Search results for: 'signaling pathways proteases'
-
 L1044 DiscoveryProbe™ NF-κB Signaling LibrarySummary: A unique collection of 73 NF-κB inhibitors for NF-κB signaling pathway research.
L1044 DiscoveryProbe™ NF-κB Signaling LibrarySummary: A unique collection of 73 NF-κB inhibitors for NF-κB signaling pathway research. -
 L1026 DiscoveryProbe™ Neuronal Signaling Library1 CitationSummary: A unique collection of 556 neuronal signaling-related small molecules for neuroscience reasearch.
L1026 DiscoveryProbe™ Neuronal Signaling Library1 CitationSummary: A unique collection of 556 neuronal signaling-related small molecules for neuroscience reasearch. -
 A2571 Pepstatin A9 CitationTarget: Cathepsins|Renin|HIV proteases|PepsinsSummary: aspartic proteases inhibitor
A2571 Pepstatin A9 CitationTarget: Cathepsins|Renin|HIV proteases|PepsinsSummary: aspartic proteases inhibitor -
 L1044P DiscoveryProbe™ NF-κB Signaling Compound Library PlusSummary: A unique collection of 178 NF-κB inhibitors for NF-κB signaling pathway research.
L1044P DiscoveryProbe™ NF-κB Signaling Compound Library PlusSummary: A unique collection of 178 NF-κB inhibitors for NF-κB signaling pathway research. -
 L1026P DiscoveryProbe™ Neuronal Signaling Compound Library PlusSummary: A unique collection of 948 neuronal signaling-related small molecules for neuroscience reasearch.
L1026P DiscoveryProbe™ Neuronal Signaling Compound Library PlusSummary: A unique collection of 948 neuronal signaling-related small molecules for neuroscience reasearch. -
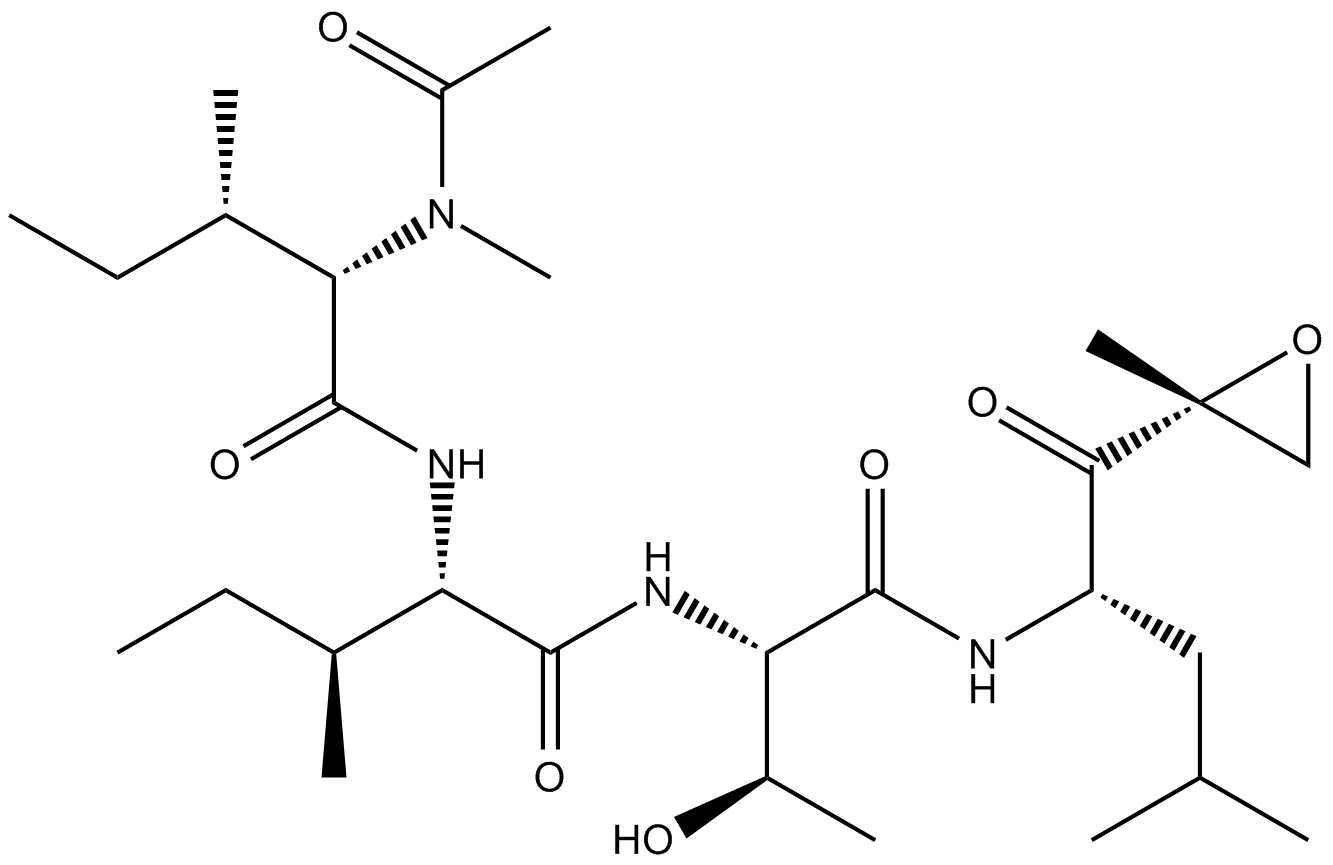 A2606 Epoxomicin25 CitationSummary: proteasome inhibitor
A2606 Epoxomicin25 CitationSummary: proteasome inhibitor -
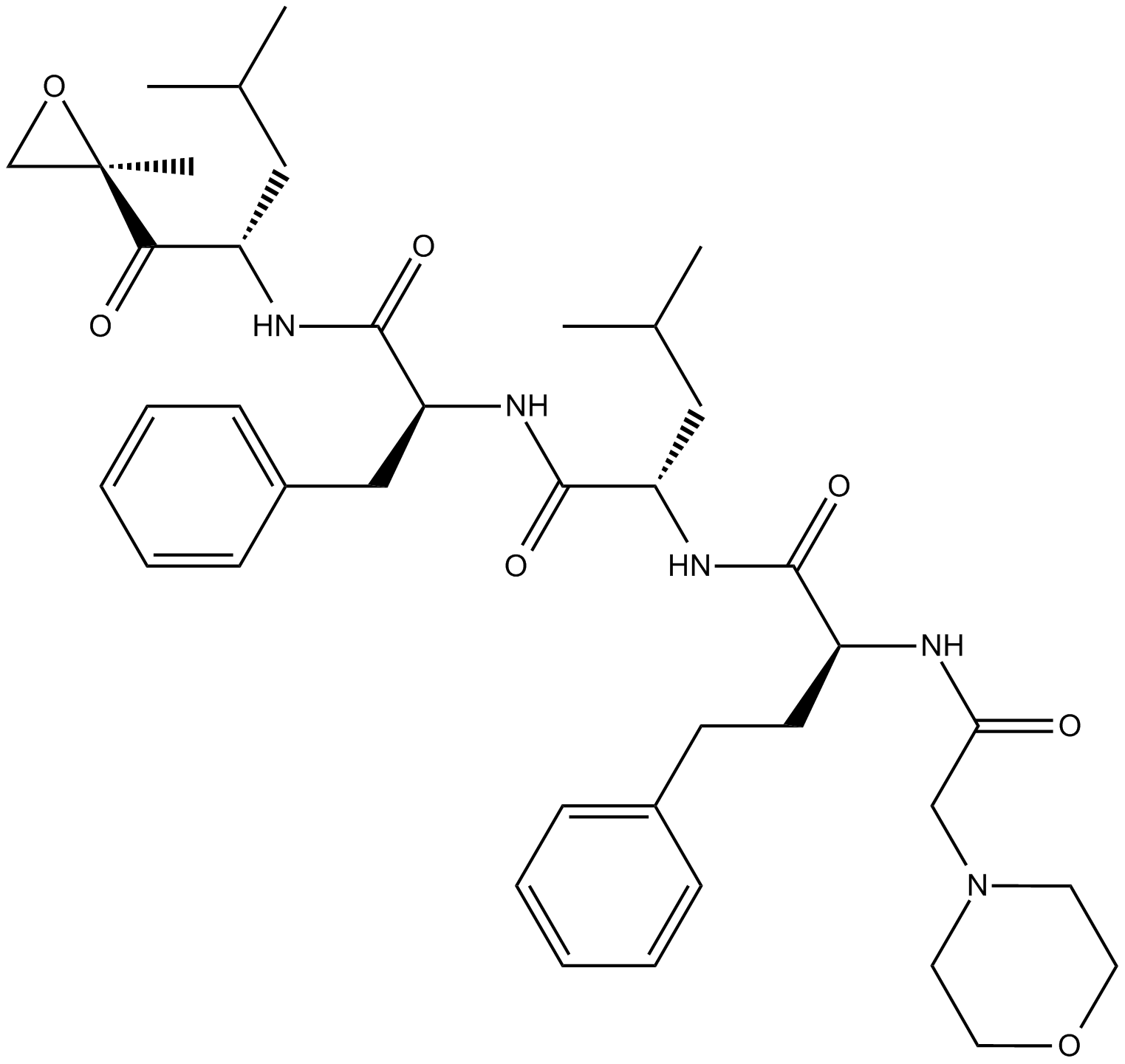 A1933 Carfilzomib (PR-171)10 CitationTarget: ProteasomeSummary: Proteasome inhibitor, epoxomicin analog
A1933 Carfilzomib (PR-171)10 CitationTarget: ProteasomeSummary: Proteasome inhibitor, epoxomicin analog -
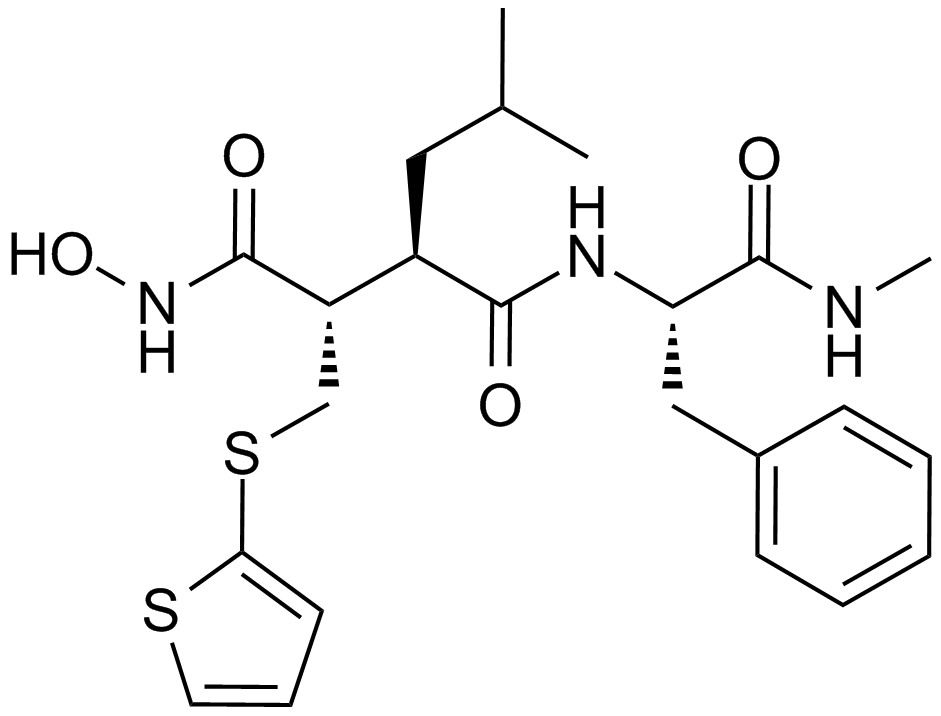 A2577 Batimastat (BB-94)17 CitationSummary: MMP inhibitor
A2577 Batimastat (BB-94)17 CitationSummary: MMP inhibitor -
 A2574 Aprotinin8 CitationTarget: Trypsin|Chymotrypsin|Kallikrein|TrypsinogenSummary: serine protease inhibitor
A2574 Aprotinin8 CitationTarget: Trypsin|Chymotrypsin|Kallikrein|TrypsinogenSummary: serine protease inhibitor -
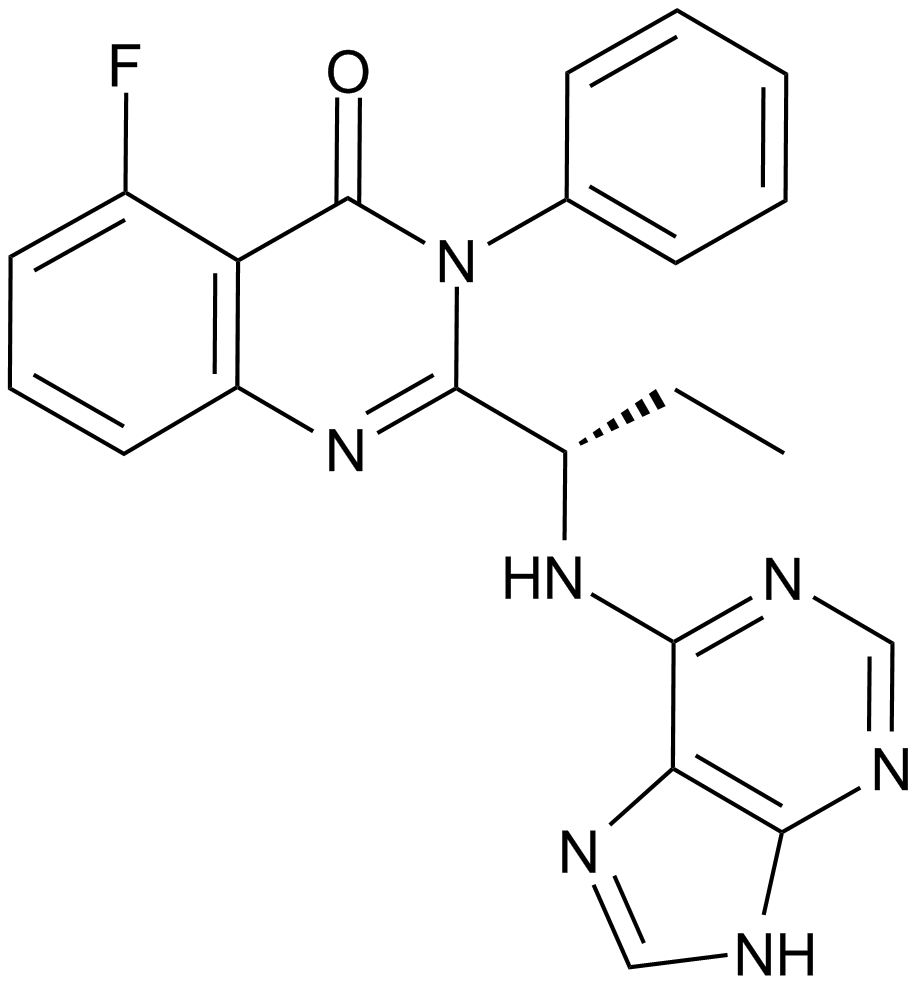 A3005 CAL-101 (Idelalisib, GS-1101)8 CitationTarget: PI3KSummary: PI3K inhibitor
A3005 CAL-101 (Idelalisib, GS-1101)8 CitationTarget: PI3KSummary: PI3K inhibitor


