Microbiology & Virology

Virology
A virus is a small infectious agent that replicates inside living cells. Viruses cause many human diseases from small illnesses, like influenza, to more deadly diseases, like hepatitis B and HIV. Our body’s immune system defends against viral infection by generating specific antibodies to bind to and neutralize viral particles and by cell mediated immunity that destroys infected host cells. read more
-
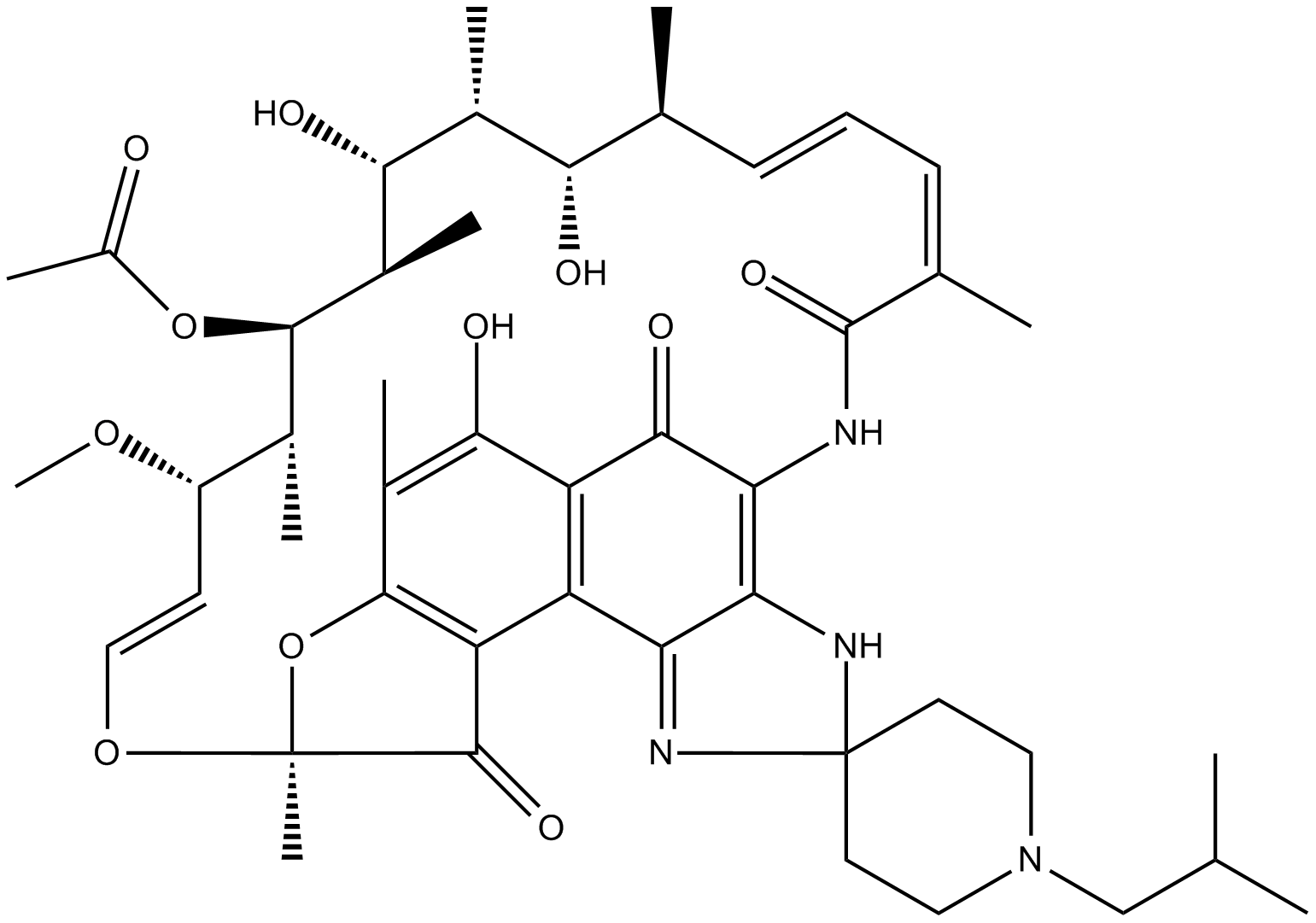 B2126 RifabutinTarget: Cytochrome P450 (CYP450)Summary: anti-TB(tuberculosis) medicine
B2126 RifabutinTarget: Cytochrome P450 (CYP450)Summary: anti-TB(tuberculosis) medicine -
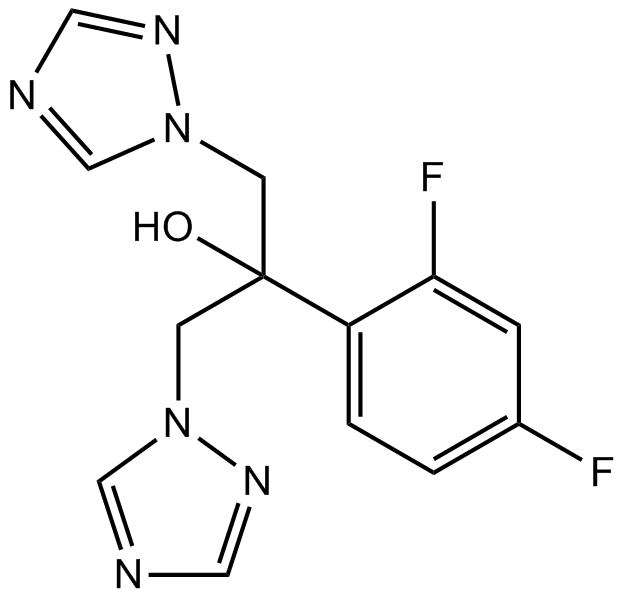 B2094 FluconazoleTarget: Cytochrome P450 (CYP450)Summary: Triazole antifungal agent
B2094 FluconazoleTarget: Cytochrome P450 (CYP450)Summary: Triazole antifungal agent -
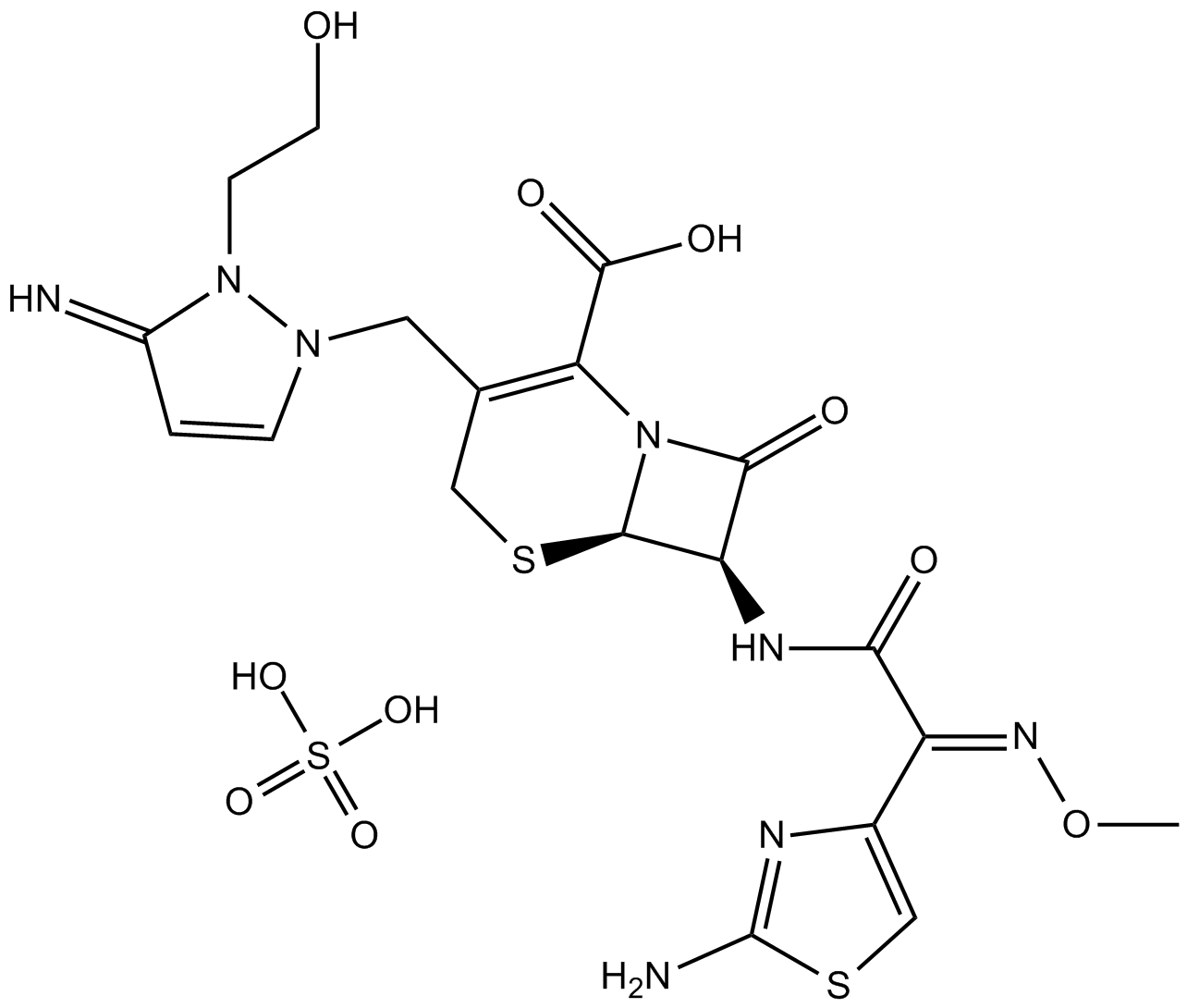 B1906 Cefoselis SulfateTarget: Peptidoglycan synthesisSummary: beta-lactam antibiotic
B1906 Cefoselis SulfateTarget: Peptidoglycan synthesisSummary: beta-lactam antibiotic -
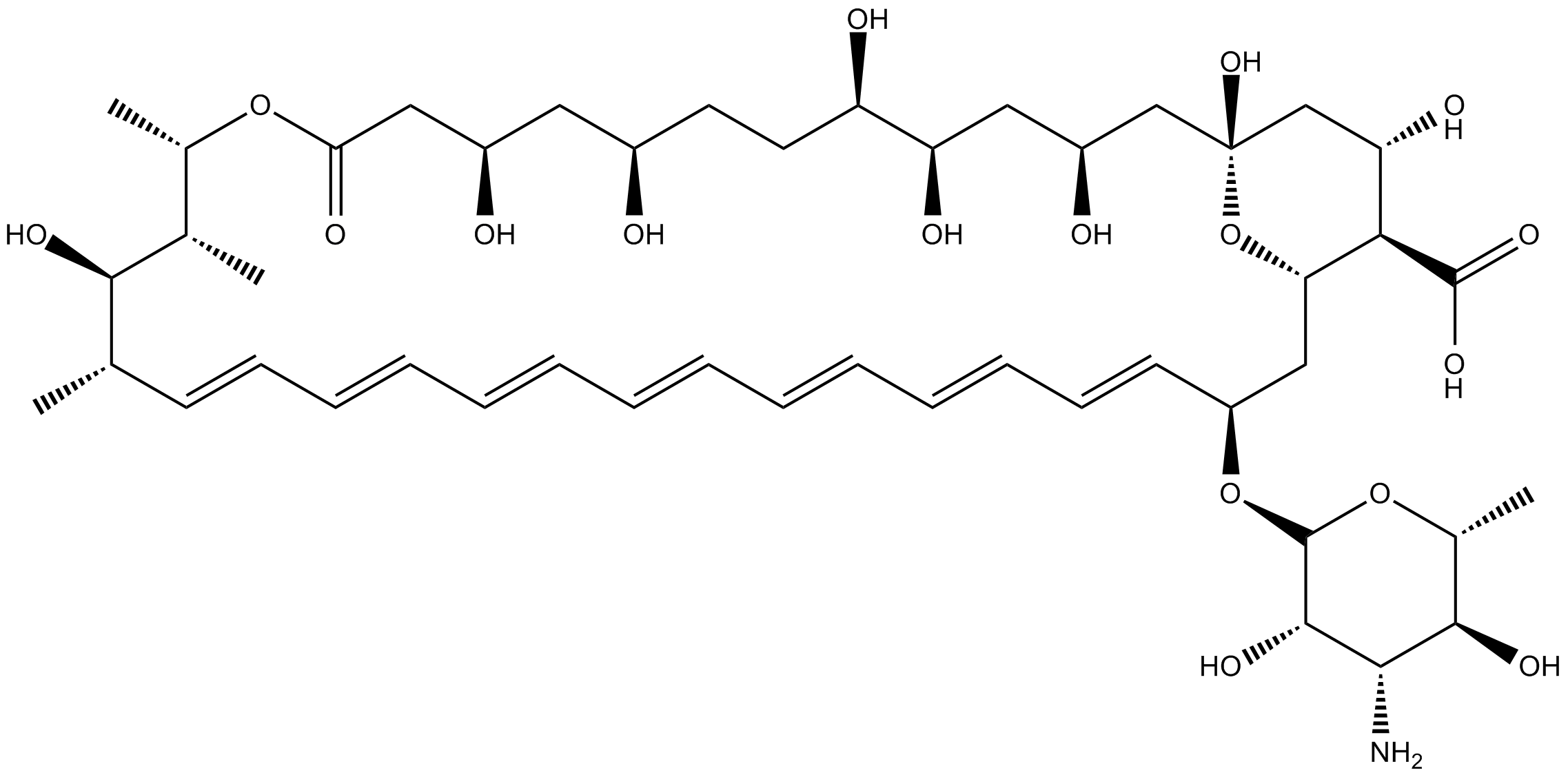 B1885 Amphotericin B1 CitationSummary: amphipathic polyene antibiotic
B1885 Amphotericin B1 CitationSummary: amphipathic polyene antibiotic -
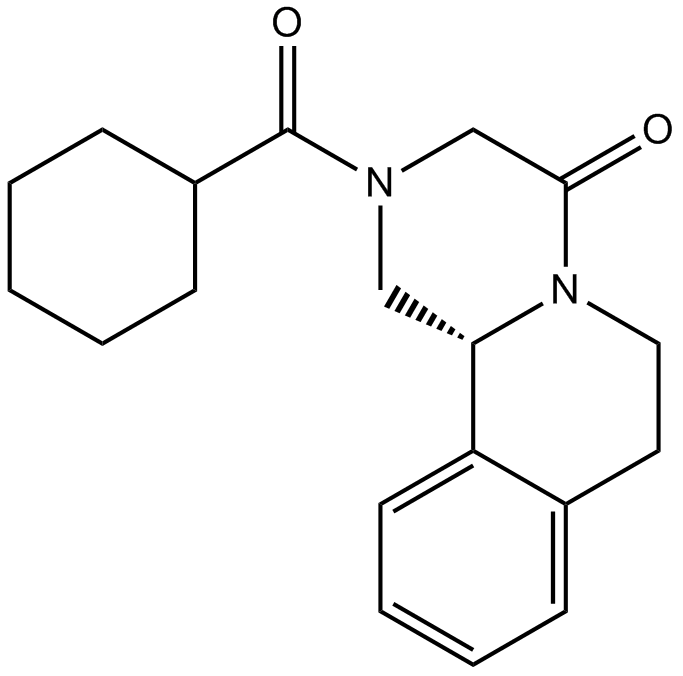 B2011 PraziquantelSummary: anthelmintic
B2011 PraziquantelSummary: anthelmintic -
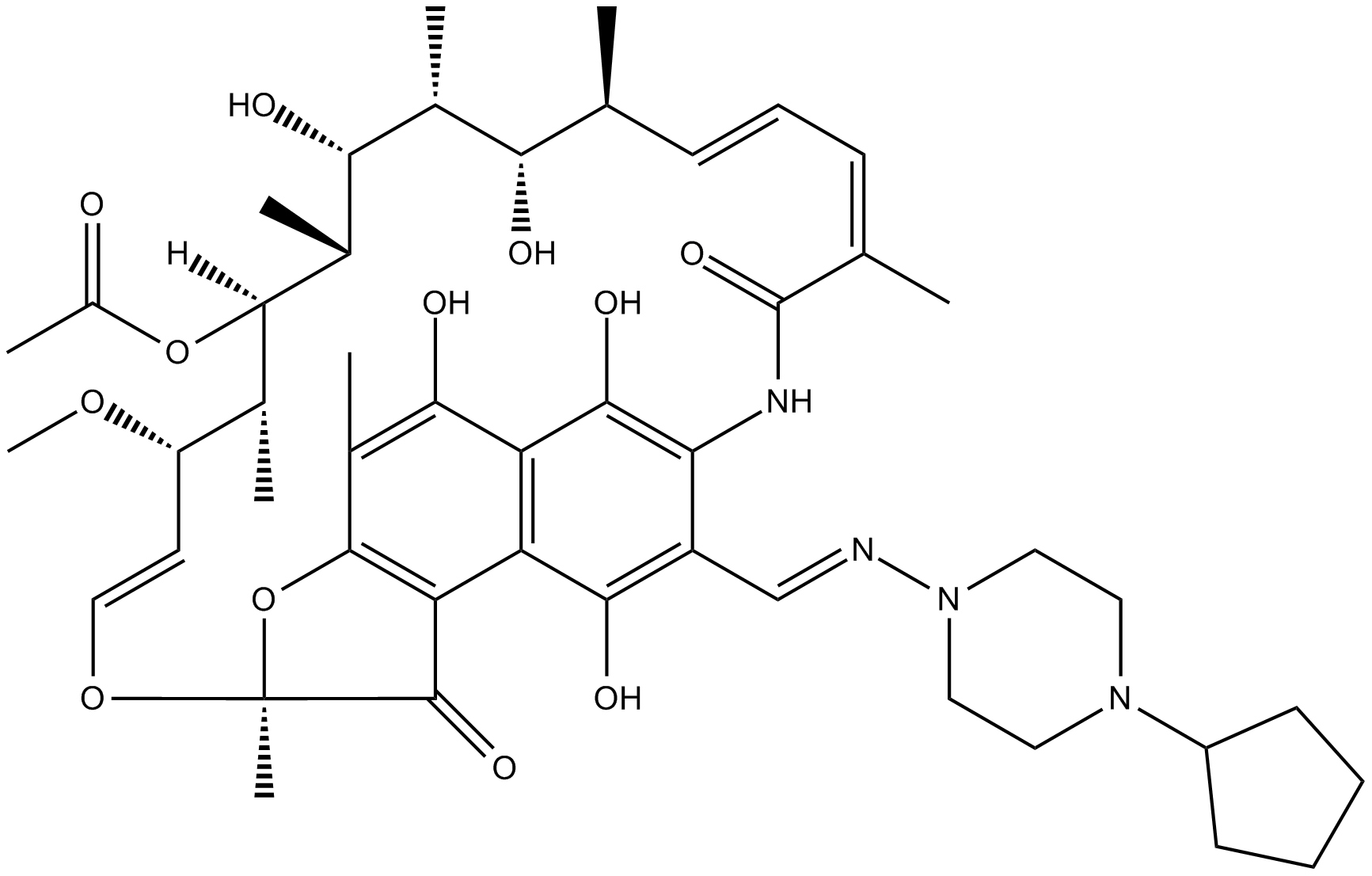 B2127 RifapentineTarget: RNA PolymerasesSummary: antibiotic drug used in the treatment of tuberculosis
B2127 RifapentineTarget: RNA PolymerasesSummary: antibiotic drug used in the treatment of tuberculosis -
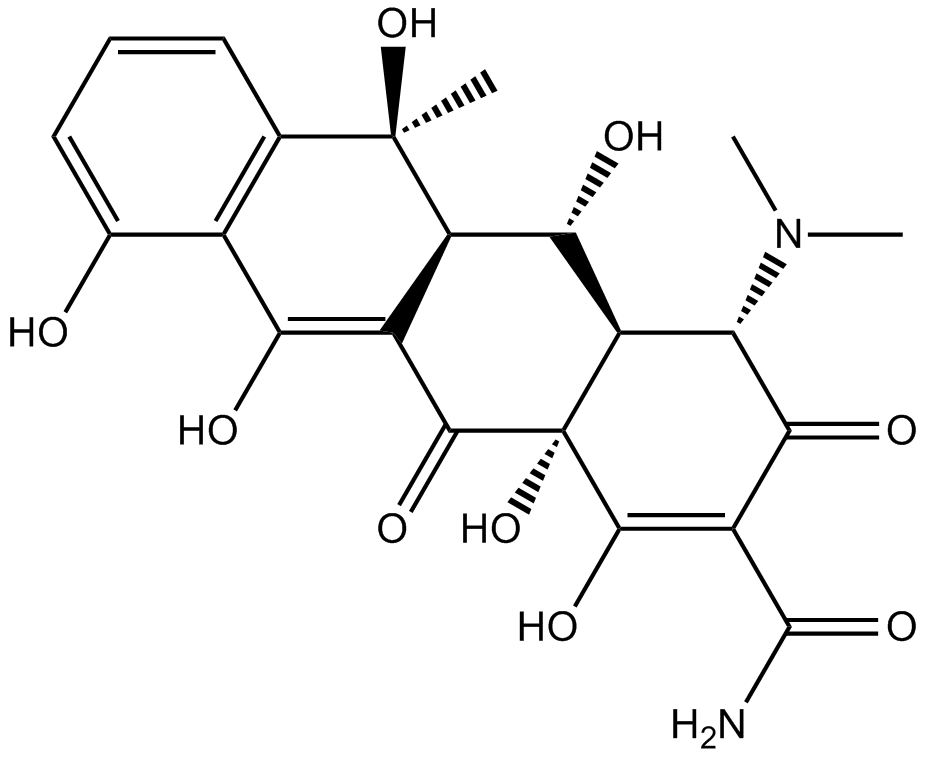 B2000 Oxytetracycline (Terramycin)Summary: broad-spectrum tetracycline antibiotic
B2000 Oxytetracycline (Terramycin)Summary: broad-spectrum tetracycline antibiotic -
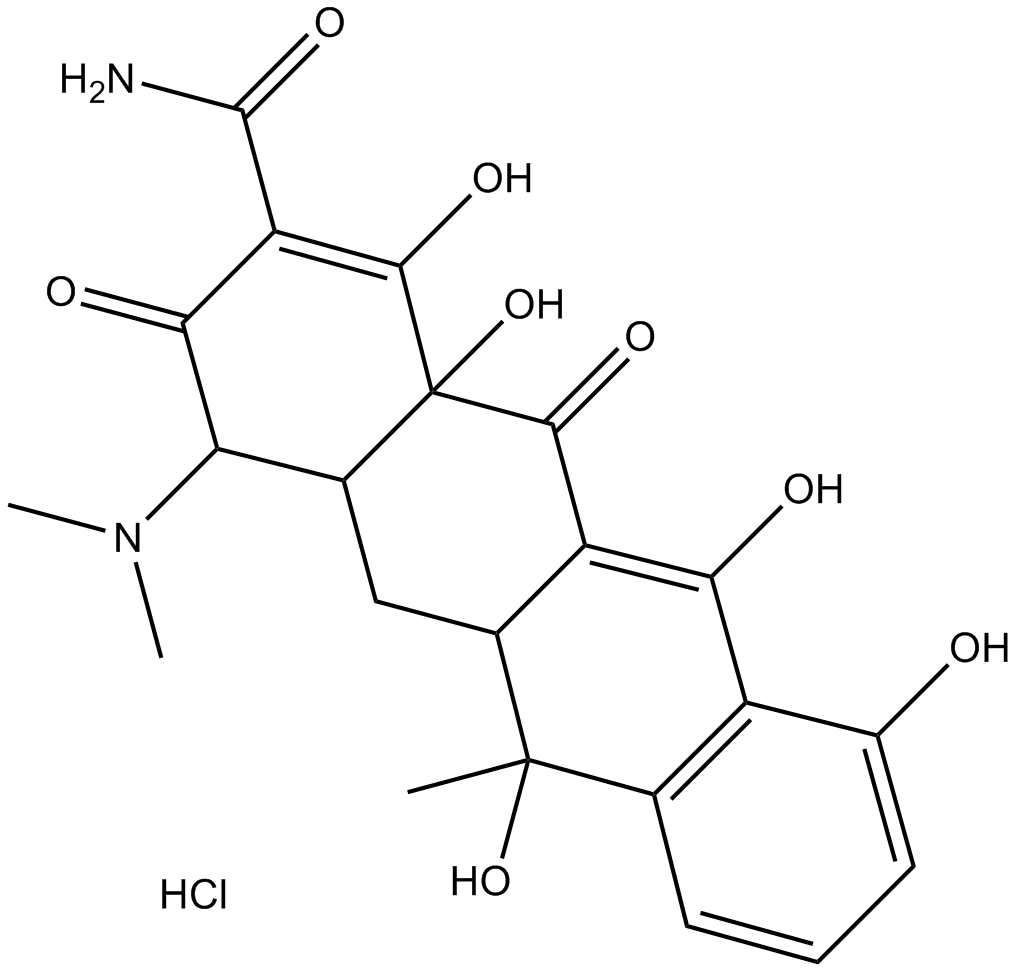 A2517 Tetracycline HydrochlorideSummary: Bacteriostatic antibiotics
A2517 Tetracycline HydrochlorideSummary: Bacteriostatic antibiotics -
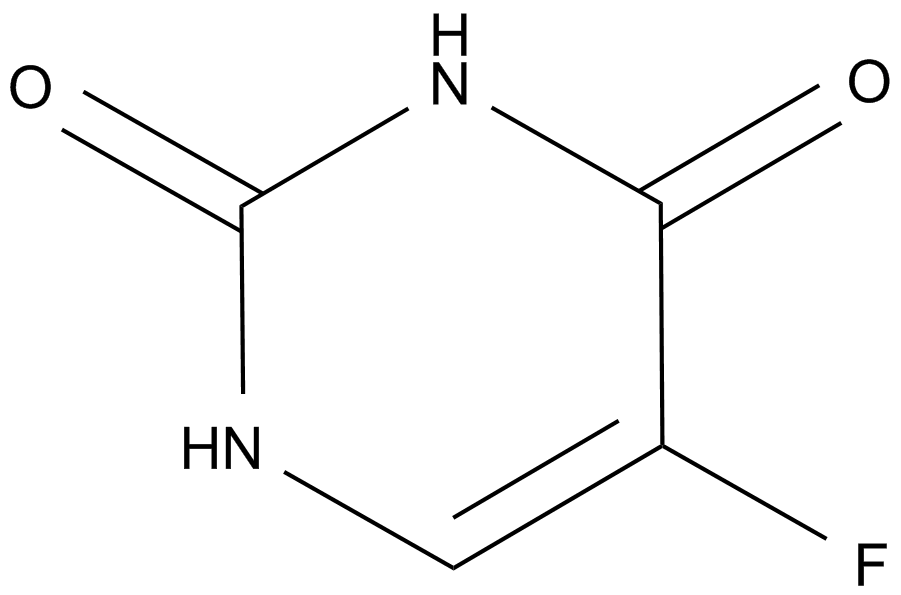 A4071 Fluorouracil (Adrucil)3 CitationTarget: Thymidylate SynthaseSummary: Antitumor agent;inhibitor of thymidylate synthase
A4071 Fluorouracil (Adrucil)3 CitationTarget: Thymidylate SynthaseSummary: Antitumor agent;inhibitor of thymidylate synthase -
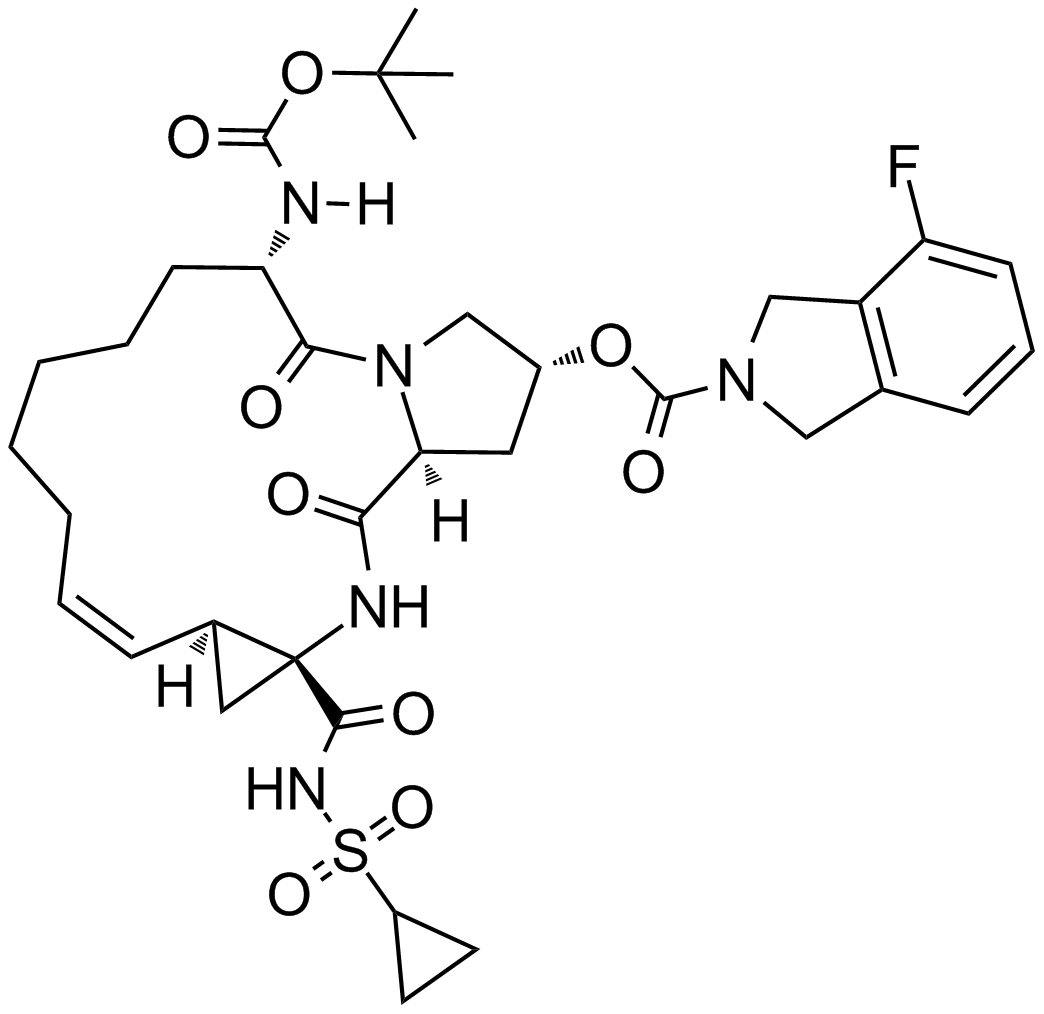 A4024 Danoprevir (RG7227)Target: HCV ProteasesSummary: HCV NS3/4A protease inhibitor
A4024 Danoprevir (RG7227)Target: HCV ProteasesSummary: HCV NS3/4A protease inhibitor

