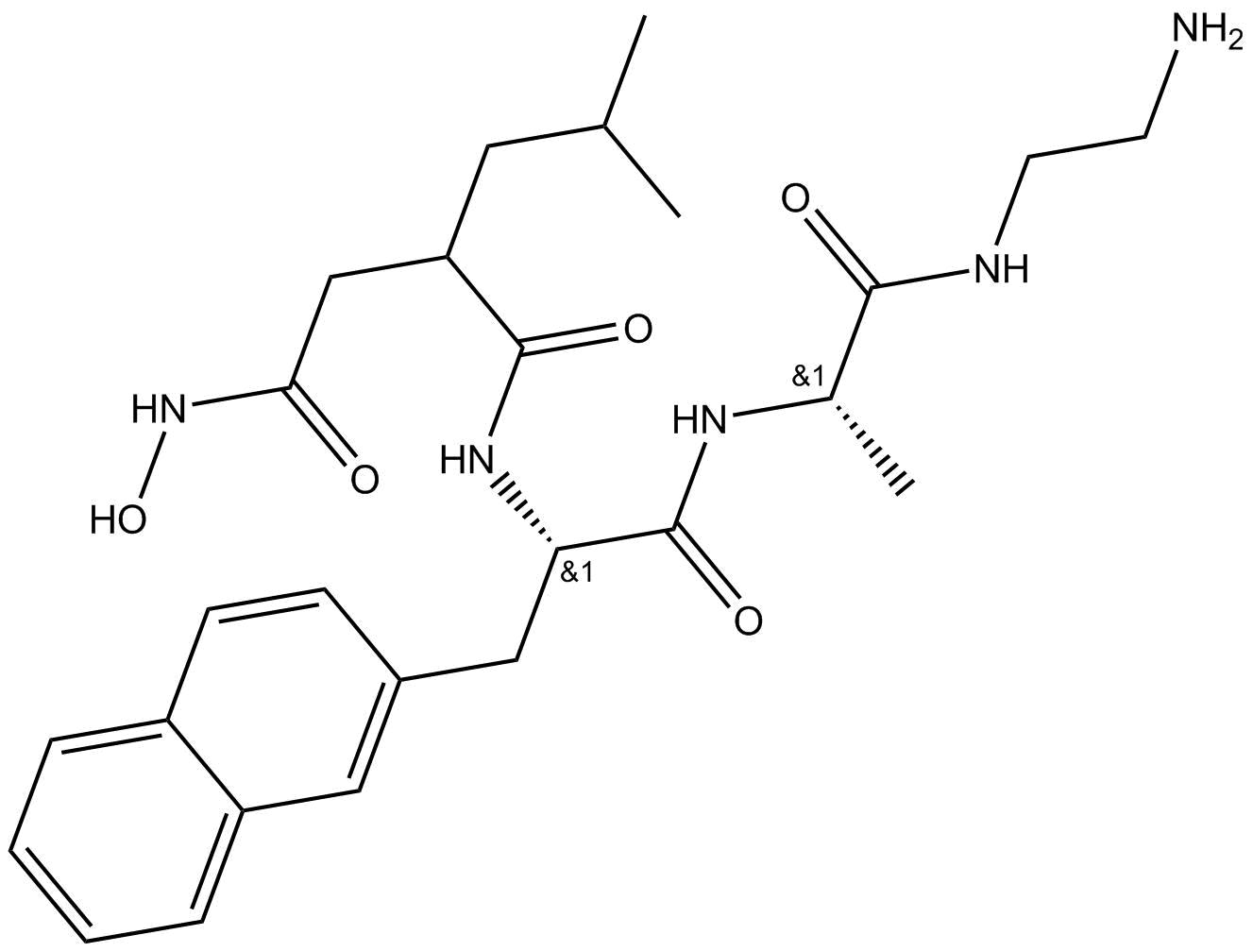 B4686 TAPI-12 CitationTarget: MMPSummary: TACE/ADAM17 inhibitor
B4686 TAPI-12 CitationTarget: MMPSummary: TACE/ADAM17 inhibitor

